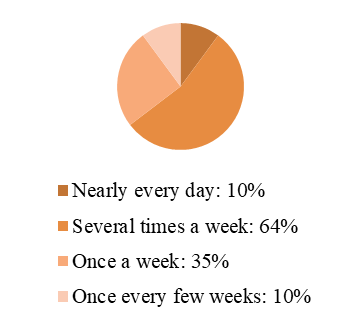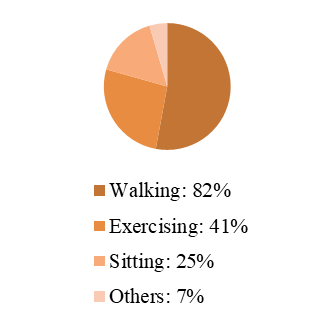1. Introduction
"Population aging" is a major issue facing urban populations in China, with an increasing number of elderly people residing in old residential communities with outdated infrastructure and inadequate service management systems [1]. Therefore, the renovation of old residential communities is imperative to meet the living needs of the people.
Since 2019, the concept of the "night economy" has gained widespread attention. The prosperity of the night economy is an important indicator of a city's economic openness and vibrancy. Improving the nighttime lighting environment is crucial for the successful development of the night economy. Currently, many old residential communities face various degrees of lighting issues due to outdated lighting facilities and a lack of outdoor lighting design, significantly affecting residents' sense of security during nighttime activities [2].
To meet the visual and activity needs of residents in old residential communities at night, designing a safe and comfortable lighting environment suitable for ordinary residents and the elderly will be an important research direction in the future for lighting and architectural fields.
2. Research subjects and content
2.1. Research subjects
North China University of Technology has a history of 76 years since its establishment in 1946. The faculty residential area on campus falls under the category of old residential communities, where a large number of elderly residents live. The infrastructure conditions are poor, and the nighttime lighting is inadequate. Based on information about the construction era, building types, area, and location, the faculty residential area of North China University of Technology was selected as the research subject.
2.2. Research content
This investigation is divided into two main parts:
1) Field Investigation: Based on the nighttime activity routes of the elderly in the campus residential area, the public activity spaces were divided into five parts. A field investigation of the current nighttime lighting environment was conducted. The content included the forms of nighttime activities of the elderly, the types of lighting in public spaces, site brightness, and road conditions.
2) Questionnaire and Interview Survey: Random questionnaires and field interviews were conducted with residents in the research area to understand their perceptions, satisfaction, needs, and suggestions regarding the nighttime lighting environment of the campus public spaces.
3. Field investigation
3.1. Summary of environmental conditions
The nighttime lighting in the entire campus is typically turned on between 19:00 and 19:30, while the peak time for outdoor activities is approximately between 18:00 and 20:00. Therefore, the chosen time for the investigation was from 18:00 to 20:00.
Within the faculty residential area, the commonly used public spaces can be broadly categorized into three types: transportation spaces, recreational spaces, and landscape spaces. The specific descriptions and corresponding nighttime lighting conditions of these areas are as follows:
Table 1. Current State of Nighttime Lighting in the Survey Area
Specific Location | Category | Environmental Conditions |
Main driveway in front of the campus hospital and other pathways between residences | Transportation Space | - Elderly activity: Walking, dog walking - Lighting type: Direct lighting, high garden lights on both sides - Brightness: Moderate - Road conditions: Hard surface, large square tiles. The road is flat, with no obstacles other than speed bumps. Can be slippery when it rains. |
Fitness equipment area next to the small hospital | Recreational Space | - Elderly activity: Exercising, chatting, taking children - Lighting type: Indirect lighting, using nearby garden lights - Brightness: Dim due to indirect lighting and obstruction by trees - Road conditions: Paved with small hard tiles, relatively flat but contains many fitness equipment and trees, requiring avoidance. |
Garden in front of the halal canteen | Landscape Space | - Elderly activity: Sitting, chatting - Lighting type: Indirect lighting, using nearby garden lights - Brightness: Moderate on the periphery, dark in the center - Road conditions: Hard small tiles, tiles are uneven and cracked due to age, road is bumpy but without other obstacles. |
4. Questionnaire and interview survey
To better understand the subjective feelings of residents in the Beihang University residential area regarding the nighttime lighting environment of public activity spaces, and to identify the main issues present, the team conducted a random questionnaire survey and on-site interviews with residents during the research process.
4.1. Demographic characteristics
In this survey, the gender ratio of respondents was roughly equal. The age structure of respondents consisted of 30% young people, 35% middle-aged individuals, and 36% elderly individuals.
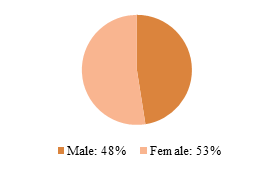
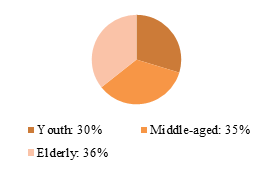
Figure 1: Gender Composition of Respondents Figure 2: Age Distribution of Respondents
4.2. Activity characteristics
The nighttime activities of residents in the Beihang University residential area mostly take place between 18:00 and 22:00, with 18:00 to 19:00 being the peak time when residents return to the area. This includes middle-aged and young people coming home from work, children and teenagers returning from school, and elderly people coming back for dinner. Before 18:00 and after dinner (when it gets dark), most of the activities in the residential area are by elderly people (over 60 years old) and underage children.
Among the respondents, most elderly people aged 65 and above are active before 18:00 and between dinner and 20:00. Due to physical limitations or poor night vision, most elderly people choose to return home before it gets completely dark.
The frequency of outdoor activities at night in the residential area is quite high, with approximately 64% of respondents engaging in these activities several times a week and 35.71% doing so once or twice every two weeks. Almost no respondents reported never going out at night, highlighting the general need for nighttime outdoor activities and the importance of a good outdoor nighttime lighting environment.
Nighttime activity types are also significantly influenced by age. About 82% of residents indicated they take walks around the residential area at night, and many middle-aged and young respondents often exercise in activity squares. Young people also go out at night for work-related reasons, social engagements, and schoolwork, causing them to return home later.
For elderly people aged 65 and above, the primary nighttime activity is chatting in the garden, with most returning home before 20:00. This may be due to insufficient lighting in activity areas, leading elderly people to prefer more static activities due to mobility issues.
|
|
Figure 3. Frequency of respondents' nighttime outdoor activities | Figure 4. Forms of respondents' nighttime outdoor activities |
4.3. Satisfaction survey
Based on relevant literature, brightness, clarity, safety, comfort, and aesthetics were selected as evaluation indicators [3]. Respondents rated their satisfaction with various aspects of the nighttime lighting environment in the residential area, and the statistical results are as follows.
Respondents gave all the nighttime lighting indicators in the Beihang University residential area a passing score of above 60, but overall scores were low, with no item scoring above 70.
Table 2. Satisfaction Evaluation of Nighttime Lighting Environment in Surveyed Areas
Evaluation Indicators | Specific Description | Satisfaction Score |
Light Brightness | Are you satisfied with the nighttime lighting brightness? | 64.8% |
Environmental Clarity | Can the nighttime lighting make things clearly visible? | 62.2% |
Environmental Safety | Does the nighttime lighting environment ensure safety? | 65.3% |
Environmental Comfort | Does the nighttime lighting environment feel comfortable? | 69.6% |
Environmental Aesthetics | Do the lighting fixtures and colors in the residential area meet your aesthetic standards? | 65.8% |
Regarding the overall satisfaction with the nighttime lighting environment in public activity spaces within the residential area, 34.5% of respondents rated it as average, 52% as satisfactory, and 2% were very dissatisfied. Many respondents indicated that the overall environment feels unpleasant during nighttime activities. Nearly half of the respondents believe that the lighting on the sidewalks in the residential area is too dim, making it difficult for travel and activities.
5. Survey summary
Based on the aforementioned field survey and interviews, the current state of the nighttime lighting environment in the public activity spaces of the campus residential area and several issues affecting the nighttime mobility of the elderly are summarized as follows:
Uneven Brightness in Public Activity Spaces The survey revealed that lighting equipment is mostly installed along the inter-building roads without separate installations in areas with high human activity. This results in inconsistent brightness between public roads and activity areas. Additionally, because the activity areas receive indirect lighting, the brightness varies within the same area due to different distances from the light source.
Improper Lighting Equipment Setup The residential area only has high garden lights, without matching lawn lights or ground lights. High fixtures focus the light upward, creating an uncomfortable contrast with the dark sky. In summer, the dense foliage can block the high lights, resulting in uneven brightness across seasons and lower summer utilization.
Hard Paving in Activity Areas The public activity areas are paved with small square bricks, which lack integrity. Over time and after heavy rain, these bricks can become uneven and cracked, creating a bumpy surface. If the area is unevenly lit, elderly people with mobility issues are more likely to fall, which is dangerous on hard surfaces.
6. Factors affecting the safety of elderly nighttime activities
Based on the aforementioned survey, the factors affecting the safety of nighttime activity areas can be summarized as lighting conditions, paving conditions, and obstacle conditions. According to relevant literature, elderly people engaging in nighttime activities can be categorized into three types [4]: Elderly with Good Mobility: Their movement is not restricted, and they can walk independently on flat surfaces. Elderly with Limited Mobility: They need assistive devices such as canes or walkers. Elderly with Severe Mobility Issues: They require wheelchairs or are bedridden most of the time. Different types of elderly people have varying sensitivities and needs regarding the conditions of the activity areas. Elderly with good mobility, aside from having reduced travel distance, speed, and activity intensity compared to younger people, can freely move like younger individuals. Therefore, this group does not have high demands regarding the paving and obstacle conditions of activity areas, as long as the ground is generally flat and obstacles are minimized. Elderly with limited or severe mobility, due to their need for assistive devices and increased vulnerability, have higher requirements for the activity areas. The ground should be maintained as flat and continuous, with no steps to facilitate wheelchair access. Additionally, there should not be excessive landscape obstacles, and sufficient flat space should be left between landscapes to ensure wheelchairs can pass through normally.
The lighting conditions of the activity areas should be consistent for all types of elderly people, focusing on illuminance, light color, and glare. Due to the natural decline in their vision, elderly people require higher illuminance. Insufficient illuminance might cause elderly people to not see the ground conditions and obstacles clearly, leading to collisions or falls [5]. The elderly have reduced sensitivity to colors and cannot easily adapt to multicolored lighting, which might cause dizziness and falls. Sudden changes in light can also trigger emotional fluctuations, which is not conducive for elderly people with fragile cardiovascular systems [6]. Furthermore, the activity areas should have uniform illuminance. Improper brightness distribution can cause discomfort and reduce the ability to observe objects, a problem more severe for elderly people. Excessive brightness or high contrast causing glare can result in temporary blindness, making nighttime travel very dangerous for elderly people.
7. Optimization strategies
Through this survey, it was found that the nighttime lighting environment in old urban residential areas has many issues. The typical problems include outdated lighting facilities, improper arrangement of lighting fixtures, and inadequate management of lighting facilities. These issues lead to insufficient or uneven brightness in nighttime activity spaces, causing many inconveniences and safety hazards for residents during nighttime travel.
In the design process of nighttime lighting environments, the needs of residents of different age groups within the community should be fully considered to make more humane optimizations.
Increase the number of lighting fixtures and arrange them reasonably to improve the overall brightness of the nighttime lighting environment. Based on personal experiences during the survey and interviews with elderly residents, the most common feedback was "too dark." However, while increasing the illumination of streetlights, it is essential not to pursue brightness excessively. Considering the elderly's higher sensitivity to glare and to avoid disturbing residents' normal rest, the increase in illuminance should be moderate, with reasonable control of light color and color temperature, to avoid adverse effects.
Choose more suitable types of lighting fixtures to enhance the uniformity and comfort of the nighttime lighting environment in residential areas. Different lighting fixtures have different emission types and can bring higher road surface brightness and uniformity to public spaces. For example, cut-off and non-cut-off fixtures: under the same conditions, non-cut-off fixtures not only result in insufficient near-ground illuminance but also cause severe glare. In contrast, cut-off fixtures limit horizontal light to some extent while extending lateral light, resulting in less severe glare. Therefore, selecting the appropriate lighting fixtures should be based on environmental conditions, fixture effects, and user needs.
Install various types of lighting fixtures and lighting modes to meet the different needs of various areas and activities. In addition to the existing courtyard lights, approximately 4 meters high, taller streetlights can be added along roadsides to improve the average illuminance of the community. Besides streetlights, decorative lighting fixtures, such as lawn lights, can be added to enhance overall aesthetics and harmony while increasing illuminance.
Improve the quality of lighting fixtures and conduct regular maintenance. The survey found that the quality of lighting fixtures within the community varied, with some being too bright, some too dim, and some not working at all. The quality of lighting fixtures should be improved to maintain consistent and even brightness, with regular inspections and timely repairs or replacements of damaged fixtures to improve nighttime lighting conditions.
8. Conclusion
Through this survey and analysis, the nighttime lighting environment issues in the residential area of North China University of Technology have been summarized as low overall brightness, uneven brightness, and improper lighting equipment setup. Corresponding optimization strategies and design measures have been proposed, providing references and bases for subsequent old community renovations.
Improving the quality of the nighttime lighting environment plays a significant role in enhancing the safety and comfort of residents' nighttime travel. A good nighttime lighting environment can provide residents with a safer outdoor environment and comfortable public spaces, positively impacting residents' physical and mental health. Emphasizing the relationship and changes between people and their environment, and promoting continuous optimization and iteration, ultimately builds a comfortable, shared, and diverse living environment.
Source of Information
All figures and tables in the text are drawn by the author.
References
[1]. Zhou, H., & Zhou, H. (2018). Investigation and research on outdoor lighting environment in residential areas in Changchun City under the background of population aging. Sichuan Cement, 2018(4), 277, 348. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-6344.2018.04.264
[2]. Fu, Y., & Li, W. (2019). Investigation and research on the nighttime outdoor lighting environment of old residential areas in Tianjin City. Shanxi Architecture, 45(20), 122-124. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2019.20.061
[3]. Liu, M., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Safety perception evaluation and simulation optimization of residential road lighting. Journal of Lighting Engineering, 32(1), 106-111, 152. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-440X.2021.01.018
[4]. Marcus, C. C., & Francis, C. (2020). People Places. Beijing: Beijing Science and Technology Press.
[5]. Zhou, H., & Xu, Y. (2021). Research on age-friendly design strategies for outdoor lighting environment in residential areas. Architecture and Culture, 2021(7), 125-126. https://doi.org/10.19875/j.cnki.jzywh.2021.07.044
[6]. Huang, H., Wang, Y., Wu, J., et al. (2017). Investigation and analysis of visual activity characteristics and lighting environment needs of the elderly. Lamp and Lighting, 41(2), 1-4, 37. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-5521.2017.02.001
Cite this article
Huang,Q. (2024). Research on the nighttime lighting environment in public activity spaces of old residential communities—A case study of the faculty residential area at North China University of Technology. Advances in Operation Research and Production Management,2,44-49.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Operation Research and Production Management
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhou, H., & Zhou, H. (2018). Investigation and research on outdoor lighting environment in residential areas in Changchun City under the background of population aging. Sichuan Cement, 2018(4), 277, 348. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-6344.2018.04.264
[2]. Fu, Y., & Li, W. (2019). Investigation and research on the nighttime outdoor lighting environment of old residential areas in Tianjin City. Shanxi Architecture, 45(20), 122-124. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2019.20.061
[3]. Liu, M., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Safety perception evaluation and simulation optimization of residential road lighting. Journal of Lighting Engineering, 32(1), 106-111, 152. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-440X.2021.01.018
[4]. Marcus, C. C., & Francis, C. (2020). People Places. Beijing: Beijing Science and Technology Press.
[5]. Zhou, H., & Xu, Y. (2021). Research on age-friendly design strategies for outdoor lighting environment in residential areas. Architecture and Culture, 2021(7), 125-126. https://doi.org/10.19875/j.cnki.jzywh.2021.07.044
[6]. Huang, H., Wang, Y., Wu, J., et al. (2017). Investigation and analysis of visual activity characteristics and lighting environment needs of the elderly. Lamp and Lighting, 41(2), 1-4, 37. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-5521.2017.02.001