1. Introduction
In the era of mass media, the influence of media discourse on financial decision-making cannot be overlooked. Commercial banks are increasingly facing a plethora of issues. Examples include the disclosure of personal information, money laundering through loans, and instances of insider trading, all of which frequently feature in major media reports. These hot-button issues, such as personal information disclosure, loan money laundering, and insider trading, have become recurrent topics in prominent media coverage [1]. The impact of media attention, emotion, and their interplay on the fluctuation of financial asset prices varies, with media attention exerting the predominant influence [2]. Additionally, considerable academic research has scrutinized the effects of media information on financial markets, particularly within the stock market [3]. Therefore, comprehending, forecasting, and standardizing financial decision-making, especially interpreting the relationship between media discourse and the financial market through the lens of social psychology, holds paramount theoretical and practical significance. This study adopts the Credit Suisse Group as a case study to analyze the ramifications of rumors on group customer behavior, to unveil the impetus behind media discourse and its influence mechanism on financial decision-making in the era of mass media while furnishing valuable insights and recommendations for the risk management and investment decision-making of financial institutions.
This study aims to explore the motivations driving financial decision-making in the era of mass media from the perspective of social psychology, with a particular focus on the influence of media discourse on the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group.
Through the lens of social psychology, this paper interprets the impact of media commentary on the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group. The study endeavors to provide financial institutions with profound insights into the psychological underpinnings of customer decisions, while also offering valuable insights and recommendations for the healthy evolution of financial markets.
2. Application of Social Psychology Theory in Financial Decision-Making
2.1. Social Psychological Factors Influencing Financial Decision-Making
Social psychological factors play a crucial role in shaping financial decision-making. In the era of mass media, individuals acquire abundant information through media channels, which often exerts a significant influence on their decision-making processes. Among these factors, certain key social psychological elements stand out prominently in financial decision-making. Firstly, individuals' attitudes towards and level of trust in media information significantly impact their decision-making behaviors. For instance, when rumors circulate on social media platforms suggesting the imminent collapse of a bank, such uncertain information often triggers panic and concern among individuals, consequently affecting their financial investment decisions. Secondly, individuals' social cognition and associated labels also wield considerable influence over financial decision-making. For example, a financial institution may be perceived as high-risk venture capital by the public, thus forming a social cognitive bias that impacts individuals' decisions regarding the institution. Additionally, social comparison plays a role in financial decision-making, wherein individuals evaluate and make decisions based on the actions of others. In summary, social psychological factors exert a substantial influence on financial decision-making, underscoring the importance of understanding their impact on customers of the Credit Suisse Group for a deeper comprehension of the drivers behind financial decision-making.
2.2. Impact of Social Cognition and Information Processing on Financial Decision-Making
An indispensable aspect when studying social psychology in financial decision-making is the influence of social cognition and information processing on such decisions. Bandura's social cognitive theory posits that individuals are susceptible to the viewpoints and opinions of others when forming attitudes and behaviors. Thus, when rumors about Credit Suisse Group's potential bankruptcy surface on social media, customers are prone to being influenced by the negative opinions of others, thereby developing unfavorable perceptions of the bank. Furthermore, when confronted with information overload, individuals often resort to heuristic processing methods, making decisions swiftly based on simplified rules and past experiences. Consequently, in the presence of negative emotions and uncertainties conveyed through media discourse, customers are more susceptible to emotional influences, leading to impulsive decision-making and thereby exerting pressure on Credit Suisse Group's stock.
Hence, studying the impact of social cognition and information processing on financial decision-making is of paramount importance for interpreting the influence of media discourse on the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group. By comprehending customers' cognitive styles and information processing mechanisms, we can effectively forecast customer behaviors and devise appropriate management strategies to mitigate adverse effects while enhancing customers' financial decision-making capabilities.
3. Media Influence in Financial Decision-Making
3.1. Communication Characteristics of the Media
Table 1: Influence of Media Communication on Financial Decision-Making
Propagation Characteristics |
Impact |
Broad Coverage and Rapid Dissemination Speed |
May lead to the diffusion and distortion of information, influencing perceptions and decisions regarding financial products and institutions. |
Emotive and Dramatic Nature of Media Discourse |
Exaggerates facts and evokes emotional responses, influencing financial decision-making. |
Reflects Public Opinion and Mass Sentiment |
Financial decision-makers may succumb to public pressure, compelling them to take action or adjust strategies. |
As depicted in Table 1, the extensive dissemination of information by the media may lead to the spread and distortion of information, thereby impacting the cognition and decision-making of market participants regarding financial products and institutions. Within socialized groups, individuals rely on each other through social interactions, and their beliefs and decision-making behaviors are often influenced by the individual characteristics and behaviors of other members within their social groups [4]. Financial decision-makers are frequently subject to the influence of public pressure, which compels them to take action or adjust their strategies. Therefore, understanding the communication characteristics of the media holds significant importance in interpreting its impact on financial decision-making.
3.2. Factors Affecting Media in Financial Decision-Making
In the era of mass media, media discourse plays a pivotal role in financial decision-making. From the perspective of social psychology, we can comprehend the influence of media discourse on the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group. Firstly, the authority and credibility of the media are crucial factors influencing financial decision-making. Customers tend to place greater trust in information disseminated by media organizations perceived as authoritative, while disregarding or questioning comments from non-authoritative sources. Secondly, the emotional tone of media discourse also exerts an impact on financial decisions. If media content is saturated with negative emotions, such as predicting the collapse of a bank, customers may experience anxiety and panic, resulting in adverse effects on their financial decisions. Additionally, individual cognitive biases and group dynamics contribute to the influence of media discourse on financial decision-making. For instance, herd mentality and confirmation bias may incline customers to blindly follow others' viewpoints or selectively perceive information that aligns with their existing beliefs. Therefore, investigating the factors influencing media in financial decision-making facilitates a deeper understanding of the social psychological mechanisms underlying customer behavior in the era of mass media.
4. Analysis of Customer Behavior of Credit Suisse Group
4.1. Overview of Credit Suisse Group
Credit Suisse Group, headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland, stands as one of the world's leading financial service providers. With offices in all major financial centers globally, it offers investment banking, private banking, asset management, and shared services. Renowned for its strict bank-customer confidentiality and bank secrecy, it is recognized by the Financial Stability Board as a globally significant bank. Credit Suisse is also a primary dealer and foreign exchange counterparty of the Federal Reserve [5].
In the fiercely competitive financial market, the reputation and image of Credit Suisse Group play a pivotal role in shaping customer behavior. Media discourse can directly or indirectly influence customers' trust and confidence in the group. When rumors circulate on social media predicting the bank's failure, Credit Suisse Group's stock faces considerable pressure. This influence extends beyond the stock market, affecting the behavior and decision-making of the group's clientele. It impacts the company's share price and investors' investment performance. On the flip side, news reports capture investors' attention, subsequently influencing their buying and selling behavior, thus affecting the company's stock price[3].
In summary, media discourse holds significant sway over the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group in the era of mass media. Through the lens of social psychology, a deeper understanding of the motives behind media discourse on customer behavior can be achieved. This understanding aids Credit Suisse Group in devising more effective marketing strategies, bolstering customer trust and loyalty, thereby enhancing its market competitiveness and long-term sustainability.
4.2. Characteristics of Credit Suisse Group Customer Behavior
In the age of mass media, rumors and media commentary on social platforms wield substantial influence over financial decision-making. The characteristics of customer behavior are crucial for comprehending the impact of media discourse on financial decision-making. Firstly, customers of Credit Suisse Group exhibit heightened sensitivity to media discourse. With the rapid proliferation of social media, the dissemination speed and impact of media discourse have markedly increased. Particularly, when negative remarks surface about Credit Suisse Group on social platforms, such as rumors predicting the bank's collapse, the stock price of Credit Suisse Group comes under significant pressure. Many customers swiftly adjust their decisions based on these comments, opting to sell stocks or withdraw deposits to mitigate potential financial risks. Hence, it's evident that media discourse significantly influences the emotions and actions of Credit Suisse Group's customers. Secondly, customers of Credit Suisse Group tend to seek security amidst uncertainty. To be media-responsive would mean being vulnerable to the harsh discipline imposed on market participants by market arbitrageurs, invoking the evolutionary principle of 'survival of the fittest' most often associated with competitive market processes. These presumptions are, however, based on a false premise. In our experience, institutional investors are also susceptible to media influence in their decision-making processes and indeed are actively factoring them into their considerations[6]. Media discourse often amplifies uncertainties in the financial market, triggering customer panic and apprehension. Credit Suisse Group's customers typically manage their portfolios with greater caution and conservatism, especially in the face of negative media discourse. Against the backdrop of financial crises, customers lean towards reallocating funds to relatively stable and secure investment avenues, such as purchasing low-risk bonds or conservative funds. This behavior reflects customers' attention to media commentary and their concerns regarding rapid fluctuations in the financial market, underscoring their high regard for fund safety.
Table 2: Analysis of Customer Behavior of Credit Suisse Group
Characteristics |
Description |
Sensitivity |
Customers exhibit high sensitivity to media discourse, with negative remarks impacting stock prices. |
Seeking Security |
In times of uncertainty, customers tend to migrate towards stable and secure investment channels. |
Social Media Influence |
Opinions and comments from customers' family, friends, and colleagues on social media affect their decision-making. |
In summary, customers of Credit Suisse Group exhibit a high sensitivity to media discourse, a tendency to seek security, and susceptibility to the influence of social media. Understanding these characteristics of customer behavior within Credit Suisse Group can facilitate a better comprehension of how media speech impacts financial decision-making and can provide relevant strategies and measures for financial institutions to address the drivers of financial decision-making in the era of mass media.
4.3. The Impact of Media Comments on Customer Behavior of Credit Suisse Group
4.3.1. Potential Mechanisms of Media Comments on Customer Behavior
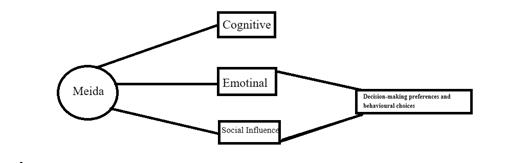
Figure 1: Potential Mechanisms of Media Comments on Customer Behavior
Table 3: Impact of Media Comments on Credit Suisse Group Customer Behavior
Impact Mechanism |
Description |
Cognitive |
Media comments influence customers' perception of risk regarding Credit Suisse Group by disseminating negative information or rumors. |
Emotional |
Media comments can induce feelings of panic, worry, or anxiety among customers, thereby influencing decision preferences and behavioral choices. |
Social Influence |
Customers are influenced by others' retweets and comments on media comments, leading to changes in their decision-making behavior. |
In early October 2022, rumors circulating on social media predicted the imminent failure of the bank, causing significant pressure on Credit Suisse's shares. Despite assertions from financial analysts regarding the bank's "strong capital base and liquidity," the Swiss National Bank pledged to closely monitor the situation. European financial experts specifically addressed the concept of "self-realization risk," highlighting that liquidity is not a concern for Swiss banks. [7] However, a substantial amount of funds was still withdrawn from the bank within a short period. it seems equally clear that the effects we identify at the local level should apply generally, i.e., to national media outlets with audiences large enough to meaningfully impact capital allocation. Specifically, beginning with Tetlockand Tetlock et al., a number of papers have shown that news stories in national newspapers are associated with substantial price responses [8.9]. Here, identification usually focuses on what kind of information a story conveys – i.e., about a firm’s cash flows, risk or sentiment.[10] In conclusion, the impact of media comments on the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group can be elucidated through the lenses of customer cognition, emotions, and social influence.
5. Conclusion
Through this study, the influence of interpreting media comments from the perspective of social psychology on the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group is discussed. The purpose of this study is to reveal the important role of media speech in shaping the motivation behind financial decision-making in the era of mass media and to analyze it using Credit Suisse Group as a case study. Firstly, the research results demonstrate that comments on social media directly impact the customer behavior of the Credit Suisse Group. When rumors about the collapse of Credit Suisse Group surfaced on social media, the shares of Credit Suisse Group faced considerable pressure. This underscores the significant influence of media speech in shaping the motivation behind financial decision-making and its potential impact on the financial market. Secondly, the theories of social psychology play a pivotal role in interpreting the motivation behind financial decision-making. This study employs social psychology theories such as social cognition theory, collective behavior theory, and group psychological models to analyze the behavior of Credit Suisse Group's customers. Lastly, this study offers several suggestions for Credit Suisse Group. In response to the influence of media comments, Credit Suisse Group should enhance communication and provide explanations to customers, promptly debunk rumors, and offer reliable information sources to bolster customers' trust and loyalty. Additionally, Credit Suisse Group can leverage the power of social media to actively shape its corporate image and enhance public recognition and goodwill.
In conclusion, this study interprets the influence of media speech on the customer behavior of Credit Suisse Group through the lens of social psychology, shedding light on the significance of the motivation behind financial decision-making in the era of mass media. This provides valuable insights for financial institutions in formulating sound financial strategies and managing customer relationships. However, this study has some limitations, and further research is needed in broader samples and over longer timeframes to comprehensively elucidate the impact of media speech on the motivation behind financial decision-making.
References
[1]. Li, Q., & Mu, G. (2022). Research on the influence of media reports on the unsystematic risk management of commercial banks [Doctoral dissertation, Inner Mongolia University]. doi: 10.27224/d.cnki.gnmdu.2022.001059
[2]. Li, Z., Su, Y., Liao, G., et al. (2018). The influence of media information on the price fluctuation of financial assets-taking the stock market as an example. *Financial Theory and Practice, 39*(03), 56-61. doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbcjb.2018.03.009
[3]. Huang, T. (2022). Research on industry media information and stock price [Doctoral dissertation, Central University of Finance and Economics]. doi: 10.27665/d.cnki.gzcju.2022.000560
[4]. Liu, Z. (2015). Social interaction, investor sentiment and financial contagion [Doctoral dissertation, Tianjin University].
[5]. Credit Suisse. (n.d.). Who we are. Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.credit-suisse.com/about-us/en/who-we-are.html
[6]. Gordon Clark , Nigel Thrift & Adam Tickell (2004) Performing finance: the industry, the media and its image, Review of International Political Economy, 11:2, 289-310, DOI: 10.1080/09692290420001672813
[7]. Smith, E. (2022, October 4). Credit Suisse to remain 'under pressure' but analysts wary of Lehman comparison. *CNBC*. Retrieved October 5, 2022, fromhttps://www.cnbc.com/2022/10/04/credit-suisse-to-remain-under-pressure-but-analysts-wary-of-lehman-comparison.html
[8]. Tetlock, P. (2007). Giving content to investor sentiment: The role of media in the stock market. The Journal of Finance, 62(3), 1139-1168.
[9]. Tetlock, P., Saar-Tsechansky, M., & Macskassy, S. (2008). More than words: quantifying language to measure firms' fundamentals, Journal of Finance, 63, 1437-1467.
[10]. ENGELBERG, J.E. and PARSONS, C.A. (2011), The Causal Impact of Media in Financial Markets. The Journal of Finance, 66: 67-97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2010.01626.x
Cite this article
Wang,K. (2024). Motivation of Financial Decision-Making in the Era of Mass Media: An Interpretation of the Influence of Media Discourse on Credit Suisse Group Customer Behavior. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,52,65-71.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Education Innovation and Philosophical Inquiries
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Li, Q., & Mu, G. (2022). Research on the influence of media reports on the unsystematic risk management of commercial banks [Doctoral dissertation, Inner Mongolia University]. doi: 10.27224/d.cnki.gnmdu.2022.001059
[2]. Li, Z., Su, Y., Liao, G., et al. (2018). The influence of media information on the price fluctuation of financial assets-taking the stock market as an example. *Financial Theory and Practice, 39*(03), 56-61. doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbcjb.2018.03.009
[3]. Huang, T. (2022). Research on industry media information and stock price [Doctoral dissertation, Central University of Finance and Economics]. doi: 10.27665/d.cnki.gzcju.2022.000560
[4]. Liu, Z. (2015). Social interaction, investor sentiment and financial contagion [Doctoral dissertation, Tianjin University].
[5]. Credit Suisse. (n.d.). Who we are. Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.credit-suisse.com/about-us/en/who-we-are.html
[6]. Gordon Clark , Nigel Thrift & Adam Tickell (2004) Performing finance: the industry, the media and its image, Review of International Political Economy, 11:2, 289-310, DOI: 10.1080/09692290420001672813
[7]. Smith, E. (2022, October 4). Credit Suisse to remain 'under pressure' but analysts wary of Lehman comparison. *CNBC*. Retrieved October 5, 2022, fromhttps://www.cnbc.com/2022/10/04/credit-suisse-to-remain-under-pressure-but-analysts-wary-of-lehman-comparison.html
[8]. Tetlock, P. (2007). Giving content to investor sentiment: The role of media in the stock market. The Journal of Finance, 62(3), 1139-1168.
[9]. Tetlock, P., Saar-Tsechansky, M., & Macskassy, S. (2008). More than words: quantifying language to measure firms' fundamentals, Journal of Finance, 63, 1437-1467.
[10]. ENGELBERG, J.E. and PARSONS, C.A. (2011), The Causal Impact of Media in Financial Markets. The Journal of Finance, 66: 67-97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2010.01626.x









