1. Introduction
Our world is experiencing a waste crisis like never before, where waste production in the unsustainable form is becoming increasingly harmful to the environment and to human health. Degradable alternatives to landfills and burning create greenhouse gas emissions, pollute the soil and water, and inefficient use of resources, and therefore a paradigm shift to sustainable options is needed. The Circular Economy promises a radical alternative with waste minimization, recycling, and resource reuse taking the place of "take, make, dispose". In this context, technology for waste treatment contributes to the realization of sustainability goals by driving efficiencies, reducing landfill use and recapturing valuable resources. This technology has radically changed the process of disposing of waste, making it possible to separate, sort and treat recyclable materials more precisely. Mechanical biological treatment (MBT) and optical sorting methods are now more commonly deployed to increase recycling rates; waste-to-energy (WTE) systems convert incomposable waste into energy, providing both a reduction of waste and an energy source. Even with these breakthroughs, it is far from easy to incorporate all these technologies into a Circular Economy model. Material pollution, infrastructure shortages and policy incoherence thwart the growth and efficiency of these technologies, especially in developing countries [1]. In this paper we explore how new technologies for advanced waste disposal can play a part in the Circular Economy, drawing on case studies from Stockholm, Tokyo and New York to see their practical benefits, successes and limitations. Stockholm is an example of a city with high-efficiency waste-to-energy infrastructure, Tokyo recycling technology, and New York the obstinacy of policy ambiguity. Through these examples, the research offers an understanding of how technologies, policies and international cooperation can help to solve global waste management problems and help transition to a Circular Economy.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Innovative Technologies in Waste Management
Technological advancements have made waste management processes more effective and efficient, particularly when it comes to recycling and resource recovery. For example, cutting-edge recycling technologies, combined with new ways to separate, sort and process various waste streams, were the key innovations. For instance, mechanical biological treatment (MBT) and optical sorting technologies are now used in landfills to sort recyclable materials more precisely and efficiently. Furthermore, WTE technologies are becoming more prevalent as a way to recycle non-recyclable waste and convert it into energy in order to reduce the amount of waste dumped in landfills. As illustrated in Figure 1, waste-to-energy systems typically comprise a single-track model, in which collected waste is transported to specialised facilities, melted down into gas or fuel by incineration, gasification or pyrolysis, and then reformed into electricity or another energy. Such systems not only offer an alternative to euthanizing waste, but also produce energy, giving us a double-edged sword in the evolution of a more circular economy. The global market for waste-to-energy technologies has exploded, thanks to these advancements and the growing attention to combining waste with energy [2].
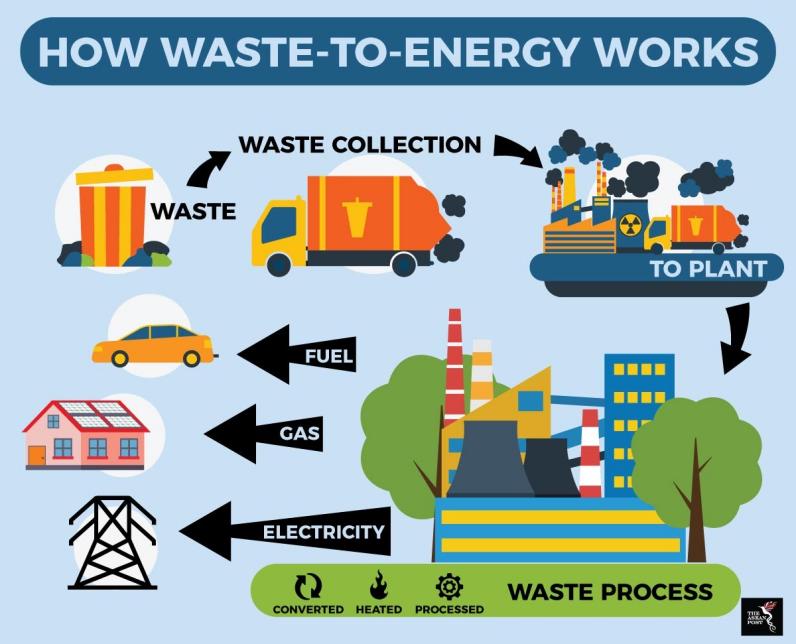
Figure 1. Waste To Energy: How This Processes Really Work? (Source:reurasia.com)
2.2. Challenges in Waste Management within the Circular Economy Framework
While technological improvements have greatly increased the productivity of waste streams, many barriers remain to fully embracing these technologies in the Circular Economy context. One of the main obstacles is the quality of reusable materials. Reverse pollution in the streams of waste, including plastic and organic waste, impedes recovery and degrades the quality and value of reclaimed materials. Research shows that a high percentage of recyclable waste is polluted, which results in substantial resource-recovery losses and require more sophisticated sorting technologies to reduce these losses. Furthermore, infrastructure gaps in most developing countries are a significant barrier to scaling of new recycling and waste-to-energy technologies. Waste systems in these areas are still almost entirely based on old-fashioned waste disposal, either via landfills or incineration, and little attention is given to resource recovery or recycling. These obstacles must be resolved, not only by technologies, but also through a reorientation of policy and a large investment in infrastructure for waste collection and capacity-building, especially in developing countries [3].
2.3. Policy Frameworks Supporting Circular Economy Initiatives
Policy is vital in bringing about the shift to a Circular Economy. Several nations already have extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, where manufacturers must assume full responsibility for the life of their products, including post-consumer waste. It’s an incentive for businesses to develop products that are longer lasting and recyclable. Further, policies like the European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan are working towards minimizing plastic waste, achieving higher recycling rates, and enabling recycled material to be used in manufacturing. But the implementation of Circular Economy strategies in practice tends to involve more than just sector-specific policies. A dissonance between policy fields – waste management, manufacturing, energy, and so on – can hold back an integrated approach to waste management and resource efficiency [4]. Therefore, intersectoral policy alignment is critical to delivering on the Circular Economy objectives, in order to ensure that technologies to address waste management are effectively promoted and stimulated.
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Collection
The study is mixed-methods and combines qualitative and quantitative information to get a holistic picture of the impact of technological waste management solutions and circular economy principles. The qualitative information was obtained mainly through a detailed analysis of the available academic literature such as journal articles, white papers and government reports that discussed both the conceptual models and implementations of advanced waste technologies. Primary qualitative data included, too, semi-structured interviews with key stakeholders such as policymakers, industry leaders, and technology vendors [5]. These interviews gave us first-hand insights into what was faced and what could be achieved with the introduction of advanced waste management. For the quantitative level, the recycling rate, energy recovery rate and waste diversion rates were taken as numbers from case studies and statistics. This multiple-source model guaranteed a robust and complete dataset to see trends and deficient deployment of technological advances within the circular economy context.
3.2. Case Study Selection
To provide a more complete overview of the practical use of waste management technologies, the case studies in this thesis were selected by virtue of their comparative nature: Stockholm (Sweden), Tokyo (Japan) and New York (USA). These cities were selected based on their leadership in implementing state-of-the-art recycling and waste-to-energy technologies, and their adoption of circular economy concepts. Stockholm is one such city, which has a fully integrated waste-to-energy system (more than half the city’s municipal garbage is converted into energy, which makes it one of the most efficient in the world). Tokyo was chosen because of its recycling facilities — vast sorting stations for the waste and the new, incinerated generation of electricity [6]. New York on the other hand is a city that faces severe policy and infrastructure gaps even though it does have waste-to-energy plants. All three cities provide a unique insight into how to do, how to succeed and what works and doesn’t work with advanced waste technologies in different socio-economic and policy contexts. This cross-sectional comparison between these environments helps to discern the best practices and potential for improvement that can be generalised for international use.
3.3. Data Analysis
The gathered data were analysed and the most important factors for how innovations in waste management might work or not, within the circular economy, were identified. We used a thematic analysis on the qualitative data where interview and review of documents were coded and classified into common themes like technological efficiency, policy facilitation, and stakeholder cooperation. Thematic work revealed patterns in the way different cities incorporated technology and aligned it with circular economy targets. Then, for the quantitative statistics, recycling percentages, waste diversion and energy-recovery efficiency of each city were used to evaluate how each city’s waste system was doing. Stockholm’s recycling and waste-to-energy data, for example, was contrasted with Tokyo’s extensive sorting success and New York’s mixed results, to compare how effective different strategies were [7]. These were then triangulated by cross-referencing qualitative and quantitative data to be accurate and reliable in order to come up with useful suggestions for the enhancement of waste management in both developed and developing countries. This synergistic approach was a powerful way to define the key success factors and roadblocks to scaling circular economy principles with new technologies of waste management.
4. Results
4.1. Development in Technology and Reduction of Waste Products
According to the case studies, the application of cutting-edge recycling technologies like optical sorting and MBT made the recycling process more efficient and also contributed to the substantial reduction of waste. In Stockholm, for example, using optical sorting in 2019 led to a 30% increase in the recycled content of mixed household waste, and this just shows the impact of precision waste sorting techniques. So too, Tokyo has had spectacular success with its WTE technologies: the city recycled nearly 60 per cent of its municipal solid waste and shifted another 30 per cent into energy. Both solutions cut Tokyo’s landfill use by less than 10% in a very Circular Economy-like manner. The recycling rates and landfill reductions in each of the three cities are shown in Table 1, which demonstrate how these technologies reduce waste and increase resource recovery. The data shown in Table 1 highlights how different the advanced technologies-heavy cities such as Stockholm and Tokyo are from the policy-poor and infrastructure-deficient cities such as New York. These developments reaffirm the centrality of technology in waste reduction and the Circular Economy objectives [8].
Table 1. Recycling Rates and Landfill Dependency Across Cities
City | Recycling Rate (%) | Energy Recovery (%) | Landfill Dependency (%) |
Stockholm | 55 | 40 | 5 |
Tokyo | 60 | 30 | 10 |
New York | 35 | 25 | 40 |
4.2. Challenges in Policy Alignment
Despite the technology, one of the main issues identified in the case studies is lack of policy coordination between waste, recycling and energy generation. In New York, for example, waste-to-energy plants are in operation and can turn non-recyclable waste into electricity, but the city does not have a formal recycling scheme. This discrepancy has led to almost 40% of recyclable materials falling into landfill, Table 2 shows. The city has not been able to adopt waste technologies as an integrated part of its overall sustainability strategy, due to this disjuncture in policies that has hindered the city from attaining its Circular Economy goals. New York, according to Table 2, is still far more landfill dependent than Stockholm and Tokyo, and needs policy changes to close the gap. Bringing together sector-wide policies on waste management is needed to ensure that advanced technologies are being put to the most efficient use and that recycling, energy recovery and landfill reduction are well aligned [9].
Table 2. Breakdown of Waste Management Practices in New York (2023)
Waste Type | Percentage (%) |
Recycled | 35 |
Energy Recovered | 25 |
Landfilled | 40 |
4.3. Policy Incentives and Barriers
This study also suggests the need for policy incentives to promote the adoption of Circular Economy policies. In policy-strong places, like Europe, EPR programmes have helped companies design for recyclability and has boosted recycling of recycled material. For instance, 70 % of plastic packaging in Sweden is now recycled due to EPR and strong state backing. Developing nations, on the other hand, have a host of obstacles to overcome, such as a lack of financial incentives and limited regulatory mechanisms. Unfunded waste-to-energy programmes and a lack of recycling infrastructure are the major challenges to scaling modern waste technologies. These challenges will require not just monetary commitments but global cooperation to pool knowledge and come up with globally consistent policies [10].
5. Conclusion
The research underscores the significance of high-tech waste management systems and policy to develop Circular Economy ideas. As the case studies of Stockholm, Tokyo and New York demonstrate in more detail, technological advancements in the form of mechanical biological treatment (MBT), optical sorting and WTE could significantly increase recycling rates, resource recovery and landfill reliance. Such technologies are a radical revolution in the view of waste – not as an end but as something to be reused to drive sustainability. The findings show that even cities with strong policies like Stockholm and Tokyo are able to incorporate advanced waste solutions seamlessly into their overall sustainability plans, yielding remarkable waste and energy recovery outcomes. But the results also point towards persistent challenges to making these technologies work and scale. Material contamination of waste streams is still a major issue and can make recycled material of poor quality and value. Lack of infrastructure, especially in developing countries, inhibits the adoption of advanced waste technologies, and so many areas still remain stuck with analogue landfill and incineration technologies. Also, the fact that no one in the waste management, recycling and energy generation sector is on the same policy page (which was mentioned in New York) slows progress toward Circular Economy targets. These are the kinds of issues where technology isn’t enough: we need an integrated system that brings together technological innovation, good governance, cross-sectoral policy coordination and large-scale infrastructure and capacity-building investments. Defending against these obstacles requires a multi-pronged approach. It’s time for policymakers to design co-facilitating incentives – like extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies and recycling programmes – that drive industries to become more sustainable and to make products recyclable. The international cooperation is also necessary to exchange practices, coordinate resources, and establish globally consistent waste reduction and resource recovery policies. Developing countries especially need a large amount of financial and technical support to create the infrastructure to build efficient waste management processes. These resources can only be plugged by the private sector, public-private partnerships and global financing systems. This study shows why it’s so important to approach waste management as not just another problem, but as part of the larger picture of sustainability. If city and country can approach the technical, policy and infrastructure issues holistically, they can do a lot to mitigate waste, recover scarce resources and contribute to sustainability goals worldwide.
Contribution
Yan Yu and Zhangyu Wang contributed equally to this paper
References
[1]. Salmenperä, H., et al. (2021). Critical factors for enhancing the circular economy in waste management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 280, 124339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124339
[2]. Hossain, R., et al. (2022). Full circle: Challenges and prospects for plastic waste management in Australia to achieve circular economy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 368, 133127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133127
[3]. Chioatto, E., & Sospiro, P. (2023). Transition from waste management to circular economy: the European Union roadmap. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25(1), 249-276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01845-7
[4]. D'Adamo, I., et al. (2022). Assessing the relation between waste management policies and circular economy goals. Waste Management, 154, 27-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.07.014
[5]. Hemidat, S., et al. (2022). Solid waste management in the context of a circular economy in the MENA region. Sustainability, 14(1), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010480
[6]. Kharola, S., et al. (2022). Barriers to organic waste management in a circular economy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 362, 132282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132282
[7]. Negrete-Cardoso, M., et al. (2022). Circular economy strategy and waste management: a bibliometric analysis in its contribution to sustainable development, toward a post-COVID-19 era. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(41), 61729-61746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20467-9
[8]. Kaszycki, P., Głodniok, M., & Petryszak, P. (2021). Towards a bio-based circular economy in organic waste management and wastewater treatment–The Polish perspective. New Biotechnology, 61, 80-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2021.03.006
[9]. Mihai, F.-C., et al. (2021). Plastic pollution, waste management issues, and circular economy opportunities in rural communities. Sustainability, 14(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010020
[10]. Spišáková, M., et al. (2022). Waste management in a sustainable circular economy as a part of design of construction. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094553
Cite this article
Yu,Y.;Wang,Z.;Chen,Q.;Chen,Q. (2025). Innovative Approaches to Waste Management in Circular Economy: Technological Advancements and Policy Implications. Journal of Fintech and Business Analysis,2(1),11-15.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Fintech and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Salmenperä, H., et al. (2021). Critical factors for enhancing the circular economy in waste management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 280, 124339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124339
[2]. Hossain, R., et al. (2022). Full circle: Challenges and prospects for plastic waste management in Australia to achieve circular economy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 368, 133127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133127
[3]. Chioatto, E., & Sospiro, P. (2023). Transition from waste management to circular economy: the European Union roadmap. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25(1), 249-276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01845-7
[4]. D'Adamo, I., et al. (2022). Assessing the relation between waste management policies and circular economy goals. Waste Management, 154, 27-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.07.014
[5]. Hemidat, S., et al. (2022). Solid waste management in the context of a circular economy in the MENA region. Sustainability, 14(1), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010480
[6]. Kharola, S., et al. (2022). Barriers to organic waste management in a circular economy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 362, 132282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132282
[7]. Negrete-Cardoso, M., et al. (2022). Circular economy strategy and waste management: a bibliometric analysis in its contribution to sustainable development, toward a post-COVID-19 era. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(41), 61729-61746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20467-9
[8]. Kaszycki, P., Głodniok, M., & Petryszak, P. (2021). Towards a bio-based circular economy in organic waste management and wastewater treatment–The Polish perspective. New Biotechnology, 61, 80-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2021.03.006
[9]. Mihai, F.-C., et al. (2021). Plastic pollution, waste management issues, and circular economy opportunities in rural communities. Sustainability, 14(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010020
[10]. Spišáková, M., et al. (2022). Waste management in a sustainable circular economy as a part of design of construction. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094553









