0. Introduction
The freshness and quality of vegetable products in supermarkets decrease sharply over time, and if they are not sold out on the day, they will be difficult to sell the next day. This not only causes waste of goods but may also have a negative impact on the profitability of the supermarket. Therefore, it is crucial for supermarkets to develop an effective replenishment plan. To address the above problems, this paper proposes a model for replenishing supermarket dishes based on the complete knapsack problem.
Unlike the partial knapsack problem, the complete knapsack problem requires that each item be either completely untaken or taken in its entirety. This means that we cannot divide an item into multiple parts, each with different weights and values. Therefore, in the complete knapsack problem, we need to select items with high value as much as possible while meeting the backpack's weight limit. Solutions to the complete knapsack problem can use dynamic programming, genetic algorithms, etc.
The usage scenario of this paper is the supermarket, and the optimal replenishment quantity is obtained through the "selection—crossover—mutation" iterative method based on the genetic algorithm.
This paper is based on Problem C of the 2023 National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition, according to the saleable varieties from June 24 to 30, 2023, to give the single-item replenishment quantity for July 1, and maximize the profit of the supermarket.
1. Problem analysis
The solution approach to the total daily replenishment quantity for various vegetable categories on July 1, 2023, is primarily divided into two parts. The first part addresses the issue of dish selection, and the second part deals with the daily replenishment strategy, which is based on proportionate allocation of demand and the complete knapsack problem, respectively. The specific approach and process flowchart are as follows:
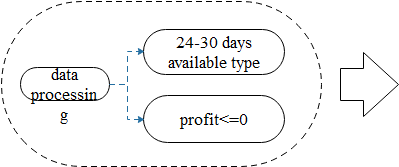
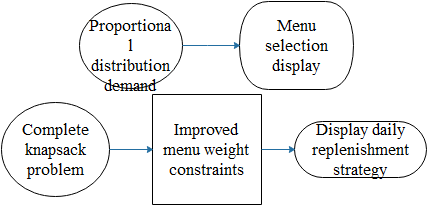
Figure 1: Flowchart of the Approach
2. Data preprocessing
To better determine the types of dishes for daily replenishment, this paper preprocesses recent loss rate data of vegetable products.
First, to represent the sales stability of the current dishes over three years, this paper calculates the total profit and total quantity sold over three years divided by the total number of days sold, obtaining the average daily profit and average daily quantity, i.e., profit and average quantity. Moreover, the stability of dish sales over three years is represented by profit/average quantity = average profit.
This paper considers the 251 dishes that do not appear in sales transaction data as unpopular dishes and excludes them. Ultimately, five dishes, led by local spinach and lotus root, were excluded.
Table 1: Excluded Unpopular Items
average quantity |
product code |
product name |
0 |
102900005116776 |
local spinach |
0 |
102900005116042 |
lotus root |
0 |
102900011023648 |
Wuhu green pepper(2) |
0 |
102900011032145 |
Wuhu green pepper(portion) |
0 |
102900011011782 |
Cordyceps Flower (Box)(1) |
At the same time, this paper excludes goods that cause profit loss to the supermarket due to returned dishes. Finally, six dishes led by large Chinese broccoli were excluded.
Table 2: Excluded Items Due to Returns
profit |
average quantity |
product code |
product name |
-0.004397078 |
0.00683105 |
102900011008492 |
Brassica oleracea var. italica |
-0.037031963 |
0.02283105 |
102900011021644 |
Oenanthe javanica |
-0.160730594 |
0.002739726 |
102900011030400 |
Hongshan Vegetable Stalk Premium Handbag |
-0.34173516 |
0.002739726 |
102900011030417 |
Hongshan Vegetable Stalk and Lotus Root Assorted Gift Box |
-0.004503717 |
0.004548858 |
102900011033999 |
Solanum melongena var. esculentum(1) |
To determine the saleable varieties between June 24 and 30, 2023, this paper extracted dishes that had been sold during June 24-30 in previous years from the data. The rest were considered unsold dishes, thus selecting 148 types of dishes for choice.
Given the limited sales range of the supermarket's fresh section, to maximize profits, a more optimized single-item replenishment plan must be formulated within a limited range. According to the requirements, the total number of single items needs to be controlled between 27-33. To enrich the variety of supermarket dishes and provide more choices for customers, this paper plans to replenish 33 kinds of single items.
Based on the daily replenishment quantity of each category on July 1, the selection number of single items is distributed according to the proportion of daily replenishment quantity of each category. Through calculation, it is found that aquatic rhizome: cauliflower: eggplant: edible mushroom: pepper: leafy = 1:2:4:5:9:12. Therefore, among the 33 kinds of vegetable single items to be selected, this paper will choose 1 kind of aquatic rhizome item, 2 kinds of cauliflower items, 4 kinds of eggplant items, 5 kinds of edible mushroom items, 9 kinds of pepper items, and 12 kinds of leafy items.
Based on the description above, the number of single items to be selected in different categories has been determined. To maximize the supermarket's profit, this paper selects a few items with the highest profit ratio as the selection targets. Knowing that the profit ratio = average profit / loss rate, and since the loss rate of some items is 0, the corresponding profit ratio is calculated to be infinity. For ease of calculation and comparison, this paper changes the loss rate of items with a 0% loss rate to 0.01% for further calculations to obtain the profit ratio of each item within its category. By sorting the profit ratios, the 33 items to be replenished from the 6 major categories are selected in proportion as follows: broccoli, Zhi Jiang green stalk scattered flowers, lotus root (1), purple round eggplant, purple eggplant (1), flower eggplant, long line eggplant, white jade mushroom (box), crab-flavored mushroom (box), seafood mushroom (pack), pig stomach mushroom (box), double mushroom (box), green Hang pepper (1), purple spiral pepper, fruit pepper, millet pepper, combined pepper series, rainbow pepper (2), red sharp pepper, red Hang pepper, red lantern pepper 9(2), red lantern pepper (1), baby bok choy, baby cabbage, perilla, Chinese broccoli, ice plant, panax notoginseng, wood ear vegetable, daylily (2), loofah tip, sweet potato tip, daylily (1), rapeseed mustard.
3. Model establishment for determining single item replenishment quantity based on the complete knapsack problem
After data processing, the average profit for 33 dishes is obtained, with each dish having a minimum demand quantity and requiring at least 2.5 kilograms to be selected. Therefore, based on the greedy algorithm, this paper optimizes the daily replenishment quantity of the 33 dishes into 6 complete knapsack problems, and obtaining the maximum value of each knapsack can yield the maximum profit for the supermarket on that day.
The complete knapsack problem can be simply described as follows: if there are i types of items and a backpack with limited capacity, assuming that an infinite number of each type of item is available, the volume of the i-th type of item is v and its value is w. The problem is to determine how to pack these items into the backpack so that the total volume of the items does not exceed the backpack's maximum capacity and the total value is maximized. To ensure the maximum profit for the supermarket, this paper considers the minimum demand quantity of each dish as the capacity of the backpack and establishes the following objective function:
\( Max\sum_{i=1}^{33}n_{i}a_{i}v_{i} \)
Subject to the constraints:
\( 27≤\sum_{i=1}^{251}a_{i}≤33 \)
\( n_{i}≥25 \)
\( \sum_{i=1}^{33}n_{i}w_{i}≥min-weight \)
Solving the above equation will yield the maximum profit for the current backpack.
4. Solving the complete knapsack problem using genetic algorithms
Genetic algorithms are search algorithms that simulate the principles of natural selection and genetics, based on the theory of evolution by Darwin. In the basic operation of genetic algorithms, it is first necessary to initialize the algorithm's operating parameters. Specifically, this includes setting the evolution generation counter t=0 and defining the maximum number of generations T to ensure the algorithm terminates after a certain number of iterations, avoiding an infinite loop. Meanwhile, M individuals are randomly generated as the initial population P (0), laying the foundation for the algorithm to start searching for the optimal solution.
Next, these initially generated individuals undergo a fitness evaluation to determine their viability within the population P (t). Fitness evaluation is a crucial step in genetic algorithms, directly affecting which individuals are retained and participate in the reproduction of the next generation. Based on the fitness evaluation of individuals, a selection operator is applied to the population, ensuring that individuals with higher fitness have a greater chance of being selected, simulating the process of natural selection.
The application of the crossover operator is another core aspect of genetic algorithms. This operation introduces new gene combinations while retaining the genes of excellent individuals, increasing the diversity of the population. This process simulates the mating process of biological organisms and is key to the algorithm's effective exploration of the solution space.
Furthermore, the role of the mutation operator cannot be overlooked. It introduces new variations by randomly changing some gene values in an individual's gene sequence, helping the algorithm to escape local optima and enhance its global search capability. Through selection, crossover, and mutation, the population P(t) evolves into the next generation P (t+1).
If the evolution generation counter t reaches the maximum number of generations T, the algorithm terminates. At this point, the individual with the highest fitness among all generated individuals is selected as the optimal solution, and the result is output. This process not only demonstrates the self-organizing, self-adapting, and self-learning characteristics of genetic algorithms but also showcases their powerful ability to solve optimization problems. By simulating the natural evolutionary process, genetic algorithms can effectively find the optimal or near-optimal solution in a complex search space. The specific process is illustrated in the following diagram:
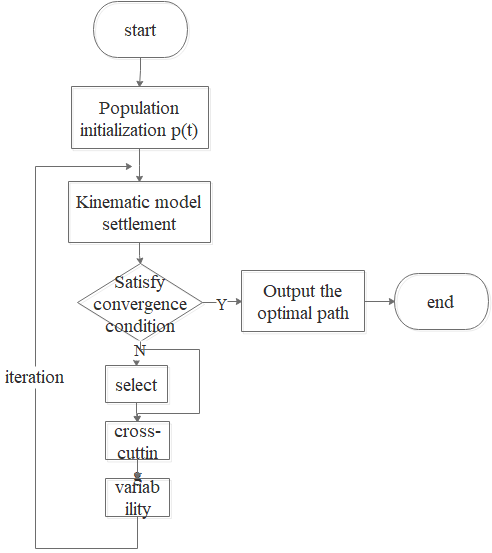
Figure 2: Flowchart of Genetic Algorithm
To ensure that the daily replenishment quantity of each dish is not less than 2.5kg, this paper sets the weight of each dish at 2.5kg, ensuring that the genetic algorithm does not produce a situation where the current dish does not meet the 2.5kg requirement during iteration. To allow for fractional selection times for dishes, the following modification is proposed for the initialization of the genetic algorithm population:

Figure 3: Genetic Algorithm Initialization Debugging Diagram
Furthermore, during the iteration of the genetic algorithm, it may occur that although the optimal solution is reached, the capacity of the knapsack is not maximized, i.e., the total weight of the current dishes does not meet their minimum demand quantity. Therefore, this paper performs an equal value inflation on the daily replenishment data for each dish. Taking the price of eggplants as an example: based on the minimum demand quantity of 22.95kg for eggplants on July 1 obtained from problem two, this paper sets the maximum capacity of the knapsack at 22.95kg, with the value of the items being the average profit of each dish. To ensure code execution efficiency, the population size is changed to 50.
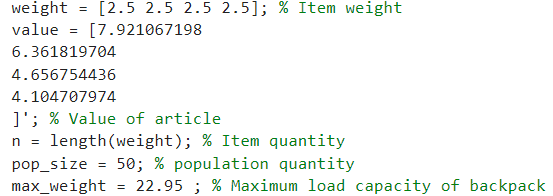
Figure 4: Display of Genetic Algorithm Parameters
The final results are as follows:

Figure 5: Display of Genetic Algorithm Results
The results indicate that Purple Round Eggplant is selected 2.3604 times, Purple Eggplant 2.1165 times, Flower Eggplant 2.0272 times, and Long Line Eggplant 2.3097 times, with each selection being 2.5kg. However, the total weight is only 22.0344kg, not meeting the minimum demand. Therefore, an equal value inflation is performed on the weights of these four types of eggplants, resulting in the following:
\( Purple Round Eggplant:\frac{22.95}{22.0344}×2.5×2.3604=6.15kg \)
\( Purple Eggplant:\frac{22.95}{22.0344}×2.5×2.1165=5.51kg \)
\( Flower Eggplant:\frac{22.95}{22.0344}×2.5×2.0272=5.28kg \)
Long Line Eggplant \( :\frac{22.95}{22.0344}×2.5×2.3097=6.01kg \)
\( 6.15+5.51+5.28+6.01=22.95kg \)
Meeting the minimum demand criteria. Using the above method to calculate all knapsacks, the final results are as follows:
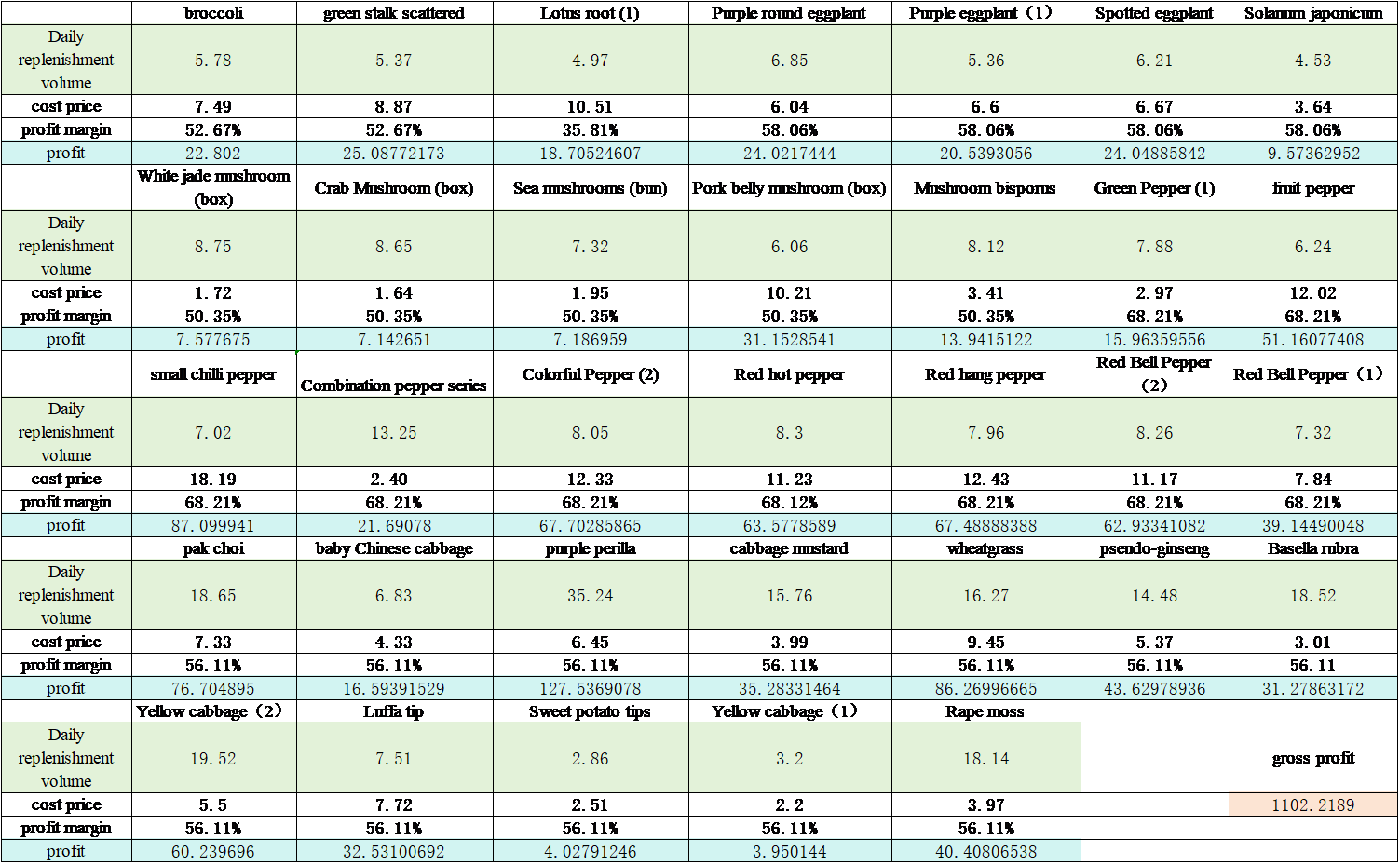
Figure 6: Display of Complete Knapsack Algorithm Results
As shown in the figure, the total profit is 1102.2189 yuan.
5. Recommendations
To ensure the supermarket's replenishment and pricing strategies are more comprehensive, relying solely on given data such as sales volume, unit price, and loss rate is far from sufficient. Besides these most intuitive influencing factors, many external conditions can impact the supermarket's sales performance. Here, we propose recommendations and rationales for enhancing the supermarket's sales strategy from five aspects:
5.1. Weather
Different weather conditions can change people's shopping needs and desires. Extreme weather events like typhoons, heavy rain, and blizzards may hinder shopping behavior; extremely hot or cold weather can also reduce the desire to shop. However, during some cold days in winter and hot days in summer, people may choose different dishes.
5.2. Supplier data
Cooperation data with vegetable suppliers, including delivery times, prices, and product quality. Optimizing the genetic algorithm into a multi-objective genetic algorithm and setting weights for supermarket and supplier data can effectively increase supermarket revenue. Simultaneously, establishing a supplier location optimization problem can reduce the transportation costs of various vegetables to a minimum.
5.3. Customer data
Customers of different age groups may have different shopping preferences and habits. Collecting information about customer buying habits, preferences, and demographic data, and applying this information to the daily replenishment model established in this paper, the predicted results can help the supermarket in personalized promotion activities and pricing strategies to attract more customers.
5.4. Evaluation data
Timely understanding of customers' opinions and suggestions on the supermarket can create a better shopping environment for customers. Also, adding an evaluation model for dishes in the data preprocessing step of the daily replenishment model and incorporating these evaluation data into the evaluation model combined with the average profit filtering principle can make the supermarket's dish selection more precise.
5.5. Quality inspection data
Record the results of daily post-sale vegetable quality inspections, including freshness, damage rate, etc. Add a data preprocessing model before the complete knapsack problem model for the next day's replenishment, incorporating quality inspection data into the data preprocessing step. This can effectively improve the effectiveness of daily replenishment, making the results more accurate.
6. Conclusion
This paper utilizes the dataset provided by the 2023 National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition, converting the profit maximization problem into a complete knapsack problem through a greedy algorithm. To ensure that the weight of the dishes meets the requirement of more than 2.5kg, we initially assume that each dish weighs 2.5kg. Based on this, we use a genetic algorithm to determine the selection frequency of each dish, and by inflating the weight of the dishes equally, we ultimately achieve a maximum profit of 1102.2189 yuan.
References
[1]. Zheng, A. M. (2007). Research on the general parts safety stock model based on supply lead time [Doctoral dissertation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology]. Hubei, China.
[2]. National College Students' Mathematical Modeling Competition. (2023, September 7). National College Students' Mathematical Modeling Competition. Retrieved from http://mcm.edu.cn
[3]. Zhang, Y. (2017). Research on the variable value 0-1 knapsack problem model and its optimization algorithm [Doctoral dissertation, Beijing Jiaotong University]. Beijing, China.
[4]. Li, G. L., & Zhu, X. L. (2007). The 0/1 knapsack problem. Microcomputer Applications, 23(4), 12-14.
[5]. Chen, Z., Zhong, Y. W., & Lin, J. (2021). A hybrid greedy genetic algorithm for solving the 0-1 knapsack problem. Journal of Computer Applications, 41(01), 87-94.
[6]. (2021). Research on the optimization method of complex knapsack problem model based on genetic algorithm [Doctoral dissertation, Anqing Normal University]. Anqing, China.
[7]. Yan, T. S. (2007). Solving the 0/1 knapsack problem with a hybrid genetic algorithm based on a greedy algorithm. Modern Computer (Professional Edition), (08), 14-17.
Cite this article
Wang,R.;Pan,T.;Li,F.;You,S. (2024). Research on the daily replenishment model based on the complete knapsack problem. Advances in Operation Research and Production Management,2,10-16.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Operation Research and Production Management
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zheng, A. M. (2007). Research on the general parts safety stock model based on supply lead time [Doctoral dissertation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology]. Hubei, China.
[2]. National College Students' Mathematical Modeling Competition. (2023, September 7). National College Students' Mathematical Modeling Competition. Retrieved from http://mcm.edu.cn
[3]. Zhang, Y. (2017). Research on the variable value 0-1 knapsack problem model and its optimization algorithm [Doctoral dissertation, Beijing Jiaotong University]. Beijing, China.
[4]. Li, G. L., & Zhu, X. L. (2007). The 0/1 knapsack problem. Microcomputer Applications, 23(4), 12-14.
[5]. Chen, Z., Zhong, Y. W., & Lin, J. (2021). A hybrid greedy genetic algorithm for solving the 0-1 knapsack problem. Journal of Computer Applications, 41(01), 87-94.
[6]. (2021). Research on the optimization method of complex knapsack problem model based on genetic algorithm [Doctoral dissertation, Anqing Normal University]. Anqing, China.
[7]. Yan, T. S. (2007). Solving the 0/1 knapsack problem with a hybrid genetic algorithm based on a greedy algorithm. Modern Computer (Professional Edition), (08), 14-17.









