

About ACEThe proceedings series Applied and Computational Engineering (ACE) is an international peer-reviewed open access series that publishes conference proceedings from various methodological and disciplinary perspectives concerning engineering and technology. ACE is published irregularly. The series contributes to the development of computing sectors by providing an open platform for sharing and discussion. The series publishes articles that are research-oriented and welcomes theoretical and applicational studies. Proceedings that are suitable for publication in the ACE cover domains on various perspectives of computing and engineering. |
| Aims & scope of ACE are: ·Computing ·Machine Learning ·Electrical Engineering & Signal Processing ·Applied Physics & Mechanical Engineering ·Chemical & Environmental Engineering ·Materials Science and Engineering |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

United Kingdom

Malaysia

United Kingdom

United Kingdom
yilun.shang@northumbria.ac.uk
Latest articles View all articles
The fast growth of wireless communication means we need to send data reliably, even with noise and interference, which therefore makes channel coding indispensable. This paper looks at three landmark schemes that shaped modern wireless communications: Turbo codes, Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) codes, and Polar codes. Specifically, it explains the basic ideas of channel coding, and it discusses methods to approach the Shannon limit. After that, this paper describes the structure and decoding steps for each code. Turbo codes use parallel concatenation and iterative decoding. LDPC codes need sparse parity-check matrices and belief propagation. Also, Polar codes get reliability using channel polarization. Moreover, the codes are also compared based on their error performance, how complex they are to decode, the delay they introduce, and whether they are used in standards. The results reveal that Turbo codes work best for medium to long blocks but have problems with delay and error floors. LDPC codes perform well with long blocks and high throughput. Polar codes are useful for short blocks, even though they are harder to decode. This comparison shows that the codes complement each other and suggests that adaptive, AI-assisted coding could be a promising approach for 6G.

 View pdf
View pdf


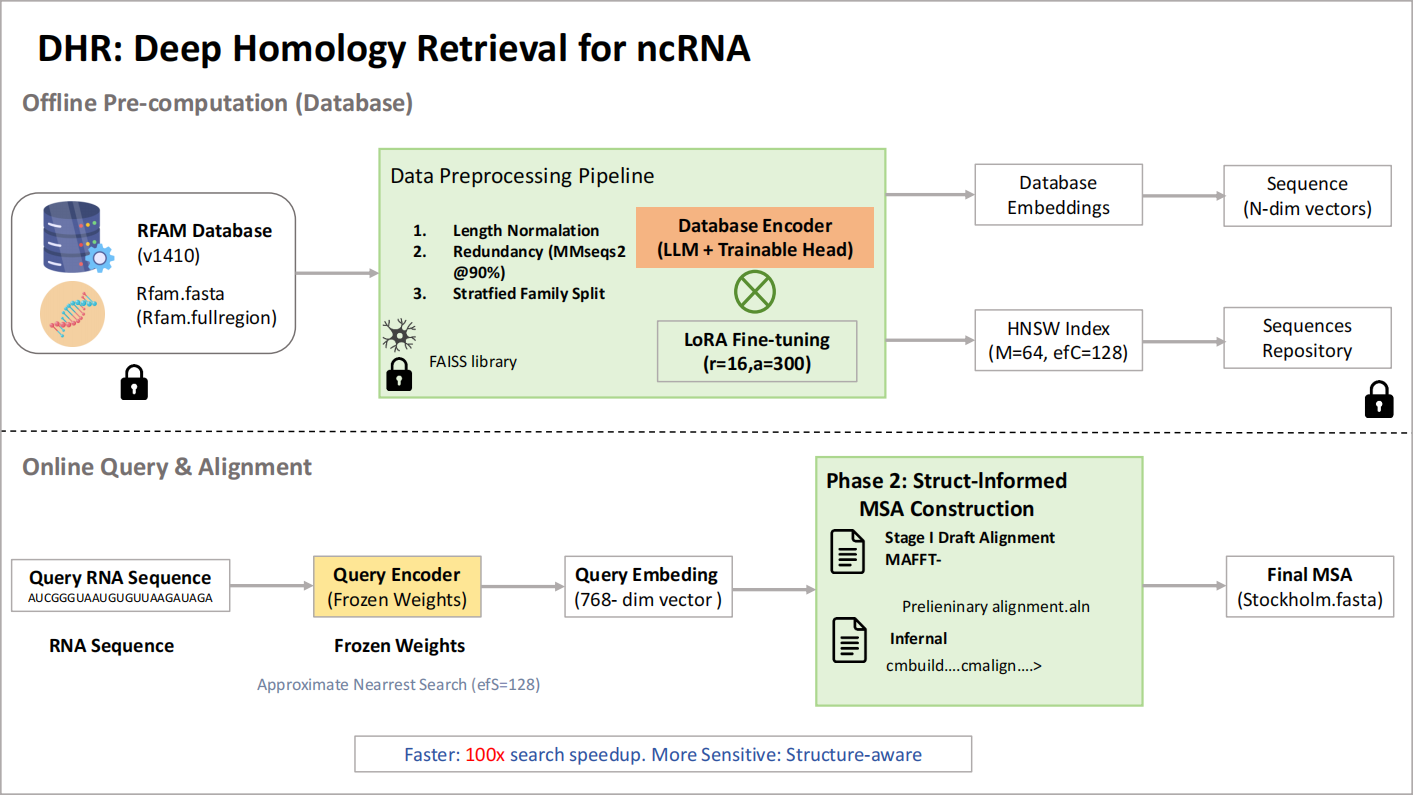
RNA’s growing therapeutic impact demands fast, structure-aware comparative analysis. Existing search tools trade speed for sensitivity: sequence-only methods are rapid but miss distant, structure-conserved homologs, whereas covariance-model pipelines are accurate but slow. We present a two-stage framework that reframes RNA homology detection as geometric retrieval in a learned embedding space, followed by structure-aware multiple sequence alignment (MSA). A frozen RNA foundation model (Rinalmo) embeds sequences; a lightweight Transformer head trained with supervised contrastive learning (family-balanced sampling, clan-aware hard negatives) sculpts the space so homologs cluster and non-homologs separate. Approximate nearest-neighbor search (FAISS/HNSW) enables sub-linear retrieval from millions of sequences. Top-khits are then aligned via a hybrid pipeline—MAFFT X-INS-i seeding and Infernal covariance-model refinement—to produce structure-consistent MSAs. On a family-level split of Rfam v14.10, Our method answers a query in 0.45 s on average (∼20×faster than BLASTn;>3,500×faster than cmscan) while achieving 0.95 precision, 0.93 recall, and 0.94 F1. Using retrieved sets, the MAFFT→Infernal workflow attains SPS = 0.91 versus 0.68 for BLASTn-based sets, enabling scalable, sensitive RNA homology discovery and downstream analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf


Large-scale language models (LLMs) have a huge scale, but they have encountered difficulties in improving social productivity, mainly due to their high cost and increasing demand for a large number of computing resources. Knowledge refining plays a key role in bridging the gap between model performance and operational efficiency, and also strengthens these two aspects. This technology refines the functions of GPT-3.5 and other models into miniature models that can be run locally at controllable cost. It can not only enable small and medium-sized enterprises and research institutions to use high-performance large-scale language models, but also ensure data security. Classical knowledge extraction framework uses label softening to achieve knowledge transfer between teacher and student models. According to the logical steps of teacher-student model alignment (similar to GPT-4), this paper mainly focuses on making the student model learn from the teacher model adaptively. This method enables the student model to get a compact model quickly, which not only absorbs the fine knowledge of the teacher model, but also reduces the consumption of computing resources and data. The existing CoT distillation methods ignore the variability of samples and the learning dynamics of student models. In this paper, an adaptive chain distillation method is proposed, so that small models can avoid the problem of reasoning sensitivity and focus on learning difficult samples. Although this will weaken its ability to analyze complex problems, we introduce an adaptive reasoning mechanism including soft prompt fine-tuning module and do experiments to verify it.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the widespread application of machine learning, particularly deep learning models, in the field of cybersecurity, the intelligence of spam filtering systems has been continuously enhanced. Deep learning classifiers, with their advantages such as character-level feature learning and semantic invariance, have become the preferred choice for deployment. However, these models rely on surface text features, making them vulnerable to adversarial attacks. As a result, they exhibit significant vulnerability when facing carefully constructed text adversarial attacks. Text adversarial attacks, through covert modifications such as synonym substitution and character perturbation, can mislead the model to misjudge malicious emails, leading to risky spam emails such as phishing and fraud passing through the defense system. This study first elaborates on three attack methods, namely character-level attack, word-level attack, and sentence-level attack. Secondly, it introduces the existing limitations of spam email attacks and then this study comprehensively reviews the key findings in the existing research results: deep learning models generally have a high attack success rate (ASR). The aim is to provide a theoretical basis for building a more robust next-generation spam email filtering system.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
Volume 211December 2025
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SPML 2026 Symposium: The 2nd Neural Computing and Applications Workshop 2025
Conference website: https://www.confspml.org/tianjin.html
Conference date: 21 December 2025
ISBN: 978-1-80590-579-0(Print)/978-1-80590-580-6(Online)
Editor: Marwan Omar, Guozheng Rao
Volume 210December 2025
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-MLA 2025 Symposium: Intelligent Systems and Automation: AI Models, IoT, and Robotic Algorithms
Conference website: https://www.confmla.org/london.html
Conference date: 12 November 2025
ISBN: 978-1-80590-567-7(Print)/978-1-80590-568-4(Online)
Editor: Hisham AbouGrad
Volume 209December 2025
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-MCEE 2026 Symposium: Advances in Sustainable Aviation and Aerospace Vehicle Automation
Conference website: https://2025.confmcee.org/kayseri.html
Conference date: 14 November 2025
ISBN: 978-1-80590-561-5(Print)/978-1-80590-562-2(Online)
Editor: Ömer Burak İSTANBULLU
Volume 208November 2025
Find articlesProceedings of the 5th International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering
Conference website: https://2025.confmcee.org/
Conference date: 12 January 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-547-9(Print)/978-1-80590-548-6(Online)
Editor: Ömer Burak İSTANBULLU
Announcements View all announcements
Applied and Computational Engineering
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Applied and Computational Engineering
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Applied and Computational Engineering (ACE) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:






