1. Introduction
Universities with industry characteristics are important carriers for cultivating top-notch innovative talents in important national fields [7], undertaking the special mission of serving the development of industries [9] and tackling “stuck-neck” technologies. However, the problem of “misalignment” between higher education and industry needs has long existed [13]. Especially against the backdrop of the rapid transformation of a new round of science and technology represented by artificial intelligence, many traditional industries are being reconstructed, putting forward higher requirements for the “multidisciplinary” [18] capabilities of management talents. The concept of interdisciplinarity has been integrated into the optimization and reform framework of the cultivation mechanism for top-notch innovative talents and has received widespread attention globally [12]. Interdisciplinarity can break the boundaries of disciplines, integrate resources, knowledge, and perspectives from different disciplines to solve major and complex problems in the country [8]. It can be seen that interdisciplinarity has already become an important driving force for innovation. However, currently, the degree of interdisciplinarity in universities is shallow. There is little involvement in interdisciplinary studies, or it only involves crossing with a few majors within the same discipline [14], which cannot fully meet the needs of industry development for composite management talents. As a result, although the abilities of talents are “extensive, broad, and diverse”, there exist problems of being “shallow, superficial, and weak”.
Currently, the interdisciplinary education model of most universities with industry characteristics is manifested as structural contradictions in three dimensions: First, there is a lack of top-level design in the interdisciplinary mechanism. The traditional organizational structure and institutional mechanisms of universities have not been deeply reformed. There is a shortage of blueprints or frameworks such as the construction of organizational structures, the training system for teachers' capabilities [10], and the evaluation system for interdisciplinary achievements [16]. Second, there is a disconnection between talent cultivation and industry practice [15]. The demand of the state for universities to cultivate composite talents due to the innovation-driven development strategy determines that interdisciplinarity needs to be closely related to the industry. The interdisciplinary teaching content of some universities has not been updated in a timely manner, and it is out of touch with emerging industries and technologies that are evolving at an extremely fast pace. Third, subject resource allocation tends to favor traditional advantageous disciplines [17]. Interdisciplinary construction requires the support of subject resources. However, the subject resources of universities with industry characteristics are generally allocated to their strong disciplines according to indicators such as subject scientific research strength and talent achievements. As a result, other weak disciplines cannot obtain the necessary resources for subject construction, such as sufficient special funds, high-quality teaching teams, and laboratory configurations, forming a vicious cycle. Just as Comrade Zhu Rongji pointed out, management science urgently needs to reconstruct knowledge connections through “the integration of natural sciences and social sciences” [11] in order to cultivate top-notch innovative talents who can lead industrial transformation. This study takes Beihang University as a typical case to reveal how universities with industry characteristics solve the problem of cultivating top-notch innovative management talents through interdisciplinarity.
2. Research design and implementation
2.1. Case selection
How to cultivate top-notch innovative talents through interdisciplinarity is a key issue in talent cultivation in universities. Relying on the characteristics of “Aerospace, Aviation and Information Technology”, the management discipline of Beihang University coordinates and integrates resources from multiple disciplinary fields. It has long focused on cutting-edge issues in the discipline of economics and management as well as major national strategic needs, achieving theoretical breakthroughs in key areas and producing research achievements with academic influence. Therefore, choosing Beihang University as a case study has certain typicality and representativeness.
On the one hand, the construction achievements of the management discipline at Beihang University rank among the top in universities across the country. In the fourth round of discipline evaluation, the Management Science and Engineering discipline of Beihang University was rated as an A-level discipline, and Public Administration was rated as an A-minus level discipline. The economics and management disciplines of Beihang University also have considerable influence globally. In the latest data of the ESI Essential Science Indicators database released by Clarivate in 2024, the “Economics & Business” discipline of Beihang University entered the top 1% of ESI rankings for the first time, marking that discipline construction has entered a new stage. On the other hand, under the professional system of Beihang University featuring “integration of aerospace, aviation, information technology and medicine, clusters of advantages in engineering disciplines, high-quality characteristics of liberal arts and sciences, and remarkable frontline interdisciplinarity”, the management discipline of Beihang University has formed a school-running system for interdisciplinary integration with distinct characteristics and remarkable achievements, becoming a demonstration benchmark for the interdisciplinarity of management disciplines in universities with industry characteristics.
2.2. Data collection and sorting
This study focuses on the cultivation mechanism of top-notch innovative talents in management disciplines driven by interdisciplinarity at Beihang University through multi-dimensional data collection and systematic collation. The case selection mainly takes the School of Economics and Management as the core research unit, supplemented by the School of Humanities and Social Sciences (School of Public Administration) and other administrative units for data collection. Two major categories of information are collected and sorted out, namely official public information, including cultivation programs, policy documents, organizational introductions, announcements and reports on the official website, and online reports, including interview materials of graduates, interpretative reports by authoritative institutions, etc. The data mainly covers dimensions such as the cultivation mechanism, the tutor team, and teacher training. The data is sorted out using the “problem-oriented - dimensional analysis” framework and classified according to the cultivation mechanism, organizational model and supporting conditions. Further analysis and extraction are carried out on the classified data, and the key factors of the interdisciplinary mechanism of Beihang University are extracted to provide experience and inspiration for other universities with industry characteristics in China to carry out interdisciplinarity to promote the cultivation of top-notch innovative talents.
3. Conclusion
3.1. Problem-oriented driving of interdisciplinarity: construction of a comprehensive research platform
The interdisciplinarity of the research platforms of the School of Economics and Management at Beihang University is not a simple superposition of subject resources. Instead, it systematically drives the cultivation of top-notch innovative talents in management through a triple mechanism of “problem-oriented, methodological intersection, and ability expansion” (see Table 1 for details) [3].
The interdisciplinary research team positions its research direction based on national strategies and industry needs, breaking the traditional path of relying on disciplinary knowledge for positioning. The establishment of the laboratories of the School of Economics and Management at Beihang University is not based on the mechanical division of the discipline catalog. Instead, it faces major national needs such as the “dual carbon” goal, the digital economy, and industrial upgrading. It expands the research scope of management from traditional issues such as organizational efficiency and resource allocation to complex problems covering the coordinated governance of the three elements of technology, policy, and behavior.
And the complex and integrated research questions require interdisciplinary methods to solve, promoting the organic integration of technical methods and social values. By integrating quantitative analysis methods such as simulation and data modeling in engineering technology with the qualitative empirical research in management, a research paradigm that coordinates data-driven and theoretical verification is constructed. This enables management to analyze the dynamic evolution laws of complex problems and propose solutions that take into account both technical feasibility and social adaptability.
The intersection and integration of methodologies also pose requirements for the capabilities of talents. Students not only need to master interdisciplinary knowledge but also need to enhance their abilities in disassembling complex problems, coordinating the interests of multiple entities, and implementing innovative solutions. This ability cultivation mechanism of learning by doing enables top-notch talents not to be simply containers for storing disciplinary knowledge but to be solution designers, which is more in line with the requirements of the industry for talents.
Table 1. The interdisciplinary situation of the laboratories related to management discipline in Beihang University
Research Institution | Research Direction | Interdisciplinary |
Low carbon Governance and Policy Smart Lab | 1. Carbon market and carbon finance 2. Aviation carbon reduction 3. Energy system modeling and policy optimization 4. Low-carbon behavior, etc. | Build a scientific research base for interdisciplinary integration and form a talent training base with integrated science and education and shared resources. At the same time, the School of Economics and Management of Beihang University will take the lead, and multiple schools of the whole university will participate in the co - construction. |
Key Laboratory of Complex Systems Analysis and Management Decision, Ministry of Education | 5. Theories and methods of management decision-making under uncertain environment 6. Massive high-dimensional data management and analysis technology, high-dimensional complex statistical data analysis model and method 7. macro complex economic system analysis and management decision-making | It deeply integrates with the advantageous disciplines of Beihang University, such as computer science and engineering, business administration, applied economics, and statistics. Aiming at the major strategic needs of the country, it forms a disciplinary system that integrates economic and management disciplines, as well as advantageous and characteristic disciplines. |
Beijing Key Laboratory of Urban Operation Emergency Support Simulation Technology | 8. Set up emergency support simulation and decision analysis technology 9. Emergency support planning and optimization technology 10. Emergency support theory, method and technical system 11. Typical application of emergency support plans and policies | It contains multiple small - scale laboratories, which respectively come from fields such as management science and engineering, emergency management, computer science and engineering, system simulation, and urban system management and resource planning. |
Key Laboratory of Data Intelligence and Intelligent Management, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology | 12. Data - and behavior-driven complex system theory and method 13. Man-machine coordination management decision theory and method 14. Transparent, safe and reliable big data modeling theory and method | The laboratory is based on the disciplines of management science and economics, mathematics, computer science, and systems science. It conducts fundamental research on key technologies in the fields of swarm intelligence and intelligent complex systems. |
3.2. Mechanism innovation promotes interdisciplinarity: organizational reconstruction and general education cultivation for students
3.2.1. Organizational reconstruction: dual-track collaboration between colleges and schools
The college system of Beihang University is one of the core measures of its education and teaching reform (see Figure 1). Beihang School, established in 2017, is a college that covers first-year undergraduate students in broad categories and strengthens general education. The college has seven residential colleges, namely Chuanyuan College, Shi'e College, Fengru College, Shijia College, Shou'e College, Zhizhen College, and Zhixing College. With the core concept of “enrollment in broad categories and integration of general education and specialized education”, it has established a talent cultivation system based on the concept of interdisciplinarity. This collaborative mechanism of “laying a foundation with general education and delving deep into specialized studies” has broken the boundaries of disciplines [5].
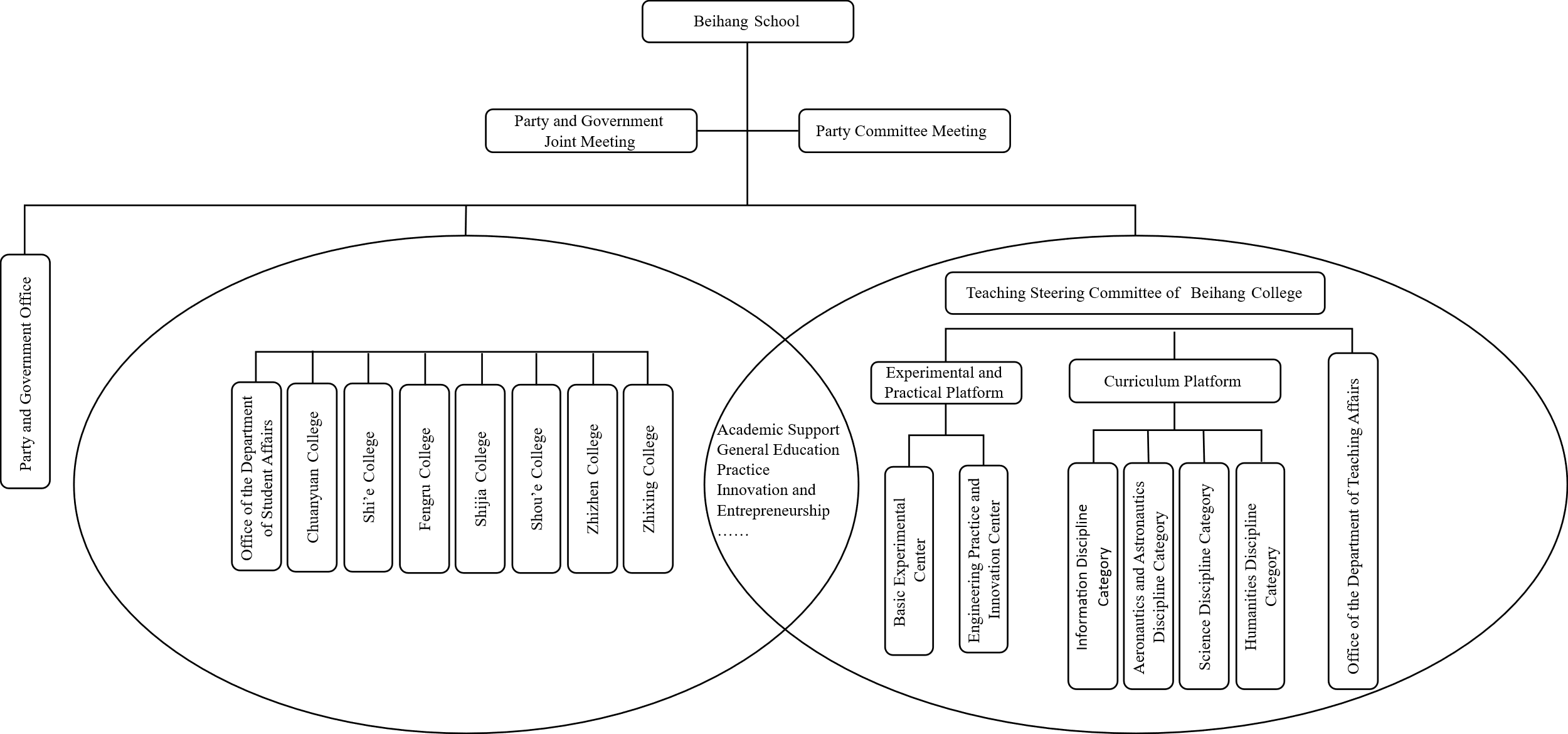
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the organizational structure of the residential colleges in Beihang University
Taking Zhizhen College - Science Experimental Class and Zhixing College - Social Science Experimental Class as examples, students of Zhizhen College can choose their majors after the first year of study and can respectively enter relevant majors in four colleges, namely the School of Economics and Management, the School of Mathematical Sciences, the School of Physics, and the School of Chemistry for study. After studying in the Social Science Experimental Class of Zhixing College, students will enter the School of Humanities and Social Sciences (School of Public Administration), the School of Foreign Languages, the Law School of Beihang University, and Institute for Advanced Studies in Humanities and Social Science of Beihang University for relevant major studies. This dual-college management mode of “the college is responsible for basic education and the school is responsible for specialized education” essentially takes promoting the cultivation of top-notch innovative talents through interdisciplinarity as the core to construct a cultivation system for enrollment in broad categories and the integration of general education and specialized education. During the period of general education cultivation, the college has established ten core curriculum groups of interdisciplinary subjects, implemented the curriculum supermarket mechanism, gathered high-quality teaching staff from around the world, and formed a curriculum system with in-depth integration of liberal arts and sciences foundation and engineering technology. Beihang School have innovatively constructed a multi-dimensional education mechanism and established a four-dimensional tutor system covering academic, ideological and political, social, and peer aspects. At the same time, Beihang School have built interdisciplinary platforms, created community-based learning spaces, and established disciplinary exchange areas such as free discussion areas and team activity rooms to stimulate innovative thinking. The dual-college system emphasizes interdisciplinarity in terms of organization, mechanism, and the allocation of soft and hard resources, and cultivates future leading talents with systematic thinking and cross-border innovation capabilities.
3.2.2. Inter-college collaboration: diversified academic exchanges
Beihang University actively promotes horizontal collaboration among colleges and cooperatively builds diversified academic exchange platforms. Table 2 shows three typical cases of interdisciplinary academic exchanges among different colleges. Firstly, there are academic exchange activities for knowledge sharing, with disciplinary knowledge lectures taking the lead. Interdisciplinary knowledge sharing activities can promote the reconstruction of the cognitive framework and form a more interdisciplinary and general knowledge system. Students majoring in management at Beihang University participate in knowledge lectures to learn about the basic knowledge and current situation of aviation, aerospace, and information fields, breaking through the information cocoon of their own disciplines, forming a knowledge network with the characteristics of the “Aerospace, Aviation and Information” industry. This makes up for the neglect of weak disciplines in resource allocation in universities with industry characteristics and also provides a basic cognitive framework for subsequent interdisciplinary research. Secondly, there are academic exchange activities for mutual learning of methods, with academic salons taking the lead. The mutual learning of research methods among different disciplines is conducive to interdisciplinary integration and the methodology for solving complex problems. Such activities generally follow the underlying logic of “translation - adaptation - innovation”. Different disciplines show and explain their own research methods, professional terms, research ideas, and methods to each other. Then, they adjust and adapt the methods of other disciplines according to the characteristics and needs of their own disciplines, so as to create new and more effective methods or theories for solving problems and promote the development of disciplines. Finally, there are academic exchange activities for joint cultivation of talents, with jointly established academic platforms taking the lead. An interdisciplinary thesis review mechanism is established to guide and evaluate scientific research achievements from multiple perspectives and improve the quality of achievements of cooperative units. The normalized academic cooperation platform provides students with opportunities for interdisciplinary practice. The construction of these diversified academic exchange platforms is a powerful measure for Beihang University to promote interdisciplinary collaboration among colleges at present and also lays a foundation for long-term academic interdisciplinary innovation and talent cultivation.
Table 2. Diversified academic exchange activities in Beihang University
Type | Cooperative College | Mode of Cooperation | Cooperation Content |
Knowledge sharing | School of Economics and Management + School of Aeronautical Science and Engineering | interdisciplinarity lecture cooperation | Yang Chao, the dean of the School of Aeronautics, gave a special lecture titled “Aviation Development and Reflections” for the teachers and students of the School of Economics and Management. He systematically analyzed the development history of China's aerospace industry and explained the importance of the discipline by combining with videos of the history of flight exploration. The leadership teams of both schools attended the event. Through interdisciplinary dialogue, the students of the School of Economics and Management gained a deeper understanding of the aerospace field. |
Mutual learning of knowledge | School of Business Management + School of Computer Science and Engineering | Academic Salon for doctoral students | A joint academic exchange meeting for doctoral students was held, focusing on the fields of cloud computing and big data. Doctoral students from both sides respectively presented cutting-edge research such as anomaly detection in graph data streams and K-means consensus clustering. Through an interdisciplinary perspective, they conducted mutual learning of research methodologies and formed an academic dialogue mechanism of “multiple dimensions for the same theme”. |
Talent co-breeding | School of Business Management + School of Computer Science and Engineering | Big data academic forum co-construction | They jointly undertook the university-level postgraduate academic forum. The deans of the two schools jointly proposed the development path of interdisciplinary disciplines of “industry-university-research + internationalization”. Experts such as Professor Ma Shuai were organized to give special reports on graph search and social networks. A cross-school thesis review mechanism was established. More than 300 postgraduate students were mobilized to participate, forming a normalized academic cooperation platform in the field of big data. |
3.2.3. General education cultivation: curriculum system design
In the field of postgraduate education, Beihang University has always been unwavering in implementing the core concepts of the Great Wall Action Plan, that is, focusing on consolidating the foundation, strengthening interdisciplinary integration, expanding academic horizons, and promoting innovative development. Beihang University has specially set up an interdisciplinary curriculum module in its postgraduate cultivation program. This module clearly stipulates that postgraduate students should select courses across college boundaries and must choose among first-level disciplines. At the same time, students are required to complete at least 3 credits in this module. It is worth noting that the definition criteria for interdisciplinary courses strictly require them to be disciplinary theoretical courses or professional theoretical courses, excluding ideological and political courses, experimental courses, practical courses, comprehensive literacy courses, and public basic courses [4]. In fact, the selection of interdisciplinary courses has been promoted in universities for a long time, but most of them include general elective courses for the whole university. When students study interdisciplinary knowledge, they have problems such as insufficient in-depth study, inability to apply the knowledge, and lack of understanding of integration. However, this mechanism provides external coercive force for the interdisciplinarity of Beihang University, greatly promoting the collision of diversified knowledge. By integrating theories and methods of multiple disciplines, it not only broadens the knowledge boundaries of students but also cultivates their comprehensive abilities to deal with complex problems, laying a solid foundation for them to grow into top-notch innovative talents.
3.3. Integrating cross-domain resources to strengthen interdisciplinarity: promoting collaboration across units and regions
3.3.1. Collaboration across units: cultivation of industry-specific talents
In order to give full play to its industry characteristics in the fields of “Aerospace, Aviation and Information”, Beihang University actively promotes the sharing of advantageous professional resources and industry resources among various disciplines, helping each discipline to become a competitive benchmark for the construction of industry characteristic disciplines with industry characteristics. Beihang University has reached cooperation with the people's governments of prefecture-level cities in emerging fields such as information technology, intelligent manufacturing, and aerospace, jointly promoting scientific and technological innovation and regional development. At the same time, Beihang University has also signed cooperation agreements with China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation Limited (CASIC) and Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China Ltd (COMAC), promoting the collaborative innovation of production, education, research and application around relevant industries. Relying on its industry characteristics, the School of Economics and Management of Beihang University has visited and studied at companies such as AVIC Qingyun Aviation Instrument Co., Ltd. and AVIC Chengdu Aircraft Industry (Group) Co., Ltd., giving full play to the disciplinary characteristics of experience induction in management, helping enterprises to precipitate tacit knowledge and experience, and assisting in the dissemination of corporate brand value, thus becoming a model of school-enterprise cooperation. The cooperation models of production, education and research brought about by school-enterprise cooperation, such as student internship and employment bases and enterprise case bases, promote students' interdisciplinary and cross-field learning and communication from a practical level. Management students can closely combine theoretical knowledge with actual business scenarios. By participating in the project operation and process optimization of enterprises, they can deeply understand the operation logic of different industries. In addition, in an interdisciplinary environment, management talents and engineering and technical talents work closely together, enabling them to view problems from both technical and management perspectives, greatly improving their ability to solve practical problems. This not only lays a solid foundation for their future engagement in various industries, but also enables them to stand out in the job market, becoming composite management talents with interdisciplinary literacy and the ability to lead the innovative development of enterprises, and effectively promoting the vigorous development of management talents in the direction of adapting to the diversified needs of the industry.
3.3.2. Cross-regional collaboration: cultivation of international talents
Intercollegiate overseas joint cultivation is an important strategic measure for Beihang University to promote interdisciplinary integration and cultivate top-notch innovative talents. The joint cultivation project in management at Beihang University mainly focuses on doctoral students and implements a dual-degree joint cultivation mechanism. During the cultivation period, students conduct research and study at the cooperative universities respectively and finally obtain degree certifications from both sides. In the process of joint cultivation, the cooperative universities adhere to the concept of “resource complementarity, mutual assistance and sharing” and provide students with comprehensive academic support. Taking the joint cultivation project of doctoral students between Beihang University and City University of Hong Kong as an example, students can not only draw on the professional advantages of the two universities in the fields of management science and engineering, public administration, etc., share high-quality teaching staff and scientific research resources, but also have in-depth contact with the characteristic disciplines of the cooperative universities. On the one hand, they can benefit from the strong professional accumulation of Beihang University in the fields of “Aerospace, Aviation and Information”, and on the other hand, they can integrate into the academic atmosphere of the top majors of City University of Hong Kong, such as business administration, architecture, law, computer science and technology.
Overseas joint cultivation has promoted the intersection and integration of different disciplinary fields, providing a broader academic vision for innovative research. At the same time, it has constructed an internationalized talent cultivation system, promoted the in-depth sharing of educational concepts and academic resources, and laid a solid foundation for cultivating leading talents with a global perspective. Under this interdisciplinary and cross-regional talent cultivation mode, an increasing number of composite talents with international competitiveness will be cultivated. Students will be able to integrate the knowledge systems of different disciplines, enhance their ability to solve complex problems, and provide high-quality innovative talents for the national strategic development.
Table 3. Master's and doctoral joint training programs related to management discipline in Beihang University
Type | Item Type | Joint Unit | General Situation |
Master's co-training | Jointly cultivated popular science dual-master's degree program | the School of Humanities and Social Sciences (School of Public Administration) and The Australian National University | Implement the two-year “1+1” cultivation program to obtain a Master's Degree in Education from Beihang University and a Master's Degree in Science Communication from the Australian National University. |
Doctoral co-training | Jointly cultivated doctoral student program [6] (by the Graduate School of Beihang University in 2023) (including Management Science and Engineering, Public Administration) | Beihang University and City University of Hong Kong | Implement the four-year “2+2” cultivation program to obtain the graduation certificates and degree certificates of doctorate students from both universities simultaneously. |
Doctoral co-training | The dual-doctoral degree program between Beihang University and Paris-Saclay University (covering the field of energy management) | Beihang University and Paris-Saclay University | Implement the three-year “1+1+X” cultivation program to obtain the graduation certificates or academic degree certificates issued separately by the two universities. |
Collaborative cooperation | Signing of the Memorandum of Cooperation between Beihang University and CPA Australia | Beihang University and CPA Australia | Carry out cooperation in aspects such as building communication platforms and providing internship opportunities, and jointly create favorable conditions for the growth and development of MPAcc students of Beihang University. |
4. Insights
In the current era background of rapid knowledge iteration and an increasingly obvious trend of discipline integration, interdisciplinarity has become a key path for cultivating top-notch innovative talents. Students cultivated under the interdisciplinary mechanism are able to possess the ability to integrate resources from different disciplines, thereby enhancing their ability to solve complex problems [2]. Referring to the practices of Beihang University in promoting the cultivation of top - notch innovative management talents through various interdisciplinary efforts (see Figure 2), this paper puts forward the following suggestions to provide a reference for the interdisciplinary construction of universities with industry characteristics to promote the cultivation of top - notch innovative management talents.
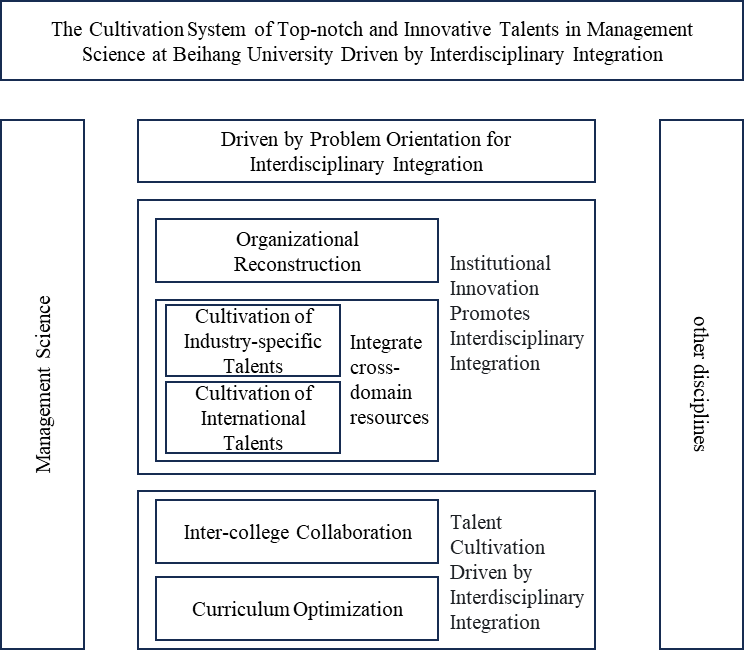
Figure 2. The cultivation system of top-notch innovative talents in management discipline of Beihang University driven by interdisciplinarity
4.0.1. Strengthening scientific research of interdisciplinarity—with key focus on major national strategies
The research directions of management in various universities should have a problem - awareness, applying disciplinary knowledge to solving major national problems, and promoting the integration of methods in interdisciplinary research and the construction of talent capabilities through researching problems. Regarding issues such as resource management in the national sustainable development strategy, management collaborates with multiple disciplines such as environmental science, economics, and computer science to carry out joint research. For example, in the field of low - carbon governance and policy research, management coordinates with multiple disciplines including environmental science and economics to solve problems. Environmental science is responsible for assessing the current situation of carbon emissions, monitoring the carrying capacity of the ecological environment for carbon emissions, and providing detailed environmental data. Economics uses cost - benefit analysis to weigh the economic feasibility of different low - carbon policies. For instance, it calculates the impact of carbon tax implementation on enterprise costs and economic development. Management integrates information and formulates a low - carbon policy system covering aspects such as industrial planning and energy management. In this process, the research methods of different disciplines are integrated. Students and teachers involved in the research have their capabilities comprehensively enhanced while solving practical problems, breaking the gap in research and application between disciplines.
4.0.2. Strengthening the institutional construction of interdisciplinarity—vigorously carrying out organizational reforms and joint cultivation programs
Break through the traditional organizational structure of independent departments in universities and implement the dual - college management system. Aiming to enable students to have a general knowledge boundary and a vertical professional knowledge base, universities can select outstanding teachers from different disciplinary backgrounds to form a tutor team and formulate personalized training programs for students. In terms of general education, basic courses covering various fields such as humanities and social sciences, and natural sciences are offered to equip students with extensive knowledge reserves. In terms of professional training, professional colleges provide in - depth guidance based on students' professional directions, enabling them to deeply understand the knowledge of industry characteristics, achieve the combination of breadth and depth of knowledge, and allow students to understand disciplinary knowledge from different perspectives, effectively avoiding the singularity of the knowledge system.
Meanwhile, in the context of globalization, knowledge and resources are flowing at an accelerated pace on a global scale, and international higher education has received much attention [1]. Taking Beihang University as an example, transnational and cross - regional cooperation is of great significance in breaking the limitations of traditional talent cultivation. Each university should adhere to the principle of “resource complementarity, sharing and mutual assistance”, accurately locate its own high - quality resources and weak points, and promote transnational and cross - regional joint cultivation cooperation. During the cooperation period, in - depth cooperation should be emphasized, and multiple high - quality resources should be used to cultivate talents. Practices such as lectures by star mentors, dual - mentor management training, and joint research should be promoted. In terms of school - enterprise joint cultivation, universities and enterprises should establish close cooperation ties. Enterprises, based on industry demands and cutting - edge trends, provide practical topics and internship positions for universities, while universities use their scientific research capabilities to assist enterprises in technological upgrading and management optimization. Through means such as jointly building internship bases, offering enterprise - customized courses, and jointly guiding graduation projects by mentors, students can deeply participate in enterprise practice on the basis of theoretical learning, cultivating composite talents who not only have a solid grasp of management theory but also are familiar with industry practices and market demands.
4.0.3. Strengthening the construction of talent cultivation for interdisciplinarity—academic exchanges and curriculum design
The interdisciplinary construction of management disciplines in universities should actively promote three types of academic exchange activities, namely knowledge sharing, methodological mutual learning, and joint talent cultivation. Academic popular science lectures, academic method seminars, and academic forums should be regarded as important indicators for the construction of each discipline. This can be used to re - allocate subject resources and alleviate the problem of unbalanced subject resource allocation in universities with industry characteristics. Academic popular science lectures are open to all students. Experts from different disciplinary fields are invited to explain cutting - edge disciplinary knowledge in a simple and profound way, stimulating students' interest in different disciplines and industries. Academic method seminars focus on the exchange of research methods in various disciplines. Teachers of management disciplines and those of other disciplines jointly explore how to apply different disciplinary methods to the analysis of complex problems. Academic forums provide a high - level communication platform for teachers and students, promoting the collision of ideas from different disciplines and forming new research ideas.
In terms of the curriculum system, students are required to take first - level discipline courses across colleges and disciplines. The training program for management majors can also set up interdisciplinary courses that integrate engineering and management, as well as liberal arts and sciences. This allows students to understand the new changes in enterprise management in the digital age, broadens students' horizons, and breaks the situation where students' thinking is limited to a single discipline.
References
[1]. Carvalho, N., Rosa, M. J., & Amaral, A. (2022). Cross-Border Higher Education and Quality Assurance. Results from a Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Studies in International Education, 27(5), 695-718. http://doi.org/10.1177/10283153221076900
[2]. Schijf, J. E., Van, D. W. G. P., & And Jansen, E. P. W. A. (2023). Measuring interdisciplinary understanding in higher education. European Journal of Higher Education, 13(4), 429-447. http://doi.org/10.1080/21568235.2022.2058045
[3]. H. J. J. G. Bei. (n.d.). Research Institutions - School of Economics and Management, Beihang University. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://sem.buaa.edu.cn/kxyj/yjjg.htm
[4]. H. J. J. G. Bei. (2023). 2023 Postgraduate Training Plan - School of Economics and Management, Beihang University. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://sem.buaa.edu.cn/info/1035/12509.htm
[5]. H. X. Y. Bei. (n.d.). College Introduction - Beihang College. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://bhc.buaa.edu.cn/xygk/xyjs.htm
[6]. J. H. K. H. Bei. (2023). Application Notice for the 2024 Joint Training Program for Postgraduate Students between Beihang University and City University of Hong Kong - Graduate School of Beihang University. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://graduate.buaa.edu.cn/info/1058/9848.htm
[7]. T. Z. Han. (2022). How Traditional Dominant Disciplines Empower the Cultivation of Top-Notch Innovative Talents in Universities - An Analysis Based on 33 Industry-Characteristic Universities in China. Jiangsu Higher Education (01), 83-90. http://doi.org/10.13236/j.cnki.jshe.2022.01.011
[8]. Y. X. Lu. (2005). The Significance of Interdisciplinary and Interdisciplinary Sciences. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (01), 58-60. http://doi.org/10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2005.01.014
[9]. G. X. Ma, D. F. Huang, Z. X. Yu, & P. Lu. (2024). Research on the Evaluation Index System for the High-Quality Development of Higher Education in Industry-Characteristic Universities. Technology Wind (27), 16-18. http://doi.org/10.19392/j.cnki.1671-7341.202427006
[10]. F. Qiu, L. M. Luo, & G. H. Qian. (2024). Cultivation of Interdisciplinary Talents in Universities: Historical Context, Realistic Dilemmas, and Practical Approaches. Applied Higher Education Research, 9(04), 8-14.
[11]. Z. H. Sheng, H. Huo, X. T. Chen, Z. Y. Liu, & W. X. Xu. (2021). Forging Ahead and Innovating Ceaselessly - A 70-Year Review, Reflection, and Prospect of the Management Science and Engineering Discipline in China. Management World, 37(02), 185-202. http://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2021.0027
[12]. X. P. Tian, & S. J. Jiang. (2023). The Interdisciplinary Mechanism Innovation and Its Enlightenment for the Cultivation of Top-Notch Innovative Talents in Universities - A Case Study of “Intelligence+” at Carnegie Mellon University. Research in Educational Development, 43(23), 59-67. http://doi.org/10.14121/j.cnki.1008-3855.2023.23.012
[13]. H. W. Wen. (2025). Challenges and Optimization Strategies for the Structure System of Higher Education in China in the Digital Economy Era. The Science Education Article Collects (05), 17-20. http://doi.org/10.16871/j.cnki.kjwh.2025.05.004
[14]. Y. M. Xi, & B. Chen. (2023). Interdisciplinary Construction Should Return to the Original Intention of “Educating People”. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://paper.sciencenet.cn/htmlnews/2023/12/514042.shtm
[15]. H. J. Zhang, C. Ma, X. Wei, J. L. Liu, & Y. D. Zhang. (2024). Exploration and Practice of the Training of Outstanding Engineers under the School-Enterprise Collaborative Education Model. Universities and Disciplines, 5(04), 68-75.
[16]. X. B. Zhang, & B. C. Liu. (2023). The Interdisciplinary Talent Training Mechanism: Theoretical Logic, Realistic Problems, and Optimization Paths. University Education Science (06), 43-51.
[17]. Y. Q. Zhang, & Y. B. Zhou. (2025). Dilemmas and Countermeasures in the Interdisciplinary Construction of Universities. Western China Quality Education, 11(01), 55-58. http://doi.org/10.16681/j.cnki.wcqe.202501014
[18]. Y. Y. Zhang. (2008). The Positioning of the Disciplinary Attributes of Management - From the Perspective of Interdisciplinary. Social Science Management and Review (03), 17-25.
Cite this article
Yang,X.;Zheng,Y.;Sui,Y.;Guo,J. (2025). Research on the cultivation mechanism of top-notch innovative talent of management in universities with industry characteristics driven by interdisciplinary—a case study of Beihang University. Journal of Education and Educational Policy Studies,3(2),12-20.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Education and Educational Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Carvalho, N., Rosa, M. J., & Amaral, A. (2022). Cross-Border Higher Education and Quality Assurance. Results from a Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Studies in International Education, 27(5), 695-718. http://doi.org/10.1177/10283153221076900
[2]. Schijf, J. E., Van, D. W. G. P., & And Jansen, E. P. W. A. (2023). Measuring interdisciplinary understanding in higher education. European Journal of Higher Education, 13(4), 429-447. http://doi.org/10.1080/21568235.2022.2058045
[3]. H. J. J. G. Bei. (n.d.). Research Institutions - School of Economics and Management, Beihang University. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://sem.buaa.edu.cn/kxyj/yjjg.htm
[4]. H. J. J. G. Bei. (2023). 2023 Postgraduate Training Plan - School of Economics and Management, Beihang University. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://sem.buaa.edu.cn/info/1035/12509.htm
[5]. H. X. Y. Bei. (n.d.). College Introduction - Beihang College. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://bhc.buaa.edu.cn/xygk/xyjs.htm
[6]. J. H. K. H. Bei. (2023). Application Notice for the 2024 Joint Training Program for Postgraduate Students between Beihang University and City University of Hong Kong - Graduate School of Beihang University. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://graduate.buaa.edu.cn/info/1058/9848.htm
[7]. T. Z. Han. (2022). How Traditional Dominant Disciplines Empower the Cultivation of Top-Notch Innovative Talents in Universities - An Analysis Based on 33 Industry-Characteristic Universities in China. Jiangsu Higher Education (01), 83-90. http://doi.org/10.13236/j.cnki.jshe.2022.01.011
[8]. Y. X. Lu. (2005). The Significance of Interdisciplinary and Interdisciplinary Sciences. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (01), 58-60. http://doi.org/10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2005.01.014
[9]. G. X. Ma, D. F. Huang, Z. X. Yu, & P. Lu. (2024). Research on the Evaluation Index System for the High-Quality Development of Higher Education in Industry-Characteristic Universities. Technology Wind (27), 16-18. http://doi.org/10.19392/j.cnki.1671-7341.202427006
[10]. F. Qiu, L. M. Luo, & G. H. Qian. (2024). Cultivation of Interdisciplinary Talents in Universities: Historical Context, Realistic Dilemmas, and Practical Approaches. Applied Higher Education Research, 9(04), 8-14.
[11]. Z. H. Sheng, H. Huo, X. T. Chen, Z. Y. Liu, & W. X. Xu. (2021). Forging Ahead and Innovating Ceaselessly - A 70-Year Review, Reflection, and Prospect of the Management Science and Engineering Discipline in China. Management World, 37(02), 185-202. http://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2021.0027
[12]. X. P. Tian, & S. J. Jiang. (2023). The Interdisciplinary Mechanism Innovation and Its Enlightenment for the Cultivation of Top-Notch Innovative Talents in Universities - A Case Study of “Intelligence+” at Carnegie Mellon University. Research in Educational Development, 43(23), 59-67. http://doi.org/10.14121/j.cnki.1008-3855.2023.23.012
[13]. H. W. Wen. (2025). Challenges and Optimization Strategies for the Structure System of Higher Education in China in the Digital Economy Era. The Science Education Article Collects (05), 17-20. http://doi.org/10.16871/j.cnki.kjwh.2025.05.004
[14]. Y. M. Xi, & B. Chen. (2023). Interdisciplinary Construction Should Return to the Original Intention of “Educating People”. Retrieved 2025-3-25 from https://paper.sciencenet.cn/htmlnews/2023/12/514042.shtm
[15]. H. J. Zhang, C. Ma, X. Wei, J. L. Liu, & Y. D. Zhang. (2024). Exploration and Practice of the Training of Outstanding Engineers under the School-Enterprise Collaborative Education Model. Universities and Disciplines, 5(04), 68-75.
[16]. X. B. Zhang, & B. C. Liu. (2023). The Interdisciplinary Talent Training Mechanism: Theoretical Logic, Realistic Problems, and Optimization Paths. University Education Science (06), 43-51.
[17]. Y. Q. Zhang, & Y. B. Zhou. (2025). Dilemmas and Countermeasures in the Interdisciplinary Construction of Universities. Western China Quality Education, 11(01), 55-58. http://doi.org/10.16681/j.cnki.wcqe.202501014
[18]. Y. Y. Zhang. (2008). The Positioning of the Disciplinary Attributes of Management - From the Perspective of Interdisciplinary. Social Science Management and Review (03), 17-25.









