

Volume 177
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA 2025 Symposium: Applied Artificial Intelligence Research
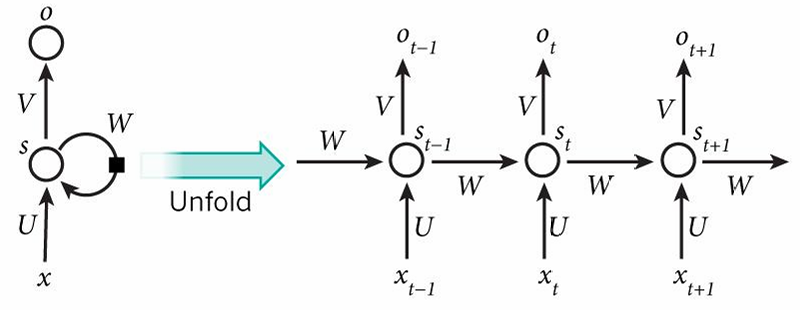
As urban traffic congestion continues to intensify, predicting short-term traffic flow has become essential to enabling real-time control in intelligent transportation systems (ITS). However, traditional models face significant limitations in capturing the spatiotemporal and nonlinear characteristics of traffic data. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, with their gated mechanisms, can effectively model long-term dependencies and periodic patterns in traffic flow. The accuracy of these predictions directly influences decision-making in scenarios such as traffic guidance and emergency management, offering substantial practical value for improving road network efficiency. This study constructs an optimized LSTM model to evaluate its effectiveness in short-term traffic prediction and to compare predictive performance across different time granularities. A dual-layer LSTM architecture is employed, incorporating the Adam optimizer, Dropout, and early stopping as regularization strategies. Using urban traffic monitoring data from the United States, both hourly and daily prediction models are developed for experimental validation. Results indicate that the hourly prediction model (MSE = 0.0709) markedly surpasses the daily model (MSE = 0.2987), effectively identifying recurring patterns like rush periods in the morning and evening. These outcomes offer a practical solution for adaptive traffic regulation.

 View pdf
View pdf


Semantic segmentation has undergone a remarkable transformation from traditional computer vision approaches to sophisticated deep learning architectures, culminating in the revolutionary capabilities introduced by foundation models. This comprehensive survey examines the technical progression of semantic segmentation methodologies, with particular emphasis on vision foundation models, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM) and Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP). This paper systematically analyzes how these large-scale pretrained models enable previously unattainable capabilities, including zero-shot learning and cross-domain generalization while identifying persistent challenges regarding computational efficiency and boundary precision. The investigation encompasses critical applications across medical imaging, remote sensing, and video understanding domains, revealing both transformative benefits and technical limitations. It concludes that foundation models represent a fundamental paradigm shift requiring hybrid approaches that effectively combine general capabilities with domain-specific optimizations.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the vigorous development of global trade, the shipping market has put forward higher requirements for the legal applicability and risk allocation mechanism of charter contracts, and the rent payment clause in time charter contracts directly affects the balance of rights and obligations between carriers and charterers. Time charter contract is a special legal phenomenon in the field of contract law,which as an important part of maritime law as well as adjusted by various countries’ contract laws,it involves numerous complex legal issues.The time charter contract contains massive contracts,this article focuses on the identity that carrier assumes under the rent payment clause in the shipping market and reduces the risk of cargo transportation by studying the contract and find out the problems’ solutions.The discussion on the optimization of the risk allocation mechanism of charter ship contracts not only helps to safeguard the rights and interests of all parties, but also provides theoretical support for improving international maritime shipping rules and promotes the standardized development of the shipping market.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid advancement and widespread adoption of large language models (LLMs), an increasing number of individuals have incorporated these models into their daily routines. To address persistent challenges in travel planning, this paper proposes an LLM-powered specialized travel planning system. By processing concise yet essential user inputs, the system can generate comprehensive travel plans tailored to individual requirements. This study designs user input templates and evaluates the response quality of the large language models Deepseek and Kimi. The responses are assessed and compared using predefined metrics to establish a preliminary system framework and identify limitations, such as insufficient information input, the computational complexity of evaluation metrics, and inefficient and deficient information output. This paper provides potential solutions that include API (application programming interface ) integration, enhanced user-system interaction, optimized prompt engineering, and implementation of advanced algorithms. This paper systematically reviews the system design, identifies prevailing challenges, and outlines future development trajectories. It validates the feasibility and potential of the Large Language Model Travel Planning System while establishing a comprehensive framework for LLM-based planning research, serving as a valuable reference for researchers in related fields.

 View pdf
View pdf


Inspired by biological olfaction, the electronic nose is a modern detection instrument that mimics the structure and function of the olfactory system. It has been successfully applied in various fields, including industry and food testing. Wine is a globally beloved alcoholic beverage, and the technology used for wine quality detection plays a crucial role in ensuring the healthy development of related industries. The use of electronic noses in wine detection offers potential advantages such as rapid analysis and portability. This paper provides a comprehensive review of research on wine aroma detection using electronic noses, explores deep learning methods for processing e-nose data, and discusses the application and future prospects of combining electronic noses with deep learning in the wine industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


The search and matching of candidates constitutes the core link of an enterprise's recruitment process. In human resource management, recruitment is a crucial step for enterprises to attract outstanding talent, directly affecting the company’s future development. This review aims to conduct a comprehensive review and synthesis of the application methodologies, challenges, and development prospects of machine learning in employee recruitment within the era of big data. Research has found that in the digital age, the transformation of the recruitment process in enterprises is an inevitable trend. Machine learning is capable of precisely extracting crucial information from a vast number of resumes. It can promptly adapt to the evolving requirements of enterprises, automatically align with market trends, and rapidly identify highly-matched candidates for enterprises, thereby significantly streamlining the candidate search process. During this process, enterprises should seize the opportunities presented by technological development and propose corresponding solutions to address the associated risks and challenges. Furthermore, this review summarizes and discusses the future development prospects in the domain of employee recruitment, providing practical references for enterprises and human resources departments.

 View pdf
View pdf


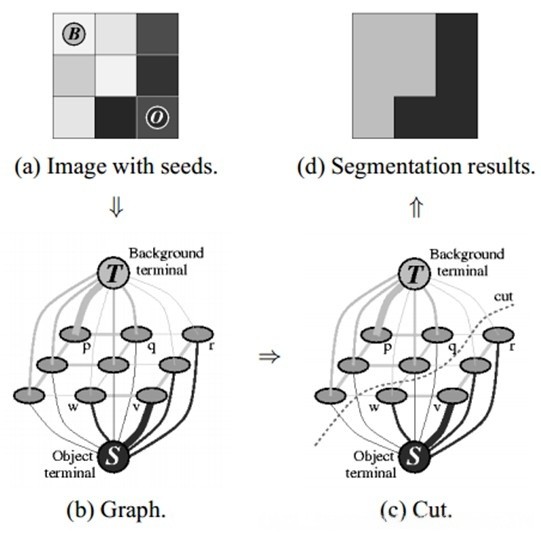
Generating images with dynamic expressions has become a key component of the social media industry. To enhance the realism, it is crucial to remove the potential distortion in the face image. Unfortunately, videos produced by PIrenderer often exhibit facial blur due to inadequate segmentation between foreground and background. In this paper, GrabCut and MODNet are used to post-process the videos generated by PIrenderer and then fuse them. Our proposed method can guarantee to reduce the influence of background on the face when generating dynamic expression videos. These post-processing steps optimize dynamic facial expression rendering, mitigate the face distortion problem, and ultimately produce more realistic video output.

 View pdf
View pdf


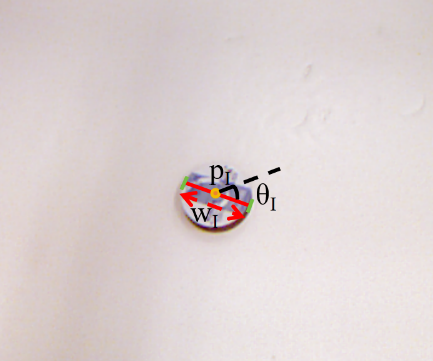
In recent years, advancements in robotics have significantly heightened interest in robotic arm grasping, a critical capability for intelligent robotic systems. Nevertheless, achieving autonomous and precise grasping remains a formidable challenge. Despite extensive research exploring diverse neural network architectures integrated with deep learning for robotic grasping, the achieved accuracy levels frequently fail to meet practical requirements. This study proposes a novel Unet-DGN-L2 neural network architecture, which employs the Unet framework as the primary mechanism for feature extraction while integrating a decoupled grasping network to generate pixel-wise grasping representations. To address the issue of overfitting, L2 regularization is incorporated, resulting in a robust model for predicting grasping poses. Evaluated on the Cornell dataset, the proposed Unet-DGN-L2 architecture achieves a grasping accuracy of 86%, demonstrating substantial improvements in autonomous and precise object grasping. This advancement enhances the applicability of intelligent robots in real-world scenarios, particularly in fields such as industrial automation, thereby contributing to the progression of robotic manipulation technologies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Electromyography (EMG) signals, as important bioelectric signals reflecting human muscle activity, have broad application prospects in fields such as human-computer interaction, prosthetic control, and motion recognition. However, electromyographic signals themselves are susceptible to noise interference such as motion artifacts and power interference, and traditional filtering methods are difficult to effectively distinguish signals from complex background noise. Meanwhile, traditional feature engineering relies on manual experience, which limits the model's generalization ability and real-time processing performance. In response to the above issues, this article proposes an end-to-end electromyographic signal processing method based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which is used to simultaneously achieve signal denoising and motion pattern recognition. Firstly, the original electromyographic signal is segmented using a sliding window method and standardized; Subsequently, the processed data is input into a CNN model consisting of multiple layers of convolution and pooling structures, which automatically extracts time-domain features and completes classification. During the model training phase, the introduction of cross entropy loss function and Adam optimization algorithm improves the convergence speed and classification accuracy of the model. We used an open-source surface Electromyographic (sEMG) dataset on the PhysioNet platform for validation and compared its performance with traditional support vector machine (SVM) methods. The experimental results show that the proposed method is significantly better than traditional methods in key indicators such as accuracy and F1 score, and has better robustness and real-time performance. This study demonstrates the potential of deep learning in electromyographic signal processing, providing technical support for future intelligent prosthetic control and high-precision human-machine interaction systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


Face recognition under occlusion has become a critical research focus due to its widespread applications in surveillance, authentication, and human-computer interaction, and the frequent presence of masks, glasses, or other obstructions in real-world settings. This review systematically examines the evolution of techniques designed to handle occluded facial inputs, covering both traditional approaches and deep learning-based methods. Traditional techniques such as subspace regression, local feature analysis, and robust estimation provide interpretable and efficient solutions but are often sensitive to large or unstructured occlusions. Recent advances in deep learning, including CNNs, GANs, and self-supervised architectures, have significantly improved occlusion robustness by enabling feature reconstruction, landmark detection, and semantic completion. A comparative analysis of 22 representative studies is presented, categorized by occlusion type, methodological framework, and performance on benchmark datasets. Based on current limitations, this paper outlines future directions, including lightweight model design, multimodal fusion, and standardized occlusion-aware evaluation metrics. This review aims to provide a comprehensive reference for researchers and practitioners seeking to develop more reliable and generalizable face recognition systems under real-world occlusion challenges.

 View pdf
View pdf




