1. Introduction
With China's urbanization progressing at a rapid pace, problems such as rainwater runoff pollution, flood disaster and water resource shortage have become increasingly prominent. Some natural storage spaces of water such as rivers and lakes are filled and occupied, which intensifies the pressure of waterlogging prevention objectively [1]. In order to solve urban waterlogging, the idea behind sponge city was put forward. When a city responds well to environmental changes and natural disasters, it is said to have "elasticity" or be a "sponge city." When it rains, sponge city collects, purifies, and stores the water. When needed, sponge city "releases" and uses the water that was collected [2]. Construction of sponge cities should adhere to the ecological priority guidelines and incorporate both organic and artificial methods [2]. In order to encourage the use of rainwater resources and ecological environment conservation, sponge city should boost the accumulation, infiltration, and purification of rainwater in urban areas in accordance with the premise of assuring the security of urban drainage and reducing waterlogging. Sponge city building requires systematizing Groundwater, surface water, and natural precipitation; Coordination of water supply, drainage, and other aspects of water recycling, along with consideration of the project's complexity and duration [3]. Sponge city development in China has lagged behind those of advanced nations in Europe and North America [4]. The "sponge city" being built in China is currently through a period of fast expansion. However, compared with foreign rainwater management technology, there are still some shortcomings to be improved [4]. Starting from the first batch of sponge city pilot projects in 2015, the number of national sponge city pilot projects has reached 67 by 2021, among which 20 cities including Tangshan and Changzhi were selected as the first demonstration cities [5]. Based on the current situation of China's development of sponge cities, this paper summarizes and analyses the achievements achieved at the present stage and discusses the problems and risks of sponge city construction. In view of the existing problems, some countermeasures are proposed, hoping to provide reference for the construction of sponge city in the future.
2. Proposal of sponge city construction
2.1. Water resource shortage
The demand for water resources in cities is rising as a result of China's urbanization process as cities grow. However, the construction of roof, road, ground and other facilities led to the hardening of underlying surface, and 70% ~ 80% of rainfall could not penetrate to form runoff, and groundwater recharge was seriously insufficient [3]. Table 1 shows the statistics of water resources of China in recent years [4].
Table 1. Water resources in China [4].
Total water ( \( ×{10^{8}}{m^{3}} \) ) | Surface water ( \( ×{10^{8}}{m^{3}} \) ) | Groundwater ( \( ×{10^{8}}{m^{3}} \) ) | Precipitation ( \( ×{10^{8}}{m^{3}} \) ) | Per capita value ( \( ×{10^{8}}{m^{3}} \) ) | |
2000 | 27700.8 | 26561.9 | 8501.9 | 60092.0 | 2193.9 |
2001 | 26867.8 | 25933.4 | 8390.1 | 58122.0 | 2112.5 |
2002 | 28261.3 | 27243.3 | 8697.2 | 62610.0 | 2207.2 |
2003 | 27460.2 | 26250.7 | 8299.3 | 60415.5 | 2131.3 |
Data show that by 2023, China's per capita water resources are less than 2200 \( {m^{3}} \) , about a quarter of the world's per capita water, and China is also one of the 13 water-poor countries in the world. There are three kinds of water shortages: water shortages, water shortages and technical water shortages. Water scarcity based on resources is the most prevalent kind of water scarcity, caused by either water scarcity or per capita water scarcity because of the large population.
Water supply shortage caused by water shortage may lead to agricultural production reduction, industrial development slowdown, domestic water supply interruption and other problems. If the local water shortage is serious enough to threaten the safety of groundwater and environmental flow, it will also lead to the emergence of groundwater funnel and degradation of ecosystem services and other serious consequences [3]. At the same time, relevant studies predict that China's water stress will continue to increase in the coming period [5].
2.1.1. Irrational use of water resources. Farmland irrigation water's effective utilization coefficient will only be 0.50 by 2021, considerably below the advanced level of 0.7 to 0.8 in the rest of the world. More than 50 billion cubic meters of water are not available each year. Water shortages affect two thirds of cities, but 300 million people in rural areas lack access to safe drinking water. From a broad perspective, it is a successful means of preventing the waste of water resources to support the development of moral civilization and promote "saving resources" good living practices. A tight and acceptable urban planning layout is a practical way to prevent the waste of water resources from an urban planning standpoint [5].
2.1.2. Excessive development of water resources. For example, 76% of the water resources in the Yellow River Basin, both 53% and 100% of the resources in the Huaihe River Basin have been used and exploited. A number of ecological and environmental issues will arise if water resources are exploited to the point that the environment can no longer support them.
2.1.3. Serious water pollution. In China's water functional zones, just 46% of the water quality is up to par. In 2010, two-thirds of lakes were eutrophicated, and 38.6% of riverbeds were inferior to Class III water. Water pollution will result in a decline in water quality, harm to the ecological balance, and long-term environmental damage. Additionally, water pollution has had a negative impact on how industry and agriculture have developed. Polluted water will cause harm to machinery and equipment in industrial production, while it will also modify the soil's structure in agricultural production, reduce crop quality and yield, accumulate in plants, and eventually enter people's bodies through food [5].
2.2. Urban waterlogging problem
Waterlogging refers to the phenomenon that heavy precipitation events or continuous precipitation events in a certain region exceed the drainage capacity of urban rainwater facilities, resulting in ground water accumulation [6]. Waterlogging occurs frequently in Chinese cities, with obvious seasonality and obvious regularity in urban distribution [7].
One of the nations where floods frequently happen is China. For example, different type and degree of flood may have happened on about two-thirds of its territory. Because 70% of the country's fixed assets, 44% of the population, 1/3 of the cultivated land, nearly 100 cities, infrastructure and industrial and mining enterprises are situated in the river's middle and lower sections, the objective conditions are very easy to be seriously threatened by floods. Furthermore, extreme weather and heavy rain are common in the context of global climate change. The frequent occurrence of rainstorm events leads to the frequent occurrence of waterlogging in many cities. The occurrence of rainstorm in a short term will cause flooding in most areas of the city, seriously interfere with the normal order of the city, and even lead to greater economic losses and serious casualties [7]. Moreover, the worsening of climate warming and the high-quality development of urbanization in China lead to more frequent extreme precipitation [6]. According to figures from the Ministry of Water Resources and Emergency Management's National Disaster Reduction Centre, more than 60,000 people died as a result of floods between 1991 and 2020. This amounted to an annual direct economic loss of 160.4 billion yuan, or approximately 4.81 trillion yuan. Waterlogging disasters are serious and representative: according to data given by Beijing government agencies, the "July 21" rainfall in 2012 caused 10,660 house collapses, 1.602 million people were harmed, the economic loss was 11.62 billion yuan, and 79 people perished. On July 26, 2017, a massive flood broke out in Shaanxi Province, affecting 104,700 people and killing 4 [8].
2.3. Sponge city concept
Sponge city includes the moisture properties of rainwater absorption, storage and release, as well as the mechanical properties of compression, rebound and recovery. In the process of rainfall, the city can permeate, reduce emission and collect, store and utilize rainwater [1]. Figure 1 shows a schematic of a sponge city [9]. As early as the middle of 20th century, sponge city planning has been deeply studied abroad. Australia advocated a water-sensitive city to scientifically improve the water recycling system, whereas the United States proposed low-impact development in urban design to create a rainwater management system [8].
Sponge city is inspired by the urban hydrological law and takes planning and construction as the carrier to optimize the green and grey infrastructure design and change the way of rainwater collection. Sponge City fully exploits the accumulation, penetration and slow release of urban spongy bodies on rainwater runoff, realizes the goals of urban Utilization of resources for water and restoration of water ecology and environment, flood control and drainage, and reduces natural calamities and environmental changes have an impact on the city. The connotation of sponge city includes: reducing flood peak discharge; Reduce water pollution; Improve the water ecological environment; Strengthen the utilization of rainwater and flood resources [1]. Sponge city is a comprehensive system combining theory system and practice system. Its basic connotation is mainly as follows: (1) Protecting urban original ecosystem: urban original ecosystem is an important channel for urban runoff and rainwater discharge. Receptacle and storage space can protect water-sensitive places such as rivers, lakes, wetlands, and ditches while leaving enough water to provide for protection. (2) Ecological restoration: Sponge city deviates from typical urban construction methods and use ecological measures to repair environmental damage and water contamination. (3) Low impact development: Low impact development refers to the effective control of urban development, which includes reserving enough ecological land, managing the proportion of hardened area of the city's underlying surface, and minimizing damage to the urban ecological environment [9].
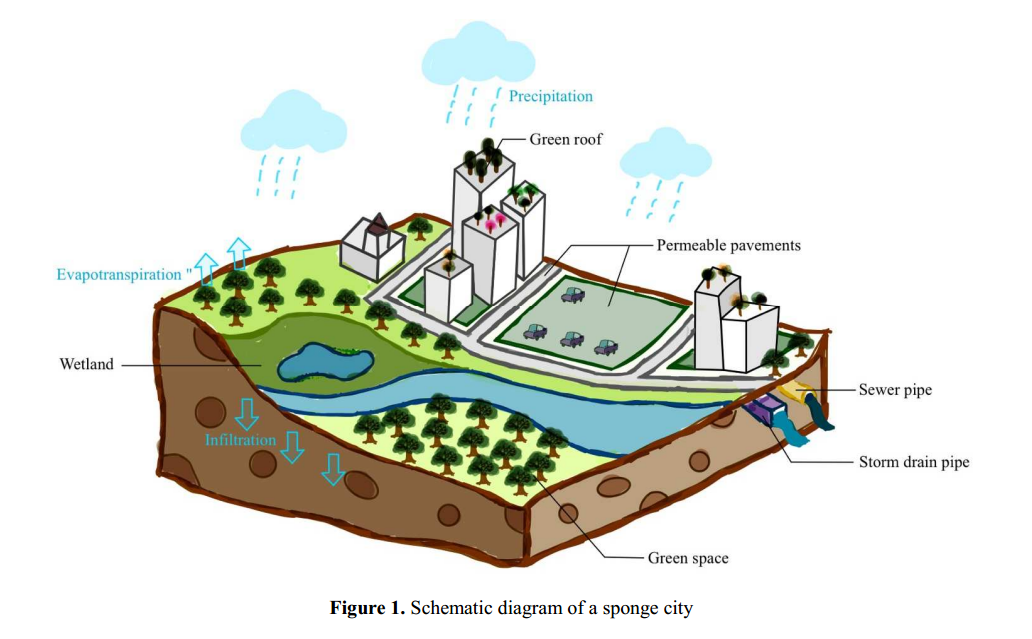
Figure 1. A schematic of a sponge city [9].
3. Construction and development status of sponge city
3.1. Construction status of sponge cities in China
China's implementation approach has been developed based on recent research into sponge city building. In this system, the government is primarily accountable. The federal government promotes sponge city development and management, while local governments are the organizers. Sponge city construction offices or committees are usually set up, which include officials from urban planning, construction, landscaping, transportation, environmental protection, water resources and other relevant municipal councils or agencies. Sponge City Construction Office or committee is responsible for all matters connected to sponge city construction and management [10].
As the promoter of sponge city construction and management, the Chinese government has successively issued corresponding policies, regulations, systems and technical standards. China should actively promote the low-impact mode of growth and building, according to the Notice of The General Office of the State Council on the building of Urban Drainage and Waterlogging Facilities published in 2013. The decision to conduct Sponge City construction pilot work was made in 2014 by Circular of the Ministry of Finance on Conducting Sponge City Construction Pilot Work Supported by Central Finance [2]. The Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development announced the first batch of prototype sponge cities in 2015, including six in East China, one in North China, one in South China, three in Central China, one in Northeast China, three in Southwest China, and one in Northwest China. The regional distribution is depicted in Figure 2 [11].
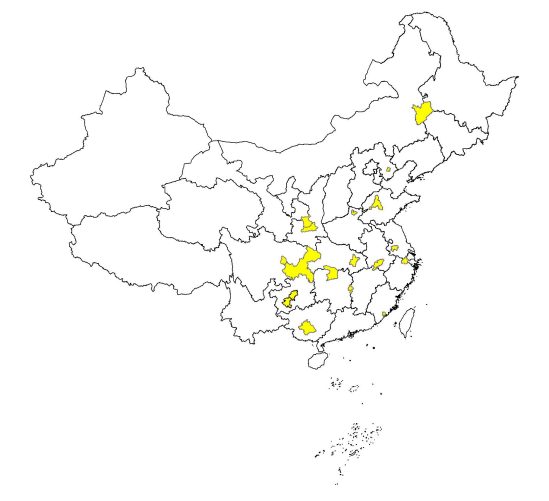
Figure 2. The regional distribution [11].
According to the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, sponge cities should cover at least 20 percent of China's urbanized areas by 2020, and at least 80 percent by 2030. Under the guidance of national policies, the academic circle has gradually shifted the focus of sponge city research from concept and connotation to method system, providing the groundwork for the development of a rigorous and effective evaluation methodology for the effect of sponge city construction. The sponge city evaluation model constructed by many scholars covers environmental performance, market demand, public participation and other aspects, which can reflect the key issues of sponge city project construction in a more comprehensive way [11]. Meanwhile, residents say that sponge cities are of great help in reducing urban floods and easing traffic [12].
3.2. Progress of technical level
Low impact development technology is the key technical measure of sponge city construction. Compared with traditional measures, low-impact development technology has obvious advantages. It is an innovative concept, and its main technical measures include biological retention pond, grassland channel, vegetation cover and permeable pavement, etc. [2]. In terms of materials, Sponge City uses a new type of permeable pavement material that has been improved on the surface. By taking advantage of the permeability property of water molecules, the water molecules penetrating into the material will accumulate and eventually merge into the soil layer on the ground. According to different functions used, they can be divided into four categories: pervious brick, pervious concrete material, natural pervious material and new pervious material [13]. In addition, waste resources such as silt and glass can also be treated by technical methods and become a new material for the construction of sponge city [2].
3.3. Results of pilot cities: a case study of Jiaozuo city in Henan province
Jiaozuo is a warm temperate sub-humid monsoon climate. The sunshine time is long, the heat is sufficient, the frost - free period is long, the water is hot at the same time, the precipitation varies greatly between the year. The surface water resources in Jiaozuo City are scarce, and in recent years, they show a trend of decreasing gradually. The total amount of groundwater in urban areas is small and has been polluted. According to the data of Jiaozuo meteorological Station, the annual average monthly precipitation of Jiaozuo in 2022 is shown in the Figure 3 [14].
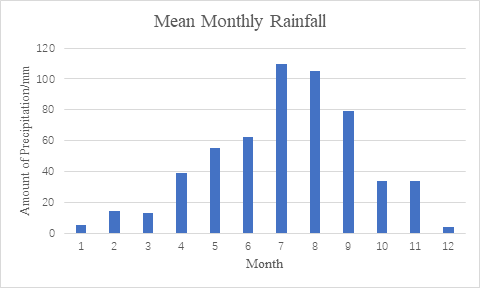
Figure 3. the annual average monthly precipitation of Jiaozuo in 2022[14].
Jiaozuo City takes the standard construction of sponge city as an opportunity to solve the severe problems of water resources. Jiaozuo City builds sponge cities based on current urban conditions and relevant planning, and comprehensively improves the management level of Jiaozuo City's water security, water resources, water environment and water ecology construction. According to the Jiaozuo Sponge City Standard Construction Three-Year Implementation Plan, the sponge city construction of Jiaozuo involves 151 projects in 7 categories, with a total investment of 4.233 billion yuan. After the sponge city was built, according to the water quality test results, the water quality of the original 10 black and smelly water bodies in Jiancheng District of Jiaozuo City basically reached the standard after treatment, and there was no black and smelly water [11]. Moreover, the public opinion poll showed that the surrounding residents were satisfied with the water bodies' treatment outcomes, and there was no event that led to a complaint being filed. There has been varied degrees of improvement in each of the four areas of water ecology, water resources, water environment, and water security [11].
4. Main problems and countermeasures of sponge city construction
4.1. Risk early warning system
Sponge city construction involves multiple stakeholders, including technology, capital and other factors. Compared with other large-scale public projects, its risk reduction and management are highly complicated. Sponge city construction across the country requires a large investment volume and high social attention. Once the risk is difficult to control, it will have a significant impact on the local economy and society. After tracing the theoretical achievements of sponge city, it is found that the risk research of this emerging field is still in the initial stage, and the risk early-warning research of the whole life cycle is still blank. The research results of the early warning system are mainly rainwater monitoring and early warning system, urban rainstorm disaster early warning system and flood early warning and dispatching system, aiming at starting emergency warning and response by monitoring the changes of natural disasters such as rainfall and flood. These early warning systems are mainly used in the operation stage after the completion of sponge city projects, ignoring the need for risk early warning in other stages, so it is unable to comprehensively prevent and control the risk of sponge city construction. In the future, it is necessary to deeply study the risk factors existing in the whole life cycle of sponge city construction, strengthen the "prevention in advance" measures, establish the risk early warning system of sponge city construction, accelerate the construction of sponge city risk prevention and control system [13].
4.2. The pertinence of planning
Different cities differ in terms of development level, urban planning, natural conditions and climate. Sponge city construction planning for different cities should be based on local conditions and comprehensive consideration [15]. To ensure the maximum exploitation and utilization of the environment's own potential, at the same time with the city's future economic development planning.
For example, in planning new areas, the idea of building sponge cities should be implemented in the planning stage, and the original rivers, lakes, wetlands and ponds should be protected to the maximum extent. On this basis, the yearly runoff control rate overall should be taken as a control index for construction, in order to maximize the absorption, retention and slow-release effects of low-impact development facilities on rainwater. For planning new areas, the idea of building sponge cities should be implemented in the planning stage, and the original rivers, lakes, wetlands, pits and so on should be protected to the maximum extent. On this basis, the total annual runoff control rate is taken as a control index for construction, to give great consideration to the rain's ability to absorb, hold, and slowly release water by low-impact development facilities, and to lessen the negative effects of construction and urban development on the environment [11].
For existing built-up areas, sponge city development should strengthen ecological restoration while focusing on reducing urban flooding and foul-smelling waterbodies. Sponge city construction should realize organic renewal and avoid large-scale demolition construction. At the same time, sponge measures such as "seepage, stagnation, storage, purification, use and drainage" are selected according to local conditions to give full consideration to the site's natural storage, seepage, and purification capabilities while avoiding overengineering.
4.3. The applicable rules and laws
In general, the sponge city planning legal system at the national level is lacking. There is no special legislation for reference, the rules and standards governing matching sets aren't flawless, and the construction of a high-level comprehensive legal system is lacking.
First of all, in the planning before the construction of sponge city, the legal basis level is not high, the supervision legal responsibility system is not sound, the neglect of the "ecological background" and the unclear level of "fragmentation" prominent legal problems. To solve the above problems, government should establish legal countermeasures, improve the level of planning legislation, clarify the supervision responsibility of planning implementation, and strengthen the system construction of planning basis. Secondly, there are legal problems in the concrete construction of sponge city, such as imperfect professional standards, single operation mode, imperfect construction, operation and control system, and imperfect performance appraisal mechanism. In this regard, the "grey and green combination" and "sponge +" modes can be adopted for construction, to enhance the sponge city's policy incentive system, as well as the path of operation and overall process control systems. Finally, in sponge city's management system, the legislative level is not high, the management mechanism is not sound, and the assessment and supervision content are lacking. It is suggested to improve the system of laws and regulations and establish a sound supervision and restriction mechanism. At the same time, relevant departments can consider refinement the functions of various departments of "Sponge Office", promote the normalization of sponge city management joint meetings, and establish a grass-roots water control linkage mechanism [16].
5. Conclusion
Sponge city is a novel concept of urban development, which includes a large number of engineering construction practices reflecting the concept of "ecological priority and green development", covering multi-disciplines, multi-fields and multi-departments of urban construction. China is currently in the initial stage of sponge city construction, and there are many problems. The systematic engineering of sponge city construction needs a lot of practice and constant exploration and improvement under this premise. Based on the water resources challenges faced by Chinese cities, this paper expounds the connotation of sponge city and the relevance of its construction. According to the current situation of sponge city construction in China, this paper summarizes the achievements of sponge city construction at the present stage and analyzes the existing problems and solutions for reference. The construction of sponge cities in the future needs to start from the actual situation in China. It is necessary to promote the construction of risk early warning system, improve relevant policies, laws and regulations, enhance the public's understanding of sponge cities, and provide a strong guarantee for the development of sponge cities with Chinese characteristics.
References
[1]. Fan M 2019 Study on the Utilization of Rainwater Resources in Sponge City (North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power).
[2]. Pan L, Yuan S and Liu Y 2022 Current status and research progress of sponge city construction Sichuan Water Resources 43(06) pp131-134.
[3]. Zhou X 2022 Evaluation of Water Scarcity in China considering Inter-basin Water Transfer (Dalian University of Technology).
[4]. National bureau of statistics of china 2004 Water resources situation (2000-2004) (http://www.stats.gov.cn/zt_18555/ztsj/hjtjzl/2004/202303/t20230302_1922995.html).
[5]. Li J 2019 Research on Rational Utilization of Urban Water Resources Based on Sponge City Theory-Making Comparison between China and Singapore Water Resources Protection 37 (6) pp 80-87.
[6]. Cao J 2021 Prediction of Urban Flood Risk in China under the Background of Global Warming (Lanzhou University).
[7]. Zheng X 2021 Research on urban waterlogging risk control based on the concept of "sponge city"—taking Ningbo City as an example (Zhejiang University Of Technology).
[8]. Mi R 2020 Research on Sponge City Planning and Construction under Different Urban Needs (Southwest University Of Science And Technology).
[9]. Shao Y and Ma K 2022 Sponge City As A Civil Engineering Solution To Climate Change That Improves Urban Flood Resilience E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB) pp 1-4.
[10]. Yin D, Xu C, Jia H, Yang Y, Sun C, Wang Q and Liu S 2022 Sponge City Practices in China: From Pilot Exploration to Systemic Demonstration Water 14 (10) pp 1531- 53.
[11]. Li N 2021 Research on on Evaluation Index System of Sponge City Construction in Residential Area (Zhengzhou University).
[12]. Luo P, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Zhang S, Yu W, Zhu X, Huo A, Wang Z, He B and Nover D 2022 Comparative Assessment of Sponge City Constructing in Public Awareness, Xi’an, China Sustainability pp 1-17.
[13]. Zhu D and Yao Y 2023 Research on Application of Permeable Pavement Materials in Sponge City Construction Value Engineering 42(4) pp103-105.
[14]. National Meteorological Center of CMA 2022 2023-05-05 http://www.weather.com.cn/weather 40d/ 101181101.shtml.
[15]. Wang Y 2021 Research on Risk Early Warning System of Sponge City Construction (Zhejiang University Of Technology).
[16]. Wang S 2020 Research on Some Legal Issues of Sponge City Constructio (Hebei University).
Cite this article
Zhu,J. (2023). Research on the problems and strategies of sponge city construction in China. Applied and Computational Engineering,24,83-90.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Functional Materials and Civil Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Fan M 2019 Study on the Utilization of Rainwater Resources in Sponge City (North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power).
[2]. Pan L, Yuan S and Liu Y 2022 Current status and research progress of sponge city construction Sichuan Water Resources 43(06) pp131-134.
[3]. Zhou X 2022 Evaluation of Water Scarcity in China considering Inter-basin Water Transfer (Dalian University of Technology).
[4]. National bureau of statistics of china 2004 Water resources situation (2000-2004) (http://www.stats.gov.cn/zt_18555/ztsj/hjtjzl/2004/202303/t20230302_1922995.html).
[5]. Li J 2019 Research on Rational Utilization of Urban Water Resources Based on Sponge City Theory-Making Comparison between China and Singapore Water Resources Protection 37 (6) pp 80-87.
[6]. Cao J 2021 Prediction of Urban Flood Risk in China under the Background of Global Warming (Lanzhou University).
[7]. Zheng X 2021 Research on urban waterlogging risk control based on the concept of "sponge city"—taking Ningbo City as an example (Zhejiang University Of Technology).
[8]. Mi R 2020 Research on Sponge City Planning and Construction under Different Urban Needs (Southwest University Of Science And Technology).
[9]. Shao Y and Ma K 2022 Sponge City As A Civil Engineering Solution To Climate Change That Improves Urban Flood Resilience E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB) pp 1-4.
[10]. Yin D, Xu C, Jia H, Yang Y, Sun C, Wang Q and Liu S 2022 Sponge City Practices in China: From Pilot Exploration to Systemic Demonstration Water 14 (10) pp 1531- 53.
[11]. Li N 2021 Research on on Evaluation Index System of Sponge City Construction in Residential Area (Zhengzhou University).
[12]. Luo P, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Zhang S, Yu W, Zhu X, Huo A, Wang Z, He B and Nover D 2022 Comparative Assessment of Sponge City Constructing in Public Awareness, Xi’an, China Sustainability pp 1-17.
[13]. Zhu D and Yao Y 2023 Research on Application of Permeable Pavement Materials in Sponge City Construction Value Engineering 42(4) pp103-105.
[14]. National Meteorological Center of CMA 2022 2023-05-05 http://www.weather.com.cn/weather 40d/ 101181101.shtml.
[15]. Wang Y 2021 Research on Risk Early Warning System of Sponge City Construction (Zhejiang University Of Technology).
[16]. Wang S 2020 Research on Some Legal Issues of Sponge City Constructio (Hebei University).









