1. Introduction
In industries like banking, characterized by high levels of digitization, the relentless growth and innovation in business operations have led to the expansion and sophistication of IT systems. Within this landscape, IT operations (ITOps) have emerged as a vital component of IT service delivery, tasked with navigating increasingly complex business requirements and diverse user demands. As the scale of data center infrastructure continues to swell, encompassing servers, storage, databases, and network resources, the need for efficient resource management becomes more pronounced. Moreover, stringent regulatory mandates, combining on-site inspections with remote audits, place greater emphasis on standardization, compliance, and governance in ITOps practices.
The escalating demands of [1]IT applications necessitate a more nuanced approach to ensure that IT services remain flexible, secure, and resilient.As a result, automated operations (autoOps) have garnered significant attention as a cornerstone of modern IT service assurance.This article aims to explore the intersection of automated operations and enterprise cloud resource management, specifically focusing on optimization and governance strategies. By examining real-world deployments and theoretical frameworks, we seek to provide insights for experts and practitioners engaged in the development and implementation of autoOps platforms within cloud environments. Through an analysis of industry best practices and emerging trends, this research endeavors to elucidate effective approaches for enterprise cloud resource optimization and management, enhancing efficiency, security, and resilience in IT operations.
2. Related work
2.1. Traditional operation and maintenance mode
Generally speaking, enterprise IT can be divided into three stages, the first stage is the mainframe era, characterized by the recording and processing of core financial data, IT system problems do not affect the operation of the business. The second stage is the information age, characterized by the recording and processing of core production data, and the failure of IT systems will cause some businesses to stop running. The third stage is the digital era, which is characterized by the recording and processing of comprehensive data of enterprises, the growth of data volume by tens of times, and the management of production and operation of enterprises by digital means, and the problem of IT system will seriously affect the normal operation of enterprises. The traditional operation and maintenance mode is mainly the maintenance management in the first and second phases, and the new operation and maintenance mode must be used in the third phase. The traditional O&M mode mainly maintains applications based on chimney architecture, while the new O&M mode maintains applications based on microservices distributed architecture. [2]The concept of microservice distribution has been put forward for 20 or 30 years, and the theory and practice are very mature. In recent years, driven by the digital economy, it has flourished and become the mainstream mode of running applications in production environments.
The original purpose is to improve the efficiency of operation and maintenance with the help of automated tools. [3]Unexpectedly, it hindered the improvement of operation and maintenance efficiency.In the past two years, many enterprises have chosen to re-implement the operation and maintenance mode more in line with modern automatic intelligence methods, and to achieve the upgrade from ordinary operation and maintenance to CloudOps Technology and maintenance, we must first do the following basic skills, otherwise automated operation and maintenance will only be a flash in the pan and cannot continue to support operation and maintenance work.
2.2. CloudOps Technology
CloudOps is actually automated operation and maintenance on the cloud,CloudOps = Cloud x DevOps, emphasizing it is to make full use of the characteristics of the cloud itself to better practice [6]DevOps, accelerate the rapid and stable delivery of business value, its core point is to emphasize the characteristics of the cloud itself, without the need for our repeated development. The characteristics of the cloud itself include the high elasticity, high standardization, high automation and self-service mode of the cloud, which means that users can access it according to their own needs, without relying on any other capability support.
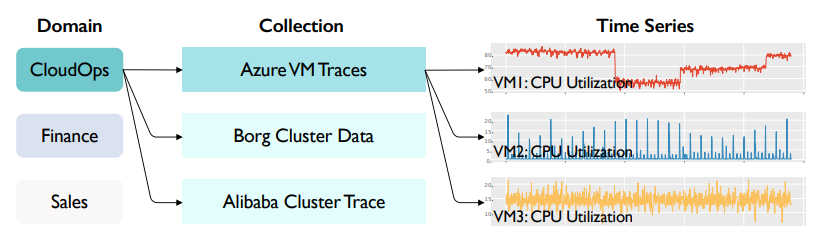
Figure 1. CloudOps implementation process architecture diagram
CloudOps defines the five dimensions that enterprises focus on in the process of cloud and cloud management, and it echoes the five common pain points of cloud customers we mentioned earlier. They are Cost, Automation, Reliability, Elasticity and Security, abbreviated as CARES[4]. For example, the cost optimization tool solves the cost problem, the automation capability solves the problem of automated operation and maintenance efficiency, the reliability capability can be used to improve the stability of the business and shorten the time of service loss, the elasticity capability solves the problem of application availability, and the security compliance capability improves the security of the business. [5]Therefore, CloudOps is not only an operation and maintenance concept, but also represents the general term for Cloud Vendors to provide you with a set of standardized tools around the operation and maintenance experience.
2.3. Enterprise cloud resource management
Corporate strategy is the anchor of all corporate activities. Strategic goals are long-term goals, while business goals are short-term tasks. This requires that enterprise resources must match the goals of the organization, not only to ensure the long-term strategy of resource supply compliance and rationality, but also to provide enough flexibility to ensure the short-term goals. Under the premise of clear and clear consensus, the responsibilities and authority of the organization should be clarified, and the capacity budget indicators of the business system should be implemented. Therefore, organizational resource management must be able to construct multi-level organizations based on roles or users, and can allocate resource quotas and expense quotas for each organization. At the same time, when the organization or resources change due to business reasons, it must be able to flexibly adjust the organizational structure and resource allocation.
Therefore, the core of the enterprise cloud is to use cloud resources, and the resources on the cloud have "out-of-the-box" and "elastic payment" ways. How to manage resources is to consider how to use resources conveniently, and how to use resources safely. [6]Once the resources are abused, or there may be a series of serious consequences such as out-of-control situations and data loss. In the scope of IT management and governance, resources are in a very core position, and resources are closely related to identity, authority, financial costs, audit compliance, etc.This sets the stage for exploring CloudOps technology and maintenance, which leverages automated operations on the cloud to optimize resource management and enhance operational efficiency in the enterprise cloud environment.
3. CloudOps Enterprise cloud resource optimization practices
In the field of enterprise cloud resources, the phenomenon of inefficient and costly manual configuration is very common. A large number of irregular processes compete for resources with scheduled tasks and forget to be shut down after they are used. Although this phenomenon is reasonable, the long running of virtual machine instances also brings a lot of unnecessary cost and waste. But the challenges go far beyond that. [7]Despite the flexibility of cloud computing, we still need to balance resources to ensure that critical business processes are prioritized, while less important processes such as database imports or file transfers are prioritized. If not, critical workflows will experience delays and even failures due to this mismatch or over-fragmentation of cloud and virtual resources.
3.1. Efficient Resource Management
In the cloud native technology system, containerization has become the first choice for developers to deploy applications, and [8]Kubernetes is the preferred container orchestration and scheduling system. While containerization and Kubernetes have greatly simplified application deployment, service governance still requires deep developer involvement. The core concept of a service grid is to route requests between microservices in the infrastructure layer using proxies that run in parallel with each service, form a network-format network, and interact with microservices.
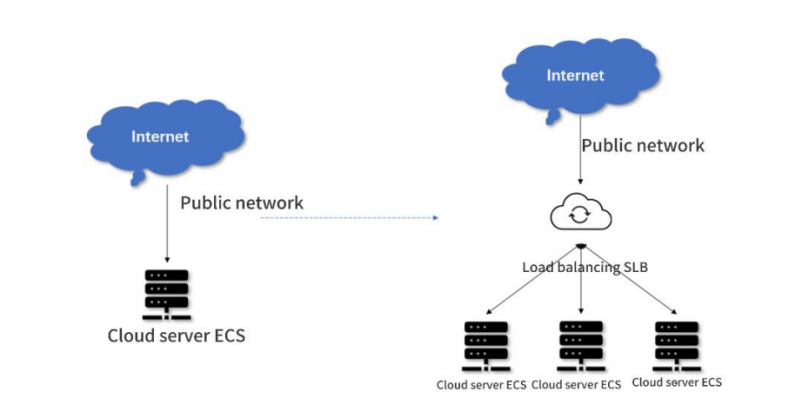
Figure 2. Cloud resource management server
Service Mesh, as an infrastructure layer dealing with communication between services, helps developers get rid of the dilemma of service communication problems, and gives the heavy work of communication control logic to the grid, so some people call it the second generation of microservices. Load balancing distributes access traffic to multiple back-end servers based on forwarding policies to achieve high concurrency and improve processing performance. In the process of enterprise O&M automation, load balancing becomes a necessary part to take into account the increasing number of services, users, and services. [9]Massive traffic is distributed to multiple servers in the background for processing to cope with high concurrency challenges.
In the operation and maintenance management of enterprise equipment, the effective management of manpower, spare parts, technology and data resources is the key to reduce the operation and maintenance cost and improve the comprehensive operation efficiency. Human, spare parts, technical and data resources play an important role in the effective management of automated cloud assets, and through reasonable planning and management of these resources, the efficient, intelligent and sustainable development of equipment operation and maintenance can be achieved.
3.2. Prioritization of Critical Workflows
In a cloud-native ecosystem characterized by high concurrency and distributed architectures, prioritizing critical workflows is essential to maintain business continuity and performance. Without proper resource allocation and workload management, essential processes may experience delays or failures due to resource contention or over-fragmentation.
A large part of daily operation and maintenance work involves configuration management and state maintenance of services. At present, configuration management based on state (system state, code state, configuration state and process state) has been greatly developed, and has made great progress in operation and maintenance. The emergence of new tools is endless and dazzling, and in practical applications, whether these tools are replaced or combined, the understanding of each specific scene and selection will be different, and eventually may be displayed in a completely different form.Many large It companies use puppet to manage and deploy software in clusters. The advantages and disadvantages are that the Web UI generates processing reports, resource lists, real-time node management, and the push command can trigger changes immediately. The disadvantages are that the installation process is more complex than other tools, and requires learning Puppet's DSL or Ruby. The installation process lacks error verification and generates error reports.
Each O&M[10] tool is only used to help personnel with O&M. Each tool has its own advantages. Puppet is applicable to automatic software configuration and deployment. SaltStack is designed for infrastructure management and can be up and running in minutes, easily managing thousands of servers, and fast enough. Ansible is used for batch operating system configuration, batch program deployment, and batch command running.
3.3. Automated monitoring and tuning
The basic principle of enterprise IT application O&M monitoring architecture is to comprehensively monitor and manage enterprise IT systems by collecting, storing, analyzing, and displaying various monitoring data. Monitoring data includes system, network, and application indicator data, event data, and log data, which can be collected by various data collectors.
The collected data can be stored in storage systems such as distributed databases, [11]NoSQL databases, or data warehouses, and transformed into visual monitoring indicators through data analysis and processing, and displayed through dashboards, charts, and reports. At the same time, IT can also monitor and alarm the monitoring data in real time through the alarm system, and automate the management and optimization of the IT system through automated operation and maintenance. Generally speaking, there must be monitoring where there is an IT system, and the distribution of IT systems in different enterprises is not the same. Some enterprises have a large number of edge systems, such as: computer, industrial computer and so on; Some enterprises have their own IDC room, and their own IT system is built in the IDC room; Some enterprises build their IT systems on the public cloud; Some enterprises establish a hybrid cloud architecture, IDC room and public cloud both.
IT monitoring system is attached to the above, for the edge system, there is a similar IOT monitoring system; The IDC room has a monitoring system for network equipment (this is generally provided by the network provider); The system on the public cloud provides a complete monitoring system by the cloud provider, such as: cloudwatch on [12]AWS; If there is a hybrid cloud architecture, it is necessary for the monitoring system construction team to integrate the monitoring system on the cloud to provide unified monitoring.
Application layer monitoring
Application layer monitoring refers to the process of real-time monitoring and management of application performance, availability, and security. Usually include:
A. Application performance monitoring: Monitoring application performance indicators, including request response time, throughput, error rate saturation rate and other golden four indicators, in order to find application performance problems and bottlenecks in a timely manner.
B. Availability monitoring: Monitors the availability of applications, including the running status, access times, and error rate of applications, to ensure the normal running and availability of applications.
C. Security monitoring: Monitoring the security of applications, including application firewalls, intrusion detection, security events, etc., to protect applications from security threats. Generally, this is the responsibility of the security team, and operation and maintenance personnel are rarely involved.
D. Log management: Collect, analyze, and visualize application log information to help users quickly discover and resolve application problems and anomalies.
3.4. Operation and maintenance data analysis and automated decision-making
The biggest difference between O&M automation and monitoring automation is whether there is a subsequent action. After we have collected all the operation and maintenance data and processed it according to the established logic, the next step is the extraction of value information and the implementation of effective actions. If we want to check whether the storage device is properly loaded, do we need to adjust the resource configuration? In traditional mode, engineers need to collect various performance logs on storage (port performance, storage controller CPU and cache, storage volume I/O performance, throughput, and so on), and collect the average and peak data within a certain period. Then, after the comprehensive judgment, the decision needs to adjust resources or does not need to adjust. If it is automated operations, we need to design the logic and experience of how engineers analyze and judge into the script. Logic can be distilled into algorithms, and experience can be distilled into probabilistic algorithms of historical data.
Most financial enterprises are faced with special holidays or periods of time for shopping and swipe-card consumption. If the situation is predictable, many relevant engineers will be on duty in advance, application engineers will observe the situation of application processing business in real time, and IT engineers will observe the usage of various resources such as computing, network and storage. IT engineers install and configure server resources prepared in advance and throw them into the resource pool. This is a common emergency solution. If it is automated operation and maintenance, we need to standard solidify the logic for engineers to judge the information monitored by applications, systems, networks, and other aspects in real time, and script a series of operations for preparing resources, initializing resources, allocating resources, and providing external services.
In summary, operation and maintenance automation is an important goal pursued by enterprise IT operations. The prerequisite for the realization of O&M automation is standardization, and the key to ensure the quality of O&M automation is the utilization of O&M data. The idea of landing O&M automation project lies in the design idea from the bottom up.
4. Conclusion
Enterprise cloud resource management plays a pivotal role in aligning organizational goals with resource utilization, ensuring both long-term strategic alignment and short-term operational flexibility. As businesses navigate the complexities of digitization, effective resource management becomes paramount, necessitating clear organizational structures, role-based access controls, and flexible resource allocation mechanisms. [20]The evolution of O&M practices from traditional to modern automated methods reflects the changing demands of the digital era. While initial enthusiasm for automated O&M projects yielded valuable insights, challenges such as tool fragmentation and scalability issues necessitated a shift towards more intelligent and efficient approaches. CloudOps technology emerges as a key enabler, leveraging automated operations on the cloud to optimize resource management and enhance operational efficiency in the enterprise cloud environment.
Furthermore, effective O&M management relies on leveraging human, spare parts, technical, and data resources to achieve efficient, intelligent, and sustainable development. By establishing standardized processes, utilizing advanced technologies, and harnessing data-driven insights, enterprises can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of O&M operations, paving the way for continued innovation and growth in the digital landscape.
In conclusion, the pursuit of O&M automation is integral to realizing the full potential of enterprise IT operations. By embracing standardized approaches, leveraging advanced technologies, and harnessing the power of data, organizations can navigate the complexities of modern cloud environments while driving efficiency, resilience, and competitiveness in their operations.
References
[1]. Mann, Zoltán Ádám. "Resource optimization across the cloud stack." IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems29.1 (2017): 169-182.
[2]. Mireslami, S., Rakai, L., Far, B. H., & Wang, M. (2017). Simultaneous cost and QoS optimization for cloud resource allocation. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 14(3), 676-689.
[3]. Sun, Y., White, J., Eade, S., & Schmidt, D. C. (2016). ROAR: A QoS-oriented modeling framework for automated cloud resource allocation and optimization. Journal of Systems and Software, 116, 146-161.
[4]. Muhammad, Tayyab, et al. "Elevating Business Operations: The Transformative Power of Cloud Computing." International Journal of Computer Science and Technology 2.1 (2018): 1-21.
[5]. Rimal, Bhaskar Prasad, et al. "Architectural requirements for cloud computing systems: an enterprise cloud approach." Journal of Grid Computing 9 (2011): 3-26.
[6]. Singh, Sukhpal, and Inderveer Chana. "Cloud resource provisioning: survey, status and future research directions." Knowledge and Information Systems 49 (2016): 1005-1069.
[7]. Christiaanse, W. R., and A. H. Palmer. "A technique for the automated scheduling of the maintenance of generating facilities." IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems 1 (1972): 137-144.
[8]. Devriendt, C., Magalhães, F., Weijtjens, W., De Sitter, G., Cunha, Á., & Guillaume, P. (2014). Structural health monitoring of offshore wind turbines using automated operational modal analysis. Structural Health Monitoring, 13(6), 644-659.
[9]. Bajrić, A., Høgsberg, J., & Rüdinger, F. (2018). Evaluation of damping estimates by automated operational modal analysis for offshore wind turbine tower vibrations. Renewable Energy, 116, 153-163.
[10]. Cord‐Ruwisch, R., Mercz, T. I., Hoh, C. Y., & Strong, G. E. (1997). Dissolved hydrogen concentration as an on‐line control parameter for the automated operation and optimization of anaerobic digesters. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 56(6), 626-634.
[11]. Fenton, R. E., & Mayhan, R. J. (1991). Automated highway studies at the Ohio State University-an overview. IEEE transactions on Vehicular Technology, 40(1), 100-113.
[12]. Rad, S. R., Farah, H., Taale, H., van Arem, B., & Hoogendoorn, S. P. (2020). Design and operation of dedicated lanes for connected and automated vehicles on motorways: A conceptual framework and research agenda. Transportation research part C: emerging technologies, 117, 102664.
Cite this article
Wu,B.;Gong,Y.;Zheng,H.;Zhang,Y.;Huang,J.;Xu,J. (2024). Enterprise cloud resource optimization and management based on cloud operations. Applied and Computational Engineering,76,8-14.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Mann, Zoltán Ádám. "Resource optimization across the cloud stack." IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems29.1 (2017): 169-182.
[2]. Mireslami, S., Rakai, L., Far, B. H., & Wang, M. (2017). Simultaneous cost and QoS optimization for cloud resource allocation. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 14(3), 676-689.
[3]. Sun, Y., White, J., Eade, S., & Schmidt, D. C. (2016). ROAR: A QoS-oriented modeling framework for automated cloud resource allocation and optimization. Journal of Systems and Software, 116, 146-161.
[4]. Muhammad, Tayyab, et al. "Elevating Business Operations: The Transformative Power of Cloud Computing." International Journal of Computer Science and Technology 2.1 (2018): 1-21.
[5]. Rimal, Bhaskar Prasad, et al. "Architectural requirements for cloud computing systems: an enterprise cloud approach." Journal of Grid Computing 9 (2011): 3-26.
[6]. Singh, Sukhpal, and Inderveer Chana. "Cloud resource provisioning: survey, status and future research directions." Knowledge and Information Systems 49 (2016): 1005-1069.
[7]. Christiaanse, W. R., and A. H. Palmer. "A technique for the automated scheduling of the maintenance of generating facilities." IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems 1 (1972): 137-144.
[8]. Devriendt, C., Magalhães, F., Weijtjens, W., De Sitter, G., Cunha, Á., & Guillaume, P. (2014). Structural health monitoring of offshore wind turbines using automated operational modal analysis. Structural Health Monitoring, 13(6), 644-659.
[9]. Bajrić, A., Høgsberg, J., & Rüdinger, F. (2018). Evaluation of damping estimates by automated operational modal analysis for offshore wind turbine tower vibrations. Renewable Energy, 116, 153-163.
[10]. Cord‐Ruwisch, R., Mercz, T. I., Hoh, C. Y., & Strong, G. E. (1997). Dissolved hydrogen concentration as an on‐line control parameter for the automated operation and optimization of anaerobic digesters. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 56(6), 626-634.
[11]. Fenton, R. E., & Mayhan, R. J. (1991). Automated highway studies at the Ohio State University-an overview. IEEE transactions on Vehicular Technology, 40(1), 100-113.
[12]. Rad, S. R., Farah, H., Taale, H., van Arem, B., & Hoogendoorn, S. P. (2020). Design and operation of dedicated lanes for connected and automated vehicles on motorways: A conceptual framework and research agenda. Transportation research part C: emerging technologies, 117, 102664.









