

Volume 2
Published on December 2023The emergence of the sharing economy provides the value reconstruction of the scarcity of idle resources, provides an efficient business model for economic growth and transformation, and becomes an important driver of supply-side reform. Didi Kuaidi is a combination of transportation and the Internet, that is, a form of application that combines actual objects with the Internet. For people's travel, it can also better meet people's short-distance needs, and a new business model makes it have a larger commercial space. At present, Didi Kuaidi ranks in the forefront of domestic Didi Kuaidi operators and seems to be able to sit in Diaoyutai from the perspective of scale. However, Didi Kuaidi still faces many challenges. This paper analyzes the connotation and role of the sharing economy, expounds the operating mechanism and development status of the sharing economy business model, and then makes a case analysis of Didi Kuaidi's business model. It puts forward policy suggestions for the healthy and sustainable development of the sharing economy, including focusing on the construction of Didi Kuaidi, improving service management procedures, actively realizing automated system operation, rational business operation, transforming operating costs, and expanding Didi Kuaidi's promotion methods. It is of great significance to the development of Didi Kuaidi.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous progress of RMB internationalization, RMB has shown the attribute of safe haven currency. This paper discusses the exhibition of RMB’s attribute of safe haven currency and the causes behind it in some special risk aversion periods recently by comparing RMB with other major currencies. The process of RMB internationalization has an important impact on the exhibition of RMB’s attribute of safe haven currency. Although convertibility and high liquidity are necessary conditions for a safe haven currency, we also see that in some special circumstances, proper control is helpful for enhancing the safe haven currency attribute of RMB.

 View pdf
View pdf


Customer experience is an important strategic process for businesses to provide personalized services to customers in order to gain competitive advantages. As it enters the intelligent stage, how to manage the intelligent customer experience has become an urgent issue to explore. Based on the customer experience theory, this article uses the grounded theory research method to conduct a multi-case study, clarifies the concept of the intelligent experience engine, and proposes a process structure model for it. Its structural level includes the contact layer, data layer, and decision layer. The research results extend the customer experience theory and have good theoretical insights and practical guidance for businesses to carry out intelligent customer experience management activities.

 View pdf
View pdf


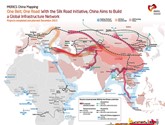
Since its inception in 2013, the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) by Chinese President Xi Jinping has emerged as a transformative economic strategy aiming to reshape the economic landscape across Asia, Eastern Europe, and Africa. This paper examines the connection between the BRI and network theory, a relatively underexplored area in the existing body of research. The BRI, covering five continents and over 100 countries, focuses mainly on South Asia, Central Asia, and Europe, including Russia, due to their central role in the initiative. The core of this paper lies in analyzing the network effects and lock-in dynamics associated with the BRI, especially in the context of developing countries. Part II delves into the positive arguments for BRI’s network effects and lock-in dynamics, drawing on Bryan Druzin’s theories and adding the concepts of resilience and cultural connectivity. Conversely, challenges to these network effects and dynamics are scrutinized, including sustainability issues, institutional flaws, fragmentism with Chinese characteristics, neo-colonial critiques, and cultural and ideological disparities. A case study focusing on the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) in Part III sheds light on both the strengths and weaknesses of the BRI’s approach. In conclusion, the paper posits that while the BRI is successfully building both material and conceptual foundations for its network, the significance of its network effects and lock-in dynamics is moderated by numerous challenges.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper examines the period from 2007 to 2020 using Chinese A-share listed companies as a research sample. From the perspectives of operational risk and information quality, the empirical analysis investigates the influence of short-term loans for long-term investments on the risk of stock price collapse. The results indicate that short-term loans for long-term investments exacerbate the risk of stock price collapse. The impact is primarily achieved through increasing corporate operational risk and earnings management, thereby intensifying the risk of stock price collapse. Simultaneously, the quality of internal control and managerial capabilities can, to a certain extent, moderate the influence of short-term loans for long-term investments on the risk of stock price collapse. This paper contributes to the research in the field of short-term loans for long-term investments and sheds light on the factors influencing the risk of stock price collapse, offering valuable insights for corporate governance and the mitigation of the risk of stock price collapse.

 View pdf
View pdf




