1. Introduction
Nowadays, with the increasing demand for various resources and the urgent need to reduce the environmental pollution caused by traditional energy, in the case of limited total resources, accelerating the development of new energy technologies and putting them into actual production has become the preferred method for countries to deal with energy, global warming and environmental issues [1-2].In recent years, with the gradual increase of EV market share, vehicle electrification has become an inevitable trend for the future development of the automobile industry. Since EV is in the state of docking charging for a long time, the peak-valley difference of holiday electricity consumption can be greatly increased if EV is connected to the power grid on a large scale during this period. If there are enough such Vehicle network systems, it will be enough to carry out systematic grid-connection control [3], which is the concept of V2G(Vehicle-to-grid).
At present, the basic functions of the V2G system include frequency regulation, voltage regulation [4], fluctuation support of renewable energy [5], realizing peak shaving and valley filling of the power grid [6-7], and filling the capacity gap of the conventional generator set as a rotating reserve [8]. The world's developed industrial countries not only give policy support to V2G, but also have conducted several technical tests on it in the past decade. Table 1 shows the technical verification projects of V2G systems in each country.
Table 1. V2G system related test items [9].
Time | Project participant | Content |
2012 | University of Delaware eV2gSM Project | The experiment of V2G system connecting to PJM's power grid, using EV energy storage resources to smooth out the discontinuity of solar renewable energy output, and evaluating the economy of providing frequency modulation services. |
2016 | Eu EEV4-City program | Support the UK, Germany, Norway, the Netherlands and other countries with good new energy development, and explore the establishment of a micro-grid system structure containing EV. |
2018 | British government VIGIL program | Funded by the UK Office for Low Emission Vehicles and others, it supports research into V2G intelligent control, with a focus on developing new vehicle-to-grid/building communication and control platforms. And actively promote the relevant technology research and development and achievement transformation. |
2020 | Fiat Chrysler Automobiles V2G | In the first phase of the project, 64 two-way fast charging points and 50kW capacity V2G facilities, with financial compensation for users, are designed to balance and regulate the Italian electricity network and increase the flexibility of electric system. |
Nowadays, EV has become a extensive use in the field of transportation, and the research on optimizing EV clustering business model and its charging station agent is also highly valued. On the one hand, EV-assisted frequency modulation system can be used as the bridge of vehicle network scheduling, and combined with the mathematical model related to on-board battery SOC, fund settlement can be automatically completed [10]. On the other hand, a set of personalized supporting services can be provided to buyers for the purpose of maximizing V2G profits based on the daily charging situation of existing EV owners [11].
Based on EV's V2G technology, this paper is divided into three parts. In the section 2, V2G grid-connected control technology is analyzed from the perspectives of active power control, reactive power control and clustering control. In the section 3, relevant commercial value of V2G after practical application is analyzed from the perspectives of EV cluster's commercial model architecture and charging station agent's commercial operation model. In addition, under the condition of ensuring the maximization of V2G commercial profit, the purpose of fully adjusting the peak-valley extreme value of the grid can be achieved by adjusting the charging price in different periods.
2. Research on V2G grid-connected control technology
1.1. Active and reactive power control
As shown in Figure 1, the single-phase V2G system, with the purpose monitoring the SOC(State Of Charge) and implementing unified conditioning, carries out real-time scheduling and control of the V2G converter system on the premise of EV charging and changing demand, actual running state of the grid, real-time electricity price and other factors [12].
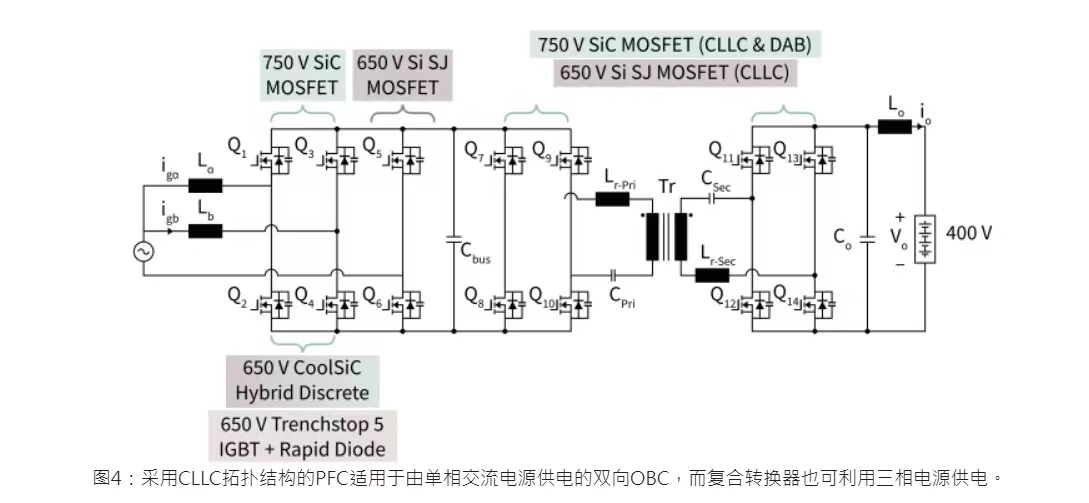
Figure.1 Single-phase system circuit.
According to the unified scheduling of the energy management and monitoring platform, the active power instruction value Prefi and reactive power Qrefi of each single-phase subsystem can be allocated according to the following formula of SOC.
Prefi = \( \frac{{SOC_{i}}×\sum _{l=1}^{m}{P_{l}}}{\sum _{l=1}^{m}{SOC_{l}}} \) , Qrefi = \( \frac{\sqrt[]{{{S_{a}}^{2}}-{{P_{refi}}^{2}}}×\sum _{l=1}^{m}{Q_{l}}}{\sum _{l=1}^{m}\sqrt[]{{{S_{a}}^{2}}-{{P_{rell}}^{2}}}} \) (1)
Prefi and Qrefi are the command values of active power and reactive power of the ith V2G subsystem respectively. Pl and Ql are the feedback values of active power and reactive power respectively. SOCi is the SOC value of the battery of sub-system i; Sa is the average apparent power output of each V2G subsystem [12]. According to the formula, V2G can realize flexible interaction with the power grid under the condition of rectification.
Based on EV owners' demands and load side power of the grid, EV hybrid power control model is established [14]. In order to match EV charging load curve with grid side load curve, the objective function in Figure 2 is established on the premise of providing reactive power compensation function and reducing distribution network cable loss [15].
F(X)={fP,fLS,fV}(2)
In the above equation, F(X) is set as the control target, and fP, fLS and fV are set as secondary targets. fP is defined as the minimum variance function of daily load curve of power grid. fLS is defined as the minimum network loss function in the total time period T. fV is defined as the minimum voltage deviation function.
In essence, the hybrid power control model makes the internal power control of the V2G system have the characteristics of reduced order through the modeling of the power complex vector, and can display the instantaneous energy of the system visually and dynamically. Since J.Holtz first used the concept of complex vector power for modeling in power electronics system in 1995 [16], it has been possible to accurately control and digitally display single-phase instantaneous power under the condition of grid voltage distortion, and stably track two independent targets controlled by grid-connected harmonics. However, in a bid to realize clustering scale control, it is still necessary to realize clustering control network of related technologies such as virtual synchronous machine and frequency division droop control .
1.2. Clustering control
At present, the biggest practical problem of V2G technology comes from the low energy utilization efficiency caused by the non-clustered EV charging mode, and the fundamental reason is that EV owners generally take private charging piles as the main way to charge, so there is great randomness and uncertainty in time and space. If it is advocated that EV in a certain region be charged in a unified charging station, then the energy channeling into the grid side through large-scale charging piles can be utilized in the most concentrated way. Figure 2 shows the structure diagram of two-way energy flow between the grid side and the charging station:
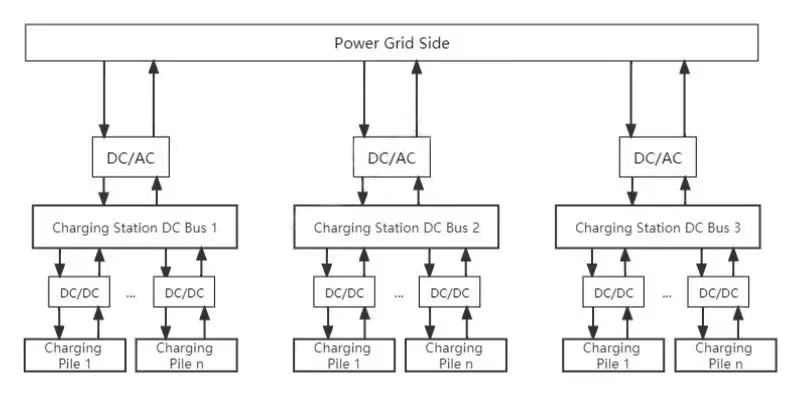
Figure 2. Two-way energy structure diagram of grid side and charging station.
Since the power transmission from the charging station to the grid side requires signal processing by inverters and filters, after EV clustering, compared with the charging mode without clustering, the charging capacity is not only increased, but also the number of grid-connected inverters is greatly reduced. Meanwhile, the fluctuation problem in the grid-connected process is more significant. Virtual synchronous machine control technology based on synchronous generator is a common method to simulate power system. Abundant experimental studies have shown that this technology can effectively solve problems of power grid impact in the traditional grid-connected mode while suppressing voltage abrupt change [17]. However, when EV is integrated into the AC microgrid as a harmonic source, the virtual synchronous machine cannot control the power fluctuation due to the harmonic wave and power quality obtained from the grid side is greatly reduced.
For harmonic control problem, currently the most mainstream method is to add harmonic compensator to power grid operation, add multi-resonance control to voltage loop [18], or series and parallel damping resistor [19], so as to reduce output voltage harmonics, but the above methods are complicated in the specific implementation process, and do not meet the needs of actual large-scale application. Based on the latest relevant research, By combining traditional sag regulation with virtual synchronous machine control through frequency division sag regulation, harmonic power stability can be guaranteed through frequency division detection, and the running time of the system can be greatly shortened.
3. Research on commercial operation of V2G grid-connected control
At present, since V2G technology has not yet achieved large-scale market investment, it has become an important research direction to reasonably develop its commercial value to achieve a win-win situation for operators and users [20].
Cooperative game refers to the game played by some participants in the way of alliance and cooperation. In a cooperative game, the players do not necessarily cooperate, but there is an external body that punishes non-collaborators [21].
In the power grid, the most common cooperative game problem is the power grid charging. Under the continuous advance of marketization, different clean energy power generation companies with different business entities can maximize the benefits of both companies and users through cooperative game theory and reasonable planning.
At present, the more popular direction is to introduce charging station agents to achieve the aim of interacting both users’ side and grid side. The basic idea is to feed back the daily charging amount to the grid according to the charging situation of EV, and then conduct real-time pricing according to the power purchase agreement signed with the grid. The primary goal is to achieve peak cutting and valley filling on the grid side, and the power purchase intention of EV owners is the secondary goal, so as to achieve the maximum cooperation game [22].
The main participants of this operation strategy are the game framework among the power grid, agents and EV owners, as shown in Figure 3 below.
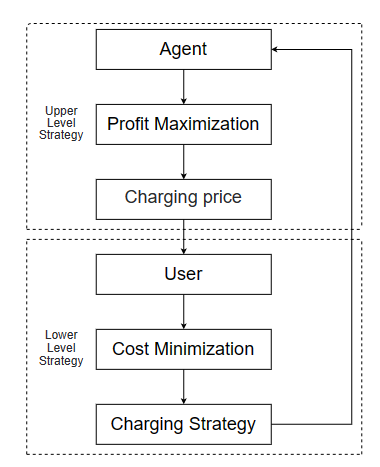
Figure 3. Game structure diagram.
From the point of view of charging station agents, in order to maximize their own interests, the ultimate objective function should meet the following requirements:
Max \( \sum _{i}\sum _{t}{C_{t}}∙{P_{it}} \) + \( \sum _{t}(δ_{t}^{-}∙W_{t}^{-}-δ_{t}^{d}∙{W_{t}}-δ_{t}^{+}∙W_{t}^{+}) \) (3)
Where, Ct is the charging price in the electricity market during time period t, Pit refers to the charging power of the i EV during time period t, δt− and Wt− are the electricity price and quantity sold by charging station agents to the electricity market during time period t, δt+ and Wt+ are the electricity price and quantity purchased by agents from the grid during time period t, respectively. The delta dt agents and the grid and Wt is t time between the contract price and contract quantity.
Meanwhile, in a bid to minimize the charging expenditure, the final objective function should meet the following requirements:
{Pt}=argmin \( \sum _{t}{C_{t}}∙{P_{t}} \) (4)
In this objective function, since Ct is calculated through the upper optimization, the above objective function means to minimize its own charging cost under the condition that the agent gives the electricity price. {Pit} corresponds to the optimal charging strategy for EV.
Generally speaking, cooperative game is the main operation mode in the commercialization process, and the primary purpose is to realize the mutual benefit and win-win among users, agents and power grid companies. For users, the purpose of charging electric cars should be achieved at the minimum cost. For agents, they need to maximize their income through reasonable operation means. For the power grid company, it is necessary to reach a consensus on signing contracts with agents on the premise of realizing peak cutting and valley filling.
4. Conclusion
At present, V2G technology is still in the verification stage and has not been put into large-scale practical use. Compared with G2V, this technology still has many shortcomings. However, in order to make up for the shortage that G2V technology can only obtain energy from the power grid end, the emergence of V2G technology has been able to efficiently complete the task of peak cutting and valley filling at the power grid end through the clustering control of EV. If the virtual synchronous machine control technology and frequency division sagging regulation technology mentioned in this paper can be put into practical application, on the premise of ensuring the stability of harmonic frequency, the operation time of relevant control system can be reduced, providing more possibilities for EV clustering into the power grid. At the same time, for the commercial value of V2G technology, it is not difficult to find in the only relevant research that its huge economic potential can not only reduce the pressure on grid side, but also improve the entire EV charging operation system by introducing charging station agents, driving the development of new industries, and bringing users personalized consumption experience based on real-time electricity price. Minimize charging costs. In general, under the beautiful vision of continuous optimization of V2G technology-related control technologies and continuous introduction of various reciprocal policies, V2G technology will certainly shine in the future stage of new energy.
References
[1]. Li Huiling, Bai Xiaomin. Influence of Electric Vehicle Charging on Distribution Network and Countermeasures [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2011(17) : 38-43.
[2]. Yan Xiao. Research on the Market Diffusion of New energy Vehicles in China under the background of low-carbon transportation [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016.
[3]. CHENG Kun. Research on Grid-connected Control and Real-time Optimization Scheduling of Electric Vehicle Cluster Based on V2G Technology [D]. Shenyang University of Technology,2022.
[4]. Guille C, Gross G. A conceptual framework for the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) implementation[J]. Energy Policy, 2009, 37(11):4379-4390.
[5]. Yao Weifeng, Zhao Junhua, Wen Fusuan, et al. Frequency modulation Strategy for Electric Vehicles in Centralized Charging Mode [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014,38 (009) : 69-76.
[6]. Li Quan. Research on Electric Vehicle grid-connection Parameter Optimization and Control Strategy.2017. Shanghai University of Engineering Science,MA thesis.
[7]. Hu J, Morais H, Sousa T, et al. Electric vehicle fleet management in smart grids: a review of services, optimization and control aspects[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 56:1207- 1226.
[8]. Nigris M D, Gianinoni I, Grillo S, et al. Impact evaluation of plug-in electric vehicles (PEV) on electric distribution networks[C]//International Conference on Harmonics & Quality of Power. IEEE, 2010.
[9]. ZHENG Xu. Research on Electric Vehicle Grid-connected Control Strategy under Vehicle Network Interaction Mode [D]. Shenyang University of Technology, 2022.
[10]. Yang Xiaodong, Zhang Youbing, Zhao Bo, et al. Automatic Demand Response Method of Electric Vehicle Charging and Discharging Based on Collaborative Optimization of Supply and Demand [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017,37 (01) : 120-130.
[11]. Cao Yuhang. Orderly Charging and discharging Strategy for electric vehicles based on Complex network in V2G mode.2022. MA thesis, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications.
[12]. Liu Bin, Song Shaojian, He Deqiang, Lin Xiaofeng. Direct Power Control of single-phase V2G System Based on Complex Vector under Harmonic Conditions [J]. Power automatic equipment, 2018, 38 (01) : 80-86.
[13]. Gao Shuang, Yuan Kai, Sun Chongbo, Song Yi, Wang Shiju. Hybrid control strategy of multi-period active and reactive power for electric Vehicle Cluster Optimization Charging [J]. Electric Power Systems and Automation,2018,30(04):1-6.
[14]. Wang Ran, Wang Ping, Xiao Gaoxi.Two-stage mechanism for massive electric vehicle charging involving renewable energy[J].IEEE Trans on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65 (6) :4159-4171.
[15]. Karfopoulos E L, Hatziargyriou N D.Distributed coordination of electric vehicles providing V2G services[J].IEEETrans on Power Systems, 2016, 31 (1) :329-338.
[16]. HOLTZ J.The representation of AC machine dynamics by complex signal flow graphs[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1995, 42 (3) :263-271.
[17]. Gu Jianing. Research on Charging and Discharging Technology of Electric Vehicle Based on Virtual Synchronous Machine [D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2020:1-7.
[18]. Li Xinqi, Travel, Lu Ziguang, et al. Harmonic suppression of Isolated Island Microgrid Based on Virtual Synchronous Generator [J]. Power Electronics Technology, 201, 55(3) : 81-85.
[19]. Li Zhi, Zhang Zhonghua, Liu Hui, et al. Analysis of Harmonic Resonance Characteristics and Suppression Strategy of LCL Energy Storage Virtual Synchronous Generator [J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 20, 41(10) : 01-08.
[20]. Wei Wei, Chen Yue, Liu Feng, et al. Agent Pricing Strategy and Electric Vehicle Charging Management in intelligent Community Based on Master-slave Game [J]. Power Grid Technology, 2015,39 (04) : 940-945.
[21]. Bai Zeyang, Ju Jian, Jiang Yanjun, Liu Yaoxian, Sun Xiaochen, Wang Jinfeng, Chen Ke. Review on key technologies of electric vehicles participating in power grid peak regulation [J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2022,24 (06) : 25-31.
[22]. Hou Hui, Wang Yifan, Zhao Bo, et al. Scheduling Strategy of EV Load Aggregator Based on Price and Incentive Demand Response [J/OL]. (2021-11-08) [2022-08-20]. Electric network technology: 1-11.
Cite this article
Cheng,X. (2023). EV grid-connected control and economic benefit analysis based on V2G technology. Applied and Computational Engineering,8,48-54.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Li Huiling, Bai Xiaomin. Influence of Electric Vehicle Charging on Distribution Network and Countermeasures [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2011(17) : 38-43.
[2]. Yan Xiao. Research on the Market Diffusion of New energy Vehicles in China under the background of low-carbon transportation [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016.
[3]. CHENG Kun. Research on Grid-connected Control and Real-time Optimization Scheduling of Electric Vehicle Cluster Based on V2G Technology [D]. Shenyang University of Technology,2022.
[4]. Guille C, Gross G. A conceptual framework for the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) implementation[J]. Energy Policy, 2009, 37(11):4379-4390.
[5]. Yao Weifeng, Zhao Junhua, Wen Fusuan, et al. Frequency modulation Strategy for Electric Vehicles in Centralized Charging Mode [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014,38 (009) : 69-76.
[6]. Li Quan. Research on Electric Vehicle grid-connection Parameter Optimization and Control Strategy.2017. Shanghai University of Engineering Science,MA thesis.
[7]. Hu J, Morais H, Sousa T, et al. Electric vehicle fleet management in smart grids: a review of services, optimization and control aspects[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 56:1207- 1226.
[8]. Nigris M D, Gianinoni I, Grillo S, et al. Impact evaluation of plug-in electric vehicles (PEV) on electric distribution networks[C]//International Conference on Harmonics & Quality of Power. IEEE, 2010.
[9]. ZHENG Xu. Research on Electric Vehicle Grid-connected Control Strategy under Vehicle Network Interaction Mode [D]. Shenyang University of Technology, 2022.
[10]. Yang Xiaodong, Zhang Youbing, Zhao Bo, et al. Automatic Demand Response Method of Electric Vehicle Charging and Discharging Based on Collaborative Optimization of Supply and Demand [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017,37 (01) : 120-130.
[11]. Cao Yuhang. Orderly Charging and discharging Strategy for electric vehicles based on Complex network in V2G mode.2022. MA thesis, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications.
[12]. Liu Bin, Song Shaojian, He Deqiang, Lin Xiaofeng. Direct Power Control of single-phase V2G System Based on Complex Vector under Harmonic Conditions [J]. Power automatic equipment, 2018, 38 (01) : 80-86.
[13]. Gao Shuang, Yuan Kai, Sun Chongbo, Song Yi, Wang Shiju. Hybrid control strategy of multi-period active and reactive power for electric Vehicle Cluster Optimization Charging [J]. Electric Power Systems and Automation,2018,30(04):1-6.
[14]. Wang Ran, Wang Ping, Xiao Gaoxi.Two-stage mechanism for massive electric vehicle charging involving renewable energy[J].IEEE Trans on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65 (6) :4159-4171.
[15]. Karfopoulos E L, Hatziargyriou N D.Distributed coordination of electric vehicles providing V2G services[J].IEEETrans on Power Systems, 2016, 31 (1) :329-338.
[16]. HOLTZ J.The representation of AC machine dynamics by complex signal flow graphs[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1995, 42 (3) :263-271.
[17]. Gu Jianing. Research on Charging and Discharging Technology of Electric Vehicle Based on Virtual Synchronous Machine [D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2020:1-7.
[18]. Li Xinqi, Travel, Lu Ziguang, et al. Harmonic suppression of Isolated Island Microgrid Based on Virtual Synchronous Generator [J]. Power Electronics Technology, 201, 55(3) : 81-85.
[19]. Li Zhi, Zhang Zhonghua, Liu Hui, et al. Analysis of Harmonic Resonance Characteristics and Suppression Strategy of LCL Energy Storage Virtual Synchronous Generator [J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 20, 41(10) : 01-08.
[20]. Wei Wei, Chen Yue, Liu Feng, et al. Agent Pricing Strategy and Electric Vehicle Charging Management in intelligent Community Based on Master-slave Game [J]. Power Grid Technology, 2015,39 (04) : 940-945.
[21]. Bai Zeyang, Ju Jian, Jiang Yanjun, Liu Yaoxian, Sun Xiaochen, Wang Jinfeng, Chen Ke. Review on key technologies of electric vehicles participating in power grid peak regulation [J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2022,24 (06) : 25-31.
[22]. Hou Hui, Wang Yifan, Zhao Bo, et al. Scheduling Strategy of EV Load Aggregator Based on Price and Incentive Demand Response [J/OL]. (2021-11-08) [2022-08-20]. Electric network technology: 1-11.









