1. Introduction
In the rapidly advancing digital age, recommendation systems have become increasingly critical [1]. These systems have emerged as powerful tools in addressing the challenges of information overload, enhancing user experiences, engagement levels, and overall satisfaction. Recommendation systems are instrumental in providing tailored solutions for clients and aiding businesses in improving customer retention and loyalty [2]. As these systems continue to evolve and incorporate smarter and real-time capabilities, it becomes crucial to assess their reliability and accuracy in depth. This research paper presents an in-depth examination of the intricate world of recommendation systems.
To this end, the paper combines three distinct Amazon datasets and applies three different recommendation models to provide comprehensive exploration [3]. The primary goal of this paper is to delve into the inner workings of recommendation models. It aims to evaluate their effectiveness and identify the key factors that drive their functionality. The research objective is to gain a clear understanding of the dynamics within these models while shedding light on potential factors that influence their accuracy and relevance.
Moving beyond surface-level analysis, this paper adopts a multidimensional approach to understanding recommendation systems. It meticulously examines the interactions between different models and datasets to evaluate their performance, adaptability, and applicability across a range of scenarios. This comprehensive examination goes beyond theoretical realms, enabling readers to navigate the complex landscape of recommendation systems with clarity and insight.
The paper also highlights the need for further research to improve the adaptability and effectiveness of recommendation systems. It underlines the significance of recommendation systems in various industries, including e-commerce, media streaming, and content recommendation on social media platforms. The research findings provide valuable insights into the design and development of more accurate and reliable recommendation systems that can effectively meet the needs of users and businesses.
In the following sections, this paper examines a variety of methods and analyses. It delves into the finer details of recommendation system behavior, exploring their intricate designs and interactions. By combining empirical observations with theoretical frameworks, this research contributes to the broader discussion on recommendation systems and how they can be optimized for real-world situations. The goal of this exploration is to provide researchers, practitioners, and stakeholders with the knowledge they need to effectively navigate the ever-evolving world of recommendation systems.
It is evident that recommendation systems have become essential in the digital age, impacting various aspects of user interactions and business strategies. From personalized product recommendations on e-commerce platforms to content suggestions on streaming services, these systems have transformed the way that people navigate the vast digital landscape. With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, recommendation systems are poised to become even more advanced, adapting to dynamic user preferences and providing personalized experiences across a wide range of industries.
The utilization of recommendation systems goes beyond the realms of e-commerce and entertainment and extends into areas such as healthcare, finance, and education, where personalized recommendations can significantly improve outcomes and decision-making processes. For example, healthcare providers can use recommendation systems to suggest appropriate treatment plans based on patient data, thereby enhancing the quality of care provided. Similarly, financial institutions can offer tailored investment options based on individual risk profiles, helping customers make better financial decisions.
Furthermore, recommendation systems have also gained relevance in social networks and online communities, facilitating personalized content discovery and improving user engagement [4]. By analyzing user behavior and preferences, these systems can recommend relevant connections, groups, and content, fostering a sense of community and enhancing user satisfaction and engagement with the platform.
In conclusion, recommendation systems have become indispensable tools in the digital world, enhancing user experiences and providing businesses with valuable insights into customer preferences. As these systems continue to advance and adapt to changing user needs and market conditions, it is essential to have a deep understanding of their inner workings to ensure their reliability, accuracy, and optimal performance. With their broad applications and significant potential to shape the future of digital interactions and personalized experiences, recommendation systems continue to play a crucial role in enhancing the overall user experience while driving businesses towards success.
2. Method
2.1. Dataset
The comprehensive exploration of data attributes, including structural intricacies, compositional elements, distributional characteristics, and inter-relationships, forms the foundation of this data analysis. The dataset under examination was compiled by Dr. Jianmo Ni at UCSD and includes 233.1 million reviews spanning from May 1996 to October 2018 [5]. This dataset encompasses various variables, such as reviewer ID, product ID, helpfulness votes, verification status, and intrinsic product aspects like size and color. The dataset also includes textual information, comprising comprehensive reviews and concise summaries. For the purposes of this paper, specific attributes including reviewer ID, product ID, review text, and associated ratings are of particular interest. By selectively aggregating these attributes, a novel dataset is created to facilitate subsequent analytical endeavors. Before proceeding with further analytical procedures, necessary data preprocessing steps are essential. The following Table 1 outlines the handling of missing values.
Table 1. Missing values in datasets.
Dataset Name | Feature Name | Missing Counts | Percentage |
Sports & Outdoors | review text | 2,454 | 0.049% |
Movies & TV | review text | 3,082 | 0.077% |
Video Games | review text | 1,715 | 0.034% |
It is evident that a minor proportion of the dataset exhibits missing values, only within the review text feature. These instances of missing data, which constitute a marginal fraction, are expeditiously resolved by expurgating affected instances from the dataset, ensuring the overall integrity of subsequent analyses.
2.2. Models
Three distinct recommendation methods were employed to evaluate the performance of the underlying dataset.
2.2.1. Dot Product.
Dot Product, a fundamental computational technique, plays a significant role in matrix factorization-based recommendation systems for estimating user-item interactions or rating scores [6]. Matrix factorization is employed in this model, which involves deriving embeddings [7]. By acquiring user and item embeddings, this framework can develop a predictive model that uses dot product operations to predict user-item interactions and provide recommendations. The implementation protocol follows the sequence below:
Firstly, two separate input layers are created, one for items and the other for users.
Then, an item embedding path is constructed to represent each individual item using distinctive vectors that capture important features reflecting the characteristics of the item. Similarly, a user embedding path is established to encapsulate user preferences and tendencies.
After these initial steps, the dot product operation is performed, resulting in the formalization of the predictive model. Higher dot product values indicate a greater probability of user affinity towards the associated item, while lower values indicate reduced user interest.
After completing the previous steps, the next stage is to compile the model. The chosen optimization algorithm is Adam, and the loss function used is Mean Squared Error (MSE). The model is then trained through iterations to optimize the embeddings, leading to improved predictive capability. The optimized embeddings are preserved for future use throughout this process.
In the end, the training process is visualized by plotting the training error, which represents the loss, during the iterative training. This visualization helps to understand the model’s learning progress and its ability to improve rating predictions. It provides valuable insights into how the model is refining its predictions over time.
2.2.2. Neural Network
Neural networks have gained significant attention in recent years for their ability to effectively capture complex patterns and enhance the performance of recommendation systems [8,9]. The current model utilizes deep learning techniques to build a customized neural network specifically designed for recommendation systems. By leveraging user and item IDs as inputs, the model aims to predict user-item interactions, encapsulating the essence of personalized recommendations. The following section provides a detailed description of the implementation specifics of the model:
1) Creation of Item Embedding Path: An input layer is established to accommodate input data in the form of item IDs. Subsequently, an embedding layer is incorporated to generate dense representations, or embeddings, of items based on their unique IDs.
2) User Embedding Path Creation: A parallel procedure is initiated for user embeddings, mirroring the item embedding path.
3) Feature Concatenation: The embeddings of both items and users are combined into a unified feature vector using the Concatenate layer.
4) Incorporation of Fully-Connected Layers: The neural network architecture includes two fully connected layers. The first layer comprises 128 neurons with the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function, providing non-linearity to the network. The second fully connected layer consists of 32 neurons, also employing the ReLU activation function. The final layer is a fully connected layer with a single neuron and no activation function, resulting in a single scalar output.
5) Model Creation and Compilation: The model is created and then compiled. The optimization algorithm used is Adaptive Moment Estimation (Adam), and the loss function chosen is Mean Squared Error (MSE).
6) Training and Embedding Optimization: The model undergoes a training process to refine the embeddings and achieve optimal representations. These optimized embeddings are then saved for future use and application.
7) Training Error Visualization: The training process is visualized by plotting the training error (loss) across iterations. This visualization helps to understand the learning dynamics of the model and assess its progress in rating prediction.
2.2.3. Neural Collaborative Filtering Model
This model combines Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF) with Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to enhance item recommendations [10]. By taking advantage of both user-item interactions and textual content similarity, this hybrid approach provides more accurate and personalized item suggestions. NCF is a specialized variant of collaborative filtering that uses neural networks to learn user and item embeddings, which represent users and items as compact, dense vectors in a lower-dimensional space. In addition, Natural Language Processing techniques are integrated into the model to analyze and preprocess textual data, such as reviews and product descriptions. This helps to extract relevant information from the text and incorporate it into the recommendation process. Here, a comprehensive insight into the implementation intricacies of the model is provided.
Firstly, a pipeline for text analysis is delivered:
1) The initial stage of the data processing pipeline for textual data involves text preprocessing, which typically includes several crucial steps such as tokenization, removal of stop words, and stemming. This crucial phase ultimately leads to the creation of a document-term matrix, which represents the textual content of the document.
2) The level of similarity between different textual units such as product reviews is determined by calculating the cosine similarity between them. This technique allows for the quantification of textual resemblance between different reviews, providing a numerical representation of their similarity.
3) The creation of a user-item matrix involves the combination of both rating information and review similarity measures. This fusion allows for the incorporation of both user interactions and textual features into one comprehensive representation of user-item relationships.
Secondly, a hybrid NCF model is constructed.
1) Input Layers: During both the training and prediction stages, the input data includes user and item IDs, which serve as essential components for the recommendation system.
2) Embedding Layers: To capture latent propensities, user and item IDs are transformed into dense embeddings. These embeddings effectively encapsulate hidden patterns and preferences related to users and items in a dense numerical representation. This allows the recommendation system to leverage these latent factors for accurate predictions and personalized recommendations.
3) Flattening: To transition from 2D embeddings to 1D vectors, the embeddings for user and item IDs are flattened into 1D arrays. This flattening process allows for more straightforward manipulation and concatenation of the embeddings.
4) Concatenation: By merging the acquired user and item representations, a unified feature vector is generated. This process involves combining the flattened user and item embeddings into a single vector that captures the combined information and relationships between users and items.
5) Dropout Regularization: During the training process, a portion of the inputs is stochastically nullified, leading to concerns about mitigating overfitting and improving generalization capabilities.
6) Hidden and Output Layers: The output of the dropout layer is connected to a fully connected hidden layer consisting of 64 neurons, using the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function for computation. After this, an output layer is employed to synthesize the final prediction score for the user-item interaction without an activation function.
7) Model Compilation: The Mean Squared Error (MSE) is designated as the loss function, guiding the model during training by quantifying the difference between predicted and actual values.
Thirdly, during the training process, the model undergoes a regimen to optimize its embeddings, refining them to produce optimal representations. These refined embed-dings are then stored for future use.
3. Result
Analysis of the training errors for these three models are shown in Figure 1. It is observed that the Dot Product Model initially exhibits a higher error, surpassing 20. In contrast, both the Neural Network Model and the NCF with NLP Model demonstrate similar initial errors.
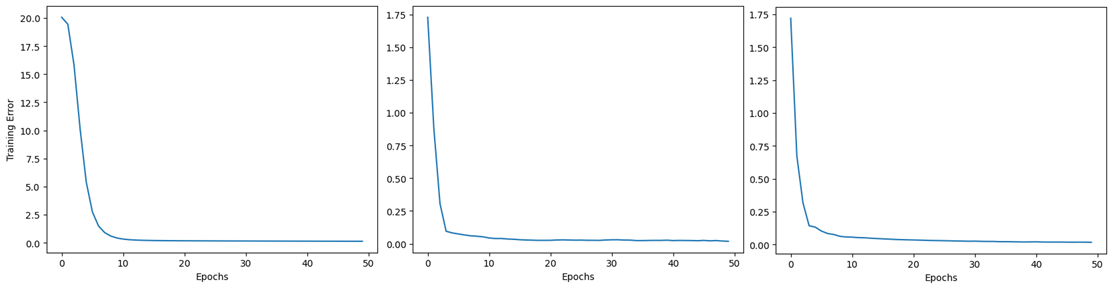
Figure 1. Loss of three models (Figure Credits: Original).
An analysis of Mean Squared Error (MSE) across all models, as shown in Figure 2 provides additional insights. Particularly, the NCF with NLP Method Model achieves the lowest MSE, followed by the other two Deep Learning-based Models.
In a hypothetical scenario where the SVD model is considered as the reference base model, conducting paired t-tests and calculating effect sizes with respect to the base model results in the following tabular representation as shown in Table 2. It is important to note that within the “Effect Size” column, negative values indicate better performance in relation to the base model in this context. Therefore, Deep Learning Based Models emerge as outperforming the SVD Model. Following this, correlations are established based on the predictive outcomes of each model on the test dataset.
Table 2. Result of T-test and effect size.
model | t-statistic | p-value | effect size |
Dot Product | -5.973 | 0.0000 | -2.977 |
NN | -6.771 | 0.0000 | -2.683 |
NCF-NLP | -11.980 | 0.0000 | -3.692 |
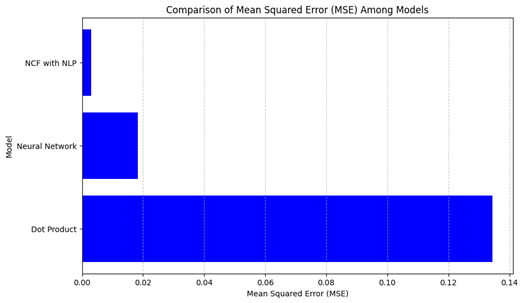
Figure 2. Mean square error comparison (Figure Credits: Original).
4. Discussion
The evaluation of the models has provided valuable insights into their predictive abilities and performance characteristics. The comprehensive analysis, including MSE values, statistical tests, cluster analysis, and exploration of the correlation matrix, has given us a detailed understanding of the strengths and limitations of each model. The low MSE values observed in the Dot Product model, Neural Network model, and NCF model with NLP indicate their effectiveness in uncovering hidden patterns in the dataset and providing accurate recommendations. These empirical results align with the initial expectations.
Furthermore, the statistical analyses strongly support the superior performance of specific models compared to the baseline model. The negative t-statistics and small p-values for the Dot Product model, Neural Network model, and NCF model with NLP demonstrate their significant outperformance. The effect sizes further emphasize the practical significance of these differences, with values exceeding 0.8 indicating substantial significance.
The success of deep learning-based algorithms, exemplified by the Dot Product model, Neural Network model, and NCF model with NLP, can be attributed to their ability to extract intricate features and learn nuanced representations from complex datasets. The layered architecture and parameter optimization of neural networks enable them to capture nonlinear relationships, leading to a better understanding of user preferences and item correlations. The incorporation of NLP techniques in the NCF model enhances its ability to comprehend textual context, resulting in more precise and contextually-tailored recommendations.
The practical relevance of these models is evident in popular platforms such as Netflix, Amazon, and TikTok. Future research is likely to focus on reinforcement learning-based methodologies that manipulate exploration-exploitation trade-offs, incorporate NLP methodologies, and enhance recommendation systems with precision-guided approaches.
5. Conclusion
In this analysis and evaluation of recommender models, an investigation into the complexity and effectiveness of three distinct recommendation models are conducted utilizing three different Amazon datasets. By examining the evaluation results, valuable insights are achieved into their predictive abilities, performance characteristics, and factors that may impact their accuracy and relevance. The Dot Product model, Neural Network model, and NCF model with NLP approach exhibited exceptional accuracy in capturing underlying patterns and generating precise recommendations. Additionally, the practical applications of these models are conducted, emphasizing the challenges posed by data sparsity and the cold start problem. Data sparsity means the scarcity of interaction data for specific users or items, while the cold start problem refers to recommending items to new users or newly added items within the inventory. Addressing these challenges requires further research and enhancements in acquiring valuable information and integrating real-time data.
References
[1]. Ko, H., Lee, S., Park, Y., & Choi, A. (2022). A survey of recommendation systems: recommendation models, techniques, and application fields. Electronics, 11(1), 141.
[2]. Isinkaye, F. O., Folajimi, Y. O., & Ojokoh, B. A. (2015). Recommendation systems: Principles, methods and evaluation. Egyptian informatics journal, 16(3), 261-273.
[3]. Jin, W., Mao, H., Li, Z., Jiang, H., Luo, C., Wen, H., et al. (2023). Amazon-M2: A Multilingual Multi-locale Shopping Session Dataset for Recommendation and Text Generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09688.
[4]. Wei, Y., Ma, H., Zhang, R., Li, Z., & Chang, L. (2021). Exploring implicit relationships in social network for recommendation systems. In Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 386-397.
[5]. Recommender System Using Amazon Reviews, URL: https://www.kaggle.com/code/saurav9786/recommender-system-using-amazon-reviews. Last Accessed: 2023/09/10
[6]. Koren, Y., Bell, R., & Volinsky, C. (2009). Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer, 42(8), 30-37.
[7]. Xue, H. J., Dai, X., Zhang, J., Huang, S., & Chen, J. (2017). Deep matrix factorization models for recommender systems. In IJCAI, 17, 3203-3209.
[8]. Wu, S., Sun, F., Zhang, W., Xie, X., & Cui, B. (2022). Graph neural networks in recommender systems: a survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(5), 1-37.
[9]. Paradarami, T. K., Bastian, N. D., & Wightman, J. L. (2017). A hybrid recommender system using artificial neural networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 83, 300-313.
[10]. He, X., Liao, L., Zhang, H., Nie, L., Hu, X., & Chua, T. S. (2017). Neural collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 26th international conference on world wide web, 173-182.
Cite this article
Meng,Y. (2024). Performance analysis of three recommendation algorithms on Amazon datasets. Applied and Computational Engineering,51,26-32.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Ko, H., Lee, S., Park, Y., & Choi, A. (2022). A survey of recommendation systems: recommendation models, techniques, and application fields. Electronics, 11(1), 141.
[2]. Isinkaye, F. O., Folajimi, Y. O., & Ojokoh, B. A. (2015). Recommendation systems: Principles, methods and evaluation. Egyptian informatics journal, 16(3), 261-273.
[3]. Jin, W., Mao, H., Li, Z., Jiang, H., Luo, C., Wen, H., et al. (2023). Amazon-M2: A Multilingual Multi-locale Shopping Session Dataset for Recommendation and Text Generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09688.
[4]. Wei, Y., Ma, H., Zhang, R., Li, Z., & Chang, L. (2021). Exploring implicit relationships in social network for recommendation systems. In Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 386-397.
[5]. Recommender System Using Amazon Reviews, URL: https://www.kaggle.com/code/saurav9786/recommender-system-using-amazon-reviews. Last Accessed: 2023/09/10
[6]. Koren, Y., Bell, R., & Volinsky, C. (2009). Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer, 42(8), 30-37.
[7]. Xue, H. J., Dai, X., Zhang, J., Huang, S., & Chen, J. (2017). Deep matrix factorization models for recommender systems. In IJCAI, 17, 3203-3209.
[8]. Wu, S., Sun, F., Zhang, W., Xie, X., & Cui, B. (2022). Graph neural networks in recommender systems: a survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(5), 1-37.
[9]. Paradarami, T. K., Bastian, N. D., & Wightman, J. L. (2017). A hybrid recommender system using artificial neural networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 83, 300-313.
[10]. He, X., Liao, L., Zhang, H., Nie, L., Hu, X., & Chua, T. S. (2017). Neural collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 26th international conference on world wide web, 173-182.









