

Volume 2 Issue 2
Published on September 2025The volatility of financial markets has driven the diversification of investment instruments, encouraging investors to keep improving their portfolio-picking techniques. While numerous studies based on Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) have developed accepted methods for determining optimal portfolios, not enough research has been done on the visual graphical analysis of risk preferences to accommodate diverse investors. Furthermore, by including risk-free assets in the analysis, this study presents an innovative methodology. This study's main goal is to find and analyze the risk portfolio frontier while examining the complementing of risk-free investments. Under idealized assumptions, portfolio returns and risks are formulated and solved as equality-constrained optimization problems, yielding frontier portfolios. The risk-efficient frontier and preference levels are depicted graphically, with explicit discussion of unfettered short-selling possibilities. The inclusion of risk-free assets further broadens the model’s practical applicability. The framework's viability is empirically validated using historical data from twelve stocks. These results illustrate investors can use the efficient frontier as a foundation to match portfolio selections to their own risk tolerances, providing practical guidance for adaptable wealth management.

 View pdf
View pdf


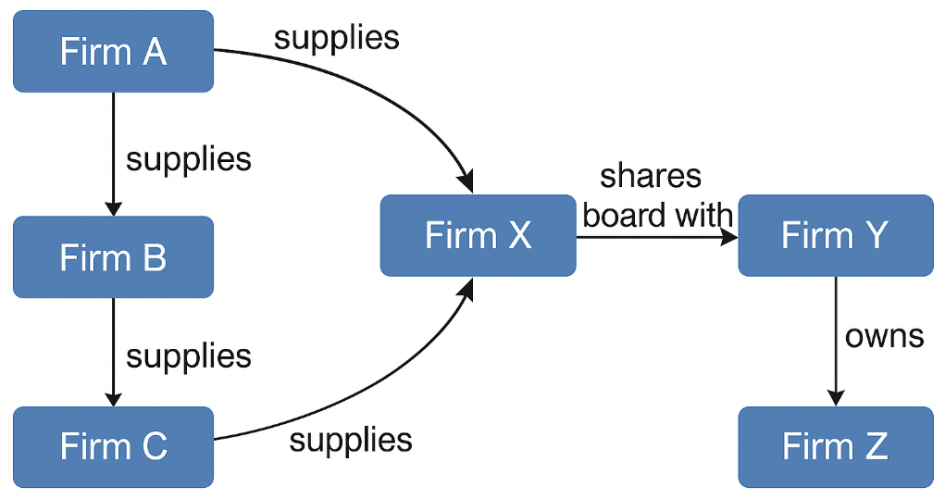
This study presents a graph neural network (GNN)-based framework for corporate default risk prediction by explicitly modeling inter-firm dependencies through supply-chain links, ownership ties, and board overlaps. We construct a heterogeneous information network (HIN) from longitudinal firm-level data (2014–2024), transforming relational structures into learned node embeddings via a three-layer relational graph convolutional network (R-GCN). These embeddings are further processed by a survival-analysis layer to estimate time-varying default probabilities. Compared to traditional financial ratio models and graph-agnostic machine learning baselines, the proposed GNN consistently outperforms in terms of AUC, F1-score, and Harrell’s C-index. Extensive ablation studies confirm the importance of incorporating economic relationships, particularly supply-chain dependencies, which exhibit the highest marginal contribution to predictive performance. Moreover, the model demonstrates robustness across economic cycles, including during the COVID-induced stress period. A case study further illustrates how GNN-based message passing reveals upstream contagion paths not captured by standalone financial metrics. The findings highlight the significant value of network-aware credit risk modeling in regulatory supervision and financial decision-making. Our approach suggests that integrating network topology into corporate risk assessment can offer timely, interpretable, and materially superior insights for early warning systems and financial resilience analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf


Financial risk monitoring is crucial for maintaining the stability and resilience of financial institutions in today’s complex economic environment. This paper explores the innovations and practical applications of intelligent technologies—including artificial intelligence, big data analytics, blockchain, and natural language processing—in enhancing financial risk monitoring. By analyzing the capabilities of these technologies in real-time risk detection, predictive modeling, and transaction transparency, the study highlights how they enable more accurate, timely, and proactive risk management. Additionally, practical cases and emerging best practices demonstrate the transformative impact of these technologies across the financial sector. The paper also discusses key challenges such as data quality, model interpretability, and regulatory compliance, as well as outlines future trends like generative AI and privacy-preserving computation that will shape the evolution of financial risk monitoring. The findings underscore the vital role of intelligent technologies in building more resilient and adaptive financial systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the advancement of the era, the status of baijiu in China has been progressively elevated, not only facilitating international exchanges but also promoting the development of Chinese culture. However, in recent years, due to the introduction of relevant national policies and transformations in the baijiu industry environment, the sector has entered a phase of profound adjustment. As a leading enterprise in the baijiu industry, Kweichow Moutai's financial performance has consistently attracted significant attention. This paper analyzes the financial reports of Kweichow Moutai from 2022 to 2024, employing methodologies, such as the Business Model Canvas, ratio analysis, and horizontal and vertical comparative analysis, to elucidate the characteristics of its business model and profitability model, which can be summarized as "scarcity + brand moat + channel control." Concurrently, the study identifies risks and challenges faced by the enterprise, including declining inventory turnover, a homogeneous product portfolio, cyclical industry fluctuations, and insufficient appeal to younger consumers. To address these issues, this paper proposes strategies such as optimizing the product matrix, deepening channel reform, implementing digital price control, and brand rejuvenation. The research unveils the underlying commercial logic behind Moutai's high profitability and highlights its exploratory significance in balancing traditional value with innovative transformation.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study focuses on two major financial tools—green bonds and impact investing—and analyzes their practical avenues for advancing the Sustainable Development Goals. Using a mixed-methods research approach, the global trend of green bond issuance, financial performance, and environmental benefits from 2015 to 2024 were systematically examined. At the same time, case studies from Southeast Asia, Latin America, Europe, and Africa were combined to obtain empirical evidence. The data show that the annual issuance of global green bonds has increased from $100 billion to $800 billion, and related projects have successfully reduced carbon dioxide emissions by millions of tons per year. The impact investment portfolio effectively supports public welfare projects, such as clean stove manufacturing and regenerative agriculture, while maintaining market-leading returns. However, there are currently three major obstacles limiting scale-up: a fragmented regulatory system, uneven disclosure standards, and an insufficient pool of professional talent. The research advocates developing a unified classification framework, formulating transparent disclosure standards, and building the capacity of institutional investors to unlock the potential of green finance. There is an urgent need for a policy-level coordination mechanism to direct capital toward long-term environmental sustainability goals.

 View pdf
View pdf


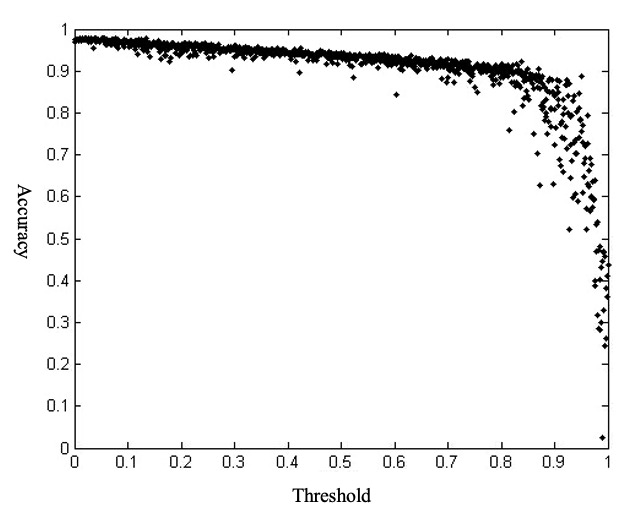
The inherent high default risk in peer-to-peer (P2P) lending necessitates robust credit risk assessment for sustainable online financial operations. This study addresses this need by developing a default prediction model for P2P borrowers using public data from the Renrendai platform in China. With approximately one million loan records, we built up a back-propagation neural network model and achieved over 85% prediction accuracy. The model was refined through two steps: generating Receiver Operating Characteristic and introducing a novel indicator, SPACE, to identify the optimal threshold interval for the final model. This research presents an enhanced credit evaluation model, offering practical implications for P2P lending risk management.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of continuous innovation in financial markets, quantitative trading strategies, characterized by data-driven decision-making, model-based analysis, automated execution, and controllable risk, have exerted a profound impact on insurance investment and risk management. This paper explores the application of quantitative trading strategies in the insurance industry, analyzing their role in optimizing insurance investment portfolios and enhancing risk management effectiveness. In the field of insurance investment, quantitative trading strategies accurately assess the risk-return characteristics of assets. By applying modern portfolio theory and integrating specific cases, these strategies achieve optimal asset allocation, significantly improving investment returns while effectively diversifying risks. In risk management, quantitative models leverage extensive historical data to identify potential risk factors, use metrics such as Value at Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR) to precisely measure risks, and implement real-time monitoring with preset risk thresholds to ensure effective control and timely warning. Additionally, stress testing and scenario analysis are employed to enhance the risk resilience of insurance portfolios. This study indicates that even though using quantitative trading strategies in the insurance industry has challenges like poor data quality, risks from the models, lack of technical skills and talent, and changes in the market, we can expect future trends such as better technology use, new ideas, applying strategies across different markets and assets, flexible risk management, and working together with regulatory technology (RegTech). The rational adoption of these strategies will continue to improve the investment efficiency of insurance funds and risk management standards, facilitating the sustainable development of the insurance industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


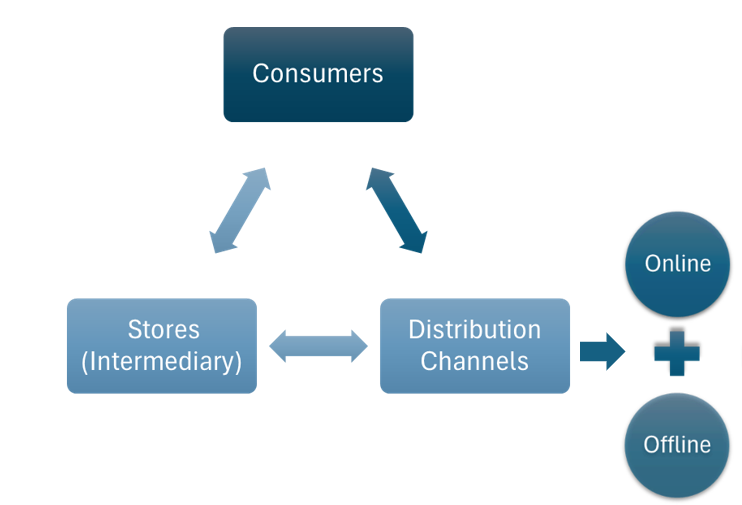
The Resource-Based View (RBV) has been widely adopted to analyse multinational enterprises' (MNEs) competitive advantages through internal resources. However, its limitations in addressing external environmental factors remain underexplored. This study critically evaluates RBV's applicability by examining Haagen-Dazs’s paradoxical performance: its success in the U.S. market versus its struggles in China. Using the VRIO framework, we identify how sustainable advantages—such as brand culture and a direct operating model—drove U.S. dominance, while temporary advantages (e.g., premium ingredients) failed in China due to local competition and market heterogeneity. Further analysis reveals that RBV overlooks critical external factors, including income disparities and competitive intensity, which significantly undermined Haagen-Dazs’s Chinese strategy. Empirical data confirm that China’s price-sensitive consumers and rising domestic brands reduced Haagen-Dazs’s market share to 1%. The findings argue that MNEs must integrate macro-environmental analysis with RBV to navigate diverse markets. This research advances international business theory by bridging RBV’s internal focus with external contingencies, offering strategic insights for MNEs expanding globally.

 View pdf
View pdf


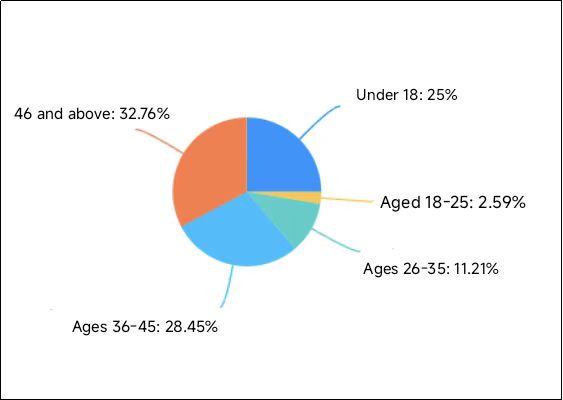
Based on the research on the revenue situation of China's online food delivery software market and analysis of the growth trends of both domestic and foreign online food delivery market platforms, a specific phenomenon has emerged that warrants special attention. This paper adopts three research methods: literature review, questionnaire survey, and case study. To collect information, thereby establishing the framework and main structure of the study. At the same time, the paper uses qualitative and quantitative analysis for additional resource search. The questionnaire for this paper was based on actual social data. In conclusion, this paper has conducted relevant analyses on this result and made a prediction that in the future, China is highly likely to achieve a truly perfect "La La Land" where "one app controls life," which aligns with the laws of economic and social development.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of increasingly severe global environmental issues and the rise of green consumption trends, this study focuses on the effect of brand green marketing strategies on enhancing consumers' environmental awareness. Based on Planned Behavior and Consumer Behavior Theory, this study adopts a quantitative research approach to develope a theoretical model with hypotheses to assess the impact of green product, promotion, and channel strategies on environmental awareness. The results show that all three green marketing strategies—green product, green promotion, and green channel strategies —have significant positive effects on consumers' environmental awareness. Among them, green channel strategies exhibit the strongest influence (β=0.407, p<0.01), followed by green promotion strategies (β=0.193, pβ=0.081, p<0.05), collectively explaining 34.9% of the variation in consumers' environmental awareness. The study provides empirical support for enterprises to optimize their green marketing mix, effectively enhancing consumers' environmental awareness and promoting the development of the green consumption market.

 View pdf
View pdf




