

About JAEPSJournal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies (JAEPS) is an open-access, peer-reviewed academic journal hosted by Peking University Research Centre for Market Economy (RCME) and published by EWA Publishing. JAEPS is published monthly. JAEPS present latest theoretical and methodological discussions to bear on the scholarly works covering economic theories, econometric analyses, as well as multifaceted issues arising out of emerging concerns from different industries and debates surrounding latest policies. Situated at the forefront of the interdisciplinary fields of applied economics and policy studies, this journal seeks to bring together the scholarly insights centering on economic development, infrastructure development, macroeconomic policy, governance of welfare policy, policies and governance of emerging markets, and relevant subfields that trace to the discipline of applied economics, public policy, policy studies, and combined fields of the aforementioned. JAEPS is dedicated to the gathering of intellectual views by scholars and policymakers. The articles included are relevant for scholars, policymakers, and students of economics, policy studies, and otherwise interdisciplinary programs.For more details of the JAEPS scope, please refer to the Aim&Scope page. For more information about the journal, please refer to the FAQ page or contact info@ewapublishing.org. |
| Aims & scope of JAEPS are: ·Economics ·Finance ·Management |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

Beijing, China
qin.econpku@gmail.com

London, United Kingdom
Canh.Dang@kcl.ac.uk

Edinburgh, UK
B.Adamolekun@napier.ac.uk

Murcia, Spain
faura@um.es
Latest articles View all articles
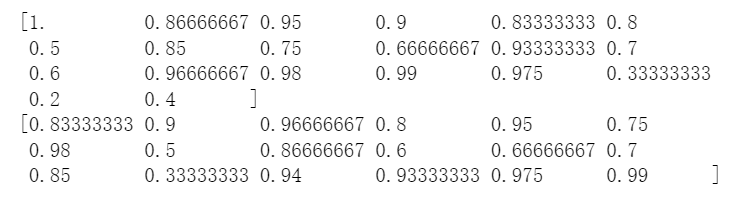
With the development of 4G and 5G networks, more and more industries in China are borrowing O2O coupons to drive offline consumption; however, many merchants randomly issue coupons leading to immeasurable marketing costs for brands, and at the same time, there is a certain interference with consumers' choice of coupons for underwriting, and there is no more scientific method to improve the redemption rate. Therefore, this paper adopts the actual data provided in the Aliyun Tianchi competition, preprocesses and feature extraction and selection of the dataset, and constructs three prediction single models based on GBDT, XGBoost and LightGBM, respectively. Through experiments, it is concluded that XGBoost has the best prediction effect and the best stability among the single models, thus XGBoost is selected as the prediction model for judging coupon usage, thus helping merchants to predict the probability of consumers using coupons, and thus realizing personalized coupon placement and improving merchants' marketing ability.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of accelerating global economic integration and digital transformation, it is crucial to strike a dynamic balance between globalization and localization in corporate supply chains for effective strategic management. From a systems integration perspective, this paper discusses core mechanisms through which digital economy platforms collaborate with human resource management (HRM) to achieve supply chain balance. By synthesizing research on global versus local supply chains, digital-economy platforms, and HRM, the author proposes a “technology—organization” collaboration framework that unveils how digital-platform empowerment and HRM-driven organizational empowerment are intrinsically linked and mutually reinforcing. Research indicates that digital economy platforms provide technological support, while HRM offers organizational capability guarantees; their collaboration optimizes the balance of the supply chain. However, existing studies are often limited by either "technological determinism" or "organizational determinism" perspectives, which lack systematic exploration of their collaborative mechanisms. Based on this gap, the paper proposes a "Platform-HRM Collaboration" theoretical framework, which elucidates the dialectical relationship between technological embedding and organizational adaptation. It reveals how the two factors form complementary and mutually reinforcing relationships at different levels of the supply chain to achieve a dynamic balance among efficiency, resilience, and innovation. This framework not only enriches interdisciplinary research in digital economy and supply chain management but also provides systematic theoretical guidance for companies to achieve coordinated globalization and localization development in complex environments.

 View pdf
View pdf


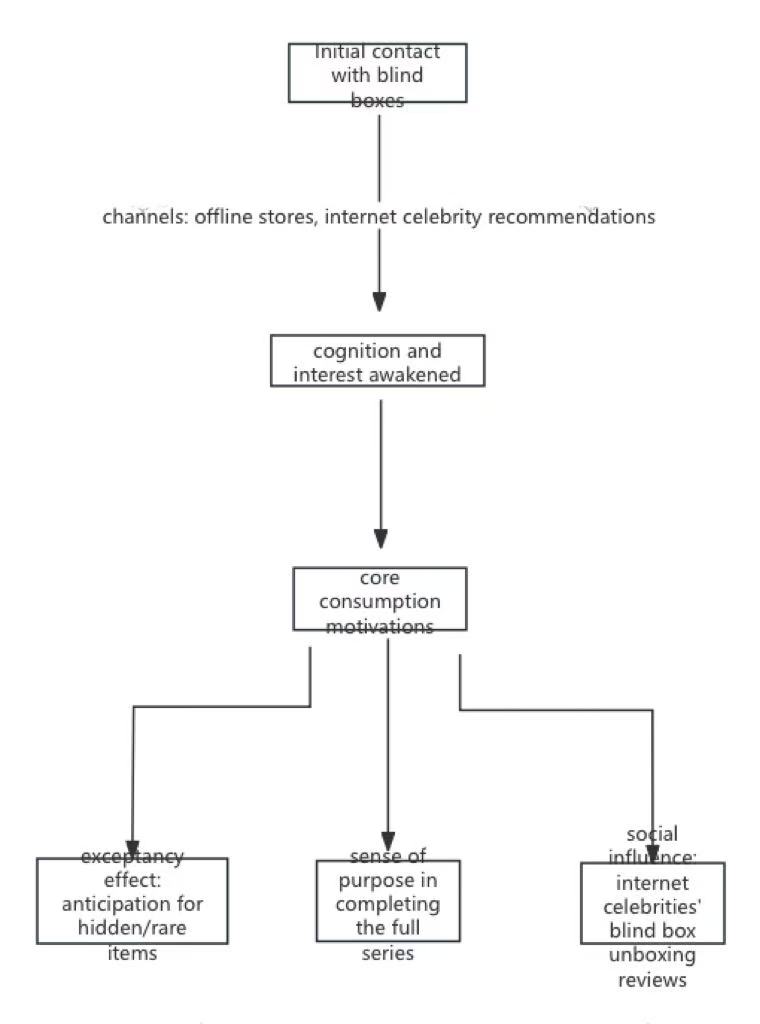
This study focuses on the phenomenon of hidden editions in blind boxes, constructs a framework of consumers' psychological decision-making, and explores the optimization path of corporate marketing strategies. Through research, it is found that scarcity, cognition and interest, and regret psychology are the main psychological driving factors affecting blind box consumption. Furthermore, based on the psychological level of consumers, this paper puts forward targeted marketing strategy suggestions from the aspects of product, price, channel and promotion. The research in this paper provides a theoretical basis for the development of the blind box market.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping corporate strategic management. In today’s dynamic global environment, organizations face increasing challenges in decision-making, resource allocation, and operational efficiency. Against this background, AI offers significant potential to enhance the speed, accuracy, and effectiveness of strategic management practices. This study examines the applications of AI in corporate strategy, with a focus on how technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and automation contribute to improving strategic decision-making. The research employs a non-empirical design, combining literature review and conceptual analysis. The study objects include enterprises across manufacturing, high-tech industries, and SMEs, as represented in existing scholarly works and industry reports. Analytical tools are theoretical models of AI integration, and data sources consist mainly of secondary materials such as peer-reviewed articles, case documentation, and industry analyses. The findings indicate that AI improves strategic accuracy and efficiency, but challenges remain regarding data quality, organizational resistance, and ethical concerns. The study concludes that successful adoption requires aligning technological advances with organizational adaptation. Furthermore, the integration of AI with big data, cloud computing, and blockchain is expected to play a central role in shaping the future of strategic management.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
2025
Volume 18May 2025
Find articlesVolume 18September 2025
Find articlesVolume 18August 2025
Find articles2024
Volume 14December 2024
Find articlesVolume 13November 2024
Find articlesVolume 12November 2024
Find articlesAnnouncements View all announcements
Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies (JAEPS) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:





