1. Introduction
In recent years, the accelerated progress of artificial intelligence (AI) has given rise to more sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) models, which can generate human-like text virtually indistinguishable from human-produced responses. Although AI-generated text is deployed across various applications, from content creation to customer support, the broader implications of these advancements on human communication still need to be explored. This research paper examines the significance of distinguishing AI-generated text from human responses and the insights that can be obtained from such differentiation. We will deploy various machine-learning models to scrutinize and classify AI-generated text and human responses with different NLP process techniques to achieve this. By pinpointing patterns and characteristics unique to each category, we aim to devise a comprehensive framework to differentiate between them, illuminating the strengths and limitations of AI models and offering valuable insights into the essence of human language and communication.
ChatGPT is one of the GPT family of language models and a sibling model to InstructGPT, which is trained to follow the instruction in a prompt and provide a detailed response. It is prepared using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, the same methods as InstructGPT, but with slight differences in the data collection setup. After GPT-3 and InstructGPT were released, many problems were pointed out: Chan (2023) emphasizes the presence of deterministic viewpoints in the contemporary AI discourse with an emphasis on the two challenges of (1) GPT-3's potential intentional misuse for manipulation and (2) unintentional harm caused by bias. In addition, she asserts that while InstructGPT represents a modest step toward eliminating toxic language and bringing GPT-3 into line with user intent, it does not offer any effective remedies for bias or manipulation [1]. In their work, Saparov and He (2022) conclude that they struggle with proof planning because they cannot methodically consider all of the possibilities when there are several legitimate deduction processes available [2].
However, the coming of ChatGPT is considered an evolution. Lund and Wang (2023) explored the benefits of ChatGPT, such as improving search and discovery, reference, and information services, cataloging and metadata generation, and content creation [3]. Biswas (2023) shows its broad uses in different fields, such as public health and global warming [4,5].
Some researchers have found some implications and constraints about ChatGPT in educational fields. By evaluating the effectiveness of its hint against those written by human tutors with 77 participants in Elementary Algebra and Intermediate Algebra, Bhandari and Pardos (2023) points out in their research that learning gains from human-created hints were substantially and statistically significantly higher than ChatGPT hints in both topic areas [6]. In addition, Alafnan et al. (2023) examine the advantages and difficulties ChatGPT offers participants in communication, business writing, and composition courses. They did 30 theory-and-application-based ChatGPT examinations and discovered that ChatGPT could replace search engines since it gives students reliable and correct information. These conclusions lay the background for our research on detecting linguistic patterns in ChatGPT-generated answers [7].
ChatGPT also has its issues and limitations, like generating human-like text virtually indistinguishable from human-produced responses. Hulman et al. (2023) use a deliberately conducted Turing test to evaluate the capacity of ChatGPT. According to the closed e-survey, approximately 60% of the participants can identify ChatGPT answers from human-generated answers. They discovered that people who had previously used ChatGPT were better able to discern between ChatGPT-generated and human responses, which may indicate that linguistic traits have a better capability for prediction than the actual content. But most of the situations are that we, especially those without experience with ChatGPT, cannot identify its answers from the human response [8].
2. Data
Our data is retrieved from a specific Github project about ChatGPT (built on GPT-3.5), which is called Human ChatGPT Comparison Corpus (HC3). The HC3 corpus is a human-ChatGPT answer text pair for a given question collected by the SimpleAI team. Data from two primary sources construct the corpus:
• Published Q&A datasets: The team uses datasets that provide questions and human expert answers, then feeds the questions directly into ChatGPT to obtain answers.
• Wiki Encyclopedia: The team crawled vital concepts and their explanations from the wiki encyclopedia, used questions formatted as "Please explain what is <concept>", and then collected ChatGPT answers.
The dataset is provided in the format of JSONL (jsonline) and has five distinct fields as shown below:
• id (integer) - the index of the question
• question (string) - the sample questions from Q&A datasets
• Human_answers (string) - human expert answers to the question
• chatgpt_answers (string) - ChatGPT generated responses to the question
• source (series) - where the answer text comes from
The pictures shown below are the general description of the size and content of the dataset.
Definition of word counts from columns "question" and "answer."
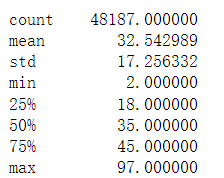
Figure 1. Word count from “question”
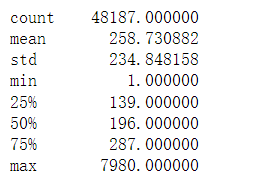
Figure 2. Word count from “answer”
Note: This table illustrates summary statistics for both the question and answer. This is representative based on word counts and corresponding statistics.
3. Methodology
In this part, we will illustrate the strategies to classify text as human or ChatGPT and estimate linguistic patterns in ChatGPT-generated answers. The main steps can be found in Fig. 3.
We will train a model for detecting ChatGPT-generated answers by finding the common linguistic patterns and structures in AI answer text. We will build several models on predicting labels in the sentence of ChatGPT answer texts, which are the Linear Regression model, LightGBM model, and Naive Bayes Classifier model, and perform a side-by-side comparison of each model's performance. We will further validate the reliability of specific and multiple models by taking a majority vote with the results of different models. Therefore, depending on the results, we may find the implicit "logic" behind ChatGPT answers.
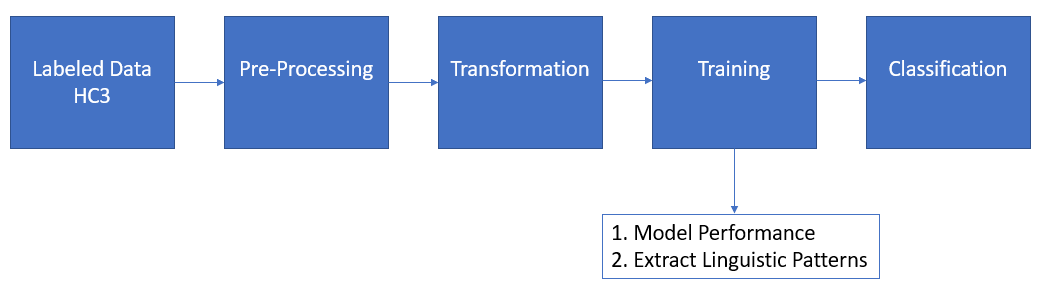
Figure 3. Methodology Note: This diagram shows the overall methodology
3.1. Data Preprocessing
First, the raw dataset is parsed, converted to .csv format, and stored into a pandas data frame using the pd.read_csv() function. We concatenate the answer columns, and to differentiate the human and ChatGPT answers, we assign type 1 to ChatGPT answers and type 0 to human responses. Then, we do the formal preprocessing:
1. We remove the quotes ('') and double quotes ("") at the beginning and end of each response.
2. We replace the new line characters (“\n”) with spaces.
3. We clean the text by removing all the non-alphanumeric characters.
4. We convert the text to lowercase letters.
5. We check and remove all the null values of the dataset.
After preprocessing the data, training and classifying the data will be easier and more efficient.
3.2. Transformation
In the transformation phase, we first count the features in the texts and do the data mining. We ignore tokens that appear less than five times in the dataset and count the number of times a pass appears in the response. In addition, we estimate the newline characters ("\n") among all the answers and use the values to form the "count" column of the dataset using the assign () function. We also keep track of the typing errors occurring in each response.
Next, we split the dataset into training and testing sets using the train_test_split() function from the sklearn_model_selection module. We utilize 25% of the data for testing and the remainder for training by setting the test_size parameter to 0.25.
3.3. Training
The models LightGBM, Logistic Regression, and Naive Bayes were chosen for comparison. The text data was converted into a matrix of token counts using the CountVectorizer class from the sklearn.feature_extraction.text module:
3.3.1. Logistic Regression. Logistic regression is a regression model based on the log-loss function. It can be used to fit binary classification tasks based on probability. This returns a model with weights in which we can predict the label of the sentence that we can compare with the initial consequences to find the linguistic patterns of ChatGPT-generated answers. Below is the function for the logistic regression model: [9]
\( Sig(X)=\frac{1}{1+{e^{-X}}} \)
• E is the log base
• X is the numerical value that needs to be transformed
3.3.2. LightGBM. LightGBM is a machine learning algorithm used for tasks like classification, regression, and ranking. It's a form of gradient boosting that uses decision trees to create a predictive model. A sample decision tree learning algorithm is shown below: [10]
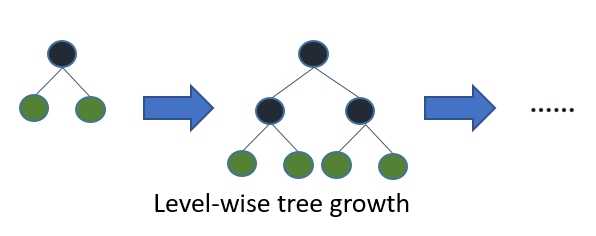
Figure 4. LightGBM Tree Algorithm
3.3.3. Naive Bayes. It is a classification technique based on Bayes' Theorem with an independence assumption among predictors. In simple terms, a Naive Bayes classifier assumes that the presence of a particular feature in a class is unrelated to the fact of any other part [11].
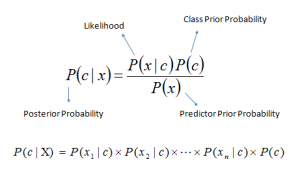
Figure 5. Naive Bayes Formula
• P(c|x) is the posterior probability of class (c, target) given predictor (x, attributes).
• P(c) is the prior probability of class.
• P(x|c) is the likelihood which is the probability of the predictor given class.
• P(x) is the prior probability of the predictor.
The CountVectorizer output served as the input for the logistic regression employed in the baseline model. A pipeline that contained the CountVectorizer and Logistic Regression model was made using the make_pipeline() function. A 5-fold cross-validation procedure was carried out on the training set using the cross_validate() function. Accuracy, f1 score, and precision were employed as scoring criteria. Each metric's average score was calculated and recorded.
The LGBM Classifier class from the lightgbm. sklearn module was used to train the LightGBM model using the same data. The training set also underwent 5-fold cross-validation using the identical scoring criteria as the baseline model using the cross_validate() function, and the scores are recorded.
A third model, Naive Bayes, was also trained. The model was developed using the MultinomialNB class from the sklearn.naive_bayes module. The RandomizedSearchCV() function was used to conduct randomized research to determine the ideal value for the hyperparameter alpha. Based on the outcomes of the randomized search, the best model was obtained using the best_estimator_attribute(). We use the same scoring criteria and record the corresponding scores.
The cross-validations were noted and examined. Each model's average scores for each metric were generated, and the results were contrasted to see which model performed better. The trained model's feature log_prob_ property was used to calculate the feature importances for the naive Bayes model. The findings were sorted and saved to a CSV file for further investigation.
3.4. Classification
The three models introduced above will each return a test accuracy and coefficient score of feature classification. Features with positive and higher coefficient scores mean this feature is more likely to appear in Chat-GPT-generated answers, and elements with negative and lower coefficients mean it is more likely to occur in human-generated solutions. The logistic regression model and naive Bayes only classified tokens, but the Light GBM model also classified phases.
4. Results
We draw our conclusion from the results, which implies the interior relationship between coefficients and linguistic patterns.
The coefficient scores generated by the Light GBM model indicate that ChatGPT is more likely to systematically use combinations of words in conversations than humans, who are more likely to use one single word in conversations. This can be determined by looking at the coefficient score generated by LightGBM, the features "important to" with a 0,89 coefficient, "sorry about" with a 0.81 coefficient, compared to features like "etc." with a -1.11 coefficient, "pretty" with a -0.86 coefficient, "thus" with a -0.65 coefficient. One of the reasons is that human is a singular example of the whole language corpus; they are more likely to come up with more prosperous and more varied word choices than ChatGPT, which pulls standard high-frequency terms from a large corpus, generating relatively repeated patterns. ChatGPT, on the other hand, tends to produce answers that are not content-specific. To further support our result, we also count line breaks in ChatGPT and human responses; ChatGPT answers are more systematic and generally used than human-generated solutions.
By analyzing the coefficient score generated by the logistic regression model, ChatGPT is more likely to use words like conjunctions. The tokens with the most outstanding value in coefficient were "so" with a 2.17 coefficient, "finally" with a 1.37 coefficient, and "overall" with a 1.32 coefficient. At the same time, humans are more willing to use words that do not contain terms with an absolute meaning. The tokens with the lowest value in coefficient were "probably" with a -1.41 coefficient and "maybe" with a -1.39 coefficient.
5. Discussion
By running the simulation and comparing the models in Fig. 6, we found that the Naive Bayes yielded the worst results. Though it has the lowest reasonable time, which makes it efficient, the test precision and f1 score are much lower than the other model. By contrast, the logistic regression model using the ngram3 transformation yields the most precise results, with the highest test precision and f1 score, while it is rather slow. This result is not surprising, just as our findings in Fig. 7 show that using line breaks in ChatGPT-generated responses is much more frequent than in human-generated responses. This illustrates a huge difference in how AI and humans differ in using natural language.
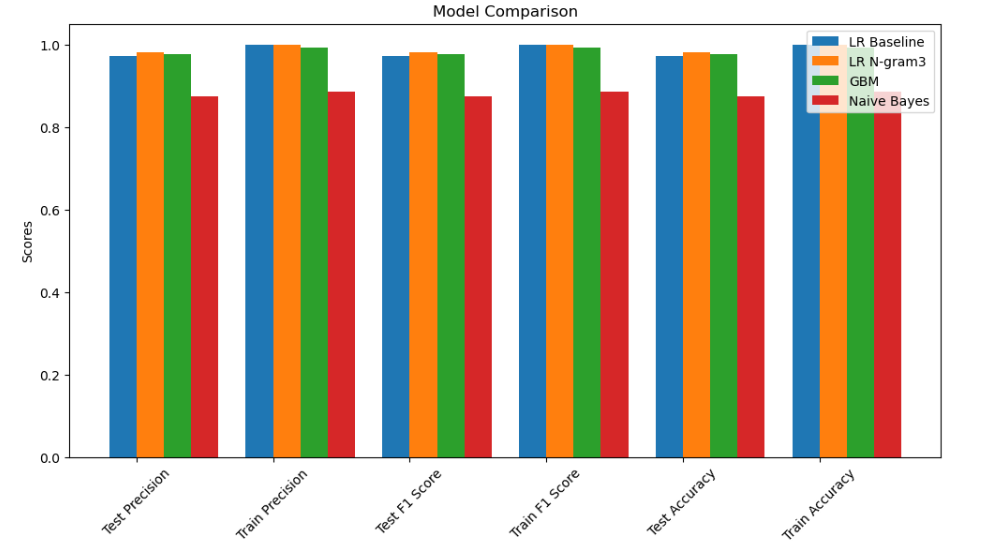
Figure 6. Diagrams of Model Performances
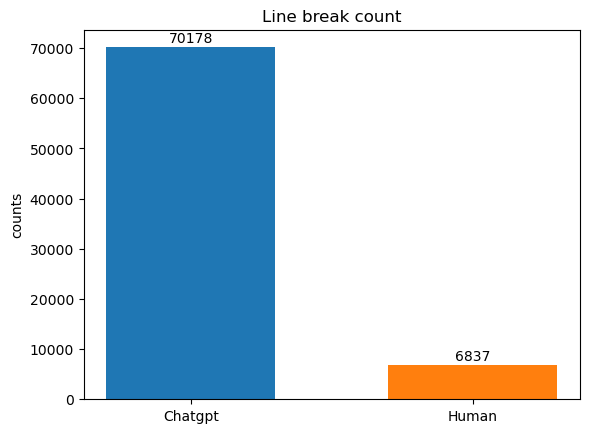
Figure 7. Line Break Count
The implementation of the research will be somewhat constrained given the variety and complexity of real-world events, even though our study on ChatGPT and human responses has a very definitive outcome. Language usage varies significantly amongst individuals, and the rate of iterative AI evolution is astounding. Because ChatGPT with GPT-3.5 was utilized to collect all of the data for the study, the results are not as universally applicable as they may be with GPT-4's technological advancements. The replies produced by GPT-4 will be smoother and the accuracy of AI for understanding and following user instructions will also improve as a result of the difference in the training model and the update of the knowledge base. But we also think there must be a connection between AI and language, and it is so significant that future investigations of it may demonstrate even greater potency.
6. Conclusion
We have proposed three alternative classification methods to distinguish linguistic patterns and coefficients. Using logistic regression, light GBM, and naive Bayes, we found that models have high accuracy in determining if the answer is AI-generated answers. We use the coefficient scores from different models to inform the interior relationship between coefficients and linguistic patterns. Results show certain linguistic practices and unique word choices for Chat-GPT-generated answers by analyzing the coefficient scores.
Acknowledgment
They contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
References
[1]. Chan, A. (2023) GPT-3 and InstructGPT: technological dystopian, utopianism, and "Contextual" perspectives in AI ethics and industry. AI and Ethics., 3(1): 53-64.
[2]. Saparov, A., He, H. (2022) Language models are greedy reasoners: A systematic formal analysis of chain-of-thought. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.01240.
[3]. Lund, B.D., Wang, T. (2023) Chatting about ChatGPT: how may AI and GPT impact academia and libraries? Library Hi Tech News., 40(3): 26-9.
[4]. Biswas, S.S. (2023) Potential use of chat gpt in global warming. Annals of Biomedical Engineering., 51(6): 1126-1127.
[5]. Biswas, S.S. (2023) Role of Chat GPT in Public Health. Annals of Biomedical Engineering., 51(5): 868-9.
[6]. Pardos, Z.A., Bhandari, S. (2023) Learning gain differences between ChatGPT and human tutor generated algebra hints. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.06871.
[7]. Alafnan, M.A., Dishari, S., Jovic, M., Lomidze, K. (2023) ChatGPT as an Educational Tool: Opportunities, Challenges, and Recommendations for Communication, Business Writing, and Composition Courses. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Technology., 3(2): 60-68.
[8]. Hulman, A., Dollerup, O.L., Mortensen, J.F., Fenech, M., Norman, K., Støvring, H., Hansen, T.K. (2023) ChatGPT- versus human-generated answers to frequently asked questions about diabetes: a Turing test-inspired survey among employees of a Danish diabetes center., medRxiv. 2023: 2023-02.
[9]. The Programming Foundation RSS. (n.d.) Module 4 - logistic regression: The Programming Foundation. https://learn.theprogrammingfoundation.org/getting_started/intro_data_science/module4/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwlumhBhClARIsABO6p-yoBFGaaW2dK6HMNlKxCMbP2_pu71NylAw2gmUMA_2g-qogZP1l_D0aAnCqEALw_wcB
[10]. LightGBM 3.3.2. (n.d.) LightGBM's documentation. https://lightgbm.readthedocs.io/en/v3.3.2/index.html
[11]. Ray, S. (2023) Naive Bayes Classifier Explained: Applications and Practice Problems of Naive Bayes Classifier. https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2017/09/naive-bayes-explained/
Cite this article
He,Z.;Mao,R.;Liu,Y. (2024). Predictive model on detecting ChatGPT responses against human responses. Applied and Computational Engineering,44,18-25.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Chan, A. (2023) GPT-3 and InstructGPT: technological dystopian, utopianism, and "Contextual" perspectives in AI ethics and industry. AI and Ethics., 3(1): 53-64.
[2]. Saparov, A., He, H. (2022) Language models are greedy reasoners: A systematic formal analysis of chain-of-thought. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.01240.
[3]. Lund, B.D., Wang, T. (2023) Chatting about ChatGPT: how may AI and GPT impact academia and libraries? Library Hi Tech News., 40(3): 26-9.
[4]. Biswas, S.S. (2023) Potential use of chat gpt in global warming. Annals of Biomedical Engineering., 51(6): 1126-1127.
[5]. Biswas, S.S. (2023) Role of Chat GPT in Public Health. Annals of Biomedical Engineering., 51(5): 868-9.
[6]. Pardos, Z.A., Bhandari, S. (2023) Learning gain differences between ChatGPT and human tutor generated algebra hints. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.06871.
[7]. Alafnan, M.A., Dishari, S., Jovic, M., Lomidze, K. (2023) ChatGPT as an Educational Tool: Opportunities, Challenges, and Recommendations for Communication, Business Writing, and Composition Courses. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Technology., 3(2): 60-68.
[8]. Hulman, A., Dollerup, O.L., Mortensen, J.F., Fenech, M., Norman, K., Støvring, H., Hansen, T.K. (2023) ChatGPT- versus human-generated answers to frequently asked questions about diabetes: a Turing test-inspired survey among employees of a Danish diabetes center., medRxiv. 2023: 2023-02.
[9]. The Programming Foundation RSS. (n.d.) Module 4 - logistic regression: The Programming Foundation. https://learn.theprogrammingfoundation.org/getting_started/intro_data_science/module4/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwlumhBhClARIsABO6p-yoBFGaaW2dK6HMNlKxCMbP2_pu71NylAw2gmUMA_2g-qogZP1l_D0aAnCqEALw_wcB
[10]. LightGBM 3.3.2. (n.d.) LightGBM's documentation. https://lightgbm.readthedocs.io/en/v3.3.2/index.html
[11]. Ray, S. (2023) Naive Bayes Classifier Explained: Applications and Practice Problems of Naive Bayes Classifier. https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2017/09/naive-bayes-explained/









