

Volume 206
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-FMCE 2025 Symposium: Semantic Communication for Media Compression and Transmission
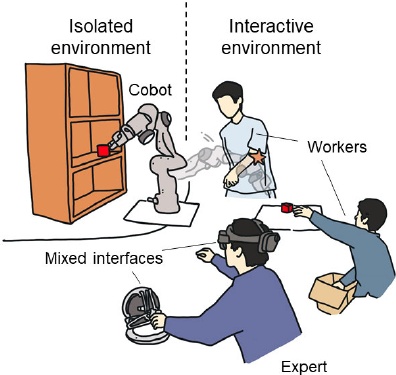
In human-robot collaboration (HRC), a balance must often be struck between the efficiency and safety of collaborative robots (cobots). Robots working closely with humans tend to lose their initiative, which means their main tasks will be paused and their efficiency will decrease; while robots that interface less with humans can operate at high speed and with high accuracy, but they are unable to adapt to new tasks or handle emergencies. In order to strike a balance between robot efficiency and human safety, this research suggests a fresh supplementary paradigm for HRC. In this approach, human experts work alongside the robots in zero-shot learning areas as the robots use vision-based adaptive controllers to complete assigned tasks. As a result, human knowledge and robot capabilities are investigated and enhanced together. A hybrid interaction interface that combines haptic devices and augmented reality enables human participation and demonstrations. The Lyapunov approach is used to rigorously demonstrate the closed-loop system's stability.

 View pdf
View pdf



Lithium-ion batteries are widely used because of their high energy density and rechargeability, but their performance and safety are highly dependent on temperature. In order to explore the universe and deep sea, high and low temperature, extreme pressure and fatal radiation are going to be faced by these batteries, it shows highly important to improve the stability and efficiency of lithium-ion batteries. Also in common electric vehicles, rechargeable battery is an important component, it determines the battery life and charging speed. High temperatures can accelerate side reactions, degrade electrode materials, and even lead to safety hazards, while low temperatures impair lithium oxidise cathode irreversibly, induce dendrite growth, and increase the risk of internal short circuits. This paper briefly introduces four kinds of common batteries, with Popular anode materials are also discussed following. Then it reviews the impacts of both high and low temperature environments on the electrochemical behaviour and structural integrity of general lithium-ion battery. The following article will make comparation among different kinds of lithium-ion batteries and analyse their properties in room and extreme temperatures. According to this article, people can make decisions among variable rechargeable batteries easier during industrial production or research.

 View pdf
View pdf


This report provides a systematic analysis of spectrum sharing between cellular networks and Wi-Fi systems. With exponential growth in wireless data traffic and emerging technologies like 5G and Wi-Fi 6, efficient utilization of unlicensed frequency bands has become a critical challenge. The paper examines technical barriers, existing coexistence mechanisms, performance evaluation methodologies, and future research directions. Fundamental differences between cellular time-division multiplexing mechanisms and Wi-Fi's competitive protocols create significant obstacles for achieving harmonious spectrum sharing. Through detailed analysis of collaborative strategies, AI-driven technologies, and physical layer innovations, the report highlights both existing advancements and unresolved challenges. Finally, it discusses emerging trends, including 6G spectrum utilization, smart metasurfaces, semantic communication, and green networks, providing a roadmap for future research and standardization efforts.

 View pdf
View pdf


The European energy crisis, exacerbated by the Russia–Ukraine conflict, exposed the fragility of gas-dependent power systems and underscored the urgent need to understand short-term substitution dynamics between conventional fossil fuels. While renewable energy is the long-term solution for decarbonization, near-term resilience depends on the balance between gas and coal. This study examines coal–gas substitution in European electricity generation, focusing on how relative fuel prices and carbon pricing influence generation patterns. A monthly panel of 27 EU member states from 2015 to 2024, the research employs fixed-effects models to estimate substitution effects, with robustness checks incorporating carbon-inclusive costs and heterogeneity tests by fuel structure and crisis periods. Results show that a 1% increase in the relative gas–coal price reduces the gas share by about 0.11, while a €10/t rise in the carbon price raises it by roughly 1.4 percentage points. Carbon pricing amplifies responsiveness to relative prices, with stronger substitution in high gas-share and low coal lock-in countries, whereas crisis conditions preserved price effects but weakened policy impacts. These findings provide new evidence on short-term resilience and inform strategies to enhance flexibility and reduce structural dependence.

 View pdf
View pdf


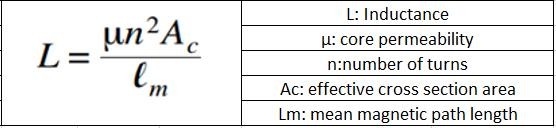
In contemporary power electronic systems, common-mode chokes are crucial parts for suppressing electromagnetic interference (EMI). High-permeability magnetic material is always desired by engineers to achieve higher inductance and better noise suppression. This article compared the inductance, impedance, and frequency response of two commonly used magnetic core structures: E-I cores and toroidal cores. Experimental results show that toroidal cores offer higher inductance at low frequencies, but their performance degrades significantly above 100 kHz due to core loss and magnetic saturation. On the other hand, the small natural air gap between the E and I elements reduces effective permeability, helping to minimize high-frequency losses and allowing the E-I core to maintain more stable characteristics across a wider frequency range. In order to address the trade-offs between permeability, inductance, and stability, the article also compares two ferrite materials (R10K and R15K) and discusses how material selection influences performance, providing useful guidance for modern common-mode choke design.

 View pdf
View pdf




