1.Introduction
With the development of society and the progress of science and technology, people's living standards have been continuously improved, and the sharing of bike has become an indispensable means of transportation in daily life. It increases the travel mode of the residents, improves the travel efficiency, and effectively alleviates the traffic pressure. The scale of bike-sharing is also expanding. However, there are still some problems with shared bikes, such as unreasonable distribution of vehicles, vehicle accumulation, and unreasonable time period of vehicle allocation, leading to vehicle shortage. In order to solve such problems, promote the development of shared bikes, improve the use efficiency of shared bikes, and solve the problems of People's Daily travel, this paper investigates and studies the problem of empty car scheduling of shared bikes.
Currently, The research on the scheduling of shared bikes mainly focuses on the following aspects: ① Research on the site selection and vehicle configuration of shared bikes [1], In this regard, the research mainly uses the idea of joint coverage site selection to establish a multi-period and multi-objective optimization model of the site selection of shared bike parking points and the vehicle configuration decision at the beginning of each point; ② Research on the optimization of shared bike scheduling [5,6,7,8,13], For example, Chen Zhiyuan's research based on spatiotemporal clustering prediction, It is mainly solved by solving the model, And to compare the scheduling effect of the algorithm, A complete framework and improved algorithm from network analysis to scheduling optimization are proposed for the scheduling problem of shared bikes; ③ Travel distribution prediction model of shared bikes on congestion index [2], The research in this area is mainly conducted on the analysis of the characteristics of the study area and influencing factors and the construction of models.
The research on the operation problems and optimization scheme of shared bikes mainly focuses on the following aspects: ① Sun Yahui and other studied the problems existing in the operation of shared bikes and their solutions [11], Proposed the planning of the bicycle parking area, To ease traffic congestion, Strengthen the risk management, Improvement methods to improve users' legal awareness; ② Research on the optimization problem of shared bike scheduling path studied by Hu Jiayue [12], By studying the relevant research results at home and abroad, Further exploration was made on the basis of our predecessors, And is based on the clustering algorithm theory, Built the mean-shift clustering algorithm, The scope of the research was scientifically divided, Thus establishing a scheduling center, The bike-sharing dispatching network with the connection between the virtual sites and the sites as the main element; ③ CAI Zhengqun and other studied the research on the use of shared bikes and the optimized management countermeasures [14], By investigating the current situation of the use of shared bikes and analyzing their management problems, The government needs to address issues such as relevant legislation, industry regulation and scientific guidance, And manage it together with the market and the people, To solve the "last mile" problem; ④ Chen Xiaolong studied the sustainable operation management scheme for the bike-sharing industry [15], Using the MBA teaching case study and writing paradigm, Select "HL Bike" as the case enterprise representative of bike-sharing research. First, the research background and purpose are explained, and the importance of the research for the bike-sharing industry is expounded.
There are some research related to urban management is mainly focused on the following aspects: ① Shared bike cycling destination of time and space characteristics and influencing factors [3], ② based on scheduling pool Shared cycling scheduling research [4], ③ Chinese mainland city built environment and sharing the relationship between the bicycle configuration [9], ④ Shared bike recommended parking point and user guide strategy planning method [10].
To sum up, this paper summarizes and analyzes the scheduling of shared bikes. Different from the above mentioned articles, this paper mainly studies the development and use efficiency of shared bikes, and analyzes the travel rules of shared bikes, but there is still a lack of research in this aspect.
2.The rules of shared bike travel
With the continuous development of the society, shared bikes also continue to provide convenience for people. In the second section, we study and analyze the development situation of shared bikes and the use efficiency of shared bikes, so as to strengthen the understanding of shared bikes, which is more conducive to the development of shared bikes.
2.1.The development overview of shared bikes
In 2014, Dai Wei, a graduate from Peking University, co-founded OFO with four partners to solve travel problems on college campuses. In May 2015, more than 2,000 shared bikes appeared on the campus of Peking University. Since the end of 2016, shared bikes have suddenly become popular in China, with shared bikes of various colors lined up on the roadside in major cities. In 2016 is the peak of Shared cycling enterprise scuffle, including more than 20 bicycle companies compete with each other, in 2016 Shared bicycle industry financing total more than 3 billion yuan, in addition to ofo:, the worship, hello, small Ming bicycle, small blue bike, small white bicycle and other small and medium-sized enterprises also follow heat rapid rise, 2016 is the most dynamic year, Shared cycling user scale reached nearly 20 million people. With the fierce competition, large enterprises continue to expand, with strong financial support, in exchange for preferential strength for customer resources, continuous burning money war, financial shortage of Xiaoming bicycle, Kuqi bicycle have stopped operation.2018 is also a chaotic year for bike-sharing companies. In February 2018, more than 20 more than 70 bike-sharing companies across the country stopped operating. At the end of the year, ofo also ended, with strong financial support such as Hello Bike and Meituan Bike coming to the end.
Figure 1. The number of bike-sharing users in China continues to rise from 2017 to 2021 (chart above: Scale of users (100 million people))
Figure 2. The size of China's bike-sharing market continues to expand from 2017 to 2021 (Figure above: Market size (100 million yuan))
2.2.The use efficiency of shared bikes
According to statistics, nearly 40 percent of people in China ride shared bikes at least once a day. Of the 1,000 people interviewed, 794 people had used 79.4 percent of shared bikes. In terms of age groups, the younger the age, the higher the proportion of people using shared bikes, and the proportion of people aged between 16 and 20 is the highest, at 93.5%. In terms of occupations, IT workers, students and financial workers used the highest proportion of shared bikes, with 97.8 percent, 93.1 percent and 92.3 percent, respectively. The survey found that nearly 80% of respondents used shared bikes frequently, 39.9% used them once or more a day, and 32.5% used them once in 2-3 days, indicating that cycling has gradually become people's daily choice. At the same time, shared bikes have become an important means of transportation for residents to take short trips.79.7% of the respondents used a shared bike within half an hour on average, of which 48.6% accounted for 15-30 minutes and 31.1% accounted for less than 15 minutes.
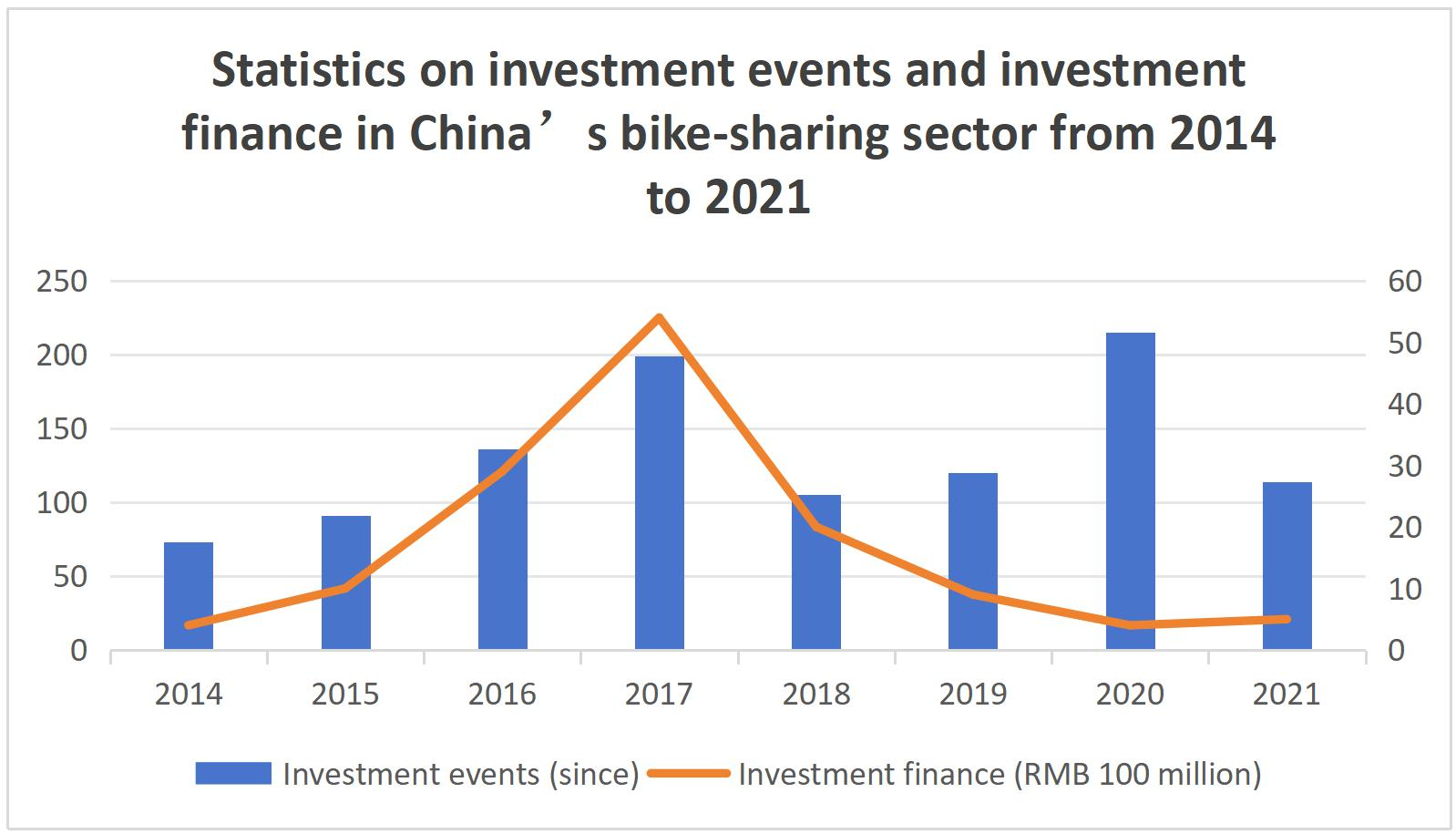
Figure 3. Investment events and investment finance in China's bike-sharing sector continued to rise from 2014 to 2017, and continued to decline from 2017 to 2020, with a slight increase from 2020 to 2021 (RMB 100 million)
Figure 4. Continuous increase from 2014 to 2017,2018 to 2020; decrease from 2017 to 2018,202020 to 2021 (above: Business registrations (home))
3.Based on the travel rules for the analysis
With the development of shared bikes, customers 'travel demand is constantly increasing. Shared bikes always appear in different places at different times, such as office buildings, subway stations, residential buildings and other places, to facilitate people's life. However, due to the improper scheduling of shared bikes, there are too many shared bikes in some areas, while some areas are too small. This will affect people's travel efficiency and increase their commuting time. We have analyzed the rules of shared bike travel to make it more conducive to people's daily life.
3.1.Type analysis
This paper mainly investigates the office buildings, subway stations and residential buildings in different time periods.7:00~9:00 is the morning rush hour. According to the survey, the number of shared bikes near office buildings continues to rise, the number of shared bikes near residential buildings continues to decline, the number of shared bikes near subway stations near residential buildings continues to rise, and the number of shared bikes near office buildings continues to decline.
Figure 5. Usage of shared bikes in each time period (as shown above: by hour)
3.2.Time period division of shared bikes
This paper investigates the morning peak hours from 7:00 to 9:00.15 minutes from 7:00 to 9:00. The first time period: 7:00~7:15, the second period: 7:15~7:30, the third period: 7:30~7:45, the fourth period: 7:45~8:00, the fifth period: 8:00~8:15, the sixth period: 8:15~8:30, the seventh period: 8:30~8:45, the eighth period: 8:45~9:00.
This article uses a normal distribution:
\( f(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{2π}σ}e^{(-\frac{(x-μ)^{2}}{2σ^{2}})} \)
The empty vehicle scheduling is studied to improve the use efficiency of shared bikes.
4.Empty vehicle scheduling model of shared bikes
4.1.Description of the parameters and the variables
N: Area type (office building, subway station, residential building)
J: Collection of residential buildings (J= {1,2,..., l})
D: assembly of subway stations (D= {1,2,..., m})
X: Office building collection (X= {1,2,..., n})
M = J∪D∪X: a collection of all sites
\( d_{i} \): The number of travel demand at site i, i=1,2,...\( |M| \)
\( T_{j} \): Every 15 minutes during the morning rush hour
𝑇1 represents 7:00~8:00....... 𝑇8 representation 8:45~9:00
j=1,2,...,8
A total of 8 time periods were included
\( K \):Total number of vehicles
\( k_{ij} \):Total number of vehicles at site i in the j time period:
\( \sum_{i=1}^{|M|}k_{ij}=k,j=1,2,...,8 \)
\( d_{ij} \):Represents the number of trips at the j th time period of the i th site
\( \sum_{j=1}^{8}d_{ij}=d_{i},i=1,2,...,|M| \)
variable:
\( x_{i^{ \prime }ij} \): Number of empty vehicles dispatched from the\( i^{ \prime } \)station to the i station in the j time period
4.2.Empty car scheduling model
The objective function is so for the unknown travel demand
Total number of unmet travel needs for the j th time period:\( \sum_{i=1}^{|M|}[d_{ij}-k_{ij}]^{+} \)
Among:\( k_{ij}=k_{i(j-1)}+\sum_{i^{ \prime }=1}^{|M|}x_{i^{ \prime }ij} \)
Overall objectives:min\( \sum_{j=1}^{8}\sum_{i=1}^{|M|}[d_{ij}-k_{ij}]^{+} \)
Constraint condition:\( k_{ij}=k_{i(j-1)}+\sum_{i^{ \prime }=1}^{|M|}x_{i^{ \prime }ij} \)
\( \sum_{i=1}^{|M|}k_{ij}=k,j=1,2,...,8 \)
\( \sum_{j=1}^{8}d_{ij}=d_{i},i=1,2,...,|M| \)
5.Examples
In order to verify the effectiveness of scheduling experiments, the following examples are constructed from real cases. There is one office building, two residential areas, and a subway station. Consider 200 households; 300 households. According to the number of shared bikes required by residents in each of the eight morning rush hours, the following table is made:
Table 1. Number of shared bikes required in each region during each time period
|
7:00~7:15 |
7:15~7:30 |
7:30~7:45 |
7:45~8:00 |
8:00~8:15 |
8:15~8:30 |
8:30~8:45 |
8:45~9:00 |
|
|
Residential area 1 |
20 |
100 |
150 |
180 |
120 |
100 |
17 |
15 |
|
Residential area 2 |
26 |
130 |
170 |
200 |
140 |
100 |
20 |
16 |
|
Total |
46 |
230 |
320 |
380 |
260 |
200 |
37 |
31 |
According to the actual situation, in the morning rush hour, about 30% of people start from residential areas, use shared bikes and arrive at subway stations; 70% start from residential areas, use shared bikes and arrive at office buildings. Therefore, this paper makes the following table of the total number of shared bikes in each time period and in each region:
Table 2. Number of shared bikes provided in each region in each time period
|
7:00~7:15 |
7:15~7:30 |
7:30~7:45 |
7:45~8:00 |
8:00~8:15 |
8:15~8:30 |
8:30~8:45 |
8:45~9:00 |
|
|
Number of 1 to subway station in residential area |
6 |
30 |
50 |
50 |
30 |
30 |
5 |
3 |
|
Number of 2 to subway stations in the residential area |
10 |
40 |
50 |
60 |
40 |
40 |
10 |
6 |
|
Number of people from 1 to office buildings in residential areas |
14 |
70 |
100 |
130 |
90 |
70 |
12 |
12 |
|
Number of people from 2 to residential office buildings |
16 |
90 |
120 |
140 |
100 |
60 |
10 |
10 |
|
Number of subway stations to office buildings |
16 |
70 |
100 |
110 |
70 |
70 |
15 |
9 |
Figure 6. Number of unmet shared bikes for empty and no empty vehicles
6.Conclusion
In summary, this paper studies the problem of empty car scheduling of shared bikes, uses statistical analysis and modeling to build a model on the basis of real life to study the problem of empty car scheduling of shared bikes, and makes different assumptions, and compares a better scheduling scheme. In the future, I will consider conducting larger studies and doing more experiments to make the model more complete and practical.
References
[1]. Liu, J., Dai, Y., Yang, F., et al. (2020). Joint coverage site selection and vehicle configuration model of shared bike parking spots. Industrial Engineering and Management, [J].
[2]. Hu, B., Sun, Y., Yuan, S., et al. (2024). Distribution prediction model of shared bikes [J / OL] considering the congestion index. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 1 - 16.
[3]. Gao, F., Li, S., Wu, Z., et al. (2019). Space and temporal characteristics and influencing factors of bike-sharing cycling destinations in the main urban area of Guangzhou. Geographic Research, 38(12), 14.
[4]. Jiang, Y., Jia, S., & Li, J. (2019). Research on shared bike scheduling based on dispatching pool. Traffic Information and Safety, 37(5), 9.
[5]. Zhang, J., Dai, Q., & Ding, Y. (2023). Research on the optimization of shared bike scheduling. Shanghai Management Science, 45(1), 119 - 124.
[6]. Chen, Z., Lin, Z., Jin, J., et al. (2022). Optimization of shared bike scheduling based on spatio-temporal clustering prediction. Journal of Management Engineering, 36(1), 13.
[7]. Zhao, T., & Liao, C. (2020). Research on the optimal scheduling of shared bikes based on market demand. Cooperative Economy and Technology, (9), 4.
[8]. Qi, Y., Liu, Y., & Wang, X. (2024). A shared bike dispatching vehicle: CN202220053317.1 [P]. CN216508694U[2024 - 09 - 12].
[9]. Cao, X., & Luo, Y. (2020). The relationship between urban construction environment and bike-sharing configuration in Chinese mainland. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University: Natural Science Edition, 59(1), 9.
[10]. Zhu, W., Wang, F. X., Yang, K., et al. (2022). Shared bike recommended parking point and user guide strategy planning method. Industrial Engineering and Management, 27(2), 45 - 50.
[11]. Sun, Y., Wang, S., & Wang, J. (2020). Analysis of the problems existing in the operation of shared bikes and their solutions. International Education Forum, 2(2), 10.
[12]. Hu, J. (2021). Research on the scheduling path optimization problem of shared bikes [D]. Southwestern University of Finance and Economics.
[13]. Li, Z., Liu, L., & Wang, C. (2021). Research on the optimization of shared bike scheduling. The Practice and Understanding of Mathematics, 51(6), 11.
[14]. Cai, Z., Huang, P., & Liang, W. (2021). — Take Hefei City as an example. Journal of Hebei North University: Natural Science Edition, 37(1), 6.
[15]. Chen, X. (2021). Case study on sustainable operation management in the bike-sharing industry [D]. University of Electronic Science and Technology.
Cite this article
Jiang,Z. (2024). Study on the empty vehicle scheduling model of shared bikes based on travel characteristics and statistical distribution. Advances in Engineering Innovation,14,48-54.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Engineering Innovation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Liu, J., Dai, Y., Yang, F., et al. (2020). Joint coverage site selection and vehicle configuration model of shared bike parking spots. Industrial Engineering and Management, [J].
[2]. Hu, B., Sun, Y., Yuan, S., et al. (2024). Distribution prediction model of shared bikes [J / OL] considering the congestion index. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 1 - 16.
[3]. Gao, F., Li, S., Wu, Z., et al. (2019). Space and temporal characteristics and influencing factors of bike-sharing cycling destinations in the main urban area of Guangzhou. Geographic Research, 38(12), 14.
[4]. Jiang, Y., Jia, S., & Li, J. (2019). Research on shared bike scheduling based on dispatching pool. Traffic Information and Safety, 37(5), 9.
[5]. Zhang, J., Dai, Q., & Ding, Y. (2023). Research on the optimization of shared bike scheduling. Shanghai Management Science, 45(1), 119 - 124.
[6]. Chen, Z., Lin, Z., Jin, J., et al. (2022). Optimization of shared bike scheduling based on spatio-temporal clustering prediction. Journal of Management Engineering, 36(1), 13.
[7]. Zhao, T., & Liao, C. (2020). Research on the optimal scheduling of shared bikes based on market demand. Cooperative Economy and Technology, (9), 4.
[8]. Qi, Y., Liu, Y., & Wang, X. (2024). A shared bike dispatching vehicle: CN202220053317.1 [P]. CN216508694U[2024 - 09 - 12].
[9]. Cao, X., & Luo, Y. (2020). The relationship between urban construction environment and bike-sharing configuration in Chinese mainland. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University: Natural Science Edition, 59(1), 9.
[10]. Zhu, W., Wang, F. X., Yang, K., et al. (2022). Shared bike recommended parking point and user guide strategy planning method. Industrial Engineering and Management, 27(2), 45 - 50.
[11]. Sun, Y., Wang, S., & Wang, J. (2020). Analysis of the problems existing in the operation of shared bikes and their solutions. International Education Forum, 2(2), 10.
[12]. Hu, J. (2021). Research on the scheduling path optimization problem of shared bikes [D]. Southwestern University of Finance and Economics.
[13]. Li, Z., Liu, L., & Wang, C. (2021). Research on the optimization of shared bike scheduling. The Practice and Understanding of Mathematics, 51(6), 11.
[14]. Cai, Z., Huang, P., & Liang, W. (2021). — Take Hefei City as an example. Journal of Hebei North University: Natural Science Edition, 37(1), 6.
[15]. Chen, X. (2021). Case study on sustainable operation management in the bike-sharing industry [D]. University of Electronic Science and Technology.









