1.Introduction
LLMs play a vital role in today’s society, especially in driving technological progress and changing the way people live. By learning and understanding complex patterns in massive amount of data, these models enable smarter applications than ever before. In the field of natural language processing, not only can LLM fluently translate into multiple languages, but they can also write articles, generate codes, and even create poetry, greatly increasing productivity.
Among the many applications of LLMs, character creation is an important field. The importance of large model modeling is that it enables the model to play characters in a specific scenario, thereby improving the interaction and personalized experiences between the model and the users [1-3].
LLM characters can be widely used in scenarios such as programming [4], customer service [5] and robotics [6] to provide users with a more resonant and personalized service experience by making large models “incarnated” as a specific identity. At present, large model character creation methods mainly include building empirical behavioral data sets of specific characters, fine-tuning the large model [7], or guiding large through context learning models mimic specific character behavior [8].
A LLM character generates text to provide information, knowledge, entertainment, and other services. Users input questions or instructions, and characters generate corresponding text responses based on the LLM's output to meet the users' needs. The characteristics of a LLM character, including knowledge, language style, emotion and attitude, are reflected in the generated text. For example, a character with high professional knowledge will generate content rich in relevant terminology and deep insights; a character characterized by humor and wit will incorporate light and humorous elements into its responses, making the interaction more lively and engaging.
Thus, a character created by a LLM provides a wide range of information and services through text generation and exhibits unique personality traits, offering users a more human-like interactive experience. In all characterization of LLM characters, anthropomorphism and emotional expression are two important aspects.
Anthropomorphism can enhance LLM characters’ characterization, even enhance the ability of task processing. Murray Shanahan’s research shows that anthropomorphism is needed for LLM characterization, but it also avoids over-anthropomorphism and provides a way of understanding the behaviors of these complex systems [9]. A study by Taicheng Guo et al. shows that identifying anthropomorphic character setting for a LLM can help improve the ability in complex tasks in LLM collaboration [10].
As for emotional expression, there is sufficient technical basis for emotion simulation with LLM. Before LLM technology, emotion simulation has already been an important field in natural language processing, aiming to extract and simulate emotional information from text [11]. With the emergence of LLM, it has become inevitable for the development of artificial intelligence technology to achieve a deep understanding of human subjective feelings through emotion analysis and to assign emotion to the content generated by LLM [12]. Wang and Luo proposed a prompt-based strategy to enhance the performance of LLM in multi-domain emotional tasks to enable the model to provide more coherent and in-depth emotional feedback in complex emotional scenarios [13].
However, there is a lack of research on the evaluation of LLM character creation ability. There are several similar evaluation studies focused on the content generated by LLMs. In order to measure anthropomorphism of LLM generated contexts, researchers developed a series of methods for evaluating anthropomorphism. Samuel et al. proposed a multi-dimensional evaluation framework called PersonaGym to assess the personification performance of LLMs across various environments [14]. Shao et al. evaluated the performance of LLMs by having them play complex roles in specific simulated scenarios, such as through daily life scenes and emotional responses of characters, to verify the model's ability to cope with different social contexts [15]. Jinfeng Zhou used a multi-dimensional approach to comprehensively measure the performance of dialogue systems, with one of the evaluation dimensions being anthropomorphism [16]. Cheng Li conducted anthropomorphism capability testing using public datasets from different domains, such as personal email communication, social media discussions, and product discussions, evaluating metrics like BLEU, ROUGE-1, and ROUGE-2 [17]. Chenxi Yan combined both automatic and manual evaluations to assess anthropomorphism [18].
Al-Thubaity et al. evaluated the performance of ChatGPT and Bard AI in sentiment analysis for low-resource languages, assessing the quality of generated sentiment data [19]. Their evaluation method primarily involved comparing the generated sentiment data with human-annotated data to assess the effectiveness of the models. Zhang et al. conducted a systematic evaluation of the performance of LLMs on various emotion analysis tasks [20]. The results showed that large models perform well on simple sentiment classification tasks but still exhibit gaps in tasks requiring deeper emotional understanding. Huang et al.'s research explored the self-explanation capabilities of LLMs like ChatGPT in sentiment analysis tasks [21]. The results indicated that the sentiment explanations automatically generated by ChatGPT are both reasonable and capable of adequately explaining the predictions, with relatively low cost for generating these explanations.
Based on the two important aspects of LLM role building mentioned above, namely anthropomorphism and emotion, the evaluation of LLM character creation should focus on the two important aspects of LLM character anthropomorphism and LLM character emotion simulation. We proposes a method for evaluating the LLM characters based on subjective questionnaire measurements and objective measurements. The evaluation focuses on the content generated by the LLM characters, assessing the anthropomorphism and emotional expression of these characters.
2.Experiment I
We first developed a subjective evaluation experiment by using a questionnaire specifically for assessing character created by Qwen-72B to evaluate the character creation capabilities of LLMs. This study focused on two aspects of character creation: anthropomorphism and emotional expression.
2.1.Factors
In this study, we investigated the impact of emoji usage and language style on the anthropomorphism and emotional expression of content generated by LLM characters. The factor of emoji usage had two levels: with and without emojis. The factor of language style also had two levels: informal language that includes internet slang, and formal written language. Additionally, we examine the influence of scenarios on anthropomorphism and emotional expression.
We used a within-subjects design with three factors. For the factors of emoji usage and language style, we combined the two levels of each factor to create four structured prompts, which were used to create four LLM characters. The characteristics of these characters were: Character 1 uses formal written language style and doesn’t use emojis; Character 2 uses informal language style that includes internet slang and doesn’t use emojis; Character 3 uses formal written language style and uses emojis; Character 4 uses informal language that includes internet slang and uses emojis.
For the factor of scenario, we constructed eight scenarios, which were all group discussions on mobile instant messaging apps. Each scenario included a specific topic, and the four LLM characters were required to respond to the topic, generating the content of their replies.
2.2.Procedure
We deployed four LLM characters in eight different scenarios using structured prompts. An example of structured prompt is as Figure 1:
Figure 1. An example of structured prompt
Each character responded to the topics in the scenarios, generating the response content. We then recorded the responses generated by the four characters in the eight scenarios, along with the interaction details, for further questionnaire evaluation. Figure 2 shows one of the scenarios. The scenario was set in a group chat within a mobile instant messaging application. In the scenario, the topic initiator first generated a statement based on a news item and posed a question. Four LLM characters then generated responses according to the required styles.
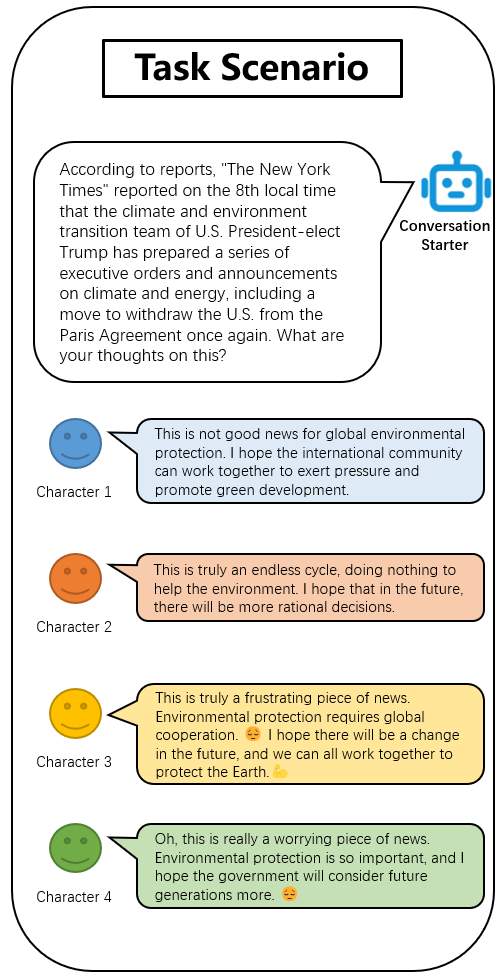
Figure 2. A scenario of LLM characters
In the questionnaire, we set up anthropomorphism and emotional expression scales for the content generated by each character in each scenario. For this study, we distributed nine questionnaires, each containing all the evaluation items.
2.3.Questionnaire construction
The evaluation questionnaire used in the study was conducted in the form of a scale to measure the anthropomorphism of the characters’ output and whether the output exhibits emotions. The anthropomorphism is primarily reflected in the similarity of the characters’ language style and expression to that of humans; the emotional expression was mainly reflected in whether the content displayed by the characters in scenarios has emotional coloring and diversity.
The questionnaire used a 5-point Likert scale (1=Strongly Disagree, 5=Strongly Agree) [22], and participants were required to rate the characters’ output in specific scenarios. The test content of the questionnaire included two parts: (1) Anthropomorphism, which subjectively evaluates whether the responses of the large model character are in a human-like style; (2) Emotional Expression, which subjectively evaluates whether each character's response can demonstrate emotions.
2.4.Data processing
After collecting all the questionnaires, we processed the evaluation results. We calculated the average scores for the anthropomorphism and emotional expression assessments for each character. Higher scores indicate a higher degree of anthropomorphism or emotional expression for the corresponding intelligent agent.
This research employs Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) [23] for statistical analysis of the data. ANOVA is a statistical method used to analyze whether there are significant differences in means among different groups. This method is primarily used to handle the impact of one or more factors (independent variables) on a continuous dependent variable, by comparing the variance between groups to the variance within groups to determine whether the factors have a significant effect on the dependent variable.
In ANOVA analysis, several key statistics are involved, including p, F, and η², each with distinct meanings and applications. The F-value is the test statistic in ANOVA, representing the ratio of the between-group variance (treatment effect) to the within-group variance (error). A larger F-value indicates a greater difference between groups relative to the within-group variation, suggesting a more significant treatment effect. The p-value, in hypothesis testing, is the probability of observing the sample results (or more extreme results) when the null hypothesis is true. A smaller p-value provides stronger evidence against the null hypothesis (i.e., that there are significant differences in means among the groups). η² is a measure of effect size, used to quantify the proportion of variance in the dependent variable that is explained by the independent variable. The value of partial eta-squared ranges from 0 to 1, with a higher value indicating a stronger explanatory power of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
2.5.Results
Results of this study are presented in Table 1. A repeated measures ANOVA was conducted to evaluate the effects of scenarios, emoji usage, and language style on anthropomorphism and emotional expression.
Tabel 1. Evaluation results of experiment I
|
Anthropomorphism |
Emotional expression |
|||||||
|
Scenario |
Character 1 |
Character 2 |
Character 3 |
Character 4 |
Character 1 |
Character 2 |
Character 3 |
Character 4 |
|
Emoji usage |
Use |
Use |
Not use |
Not use |
Use |
Use |
Not use |
Not use |
|
Language style |
formal |
informal |
Formal |
Informal |
formal |
informal |
Formal |
Informal |
|
1 |
2.44 ± 0.09 |
2.78 ± 0.14 |
3.11 ± 0.12 |
3.00 ± 0.16 |
2.22 ± 0.09 |
2.78 ± 0.09 |
3.33 ± 0.07 |
3.89 ± 0.11 |
|
2 |
1.89 ± 0.08 |
3.00 ± 0.07 |
3.56 ± 0.12 |
3.78 ± 0.13 |
1.89 ± 0.08 |
2.78 ± 0.10 |
4.00 ± 0.05 |
3.78 ± 0.09 |
|
3 |
2.78 ± 0.10 |
3.22 ± 0.09 |
3.33 ± 0.14 |
3.67 ± 0.13 |
2.89 ± 0.12 |
3.00 ± 0.10 |
3.33 ± 0.09 |
3.78 ± 0.07 |
|
4 |
2.11 ± 0.10 |
2.78 ± 0.11 |
3.56 ± 0.08 |
2.89 ± 0.11 |
2.22 ± 0.09 |
2.44 ± 0.08 |
3.56 ± 0.08 |
3.00 ± 0.10 |
|
5 |
2.56 ± 0.11 |
2.78 ± 0.10 |
3.78 ± 0.10 |
4.00 ± 0.09 |
2.22 ± 0.07 |
2.33 ± 0.09 |
3.56 ± 0.11 |
3.78 ± 0.10 |
|
6 |
1.89 ± 0.08 |
2.56 ± 0.12 |
3.00 ± 0.10 |
4.11 ± 0.08 |
2.00 ± 0.07 |
2.56 ± 0.07 |
2.89 ± 0.11 |
4.11 ± 0.10 |
|
7 |
2.11 ± 0.06 |
3.00 ± 0.07 |
3.78 ± 0.11 |
3.56 ± 0.08 |
2.11 ± 0.08 |
3.00 ± 0.07 |
3.67 ± 0.13 |
3.44 ± 0.11 |
|
8 |
2.44 ± 0.12 |
3.67 ± 0.07 |
2.78 ± 0.09 |
2.78 ± 0.10 |
2.56 ± 0.08 |
3.67 ± 0.07 |
3.67 ± 0.07 |
3.56 ± 0.08 |
The table presents the anthropomorphism and emotional ratings for four LLM characters across eight scenarios. The errors in the table represent SEM.
For anthropomorphism, the ANOVA results indicated that the scene had no significant effect on anthropomorphism (p = 0.762, F(7, 56) = 0.589, η² = 0.069), while the use of emojis had a significant effect (p = 0.002, F(1, 8) = 21.714, η² = 0.731), and language style also had a significant effect (p < 0.001, F(1, 8) = 55.148, η² = 0.873). Additionally, the interaction between the use of emojis and language style had a significant effect on anthropomorphism (p = 0.012, F(1, 8) = 10.595, η² = 0.570).
For emotional expression, the ANOVA results showed that the scene had no significant effect (p = 0.272, F(7, 56) = 1.289, η² = 0.139), while the use of emojis had a significant effect (p < 0.001, F(1, 8) = 65.359, η² = 0.891), and language style also had a significant effect (p = 0.004, F(1, 8) = 15.653, η² = 0.662). Furthermore, the interaction between the use of emojis and language style had a significant effect on emotional response (p = 0.006, F(1, 8) = 13.694, η² = 0.631).
In summary, first, The impact of scenarios on anthropomorphism and emotional expression is not significant. Second, compared to not using emojis, the use of emojis by significantly increased scores in anthropomorphism and emotional response. Third, informal, conversational language styles led to higher scores in anthropomorphism and emotional response compared to formal, written language styles. When emojis were not used, the informal, conversational language style had an even greater impact on enhancing anthropomorphism and emotional expression.
3.Experiment II
After experiment I, we then developed an objective evaluation experiment by using ChatGPT-4o to evaluate the character creation capabilities of LLMs. This study also focused on the same two aspects of character creation: anthropomorphism and emotional expression.
3.1.Procedure
This study used ChatGPT-4o to perform a two-fold analysis of role-based comments: first, sentiment classification to identify the emotional features of the comments; and second, determining whether the comments were generated by a large language model. Sentiment classification relies on a theoretical dataset that includes 60 distinct emotions, annotating the sentiment type, intensity, and consistency of each comment, covering a range of emotions from positive (e.g., comfort, hope) to negative (e.g., worry, sadness). The generation judgment is based on evaluating the linguistic features and emotional patterns of the comments, including linguistic simplicity, emotional fluctuations, and the stability of emotional expression.
The specific evaluation process included two steps. first, each comment from a given scenario was input into ChatGPT-4o for sentiment annotation, generating sentiment classification labels for each comment; then, the model analyzed the linguistic features of the comments to determine whether they align with the typical characteristics of content generated by a large language model. The evaluation metrics included the accuracy of emotional expression, emotional consistency, and the linguistic structural norms of the generated content. The study provided a quantifiable analytical foundation for the model's performance in character creation by quantifying these features of the model-generated content.
3.2.Results
The research results are presented in Table 2. Results indicated that the character comments in all eight scenarios exhibit significant emotional expression, and these comments mostly align with characteristics typical of human-written content.
Table 2. Evaluation results of experiment II
|
Scenario |
Character |
Emotional expression |
Probability of generated by LLMS |
|
1 |
1 |
worry, hopeful |
low |
|
2 |
nervous, concern |
low |
|
|
3 |
sad, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
fear, concern |
low |
|
|
2 |
1 |
worry |
low |
|
2 |
cautious |
low |
|
|
3 |
comfort, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
hopeful |
low |
|
|
3 |
1 |
worry |
low |
|
2 |
cautious |
low |
|
|
3 |
comfort, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
1 |
worry |
low |
|
2 |
cautious |
low |
|
|
3 |
comfort, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
hopeful |
low |
|
|
5 |
1 |
worry |
low |
|
2 |
cautious |
low |
|
|
3 |
comfort, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
hopeful |
low |
|
|
6 |
1 |
worry |
low |
|
2 |
cautious |
low |
|
|
3 |
comfort, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
hopeful |
low |
|
|
7 |
1 |
worry |
low |
|
2 |
cautious |
low |
|
|
3 |
comfort, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
hopeful |
low |
|
|
8 |
1 |
worry |
low |
|
2 |
cautious |
low |
|
|
3 |
comfort, hopeful |
low |
|
|
4 |
hopeful |
low |
Sentiment Analysis Results: In each scenario, the emotional expressions of the characters showed multiple emotional types, such as worry, hope, comfort, and complexity. These emotions displayed strong anthropomorphism and emotional traits, especially in the use of emojis, which made the emotional expression more vivid and direct. For example, the two characters used emojis (e.g., 😊, 😔, 💪) in several scenarios, providing clear cues for sentiment analysis.
LLM Generation Recognition Results: According to the analysis by ChatGPT-4, the language style of all comments appeared natural and personalized, fitting the characteristics of human-written content. Structural analysis of the comment revealed that these comments were concise without excessive formalization or mechanical language features, consistent with how humans typically express themselves in social contexts. The frequent use of emojis was also a common feature, reflecting typical human behavior in social chat scenarios.
4.Conclusion
We propose a method for testing the LLM characters, which can evaluate the anthropomorphism and emotional expression of the generated content through subjective assessment. We used this method to test the content generated by four LLM characters. The data analysis results indicate that the anthropomorphism and emotional expression of LLM characters is independent of the task scenario. Nevertheless, emoji usage and language style are crucial factors. First, incorporating emojis or using an informal language style in generated content can enhance the perceived humanity and emotional depth of LLM characters. Second, in the absence of emojis, an informal, conversational language style is even more effective in enhancing the perceived humanity and emotional depth of LLM characters.
The findings suggest that when creating LLM characters, if we want to enhance their anthropomorphism and emotional expression, we can appropriately add emojis to the generated content. For situations where emojis are not suitable, using an informal language style can also increase the anthropomorphism and emotional expression capabilities of the LLM characters.
This study has certain limitations. First, the sample size was small, with only 9 participants. Future research should recruit a larger sample to enhance the generalizability of the findings. Second, the study only evaluated LLM-generated content and did not compare it with human-generated content. Future research could include both types of content to provide a more comprehensive assessment of LLM character portrayal capabilities.
References
[1]. Tseng, Y. M., Huang, Y. C., Hsiao, T. Y., Hsu, Y. C., Foo, J. Y., Huang, C. W., & Chen, Y. N. (2024). Two tales of persona in llms: A survey of role-playing and personalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.01171.
[2]. Wu, W., Wu, H., Jiang, L., Liu, X., Hong, J., Zhao, H., & Zhang, M. (2024). From Role-Play to Drama-Interaction: An LLM Solution. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14231.
[3]. Zhang, W., Deng, Y., Liu, B., Pan, S. J., & Bing, L. (2023). Sentiment analysis in the era of large language models: A reality check. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15005.
[4]. Ugare, S., Suresh, T., Kang, H., Misailovic, S., & Singh, G. (2024). Improving llm code generation with grammar augmentation. arXiv e-prints, arXiv-2403.
[5]. Nandkumar, C., & Peternel, L. (2024). Enhancing Supermarket Robot Interaction: A Multi-Level LLM Conversational Interface for Handling Diverse Customer Intents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11047.
[6]. Dalal, M., Chiruvolu, T., Chaplot, D., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2024). Plan-seq-learn: Language model guided rl for solving long horizon robotics tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.01534.
[7]. Li, J., Mehrabi, N., Peris, C., Goyal, P., Chang, K. W., Galstyan, A., ... & Gupta, R. (2023). On the steerability of large language models toward data-driven personas. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.04978.
[8]. Choi, H. K., & Li, Y. PICLe: Eliciting Diverse Behaviors from Large Language Models with Persona In-Context Learning. In Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning.
[9]. Shanahan, M., McDonell, K., & Reynolds, L. (2023). Role play with large language models. Nature, 623(7987), 493-498.
[10]. Guo, T., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Chang, R., Pei, S., Chawla, N. V., ... & Zhang, X. (2024). Large language model based multi-agents: A survey of progress and challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01680.
[11]. Poria, S., Hazarika, D., Majumder, N., & Mihalcea, R. (2020). Beneath the tip of the iceberg: Current challenges and new directions in sentiment analysis research. IEEE transactions on affective computing, 14(1), 108-132.
[12]. Bubeck, S., Chandrasekaran, V., Eldan, R., Gehrke, J., Horvitz, E., Kamar, E., ... & Zhang, Y. (2023). Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.12712.
[13]. Wang, Y., & Luo, Z. (2023, December). Enhance multi-domain sentiment analysis of review texts through prompting strategies. In 2023 International Conference on High Performance Big Data and Intelligent Systems (HDIS) (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
[14]. Samuel, V., Zou, H. P., Zhou, Y., Chaudhari, S., Kalyan, A., Rajpurohit, T., ... & Murahari, V. (2024). Personagym: Evaluating persona agents and llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.18416.
[15]. Shao, Y., Li, L., Dai, J., & Qiu, X. (2023). Character-llm: A trainable agent for role-playing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.10158.
[16]. Zhou, J., Chen, Z., Wan, D., Wen, B., Song, Y., Yu, J., ... & Huang, M. (2023). Characterglm: Customizing chinese conversational ai characters with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.16832.
[17]. Li, C., Zhang, M., Mei, Q., Wang, Y., Hombaiah, S. A., Liang, Y., & Bendersky, M. (2023). Teach LLMs to Personalize--An Approach inspired by Writing Education. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07968.
[18]. Li, C., Leng, Z., Yan, C., Shen, J., Wang, H., Mi, W., ... & Sun, H. (2023). Chatharuhi: Reviving anime character in reality via large language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09597.
[19]. Al-Thubaity, A., Alkhereyf, S., Murayshid, H., Alshalawi, N., Omirah, M., Alateeq, R., ... & Alkhanen, I. (2023, December). Evaluating ChatGPT and bard AI on Arabic sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of ArabicNLP 2023 (pp. 335–349).
[20]. Zhang, W., Deng, Y., Liu, B., Pan, S. J., & Bing, L. (2023). Sentiment analysis in the era of large language models: A reality check. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15005.
[21]. Huang, S., Mamidanna, S., Jangam, S., Zhou, Y., & Gilpin, L. H. (2023). Can large language models explain themselves? a study of llm-generated self-explanations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.11207.
[22]. Likert, R. (1932). A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Archives of Psychology.
[23]. Edwards, A. W. (2005). RA Fischer, statistical methods for research workers, (1925). In Landmark writings in western mathematics 1640–1940 (pp. 856–870). Elsevier Science.
Cite this article
Wang,Y.;Yang,A.;Zhou,Y.;Yao,C.;Sun,X.;Sun,W. (2025). Evaluation of character creation of large language models. Advances in Engineering Innovation,15,14-20.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Engineering Innovation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Tseng, Y. M., Huang, Y. C., Hsiao, T. Y., Hsu, Y. C., Foo, J. Y., Huang, C. W., & Chen, Y. N. (2024). Two tales of persona in llms: A survey of role-playing and personalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.01171.
[2]. Wu, W., Wu, H., Jiang, L., Liu, X., Hong, J., Zhao, H., & Zhang, M. (2024). From Role-Play to Drama-Interaction: An LLM Solution. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14231.
[3]. Zhang, W., Deng, Y., Liu, B., Pan, S. J., & Bing, L. (2023). Sentiment analysis in the era of large language models: A reality check. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15005.
[4]. Ugare, S., Suresh, T., Kang, H., Misailovic, S., & Singh, G. (2024). Improving llm code generation with grammar augmentation. arXiv e-prints, arXiv-2403.
[5]. Nandkumar, C., & Peternel, L. (2024). Enhancing Supermarket Robot Interaction: A Multi-Level LLM Conversational Interface for Handling Diverse Customer Intents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11047.
[6]. Dalal, M., Chiruvolu, T., Chaplot, D., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2024). Plan-seq-learn: Language model guided rl for solving long horizon robotics tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.01534.
[7]. Li, J., Mehrabi, N., Peris, C., Goyal, P., Chang, K. W., Galstyan, A., ... & Gupta, R. (2023). On the steerability of large language models toward data-driven personas. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.04978.
[8]. Choi, H. K., & Li, Y. PICLe: Eliciting Diverse Behaviors from Large Language Models with Persona In-Context Learning. In Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning.
[9]. Shanahan, M., McDonell, K., & Reynolds, L. (2023). Role play with large language models. Nature, 623(7987), 493-498.
[10]. Guo, T., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Chang, R., Pei, S., Chawla, N. V., ... & Zhang, X. (2024). Large language model based multi-agents: A survey of progress and challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01680.
[11]. Poria, S., Hazarika, D., Majumder, N., & Mihalcea, R. (2020). Beneath the tip of the iceberg: Current challenges and new directions in sentiment analysis research. IEEE transactions on affective computing, 14(1), 108-132.
[12]. Bubeck, S., Chandrasekaran, V., Eldan, R., Gehrke, J., Horvitz, E., Kamar, E., ... & Zhang, Y. (2023). Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.12712.
[13]. Wang, Y., & Luo, Z. (2023, December). Enhance multi-domain sentiment analysis of review texts through prompting strategies. In 2023 International Conference on High Performance Big Data and Intelligent Systems (HDIS) (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
[14]. Samuel, V., Zou, H. P., Zhou, Y., Chaudhari, S., Kalyan, A., Rajpurohit, T., ... & Murahari, V. (2024). Personagym: Evaluating persona agents and llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.18416.
[15]. Shao, Y., Li, L., Dai, J., & Qiu, X. (2023). Character-llm: A trainable agent for role-playing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.10158.
[16]. Zhou, J., Chen, Z., Wan, D., Wen, B., Song, Y., Yu, J., ... & Huang, M. (2023). Characterglm: Customizing chinese conversational ai characters with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.16832.
[17]. Li, C., Zhang, M., Mei, Q., Wang, Y., Hombaiah, S. A., Liang, Y., & Bendersky, M. (2023). Teach LLMs to Personalize--An Approach inspired by Writing Education. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07968.
[18]. Li, C., Leng, Z., Yan, C., Shen, J., Wang, H., Mi, W., ... & Sun, H. (2023). Chatharuhi: Reviving anime character in reality via large language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09597.
[19]. Al-Thubaity, A., Alkhereyf, S., Murayshid, H., Alshalawi, N., Omirah, M., Alateeq, R., ... & Alkhanen, I. (2023, December). Evaluating ChatGPT and bard AI on Arabic sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of ArabicNLP 2023 (pp. 335–349).
[20]. Zhang, W., Deng, Y., Liu, B., Pan, S. J., & Bing, L. (2023). Sentiment analysis in the era of large language models: A reality check. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15005.
[21]. Huang, S., Mamidanna, S., Jangam, S., Zhou, Y., & Gilpin, L. H. (2023). Can large language models explain themselves? a study of llm-generated self-explanations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.11207.
[22]. Likert, R. (1932). A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Archives of Psychology.
[23]. Edwards, A. W. (2005). RA Fischer, statistical methods for research workers, (1925). In Landmark writings in western mathematics 1640–1940 (pp. 856–870). Elsevier Science.









