1 Introduction
Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) was founded in 1983, mainly serving small and medium-sized start-ups and venture capital. With strong technical strength and world-leading technology platforms and systems, SVB has an important position in the field of technology and finance in the United States. As a bank that mainly provides financing services for global science and technology enterprises, SVB has achieved rapid development in a short time, and its potential risks are also increasing at the same time. On March 8, 2023, Silicon Valley Bank announced the loss-making sale of 2.1 billion dollars of bond investment at the cost of 1.8 billion dollars of loss. On March 10, 2023, the Department of Financial Protection and Innovation of California (DFPI) declared the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank and appointed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) as the bankruptcy administrator.
After the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank, liquidity pressure was caused to the science and technology enterprises in the United States. Some of them were affected by financing difficulties and unstable sources of funds, which eventually led to a decline in stock prices and the bankruptcy of some technology enterprises. At the same time, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank led to financial market volatility, affected investor confidence, caused market panic and caused a run on the bank [1]. Finally, on March 26, 2023, the FDIC announced that First Citizens Bank and Trust Company acquired and undertook the deposits and loans of Silicon Valley Bank.
The bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank has had a significant impact on the US economy and Scientific and technological innovation enterprise, exposing the instability of the global financial system. Through an in-depth study of the causes of the bankruptcy, the analysis is mainly conducted from the perspectives of risk management and strategy, emphasizing the necessity of diversified financing and excellent risk management for the anti-risk ability of small and medium-sized enterprises. The report suggests that actively exploring diversified financing channels, using big data technology to strengthen supervision and monitoring, and strengthening international cooperation and other means will help ensure financial stability and reduce the risks that small and medium-sized enterprises may face.
A series of studies have examined the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) and its implications for the banking industry. Mustafa attributes SVB's failure to mismanagement of liquidity and interest rate risk, as well as ineffective board oversight [2]. Guo underscores the significance of bank failures in financial analysis, particularly in the context of global financial markets [3]. Holzmann emphasizes the need for proactive risk management and a robust regulatory framework to prevent financial contagion [4]. Hamurcu identifies long-term investment, cash on hand, and price-to-earnings ratios as key risk indicators for bank failures, with SVB serving as a case study [5]. These studies collectively highlight the complex interplay of factors contributing to SVB's collapse and the broader implications for the banking industry.
A review of the literature indicates that previous studies have primarily focused on the repercussions of Silicon Valley Bank's closure on the banking sector, neglecting its implications for technology enterprises or small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Consequently, this paper adopts a novel perspective, aiming to provide decision-making support for the advancement of both the banking industry and diverse enterprises by investigating the impact of this event on technology companies or SMEs.
2 Case Description
2.1 Background
At the beginning of 2020, the global outbreak of COVID-19 had a huge impact on the US economy, forcing thousands of businesses to shut down and disrupting supply chains. As shown in figure 1, the outbreak of the novel coronavirus has had a huge impact on the US Treasury, and the fiscal deficit has continued to soar. As of September 30, 2020, the U.S. federal government deficit totaled $3.1 trillion, more than three times the deficit in fiscal 2019 [6].
At the same time, it can be seen from the US financial report that the US economy experienced negative quarter-on-quarter growth in the first quarter and the second quarter of 2020, and the GDP adjusted quarter-on-quarter annualized rate of constant price was -5% and -31.4% respectively. In terms of annualized real GDP growth, the US economy grew near zero in the first quarter of 2020, -9% in the second quarter, and -2.9% in the third quarter [7]. At the beginning of 2022, the Russia-Ukraine war broke out, and prices in the United States were stable for nearly 30 years before the epidemic, and the CPI data in the United States remained below 4% from 2010 to 2020. From 2020 to 2023, the epidemic combined with the Russia-Ukraine conflict led to inflation in the United States, affecting food production and transportation, and the demand for energy also gradually increased. As a result, rent inflation, food inflation, and energy inflation are all rising, reaching as high as 9.1% [8].
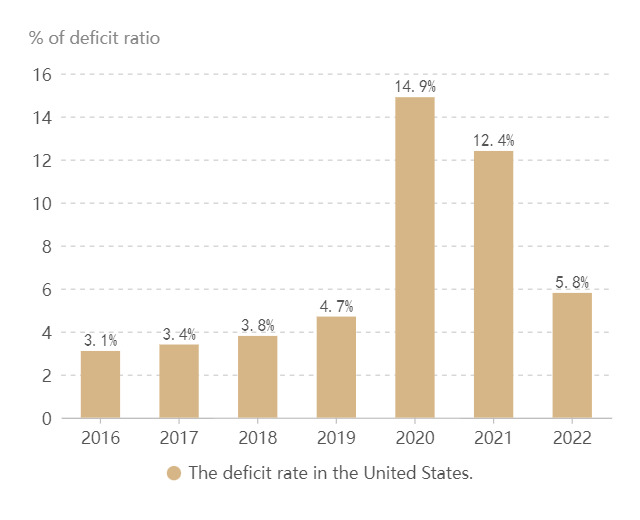
Figure 1. The federal government's fiscal 2016-2022 deficit
In the same period, the Federal Reserve introduced five rounds of monetary policies to deal with the impact of the epidemic: the first stage was to cut interest rates more than expected, and two interest rate cuts were implemented during the two critical interest rate meetings, returning to zero interest rates. The second stage is to start quantitative easing and start focusing on liquidity management. The third stage is to further inject dollar flow into the international market. The fourth stage is to pursue unlimited quantitative easing. The fifth stage is to help the real economy out of the dilemma and provide financial support [9]. After the implementation of quantitative easing policy, the financing cost of scientific and innovative enterprises is reduced, the profitability of enterprises is improved, and the risks faced by enterprises are also increased. As shown in figure 2, by the end of 2022, the deposit liabilities of Silicon Valley banks are dominated by demand deposits, and non-interest bearing deposits account for 47% of the deposit structure.
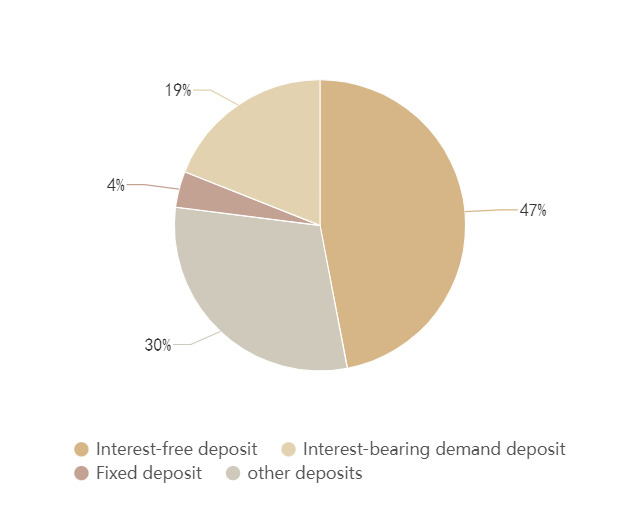
Figure 2. Silicon Valley bank deposit structure at the end of 2022
2.2 Development
Eastern Time on March 8, 2023, Silicon Valley Bank announced the sale of $21 billion in bond investments at a loss of $1.8 billion, and also unveiled plans to raise $2.25 billion by selling common and preferred shares to strengthen its balance sheet. On March 9, 2023, as investors worried about the financial condition of Silicon Valley Bank, resulting in a 60% drop in Silicon Valley Bank's share price, investors and depositors tried to withdraw $42 billion from Silicon Valley Bank, and the cash balance of Silicon Valley Bank was negative $958 million at the end of the day. On March 10, 2023, the California Department of Financial Protection and Innovation (DFPI) declared Silicon Valley Bank insolvent and appointed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) as the insolvency administrator. The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank caused a run on more banks. On March 12, 2023, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, the Treasury Department, and the Federal Reserve took the significant step of informing depositors of Silicon Valley banks that the FDIC would protect all of their funds. On March 27, 2023, First Citizens Bank assumed control of all deposits and loans from Silicon Valley Bank under the FDIC's supervision.
3 Analysis: The Impact of the Collapse of Silicon Valley Banks
3.1 The Impact of Silicon Valley Bank Bankruptcy on American Scientific and Technological Enterprises
For American enterprises, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank will cause instability and imbalance in the US financial market, which will not only lead to the blockage of capital flow and market contraction, but also make the financing difficulty of scientific and technological enterprises further increase. Especially for small and medium-sized scientific and technological enterprises, due to their relatively limited financing channels, the crisis will have a great impact on them. Secondly, the failure of Silicon Valley banks will affect the operating prices of the stock market, bond market and money market, leading to the fluctuation of currency prices and the rise of inflation.
At the same time, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley bank caused volatility to the technology stock market, triggered market panic, investor confidence was frustrated, and thus reduced the investment and financing of small and medium-sized micro science and technology innovation enterprises, resulting in their later development limited. Finally, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley banks will have a negative impact on the US economy, leading to the collapse of technology companies and the rise of unemployment, leading to large-scale unemployment and social unrest, affecting employment and consumption. Silicon Valley is one of the most important scientific and technological innovation centers in the world, and its economic stability and development also has an important impact on the stability and development of the global economy.
3.2 The Impact of Silicon Valley Bank Bankruptcy on Chinese Scientific and Technological Enterprises
For Chinese enterprises, the US dollar fund is the main source of financing channels in China's science and technology investment market. Under normal circumstances, scientific and technological enterprises that use US dollar funds to obtain financing will basically choose to open an account in a Silicon Valley bank [9]. Therefore, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank limited the financing channels of China's small, medium and micro science and technology enterprises, and at the same time led to the return of funds. Chinese science and technology enterprises and science and technology investment institutions returned funds to the Hong Kong market and the domestic market, increasing the financing difficulty of Chinese science and technology enterprises in the US capital market. At the same time, the Silicon Valley Bank incident will cause a lack of confidence in the US science and technology environment, prompting Chinese science and technology enterprises to flee the US market, or will become a long-term event [9].
The emotional contagion of panic and tight liquidity faced by the capital market will also be reflected in the development of Chinese enterprises, so that Chinese scientific and technological enterprises have insufficient confidence in the US market. Finally, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank has also triggered a heightened concern among regulatory authorities about the risks in the cryptocurrency market. In China, the regulatory authorities have been vigilant about the risks of the cryptocurrency market, and this incident may lead to more cryptocurrency investment channels being closed, further limiting the development space of investors.
3.3 The Impact of Silicon Valley Bank Bankruptcy on the Banking Industry
For the banking industry, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank has a profound impact on its main customer groups. As a bank focused on supporting innovative enterprises and the technology industry, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank has threatened the security of these customers' funds, and therefore, the reputation of the bank has been seriously affected, resulting in a decline in customers' trust in the bank. Secondly, the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley banks also has a certain degree of spillover effect on the global financial market. The failure of Silicon Valley Bank caused the rapid transmission of risk to other banks, resulting in increased volatility in global financial markets. In addition, the market's trust in other financial institutions has been shaken, which could trigger investor panic around the world.
4 Solutions
4.1 For Enterprises
Actively explore diversified financing channels, taking into account traditional and innovative channels: Scientific and technological innovation enterprise should consider establishing partnerships with multiple financial institutions, rather than relying on a single bank. This spreads the risk and prevents a similar dilemma from happening again. While considering high-risk investments, people should also choose stable financing channels with low risks.
Pay close attention to changes in the international financial market and do a good job in risk prevention: strengthen financial risk management, including fund management, risk investment and asset allocation, in order to cope with unpredictable factors such as fluctuations in the financial market and bank bankruptcy. At the same time, the financial condition and supervision of banks should be fully investigated to avoid later shocks.
Strengthen the integration of fintech into business operations: Enterprises should consider adopting fintech solutions, such as e-commerce platforms, blockchain technology, and artificial intelligence risk management systems, to enhance financial management and transaction efficiency. Additionally, big data technology can be utilized for enterprise and market data analysis, facilitating a better understanding of market dynamics. Simultaneously, leveraging financial technology tools for risk management purposes - such as artificial intelligence risk assessment systems and blockchain technology for asset traceability - will improve enterprises' ability to identify and respond to market risks.
Enhance international financial cooperation by attracting international capital and technology with an open mindset: To expand in the international market, enterprises should seek diverse financial partners while establishing partnerships with multiple financial institutions. Actively participating in international scientific and technological exchanges and cooperation through avenues like technology transfer or collaborative research and development is crucial. Formulating an international development strategy encompassing aspects like positioning in the global market, selecting suitable international partners, expanding businesses internationally etc., will ultimately enhance enterprises' competitiveness in the realm of international financial cooperation.
4.2 For Banking Industry
Pay attention to the matching of assets and liabilities to prevent liquidity risks caused by maturity mismatch. At the same time, adequate early warning to ensure adequate capital and liquidity, banks need to have sufficient liquid assets and capital. Through the integration of information technology and the financial industry, a scientific and timely detection mechanism is established to achieve effective management of liquidity. This mechanism can accurately predict the daily withdrawal demand and help banks to arrange and manage liquidity.
Reputation risk management needs to be improved. It is necessary to correctly judge the new situation of public opinion communication, increase the intensity of residual risk treatment, improve the system guarantee, and provide institutional protection for bank bankruptcy: the government should establish the corresponding deposit insurance mechanism and regulations to protect depositors in the event of bank bankruptcy. At the same time, real-time supervision and assessment of the bank's risk situation and appropriate measures are taken. This helps to reduce the broader social and economic impact of bank failures.
Diversification of investment to spread risk: Banks should pay attention to the concentration of industry, region, customer and product risks. Diversifying an asset portfolio while focusing on the development of clients and businesses in one area can help mitigate the impact of concentration risk [10].
5 Conclusion
Through the in-depth study of the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley bank and its impact on the business model of scientific and creative enterprises, it can draw the following conclusions: First, this event significantly highlights the vital importance of risk management in the operation of financial institutions. In this context, science and technology enterprises still need to deeply understand the risks, and establish a comprehensive and systematic risk management system, in order to more flexible and rapid response to the challenges of unpredictable factors, to ensure the steady operation of enterprises. Secondly, the strategic significance of diversified financing channels is more significant. Scientific and creative enterprises should take the initiative to seek and expand traditional and innovative financing channels to effectively disperse financial risks, reduce the dependence on a single financial institution, and improve the flexibility and sustainability of enterprises in the capital market. In addition, the wide application of financial technology has become an indispensable factor to enhance the competitiveness of enterprises. The introduction of advanced financial technology solutions can effectively improve the financial management efficiency of enterprises and enhance the perception and response-ability of market risks. Finally, the strengthening of international financial cooperation has important strategic value for the development of enterprises. Science and technology enterprises should actively attract international capital and technology, and formulate a clear international development strategy, in order to enhance their competitiveness in global financial cooperation and achieve a broader market expansion.
Looking to the future, enterprises will face the challenges of fierce global competition and full of uncertainties, and a series of strategic initiatives should be taken to ensure sustainable development. The priority is to continuously optimize the business model, flexibly adjust the business strategy, and innovate products and services to remain competitive. Secondly, people should increase the investment in risk management and establish a complete risk assessment system to ensure that agile decisions and implementation can be made quickly in the market turbulence. The deep integration of financial technology is regarded as the inevitable path to enhance competitiveness, introducing advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, and building a digital platform to provide reliable support for financial processes. Finally, actively participate in international cooperation, expand market territory, participate in scientific and technological exchanges and cooperation, establish strategic alliances with international partners, and respond to the challenges brought by globalization with a flexible and comprehensive strategic layout to achieve sustainable and healthy development of enterprises.
References
[1]. Erer, E., & Erer, D. (2024). The domino effect of Silicon Valley Bank's bankruptcy and the role of Fed's monetary policy. Borsa Istanbul Review, (in press).
[2]. Allagabo, O., & Mustafa, O. (2023). SVB failure: Causes and results on banking industry. International Journal of Economics and Financial Research, 9(2), 9-19.
[3]. Guo, C. (2024). Analysis and evaluation of bank failure: Evidence from Silicon Valley Bank. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, (24), 1744-1749.
[4]. Holzmann, L., & Huppertz, J. (2023). The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank–The importance of proactive risk management in order to prevent financial contagion. In Konference doktorandů (p. 70).
[5]. Hamurcu, Ç. (2023). Bank failure risk: A study on Silicon Valley Bank, Signature Bank, and Silvergate Capital Corporations. Financial Internet Quarterly, 19(02), 36-45.
[6]. Chen, Z., & Huang, J. (2022). American fiscal policy and thinking under the impact of the epidemic. China Finance, (04), 77-79.
[7]. Yang, P., Xu, Q., & Yang, Z. (2021). To review US macroeconomic policy under COVID-19. Contemporary American Review, 5(01), 15-33+123.
[8]. Cao, X. (2023). Implications of the "bankruptcy" of Silicon Valley Bank for small and medium-sized commercial banks in China. Northern Finance, (05), 82-88.
[9]. Xu, X. (2023). Analysis on the mechanism and path of financing innovation for science and technology enterprises: Based on the theory of the whole life cycle and the perspective of the Silicon Valley Bank incident. Modern Economic Research, (12), 9-17.
[10]. Jiang, S. (2024). Reasons and enlightenment for the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank. Frontiers in Business, Economics and Management, 160-162.
Cite this article
Li,C. (2024). Analysis of the Influence of the Bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank on the Scientific and Technological Innovation Enterprises. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,5,84-88.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Erer, E., & Erer, D. (2024). The domino effect of Silicon Valley Bank's bankruptcy and the role of Fed's monetary policy. Borsa Istanbul Review, (in press).
[2]. Allagabo, O., & Mustafa, O. (2023). SVB failure: Causes and results on banking industry. International Journal of Economics and Financial Research, 9(2), 9-19.
[3]. Guo, C. (2024). Analysis and evaluation of bank failure: Evidence from Silicon Valley Bank. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, (24), 1744-1749.
[4]. Holzmann, L., & Huppertz, J. (2023). The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank–The importance of proactive risk management in order to prevent financial contagion. In Konference doktorandů (p. 70).
[5]. Hamurcu, Ç. (2023). Bank failure risk: A study on Silicon Valley Bank, Signature Bank, and Silvergate Capital Corporations. Financial Internet Quarterly, 19(02), 36-45.
[6]. Chen, Z., & Huang, J. (2022). American fiscal policy and thinking under the impact of the epidemic. China Finance, (04), 77-79.
[7]. Yang, P., Xu, Q., & Yang, Z. (2021). To review US macroeconomic policy under COVID-19. Contemporary American Review, 5(01), 15-33+123.
[8]. Cao, X. (2023). Implications of the "bankruptcy" of Silicon Valley Bank for small and medium-sized commercial banks in China. Northern Finance, (05), 82-88.
[9]. Xu, X. (2023). Analysis on the mechanism and path of financing innovation for science and technology enterprises: Based on the theory of the whole life cycle and the perspective of the Silicon Valley Bank incident. Modern Economic Research, (12), 9-17.
[10]. Jiang, S. (2024). Reasons and enlightenment for the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank. Frontiers in Business, Economics and Management, 160-162.









