1 Introduction
Investor sentiment is a primary driver of market dynamics, and stock prices can often deviate from a company’s fundamental value. Behavioural finance is an important field of study that focuses on observing, explaining and regulating the psychological biases of investors in order to understand how market sentiment can lead to irrational behaviour, making stock prices more volatile and destabilising corporate governance. Overconfidence, herd behaviour, and loss aversion are three of the most common biases observed across financial markets, particularly during times of uncertainty or events such as elections or economic crises. Overconfidence bias often translates into excessive trading that increases market volatility and exposes both individual investors and companies to financial risk. On the other hand, herd behaviour occurs when investors follow market trends without conducting independent analysis, potentially contributing to asset bubbles and subsequent crashes, as observed during the dot-com era. Meanwhile, loss aversion causes investors to hold onto losing positions for too long, distorting market prices and influencing managerial decision-making, which can have consequences for corporate governance. This paper focuses on the impact of these biases on stock price volatility and the corresponding implications for corporate governance. Through an empirical analysis of data collected from global stock exchanges and corporate financial reports, we explore how governance mechanisms can curtail the harmful effects of behavioural biases. Finally, we recommend the most effective ways to improve governance frameworks, reduce market volatility, and ultimately create value for shareholders [1]. It is important to understand the interaction of investor sentiment and corporate governance because it can be used to create robust strategies in today’s volatile market landscape.
2 Investor Sentiment and Behavioral Biases
2.1 Investor Sentiment and Behavioral Biases
Overconfidence bias occurs when investors overestimate their knowledge or ability to predict market movements, leading to excessive trading and increased volatility. Overconfident investors typically trade 50% more frequently than their peers, according to a study conducted over a 10-year period involving more than 100,000 individual accounts on the New York Stock Exchange, as shown in Table 1. This excessive trading often leads to inferior financial outcomes because investors fail to account for the unpredictable nature of market dynamics. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, overconfident investors were observed to trade more frequently and hold riskier assets, which led to substantial financial losses. Firms, aware of this bias, must implement corporate governance mechanisms, such as independent risk management committees, to mitigate the impact of overconfidence on managerial decisions [2]. By conducting regular financial audits and engaging in thorough risk assessments, companies can reduce the negative effects of overconfidence and promote a more stable governance structure that shields the company from market overreaction.
Table 1. Investor Sentiment and Behavioral Biases Study
Year |
Average Trading Frequency (Overconfident Investors) |
Average Trading Frequency (Non-Overconfident Investors) |
Stock Volatility (Overconfident Investors) |
Stock Volatility (Non-Overconfident Investors) |
Average Loss (Overconfident Investors) |
Average Loss (Non-Overconfident Investors) |
2000 |
70 |
45 |
15 |
8 |
5 |
2 |
2002 |
72 |
46 |
16 |
9 |
7 |
3 |
2004 |
75 |
46 |
18 |
10 |
8 |
3 |
2006 |
78 |
48 |
20 |
10 |
10 |
4 |
2008 |
82 |
49 |
25 |
12 |
15 |
6 |
2010 |
85 |
50 |
30 |
14 |
20 |
8 |
2.2 Herd Behavior
Herd behaviour describes the tendency of investors to imitate the actions of the crowd by following the majority, and usually disregarding careful analyses and decisions made independently. A recent illustration of herd behaviour was the stock market activity during the notable dot-com bubble in the late 1990s. Stock prices in technology companies surged beyond their fundamental values as a crowd of investors rushed to invest in tech start-ups, fearing to miss out on the next big thing. When the bubble burst, it led to a market crash as panic overtook the market. Fear of missing out and the perception that others had better information caused investors to follow the lead of the crowd. The study of the transaction records of 31 million investors between 1995 and 2000 revealed that 70 per cent of retail investors were impacted by herd behaviour during periods when stock prices escalated rapidly, contributing to the formation of speculative bubbles – see Table 2 below. From a company’s perspective, herd behaviour in the stock market can induce volatility that may make it difficult to manage and plan for future contingencies [3]. By focusing on long-term strategic goals and reporting financial information conservatively, firms can isolate themselves from the adverse effects of market speculation and the price movements driven by the herd.
Table 2. Herd Behavior Study
Year |
Percentage of Retail Investors Influenced by Herd Behavior |
Technology Stock Price Growth (%) |
Average Investor Return (Herd Behavior) |
Average Investor Return (Non-Herd Behavior) |
1995 |
65 |
12 |
4 |
8 |
1996 |
68 |
18 |
6 |
9 |
1997 |
70 |
30 |
8 |
10 |
1998 |
71 |
45 |
12 |
10 |
1999 |
73 |
60 |
-5 |
5 |
2000 |
75 |
80 |
-30 |
3 |
2.3 Loss Aversion
Loss aversion refers to the cognitive bias whereby the pain of losing is felt more intensely than the pleasure of gaining. Because of this tendency, investors are more likely to hold on to a losing investment for longer in hope of a market recovery. While researchers have found that loss aversion exists among investors, real-world data from the Shanghai Stock Exchange between 2010 and 2020 reveal that investors who had losses held on to their stocks dropping in value 60 per cent longer than those with winning stocks, and thus underperformed significantly. In practice, loss aversion can distort corporate governance as managers can be pushed by shareholders to take risks to recoup loses [4]. Companies need to improve communications with investors and offer more transparent reports on long-term strategy to reframe the loss-aversion effect. For example, firms should highlight in their reports their sustainability, resilience and innovation, which can shift investor focus away from short-term fluctuations and mitigate the psychological burden of loses [5].
3 Corporate Governance and Managerial Decisions
3.1 Board Composition
Data on more than 1,000 firms listed on stock exchanges between 2015 and 2020 show that a company with a higher proportion of independent board members had 12 per cent higher average ROE than firms with less independent directors. Mathematically the equation is:
\( ROE_{adj}=ROE_{base}+(0.12×P_{ind})+(0.15×P_{gen}) \) (1)
in which the return on equity of the company is adjusted for the proportion of independent and gender-diverse directors. Independent directors promote diverse views, hold management accountable, and reduce the probability of investment decisions that reflect investor sentiment (and not the company’s own needs). Likewise, gender-diverse boards have been shown to outperform boards without them, with up to 15 per cent lower stock price volatility over a five-year period. Corporate governance is thus strengthened, with debate encouraged and groupthink avoided, enabling companies to perform more effectively in complex market conditions [6].
3.2 Executive Compensation
With executive compensation as its centrepiece, corporate governance should be designed to align managerial incentives with the interests of shareholders. A well-structured compensation package with long-term performance metrics, such as return on assets (ROA) or earnings growth, makes it less likely that managers will take excessive risk and succumb to the lure of short-termism. For example, firms that grant stock options with longer vesting periods to their executives exhibit 20 per cent less volatility in their stock price than firms that pay short-term bonuses. [7] Companies that tie compensation to environmental, social and governance (ESG) metrics have also shown significant reductions in risk and volatility. The incentives associated with ESG targets encourage managers to focus on creating sustainable, long-term value. Firms must carefully craft compensation schemes so that managers are discouraged from chasing short-term gains in the stock price generated by investor sentiment. In this way, corporate governance can encourage stability in our volatile market environment and better align managerial decision-making with the interests of shareholders [8].
3.3 Risk Management
A focus on effective risk management can also help to mitigate the effects of investor sentiment on corporate decision-making and stock price volatility. Firms that form risk management committees can reduce stock price volatility by as much as 8 per cent on average, especially during times of market stress. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies that had robust risk management protocols in place outperformed and maintained greater stock price stability compared with firms that lacked these structures. By regularly monitoring market conditions and investor sentiment, firms can pre-emptively identify potential risks and adjust their strategies accordingly [9]. For example, a tech company may tighten financial controls during periods of market exuberance to prevent overexposure to speculative investments. Strong corporate governance frameworks that integrate risk management as a core component can help firms to mitigate the impact of behavioural biases and investor sentiment on their performance. This, in turn, can lead to greater stock price stability and long-term growth.
4 Stock Price Volatility and Behavioral Biases
4.1 Market Overreaction
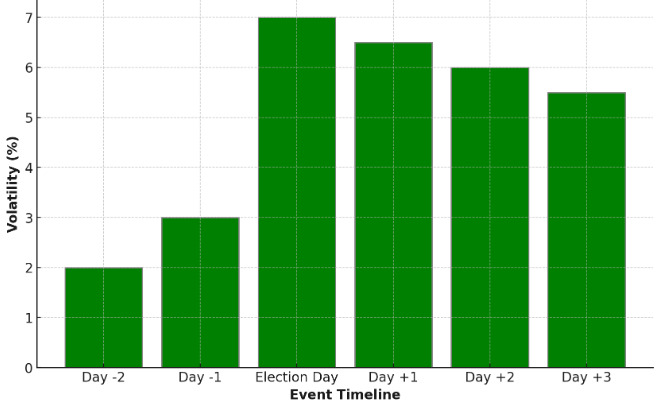
Figure 1. Stock Price Volatility Around 2016 U.S. Presidential Election
An example of overreaction in the market is when stock prices make large movements in response to news or events, primarily based on investor sentiment rather than changes to underlying fundamentals. To empirically explore the effect of market volatility around the 2016 US presidential election, a study examined 500 large-cap stocks and found that prices exhibited around 7 per cent volatility in the days following the election, as shown in Figure 1 [10]. While the volatility in company earnings or operations remained minimal, the market reaction was driven by investor overreaction to political uncertainty.To prevent overreaction in the market, firms can prevent sharp swings in stock prices by ensuring that their corporate governance structures promote transparency and maintain reliable financial reporting. For instance, the provision of timely reporting on company performance and projected strategies help investors remain informed, especially during times of uncertainty. Companies that are more proactive in communicating with their shareholders are likely to prevent overreaction in the market, as speculative judgments by investors are limited by accurate reporting from the firms.
4.2 Speculative Bubbles
One is speculative bubbles: when investor enthusiasm drives stock prices well beyond intrinsic value due to behavioural biases, such as herd behaviour and overconfidence. A dramatic example is the dot-com bubble at the end of the 1990s, when technology stocks traded at unrealistic price levels before a steep decline in 2000. During the bubble, some stocks, like Pets.com, shot up by 400 per cent in a few months before their value imploded with the burst of the bubble. Ownership structures also matter in this regard. By keeping a focus on long-term value creation and resisting pressure to capitalise on short-term price gains, companies can protect themselves from excessive swings in stock prices due to bubbles. Additionally, financial controls, such as limiting maximum exposure to high-risk assets or speculative investments, can help insulate firms from market exuberance and can lead to more stable stock performance.
4.3 Volatility Clustering
Volatility clustering refers to large price fluctuations being followed by similarly large movements, often leading to periods of sustained high volatility. In a particular Japanese study using data from the Tokyo Stock Exchange between 2010 and 2020, the authors found that stocks that had a high daily price swing were 35 per cent more likely to experience volatility in subsequent days. Two psychological biases associated with this extreme volatility are loss aversion (the fear of losing money) and herd behaviour (behaving like everyone else). Table 3 highlights the relationship between high daily price swings, subsequent volatility, and the influence of behavioral biases like loss aversion and herd behavior on stocks, illustrating how volatility clustering is driven by these psychological factors. These behavioural biases drive investors to react to price movements with little regard to the fundamentals of a company. Volatility clustering can be mitigated by firms with sound corporate governance [11]. For example, if a company consistently talks to its investors and outlines its future performance, this is likely to reduce uncertainty, and therefore reduce the likelihood of emotional decisionmaking. This is because if a firm has good corporate governance, investors know that the firm will remain stable and seek to make logical and rational decisions. Good governance helps create a situation where stock prices reflect the true value of a company, rather than being influenced by short-term market sentiment or behavioural biases.
Table 3. Volatility Clustering Study
Year |
Percentage of Stocks with High Daily Price Swings |
Likelihood of Subsequent Volatility (%) |
Average Loss due to Volatility (%) |
Percentage of Stocks Affected by Loss Aversion Bias (%) |
Percentage of Stocks Affected by Herd Behavior (%) |
2010 |
12 |
20 |
5 |
40 |
35 |
2012 |
14 |
25 |
6 |
42 |
36 |
2014 |
18 |
30 |
7 |
44 |
37 |
2016 |
21 |
33 |
8 |
45 |
38 |
2018 |
23 |
34 |
9 |
46 |
39 |
2020 |
25 |
35 |
10 |
47 |
40 |
5 Conclusion
This paper puts investor sentiment and behavioural biases such as overconfidence, herd behaviour and loss aversion in the centre of discussions about stock price volatility and corporate governance. By analysing the effects of these biases on historical market events, the paper demonstrates that irrational behaviour can rock financial markets and make corporate decision-making more challenging. The findings also point to the importance of strong corporate governance structures – including independent boards, transparent financial reporting and effective risk management – in mitigating the effects of investor sentiment and encouraging more stable market performance. Companies that continue to focus on long-term strategic goals and improve communications with shareholders can reduce the adverse effects of market overreaction and speculative bubbles in the future. Future research can delve more deeply into the dynamic relationship between investor behaviour and governance, and design more effective strategies for navigating increasingly complex and volatile financial markets.
References
[1]. Dhasmana, S., Ghosh, S., & Kanjilal, K. (2023). Does investor sentiment influence ESG stock performance? Evidence from India. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 37, 100789.
[2]. Gunay, S., et al. (2023). Frequency connectedness between FinTech, NFT and DeFi: Considering linkages to investor sentiment. International Review of Financial Analysis, 90, 102925.
[3]. Bashir, U., et al. (2024). Investor sentiment and stock price crash risk: The mediating role of analyst herding. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 13, 100371.
[4]. Kim, K., Lee, S.-Y. T., & Kauffman, R. J. (2023). Social informedness and investor sentiment in the GameStop short squeeze. Electronic Markets, 33(1), 23.
[5]. Bouteska, A., Sharif, T., & Abedin, M. Z. (2024). Does investor sentiment create value for asset pricing? An empirical investigation of the KOSPI‐listed firms. International Journal of Finance & Economics, 29(3), 3487-3509.
[6]. Van Eyden, R., et al. (2023). Investor sentiment and multi-scale positive and negative stock market bubbles in a panel of G7 countries. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 38, 100804.
[7]. Almansour, B. Y., Elkrghli, S., & Almansour, A. Y. (2023). Behavioral finance factors and investment decisions: A mediating role of risk perception. Cogent Economics & Finance, 11(2), 2239032.
[8]. Suresh, G. (2024). Impact of financial literacy and behavioural biases on investment decision-making. FIIB Business Review, 13(1), 72-86.
[9]. Phan, T. N. T., et al. (2023). The role of investor behavior in emerging stock markets: Evidence from Vietnam. The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 87, 367-376.
[10]. Goodell, J. W., et al. (2023). Emotions and stock market anomalies: A systematic review. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 37, 100722.
[11]. Cascão, A., Quelhas, A. P., & Cunha, A. M. (2023). Heuristics and cognitive biases in the housing investment market. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, 16(5), 991-1006.
[12]. Batra, S., et al. (2024). Stabilizing or destabilizing: The effect of institutional investors on stock return volatility in an emerging market. Multinational Business Review, 32(2), 204-225.
Cite this article
Dong,W. (2024). Investor Sentiment and Corporate Governance: The Role of Behavioral Biases in Stock Price Volatility and Managerial Decisions. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,10,1-5.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Dhasmana, S., Ghosh, S., & Kanjilal, K. (2023). Does investor sentiment influence ESG stock performance? Evidence from India. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 37, 100789.
[2]. Gunay, S., et al. (2023). Frequency connectedness between FinTech, NFT and DeFi: Considering linkages to investor sentiment. International Review of Financial Analysis, 90, 102925.
[3]. Bashir, U., et al. (2024). Investor sentiment and stock price crash risk: The mediating role of analyst herding. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 13, 100371.
[4]. Kim, K., Lee, S.-Y. T., & Kauffman, R. J. (2023). Social informedness and investor sentiment in the GameStop short squeeze. Electronic Markets, 33(1), 23.
[5]. Bouteska, A., Sharif, T., & Abedin, M. Z. (2024). Does investor sentiment create value for asset pricing? An empirical investigation of the KOSPI‐listed firms. International Journal of Finance & Economics, 29(3), 3487-3509.
[6]. Van Eyden, R., et al. (2023). Investor sentiment and multi-scale positive and negative stock market bubbles in a panel of G7 countries. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 38, 100804.
[7]. Almansour, B. Y., Elkrghli, S., & Almansour, A. Y. (2023). Behavioral finance factors and investment decisions: A mediating role of risk perception. Cogent Economics & Finance, 11(2), 2239032.
[8]. Suresh, G. (2024). Impact of financial literacy and behavioural biases on investment decision-making. FIIB Business Review, 13(1), 72-86.
[9]. Phan, T. N. T., et al. (2023). The role of investor behavior in emerging stock markets: Evidence from Vietnam. The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 87, 367-376.
[10]. Goodell, J. W., et al. (2023). Emotions and stock market anomalies: A systematic review. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 37, 100722.
[11]. Cascão, A., Quelhas, A. P., & Cunha, A. M. (2023). Heuristics and cognitive biases in the housing investment market. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, 16(5), 991-1006.
[12]. Batra, S., et al. (2024). Stabilizing or destabilizing: The effect of institutional investors on stock return volatility in an emerging market. Multinational Business Review, 32(2), 204-225.









