

Volume 18 Issue 6
Published on August 2025
Common prosperity is the essential attribute and fundamental goal of socialism. Sichuan Province holds a uniquely strategic position in China and constitutes a key component in the broader landscape of national common prosperity. Drawing on existing literature, this study constructs an index system for common prosperity encompassing two major dimensions: development and sharing. Using the entropy method and the entropy-weighted TOPSIS method, it quantitatively evaluates the level of common prosperity across cities and prefectures in Sichuan Province from 2009 to 2022, and further analyzes the influencing factors. The main findings are as follows: the overall level of common prosperity in Sichuan has improved, although the pace of development varies across different regions; the province exhibits a dual-core pattern of high-level prosperity centered in Chengdu and Panzhihua, with a general spatial trend of higher levels in the west and lower levels in the east. Key influencing factors include population, the tertiary sector, and consumption. Based on these findings, the paper proposes policy recommendations to promote the development of the tertiary industry and stimulate consumption growth.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the acceleration of the aging process of China's population, smart pension, as a new model of "Internet plus pension", is becoming an important breakthrough to solve the pension problem. Based on the background of China's aging society, this study combines a three-dimensional perspective of policy orientation, market dimension, and technological development. Through policy text analysis and typical case studies of the elderly care industry, it explores the investment value and risk boundary of smart elderly care projects. The results show that the scale of the smart elderly care industry is expected to reach 7.21 trillion yuan by 2025. The flourishing development of AI technology brings great convenience to smart elderly care and effectively reduces labor costs. There are investment opportunities in segmented fields, and intelligent monitoring, but people need to be alert to the challenges brought by technological iteration risks and market information differences. Research suggests that investors should focus on relevant core technological barriers and develop smart elderly care projects that are highly compatible with policies and have clear business models; actively seek cooperation with the government; and establish an investment mechanism that integrates government-guided funds with market-oriented capital. In addition, investors need to balance long-term investment and short-term returns, and design project operation models that balance social capital and public welfare attributes. Through multi-party collaboration, investment risks can be effectively reduced, and the sustainability and social benefits of smart elderly care projects can be improved.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of complexity and sustainability challenges in global supply chains, artificial intelligence technology is driving innovation in supply chain management and promoting social sustainability. The research analyzes the technological path of artificial intelligence in supply chain optimization, including multi-data fusion prediction, green supplier selection, and drone delivery. Through case analysis, this study elucidates the application of artificial intelligence in improving supply chain efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impact. The study also explores the impact of AI-driven supply chain optimization on the environment and socialeconomic aspects, including energy consumption optimization, carbon emission monitoring and reduction, and empowerment of small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, the research identifies the challenges including data security, ethical issues and technological barriers, and offers corresponding policy recommendations and future development directions. The findings reveal a theoretical model of AI driven supply chain optimization and sustainable development, highlighting future research directions while reflecting on the limitations of this study.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study focuses on the "green premium" phenomenon in wine and quantifies consumers' willingness to pay for five types of sustainable attributes through a mixed-selection Logit experiment: recycled glass packaging, carbon footprint disclosure, organic certification, biodynamic labels, and recycled plastic bottle caps. For 305 wine consumers in New York, London, and Sydney, 1,830 valid data sets were collected. The results show that the premium effect of carbon footprint disclosure is the strongest (an increase of $2.29, or 14.7%), followed by recycled glass packaging (an increase of $1.23, or 8.2%), closely followed by organic certification (an increase of $1.03, or 6.5%) and biodynamic labeling (an increase of $0.84, or 5.3%). A detailed study reveals that three types of consumer groups: environmental advocates (38%), cost-effectiveness advocates (44%), and traditional conservatives (18%) show significant differences in their sensitivity to ecological attributes. The interaction effect indicates that the carbon footprint combined with the environmental label can increase the premium by $0.36 (2.3%), while the combination of organic certification and recycled plastic bottle caps slightly weakens the overall premium. These results suggest that transparent carbon quotas and high-quality packaging are the essential elements for obtaining higher prices, particularly having a significant impact on environmentally conscious customers. The article concludes with suggestions for integrated green communication strategies, and it is emphasized that in the future, repurchase behavior patterns should be studied through long-term monitoring.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the current wave of digital transformation sweeping across various industries, this paper focuses on the driving role of corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance on digital transformation.Based on the perspectives of signaling theory and the resource-based view, a theoretical framework is constructed, and empirical analysis is conducted using panel data of Chinese A-share listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges from 2013 to 2023.The benchmark regression results indicate that corporate ESG performance significantly enhances the degree of digital transformation. Mechanism analysis reveals that corporate ESG performance facilitates digital transformation by alleviating financing constraints and promoting digital technology innovation. The conclusions of this paper hold significant implications for policy guidance and corporate strategic planning in promoting the synergistic development of digitalization and greening, providing valuable references for relevant parties to drive high-quality development of enterprises in the digital economy era.

 View pdf
View pdf


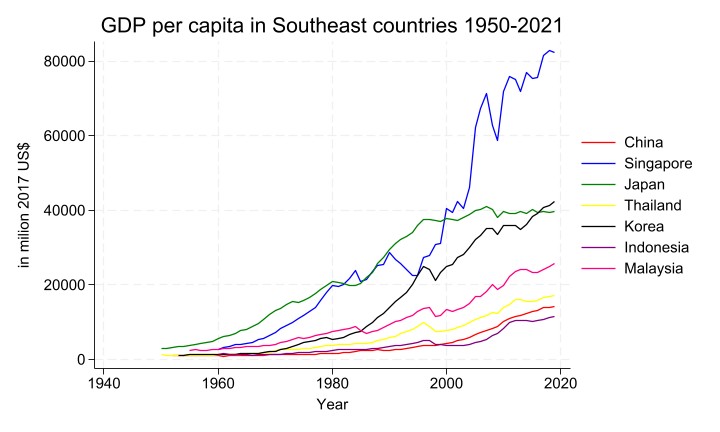
This study examines the economic development trajectories of historically and newly prosperous cities in East Asia from 1993 to 2021 using nighttime light (NTL) data. By integrating DMSP and VIIRS satellite data, the research compares growth patterns across cities like Tokyo, Singapore, Shenzhen, and Chengdu. Results reveal that historically prosperous cities, such as Tokyo, exhibit a "ceiling effect" with stagnant NTL levels, reflecting early maturity and slowed growth. In contrast, newly prosperous cities like Shenzhen demonstrate rapid NTL growth, leveraging late-mover advantages through policy support and technological adoption. The findings align with the late-mover advantage theory, highlighting divergent development paths. The study underscores the role of NTL data in tracking urbanization and economic activity, offering insights for regional development policies. Keywords: nighttime light data, economic development, late-mover advantage

 View pdf
View pdf


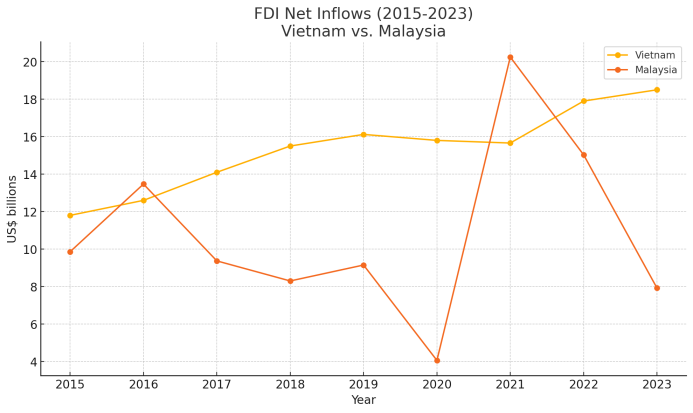
In the context of evolving economic relations between the United States and China, Southeast Asia has emerged as a key region undergoing significant transformations in regional supply chains. This paper examines how Vietnam and Malaysia have strategically re-positioned themselves, benefiting from production shifts and new investment patterns influenced by changing geopolitical and economic dynamics. Utilizing perspectives from Geo-economics and global value chain theories, the study highlights opportunities, including industrial upgrading, increased foreign investment, and enhanced geopolitical agency. It also identifies critical challenges such as infrastructure constraints, labor shortages, and geopolitical uncertainties. Ultimately, this research argues for strategic policy innovations and strengthened regional cooperation to effectively manage economic opportunities and mitigate risks.

 View pdf
View pdf


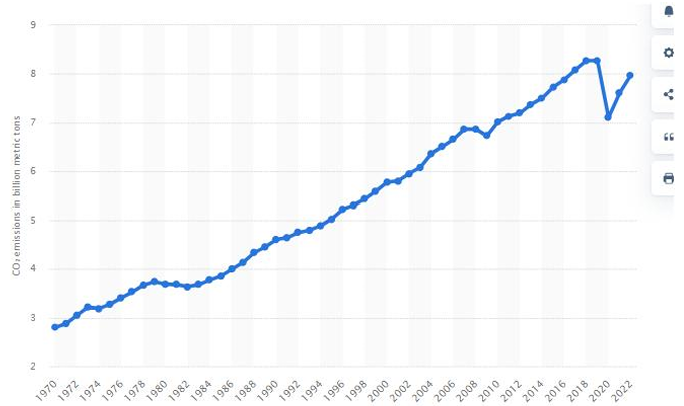
This paper examines the negative externality of pollution in the transportation sector and evaluates both existing and proposed policy responses. The transportation industry, while integral to economic development, is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to climate change. The paper first describes the magnitude and trend of carbon emissions from this sector, then reviews current market-based solutions including Pigouvian taxes and subsidies. It subsequently proposes targeted subsidies to accelerate the electrification of transportation systems as a more effective long-term policy. Drawing on empirical evidence from China, the EU, the United States, and the UK, the paper finds that subsidies have substantially promoted electric vehicle (EV) adoption and reduced emissions. However, the paper also discusses potential limitations, such as fiscal burdens on governments and limited consumer willingness to adopt EVs. Mitigation strategies, including phased subsidy implementation and increased public participation, are recommended to enhance the policy’s acceptance and sustainability. Overall, the study concludes that well-designed subsidies, supported by complementary measures, can meaningfully reduce pollution externalities in the transportation sector and contribute to broader climate mitigation goals.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study explores the countercyclical role of accounting conservatism in the business cycle, focusing on how it affects firms’ acquisition of external financing and the transmission of systemic risks. Using data from 312 listed banks and 1,047 manufacturing firms in China from 2008 to 2022, we measure robustness by dividing the absolute value of negative accrual items by total assets, we measure financing accessibility by dividing new debt issuance by assets, and we measure systemic risk by the 5% CoVaR percentile at the firm level. After using the fixed-effect model regression including the interaction term of the business cycle state and supplemented by 2SLS and system GMM methods to handle endogeneity, it was found that during the expansion period, increased robustness significantly reduced new debt issuance by banks (β = -0.042, p < 0.01), but had no significant impact on manufacturing firms. Conversely, during the recession period, robustness effectively eliminated the spillover effects of systemic risks in banks (β = -0.068, p < 0.05) and manufacturing industries (β = -0.054, p < 0.05). This indicates that conservative accounting plays the role of a procyclical credit limiter during the expansion period and a stabilizing buffer during the depression period. The research findings have implications for countercyclical disclosure policy aimed at balancing financial stability and credit availability.

 View pdf
View pdf


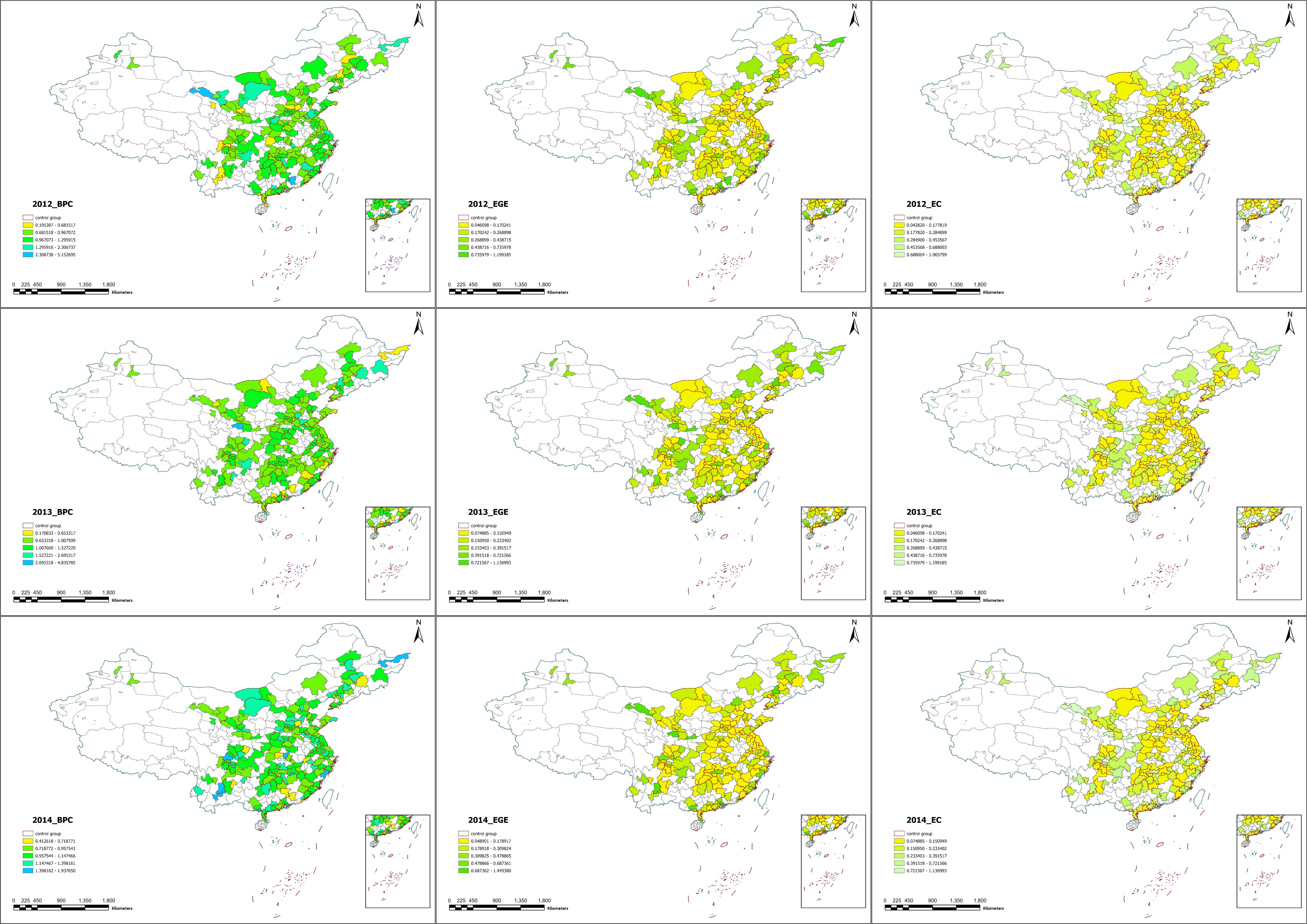
This paper explores the relationship between Smart City Construction (SCC) and Urban Environmental Governance Efficiency (EGE) in the context of China's rapid urbanization. By analysing data from 193 Chinese prefecture-level cities over the period 2007 to 2018, and focusing on the moderating roles of public education services and industrial structure rationalization, this study employs a multi-period Difference in Differences model to reveal that: (1) SCC significantly improves the efficiency of government’s urban EGE; (2) Both educational public services and the advancement of industrial structure show a negative moderate effect on EGE, while rationalization of industrial structures has positive moderate effect; (3) the impact of SCC initiatives on EGE varies due to geographic location, technological foundations, and diverse city characteristics. The paper highlights how integrating technology in urban management, exemplified by SCC, serves as a strategic approach to enhancing environmental governance. By outlining the interactive relationship between SCC and EGE, this research provides valuable insights for policymakers and urban planners aiming for a balanced approach between technological advancement and sustainable environmental governance. Moreover, the analysis offers a methodically robust framework for evaluating the strategic impact of technological innovations on urban environmental governance, contributing to the broader discourse on technology-driven urban sustainability strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf




