

Volume 16 Issue 6
Published on July 2025This study takes City S, a mega-city in North China, as the research object. Based on a thorough review of relevant literature and theoretical foundations, it employs the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method to construct a multidimensional indicator system encompassing population, economy, society, and ecology. Using statistical data from 2013 to 2020, the study quantitatively analyzes the degree of influence exerted by various driving factors on urban landscape changes. The results show that natural factors, population factors, economic development factors, and social policy factors are the primary drivers of landscape change. Social development and ecological constraints also play a role in the adjustment of urban spatial structure to a certain extent. The study further reveals the comprehensive driving mechanism underlying urban landscape evolution and provides a theoretical basis and methodological support for urban land use optimization and landscape planning. PCA demonstrates strong applicability in identifying multifactor coupling mechanisms and can serve as a scientific reference for the formulation of urban sustainable development strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper proposes a waste heat recovery system that integrates a small-scale Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) power generation unit with an air compressor using lubricating oil. An innovative design directly connects the capacitor to the scroll expander, replacing the traditional generator. Experimental results show that when the lubricating oil is at 105°C and the cooling water at 19°C, the system achieves a maximum power output of 1.754 kW and a thermal-electric efficiency of 3.91%. Once the lubricating oil flow rate exceeds a certain threshold, its impact on efficiency improvement becomes limited, whereas lowering the cooling water temperature significantly enhances efficiency (3.91% at 19°C, dropping to 2.7% at 30°C). Increasing the capacitor size allows a maximum power output of 1.667 kW and a thermal efficiency of 3.66%. This system offers an efficient solution for recovering waste heat from industrial air compressors.

 View pdf
View pdf


In today's world, High-Performance Computing (HPC) is driving scientific research forward at an astonishing rate, but behind every top HPC device lies a high-load power grid, which has sparked deep concern among environmentalists. This study develops a mathematical model to evaluate the power consumption of global HPC equipment and quantify its environmental impact, providing a basis for energy optimization and sustainable development. By systematically analyzing the global environmental impact of HPC through a series of models focused on energy consumption and related emissions, we first created a GPU survival function to estimate the global number of HPC devices in 2023. Using Monte Carlo simulation and Markov chain models, we estimated the power consumption of individual HPC centers under both full load and average utilization conditions, subsequently calculating the total annual power consumption of global HPC centers. Next, we developed models to estimate the total carbon emissions from global HPC energy consumption, considering various energy production methods and energy mix scenarios. Additionally, we created a gray prediction model to forecast the GPU market value in 2030, combining it with the GPU survival function to predict the number of global HPC centers in 2030. We also developed an electricity price fluctuation model to account for increased energy demand from other sectors and analyzed the environmental impact of global HPC centers in 2030 under different energy mix structures. Furthermore, we extended the model to assess the impact of increasing renewable energy (specifically wind energy) to 100% in the energy mix, evaluating its potential to reduce carbon emissions. Finally, we conducted a sensitivity analysis, incorporating seawater cooling for HPC centers and artificial intelligence to dynamically adjust GPU power based on wind speed predictions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Environmentally friendly lead-free metal halide scintillators have attracted significant research interest in recent years in the field of radiation detection due to their low toxicity and outstanding radioluminescent properties. However, enhancing the luminescence performance of lead-free metal halide scintillators and fabricating thin films that integrate high light output, high spatial resolution, and excellent compatibility with photodetectors remain major challenges. To address these issues, this study employs Cs₃Cu₂I₅ as the scintillating material and introduces Terbium (Tb) doping to tune its emission to match current photodetectors. A high-refractive-index flexible UV-curable adhesive, NOA170F, is used as the matrix to synthesize a Cs₃Cu₂I₅: Tb scintillating thin film featuring a large Stokes shift, high luminescence intensity, low cost, environmental friendliness, and good stability. The luminescence mechanism and X-ray scintillation properties of the film are also investigated.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the era of digital communication, the exponential growth of user-generated content across social media and online platforms has intensified the demand for effective emotion analysis tools. Traditional text-based sentiment analysis methods, however, often fall short in accurately capturing the nuances of human emotions due to their reliance on a single modality. Motivated by the need for more comprehensive and context-aware emotion recognition, this study systematically reviews the literature on both unimodal and multimodal aspect-level sentiment analysis. By comparing different approaches within the multimodal domain, we identify existing challenges and emerging trends in this research area. Our findings highlight the potential of integrating multiple modalities—such as text, images, and audio—to enhance the precision of sentiment detection and suggest future directions for advancing multimodal sentiment analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf


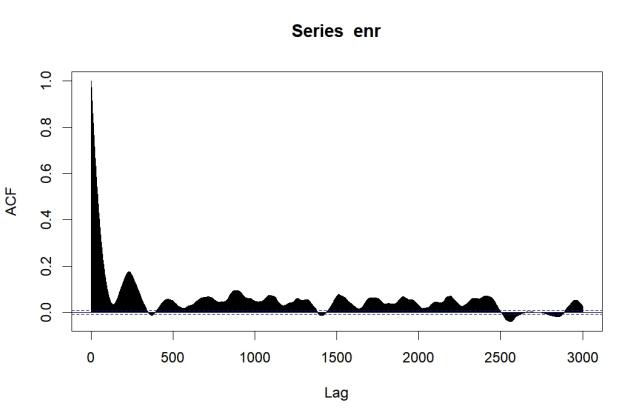
Against the backdrop of Electric Vehicle (EV) proliferation, accurately predicting the spatiotemporal distribution of charging demand is crucial. However, traditional methods face considerable challenges. This study aims to uncover the dynamic patterns of charging demand and construct a predictive framework. Methodologically, the ARIMA time series model is employed to analyze temporal features, Moran’s I index is used to assess spatial autocorrelation, and K-means clustering identifies spatial patterns. Pearson correlation and spatial regression models are integrated to quantify the influence of geographic dependency and socioeconomic factors. The results reveal a "dual-peak" temporal distribution and a "multi-core" spatial aggregation pattern of charging demand. Traffic flow and regional functional types are identified as key influencing factors.

 View pdf
View pdf


Accurate viewport prediction is crucial for enhancing user experience in 360-degree video streaming. However, due to significant behavioral differences among user groups, traditional single LSTM models tend to fall into local optima and fail to achieve precise predictions. To address this, this paper proposes a hybrid prediction model based on user clustering. First, a Density-Based Clustering Algorithm (DBSCAN) is used to group users with similar behavioral patterns. Then, a hybrid prediction model combining Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs) is designed to effectively mitigate data imbalance and overfitting through collaborative training. Experiments conducted on three real-world datasets from YouTube demonstrate that this approach significantly outperforms existing methods based on user trajectories or video saliency in terms of prediction accuracy and stability.

 View pdf
View pdf


Dielectric loss microwave absorbing materials have been widely used to mitigate electromagnetic interference and achieve radar stealth. Their design and optimization involve multiple electromagnetic parameters, such as dielectric constant, magnetic permeability, and loss factors. Traditional optimization methods typically require extensive computation and experimentation, making them inefficient and prone to local optima. In recent years, neural network algorithms, as effective nonlinear modeling and optimization tools, have found growing applications in optimizing the performance of absorbing materials. This paper explores the application of neural networks in optimizing electromagnetic parameters of dielectric loss microwave absorbing materials. Using neural networks, we predict the reflectivity values under different electromagnetic parameters and examine the patterns of variation with frequency and thickness. The results show that optimal reflectivity for various frequencies corresponds to different sets of electromagnetic parameters and matching thicknesses. As the frequency increases, the optimal dielectric constant values (both real and imaginary parts) concentrate in a lower range, especially when the material thickness is small. Finally, the consistency between predicted and experimentally measured reflectivity values confirms the reliability of the neural network-based predictions.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper presents a comprehensive review of the key technologies and recent developments in the field of Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (CUAV), systematically analyzing the latest developments in flight platform technology, propulsion and energy technology, and navigation and control systems. Special attention is given to the performance characteristics and application scenarios of fixed-wing, multi-rotor, and composite flight platforms, as well as to the advantages and limitations of lithium-ion and hydrogen fuel cells in terms of endurance, and the role of multi-sensor data fusion algorithms in navigation and control. By examining practical cases from typical fields such as aerial photography, logistics, and agriculture, this paper summarizes current technological achievements and application trends. Furthermore, it analyzes challenges in areas such as regulations and airspace management, safety, and technical limitations, while proposing future directions including technology integration, quantum communication, bio-inspired drones, and privacy and data protection. The research indicates that with the deeper application of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and quantum communication, CUAV will achieve new breakthroughs in intelligence, autonomy, and safety, providing strong technological support for low-altitude economy and smart society.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid development of industries such as artificial intelligence and big data, the demand for liquid cooling in data centers is continuously increasing. Among various technologies, cold plate liquid cooling has become one of the most widely applied methods. The performance and quality of components in the cooling system directly affect its operational and maintenance costs. This paper focuses on fluid connectors in liquid cooling systems, exploring key technical factors influencing their performance. It introduces process methods covering the entire production cycle from part machining to assembly and testing, and elaborates on critical control points at each manufacturing stage. The aim is to improve the technological level of fluid connectors. Finally, the paper briefly introduces new materials and technologies applied to fluid connectors and presents prospects for the future development of the liquid cooling industry.

 View pdf
View pdf




