1. Introduction
1.1. Research background
Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) represents a technological paradigm that intricately fuses communication and sensing functionalities, thereby facilitating their mutual augmentation.
From one perspective, communication networks can be conceptualized as an extensive distributed sensor array. Through the transmission and reception of wireless signals by network elements and the exploitation of the transmission, reflection, and scattering properties of radio waves, essential information about the physical world, such as distance, velocity, and angle, can be gleaned. Leveraging this information, ISAC underpins a diverse range of emerging services. These include high-precision positioning, gesture recognition, motion detection, passive target tracking, imaging, and environmental reconstruction, thus materializing the concept of “Network as a Sensor”.
Conversely, sensing capabilities are of paramount importance in enhancing communication performance. The high-precision positioning, environmental characterization, and spatial mapping derived from sensing can substantially optimize communication systems. This optimization enables more accurate beamforming, swifter beam failure recovery, and more cost-effective CSI tracking. Notably, sensing functions as a novel conduit bridging the physical and digital realms. It enables real-time collection and analysis of environmental features, which can then be mapped into the digital domain. This capacity furnishes the technical groundwork for constructing a “digital twin” that parallels the real world and renders low-cost intelligent sensing applications based on Wi-Fi viable within home environments.
1.2. Research significance
The existing body of research on contactless sensing technologies can be systematically classified into several distinct categories, namely: sensing techniques found on Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology [6], continuous wave radar-based sensing [7], sensing based on the ZigBee protocol [8], and Wi-Fi based sensing [9]. Among these various sensing approaches, Wi-Fi stands out with notable advantages in the integration of communication and sensing functions. This is primarily attributed to its extensive network coverage and the well-established and mature infrastructure it relies upon. In the specific context of smart home applications, Wi-Fi technology has been widely and deeply embraced. Most smart appliances are now equipped with Wi-Fi connectivity, which has effectively given rise to a comprehensive device control and connection network built upon the Wi-Fi 6 standard.
To attain full-scale intelligent automation throughout the home, it is essential to have not only stable device connectivity and precise control mechanisms but also the ability to provide proactive services. Intelligent sensing plays a pivotal role as the fundamental technical enabler for facilitating such proactive services. Consequently, the development of an efficient intelligent sensing solution that capitalizes on the stable connectivity and rich channel information inherent in existing Wi-Fi 6 networks represents a critical and indispensable step on the path towards achieving intelligent control within smart homes.
This research endeavor integrates CSI-based sensing research and conducts repeated validation using experimental data collected in actual home environments. It puts forward a novel sensing framework and methodology based on Wi-Fi 6. This proposed solution places a strong emphasis on both the feasibility of implementation and the practical requirements and demands of smart home scenarios. Considering the unique characteristics of home environments, a communication-sensing integrated CSI framework specifically tailored for household use is introduced. This framework not only offers theoretical underpinnings and practical guidance for contactless sensing applications in residential settings but also lays a solid technical foundation for the diversified and expansive development of intelligent services in the future.
2. Related works
2.1. Research status of CSI-based sensing technology
The overarching aim of this research is to make use of the extant home Wi-Fi 6 network infrastructure to endow hardware devices with sensing capabilities. The focus lies on the relationships between devices and space, as well as human-device interaction. More specifically, this study is directed towards the following aspects:
• Detection of user activities.
• Identification of the relative positions of devices within the spatial context.
• Establishment of correlations between users and their surrounding environment.
These objectives seek to integrate communication and sensing through the application of Wi-Fi 6 technology. The ultimate goal is to propel the intelligent and human-centered development of smart home applications.
2.2. Challenges of CSI sensing in home environments
Implementing activity sensing, gesture recognition, or user localization using existing Wi-Fi 6 devices in home environments is fraught with challenges, which can be mainly attributed to several crucial factors.
2.2.1. Channel state switching and interference issues
The stability of CSI is of utmost importance for detecting signal channel variations induced by human activities. In home environments, nonetheless, intense interference and abrupt channel switching exert a substantial influence on CSI stability. For instance, certain routers dynamically modify beam directions or switch channels in accordance with network quality to enhance communication performance. These automated adjustments result in recurrent CSI fluctuations (as depicted in the Figure 1), diminishing the calibration precision of traditional algorithms and undermining their capacity to identify human activities within stable environments.
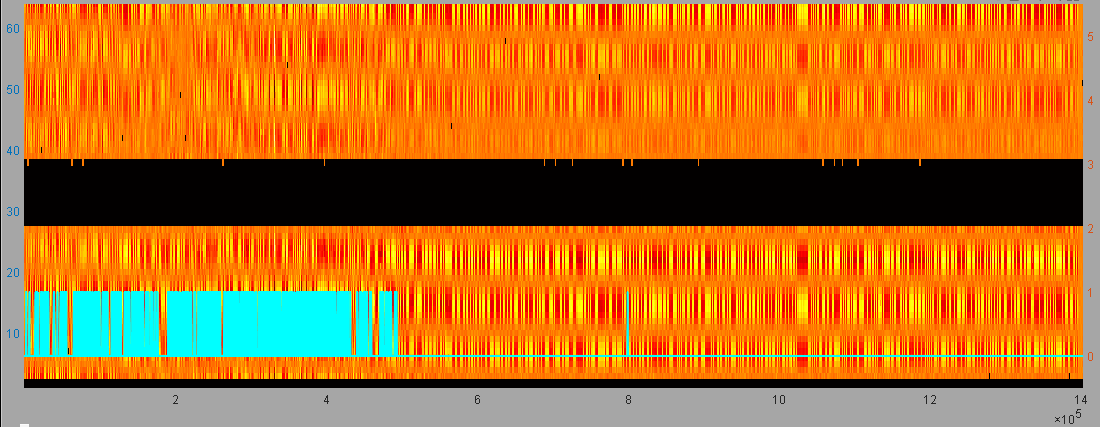
Figure 1. Frequent CSI state switching by router
(horizontal axis represents time, vertical axis represents subcarriers, and the cyan curve indicates human activity)
2.2.2. CSI generalization issue in complex environments
In contrast to the relatively ideal wireless signal propagation circumstances in laboratory settings, the propagation of wireless signals in home environments is far more intricate. The superposition of direct, reflected, and transmitted waves elevates the amplitude and complexity of CSI fluctuations. This not only renders it more likely for subcarrier alterations stemming from human movement to be conflated with channel noise, thereby diminishing the signal-to-noise ratio for motion detection, but also gives rise to unforeseen sensing ranges, such as wall penetration (as presented in Figure 2). Such an unpredictable sensing range exerts a substantial impact on user experience and system stability.
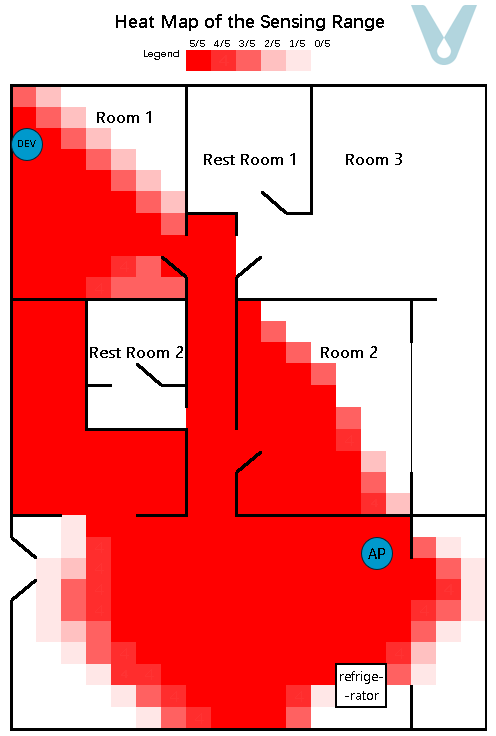
Figure 2. Wall penetration phenomenon in CSI sensing
2.2.3. Performance differences of heterogeneous terminal devices
Within home environments, diverse types of terminal devices may co-exist on the same network, thereby posing numerous challenges to CSI sensing. First and foremost, different router brands are likely to adopt distinct channel-switching strategies. This situation can further aggravate the problem of CSI generalization. Secondly, in a heterogeneous terminal environment, certain low-end devices with restricted computational resources may encounter difficulties in supporting complex sensing algorithms. Moreover, disparities in the Radio-Frequency (RF) circuit designs among various terminals can directly impact the quality of CSI and the performance of sensing.
To sum up, CSI sensing technology in home environments confronts multiple obstacles, such as channel instability, environmental interference, and generalization problems across heterogeneous devices. Overcoming these challenges is fundamental to attaining stable and reliable integration of Wi-Fi 6 communication and sensing.
2.3. Technical approach
The technical approach, contingent upon the level of technical implementation and the degree of functional complexity, is bifurcated into two core and pivotal technologies.
2.3.1. Single-device sensing
The principal objective of this research is to accomplish human motion detection using a single device. This endeavor aims to resolve the issues of generalization and adaptation across different router models, all while guaranteeing user-friendliness without the need for user intervention.
The proposed methodology entails enhancing the generalization capacity with respect to diverse router models and improving usability via techniques for adaptive Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) enhancement.
Noteworthy accomplishments of this study are as follows:
• Demonstrating broad adaptability to mainstream routers available in the market. The same algorithm can operate stably across a variety of routers, thereby fulfilling the accuracy and stability criteria defined within this research.
• Offering a user-centric, intervention-less experience. This ensures that the system is capable of rapid startup and can maintain long-term stable operation.
2.3.2. Multi-region, multi-device sensing
The principal objective of this research is to augment the multi-device collaborative sensing capacity and enhance the accuracy and granularity of whole-home sensing by means of flexible, fine-grained spatial configuration techniques.
Key implementation aspects are as follows:
• Spatial Granularity Division and Node Clustering: The dynamic configuration and optimization of the spatial sensing ranges for multiple Wi-Fi nodes within the network are carried out. This involves determining appropriate sensing areas for each node based on the layout of the home environment and the distribution of potential sensing targets, aiming to maximize the coverage and minimize redundant sensing areas while ensuring comprehensive monitoring.
• Secondary Fine-Grained Spatial Division: A further optimization of the sensing range for each spatial granularity is conducted to enhance positioning accuracy. By refining the sub-regions within each pre-defined spatial granularity, more precise identification of the location of objects or users can be achieved, considering factors such as signal attenuation, multipath propagation, and interference in different sub-areas.
• User-Space Localization Technology: The accomplishment of accurate user localization and the analysis of user-space correlations are realized using a pure Wi-Fi network. This technology exploits the unique characteristics of Wi-Fi signals, such as signal strength, phase information, and time-of-arrival differences, to precisely determine the location of users within the home environment and understand how users interact with different spaces.
Key achievements of this study are as follows:
• The flexible configuration and dynamic optimization of the spatial sensing ranges for multiple Wi-Fi nodes in the internal network are enabled. This ensures high efficiency and accuracy during node collaboration. The optimized configuration allows nodes to work in harmony, coordinating their sensing efforts to cover the entire home space effectively, with reduced interference among nodes and improved utilization of network resources.
• The sensing precision and positioning stability of users in different areas are significantly improved through secondary fine-grained spatial division. This finer-level division enables more accurate tracking of user movements, even in complex indoor environments with obstacles and varying signal conditions. As a result, the system can provide more detailed and reliable information about user activities in different parts of the home.
• User-space correlation localization based on a pure Wi-Fi network is successfully implemented. This achievement enables precise user localization without the need for additional hardware. By leveraging the existing Wi-Fi infrastructure in the home, the system can accurately determine the location of users, facilitating a wide range of intelligent applications such as personalized service delivery, energy management based on user presence, and security monitoring.
3. Key issues and core technologies
3.1. Adaptive Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) enhancement technology
This technology encompasses pattern filtering and momentum filtering as signal processing methods.
CSI data mirrors the interaction between wireless signals and the environment during their propagation, thereby encapsulating abundant physical information. Nevertheless, within complex home environments, CSI signals are highly vulnerable to multipath effects, co-channel noise interference, and the motion of non-target objects. This vulnerability results in a substantial amount of extraneous information being present in the data. To enhance the accuracy and robustness of subsequent analysis, the effective pre-processing of CSI data is of paramount importance.
Pattern filtering represents a signal selection approach grounded in prior knowledge. Its core concept is to match the features of the signal against known “useful” signal patterns (i.e., prior patterns). By doing so, it retains the desired useful signals while suppressing or eliminating interference components that do not conform to the prior features. Specifically, this algorithm postulates that the target signal exhibits certain statistical properties or structural characteristics and exploits these properties to filter and optimize the data.
The crux of pattern filtering resides in constructing rational “prior patterns” and devising efficient matching mechanisms. In the context of CSI data processing, prior patterns are typically formulated based on real-world data obtained from diverse scenarios and router models. Distinct from feature classification models, the prior patterns in pattern filtering incorporate a more extensive array of sample types that are collected in clean environments and are subject to specific calibration.
Experimental findings demonstrate that the prior knowledge employed in pattern filtering can effectively boost the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of the input signal and enhance the terminal recognition rates (see Figure 3).
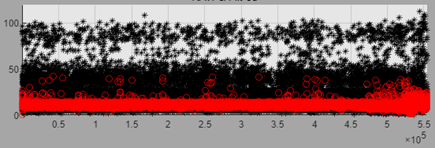
Figure 3. Single subcarrier data after pattern filtering (red curve)
To tackle the disparities in channel characteristics stemming from different Radio-Frequency (RF) channels and environments, a specialized momentum filtering signal processing method is introduced subsequent to sample collection. The fundamental concept behind this method is to continuously accumulate statistical algorithms. This accumulation serves the purpose of adaptively eliminating the Static components and extremely low-frequency components from the signal. The objective is to maximize the retention of mid-to-low-frequency signal components (ranging from 0.02 to 1 Hz) that are associated with human activity.
Momentum filtering exhibits high computational efficiency and demonstrates excellent low-frequency selectivity (see Figure 4). Moreover, the removal of DC components and low-frequency disturbances notably expedite the training speed of subsequent models. It also effectively curtails the quantity of extraneous information. Retaining only the genuinely valid signals is also of critical importance for minimizing resource utilization and enhancing generalization across diverse scenarios.
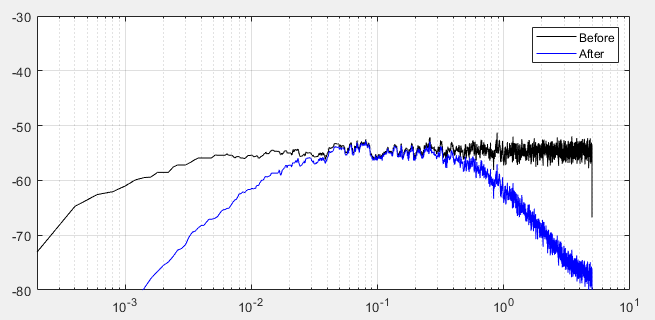
Figure 4. Characteristics of the momentum filtering (blue curve) in very low frequencies
3.2. Adversarial sample generation and quantized perception training for edge deployment
When deploying deep-learning models on low-power, miniaturized edge devices equipped with microprocessors, the resource constraints, such as limited computational power, memory, and storage, pose significant challenges to the direct application of traditional high-precision models. To surmount these obstacles, a combination of lightweight operators, operator fusion techniques, and quantized perception training is employed to enable model deployment at the edge, as detailed below:
1. Lightweight Operators: Through the selection of operators characterized by high computational efficiency and low memory usage, the overall resource consumption of the model is diminished. This strategic choice ensures that the model can operate within the limited resource boundaries of edge devices without sacrificing essential functionality.
2. Operator Fusion: During the network construction process, multiple consecutive operators are proactively merged. This fusion serves to reduce both computational overhead and memory access requirements. By streamlining the computational flow, the model can execute more efficiently on edge devices with restricted resources.
3. Quantized Perception Training (QAT): The central concept of QAT is to integrate quantization simulation into the training phase. By directly incorporating the impact of quantization into the learning process, QAT can substantially reduce the model's storage space and computational burden while preserving model accuracy. This makes the model better suited for deployment on edge devices.
In addition, to address the numerous interference signals that resemble normal human motion patterns yet are relatively sparse, sample augmentation techniques are introduced in the training samples. The core principle involves leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to generate a substantial number of high-quality virtual noise samples. This effectively enhances the model's generalization ability against misleading noise, reduces the incidence of misjudgments, and consequently improves the practical usability of motion sensing (see Figure 5).

Figure 5. Noisy data generated by adversarial network
3.3. Spatial granularity refinement technology
CSI represents a transmission -based path-monitoring approach. It monitors the transmission path between the router and the communication terminal antenna. Significantly, CSI is not circumscribed by a particular space; rather, it has the capacity to encompass the entire transmission path. For instance, this path may span from the kitchen, through the corridor, and into the living room (see Figure 6). This characteristic is commonly denoted as “ubiquitous sensing”.
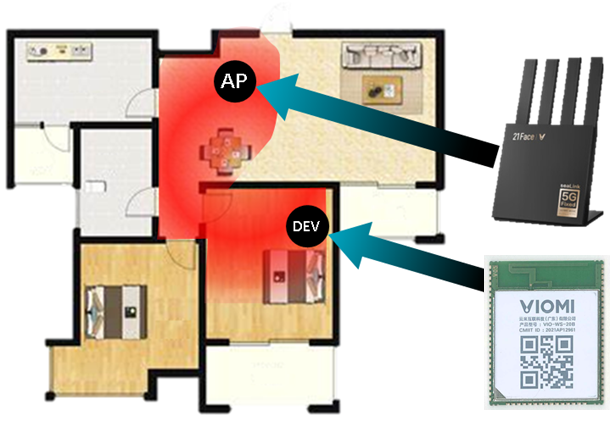
Figure 6. Path characteristics of ubiquitous sensing in a home environment
In the scenario of ideal direct transmission, under the assumption that both the signal source and the receiving node are omnidirectional transceivers, and the signal propagation mainly comprises direct waves, the sensing range of CSI adheres to the Fresnel zone distribution [10]. The so-called Fresnel zone is defined as the concentric elliptical region that is formed with a pair of wireless transceivers (usually a router Access Point (AP) and a sub-device (DEV)) serving as the focal points (see Figure 7).


Figure 7. Sensing range in open space (Fresnel zone)
It can be noted that as the distance between the device and the router increases, the sensing range of CSI becomes larger. However, an overly large sensing range, in combination with a highly complex multipath environment (where there are nearly no direct waves, a large number of reflected waves, and some transmitted waves), leads to unpredictable sensing ranges in home environments. This unpredictability constitutes a major obstacle to the application of CSI sensing in such settings.
To mitigate the sensing range and surmount the problem of user expectation not being met, this study employs a flexible and configurable spatial granularity refinement technique. The fundamental concept is to coordinate multiple devices within the local network for two rounds of spatial granularity division, refining the overlapping sensing ranges in multi-device scenarios. Specifically:
First Spatial Granularity Partitioning: The cloud-based backend exercises centralized control and aggregates network conditions from all device nodes. This includes Time of Flight (TOF) information, Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), and point-to-point fading data provided by Wi-Fi 6 communication devices. Through this data, the spatial distribution of all nodes can be estimated. By issuing commands to establish point-to-point communication between devices, the CSI information of any specified device in space can be retrieved. This enables the control and reduction of the sensing range, thus completing the first spatial granularity partitioning. Second Fine-grained Spatial Partitioning: Experimental results indicate that the impact of human activity at close and distant ranges on the complete CSI signal can be quantified. Hence, by augmenting the network structure, strengthening sample labeling, and enhancing classification capabilities, it becomes feasible to classify the proximity of targets within the given constraints, thereby completing the second fine-grained spatial partitioning (see Figure 8).
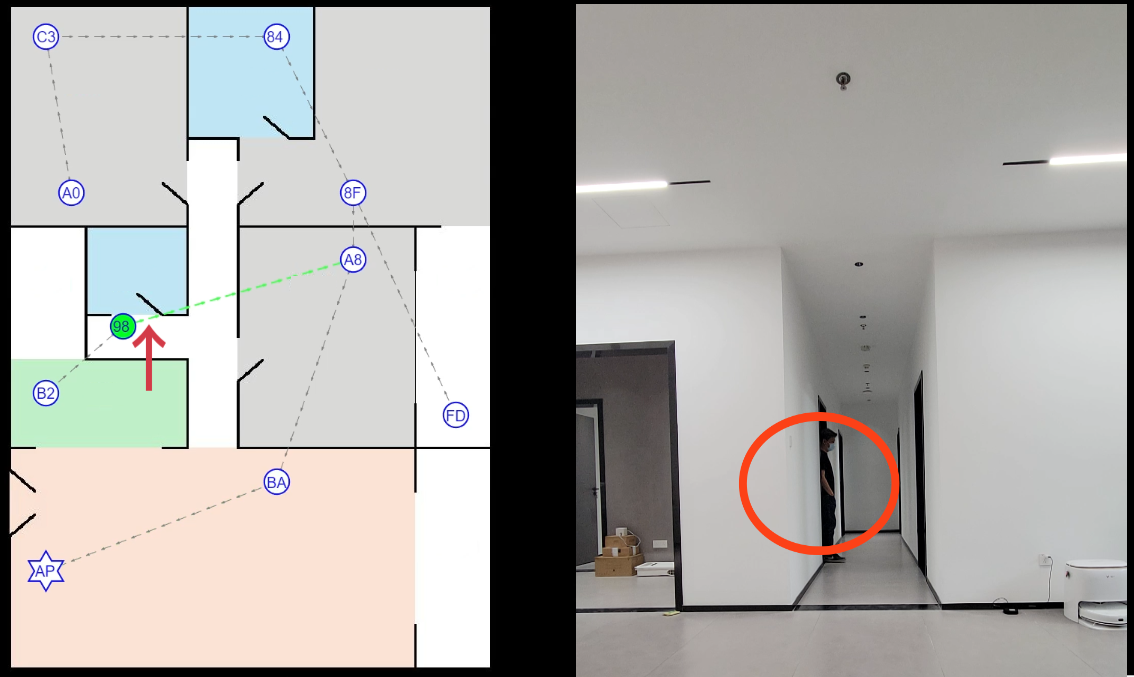
Figure 8. Implementing indoor positioning through spatial granularity refinement technology
4. Results
4.1. Experimental environment and hardware configuration
The experiments were conducted in a laboratory environment that replicated a realistic multi-room setting. The test (see Table 1) components consisted of a multipath fading scenario (aimed at determining the sensitivity and range limits for a single terminal device), a long-term hanging test (intended to evaluate the resilience against random interference effects, channel hopping pressures, and the like), and an experiment regarding the multi-device and multi-region partitioning capability (for assessing the performance of spatial granularity). The detailed experimental conditions are presented as follows:
1. Terminal Device: The communication front-end that is most prevalently utilized in smart homes was employed. In this instance, a self-developed Wi-Fi 6 communication module based on the MediaTek MT7933 was chosen. This module supports 2.4G/5G dual-band connectivity and the collection of raw CSI data.
2. Router Device: Given that there are distinct disparities in the sensitivity and accuracy of the Wi-Fi sensing function, which are attributable to the signal quality of the wireless router. Thus, apart from the Wi-Fi communication module device with the sensing function under test, wireless routers spanning different price brackets need to be prepared.
Table 1. Router models for compatibility testing
Model of Router * | Price positioning |
A-manufacture AX89 | High |
B-manufacture AX3000 | Median |
C-manufacture AX3000 | |
D-manufacture AX3 Pro | |
E-manufacture AX3000 | |
F-manufacture AC1200 | Low |
G-manufacture AC10 | |
D-manufacture AX2 Pro | |
H-manufacture 4C 300M | |
E-manufacture AX1800 | |
I-manufacture AC1900+Mesh |
(* The company name has been replaced with a code.)
3. Sampling Frequency: Taking into account the processing capacity of the terminal device and striving to minimize the load on the Wi-Fi network to the greatest extent possible, a relatively low CSI sampling rate ranging from 30 to 50 Hz has been established.
To illustrate the generalization capability of the algorithm, during the experiment, the signal strength (Received Signal Strength Indicator, RSSI) of various devices at different distances is recorded simultaneously. Moreover, for the long-term hanging test experiment, to demonstrate the anti-interference performance, the raw CSI data retrieved from the air interface of the device will be collected synchronously.
4.2. Experimental scenario setting
In order to mimic the multipath fading scenario, the devices under test and the router are positioned at numerous distinct locations within the simulated realistic multi-room environment. The test combinations are designed to encompass as wide a range of possibilities as can be achieved. The floor plan of the test environment along with the designated test points is depicted in Figure 9.
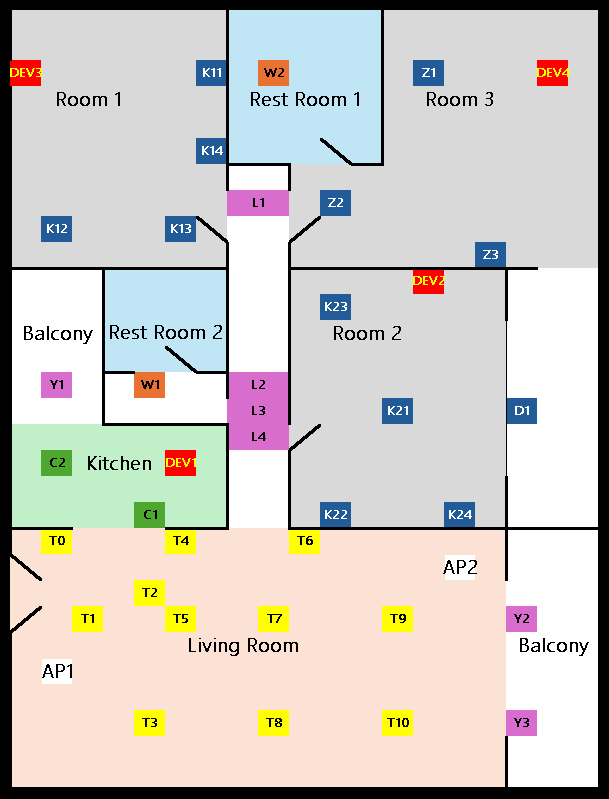
Figure 9. Arrangement of the test environment and points
To replicate the activities of actual users, the signal strength between the device undergoing testing and the router is categorized into three ranges: strong (-30 to -50 dBm), medium (-50 to -65 dBm), and weak (-65 to -75 dBm). The simulated scenario is required to incorporate signal components from direct waves, reflections, and partial penetrations. The hanging test is executed with a full working day serving as the fundamental unit. This test process encompasses the nighttime period when there is no human activity, the peak time with frequent human activities, and the lunch break featuring sporadic activities.
To simulate diverse spatial combination relationships among the devices, two scenarios regarding the router's selectable positions, specifically Position 1 and Position 2, are established. Nine groups of terminal devices under test are arranged within different independent spaces of the entire multi-room area, ensuring that there is at least one terminal device present in each space. One experimenter moves around in various areas of the multi-room, while another experimenter ascertains the real-time sensing status of all terminal devices by analyzing the internal network data packets (see Figure 10).
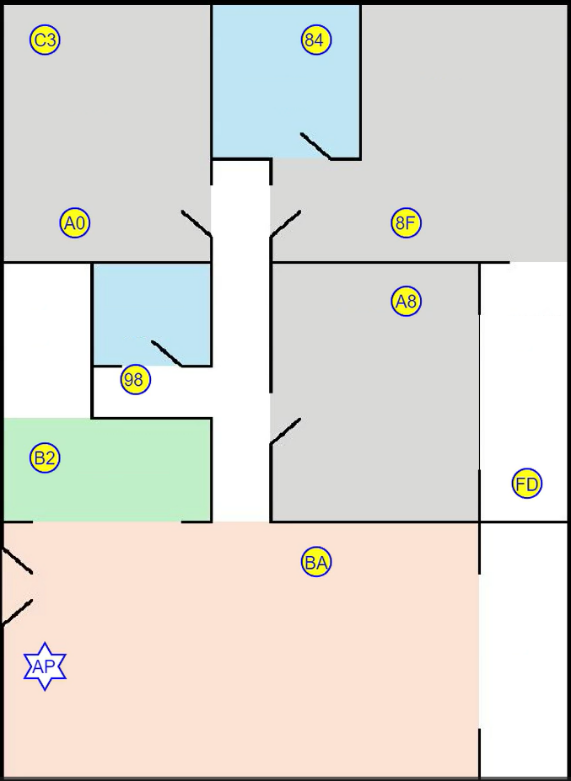
Figure 10. Device layout of the multi-device and multi-region division experiment
(The hexagram is the position of the router, and the yellow circle represents the device)
4.3. Key variables and control experiments
The independent variables consist of the beam control strategy, the adjustment of channel state parameters, the signal modulation method, and the occupancy of Wi-Fi channels in the actual environment.
The dependent variables are made up of crucial indicators like the detection accuracy rate, the false alarm rate, and the sensing range.
Regarding the settings of the control group, it involves disabling certain key technologies as the reference baseline. For instance, in the long-term hanging test experiment, algorithmic post-processing will be performed on the synchronously collected raw data, and then a comparison will be made between the results with and without the application of the mode filtering algorithm. Another case in point is that a comparison can be conducted on the performance of the sensing range, differentiating between the situations with and without the implementation of spatial granularity refinement technology.
4.4. Experimental results and data analysis
4.4.1. Multipath fading experiment of a single terminal
A gridded heat map, where the unit of measurement is 0.5 meters, is employed to depict the recognition success rate within the test area. To render the sensing boundary more visually explicit, each grid within the heat map undergoes testing five times (see Figure 11).
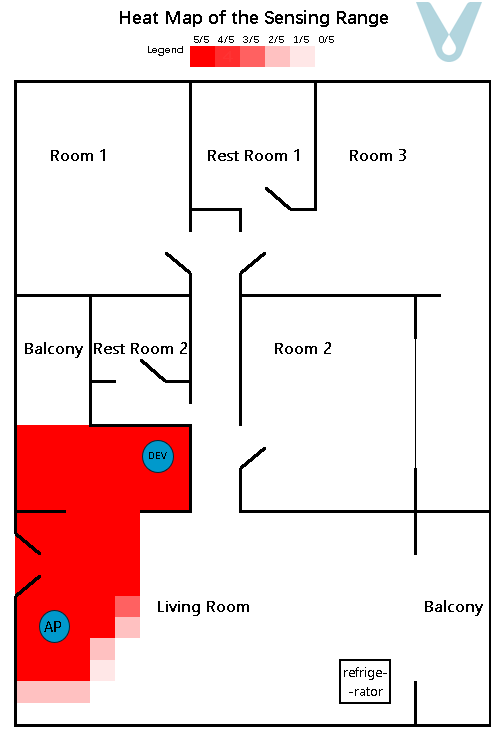
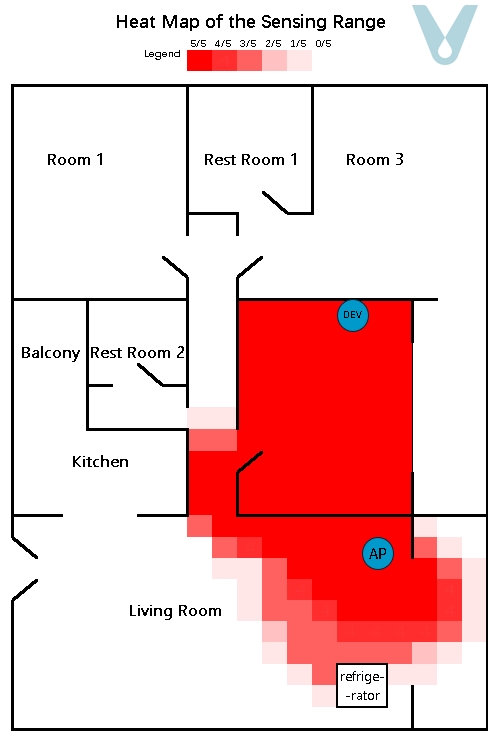
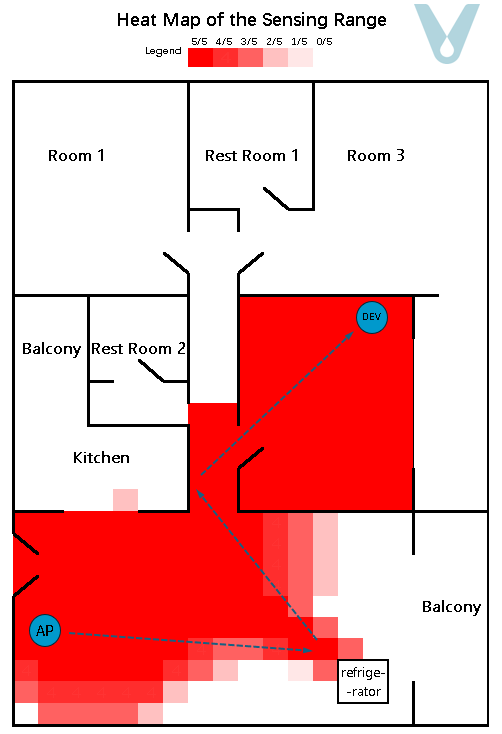
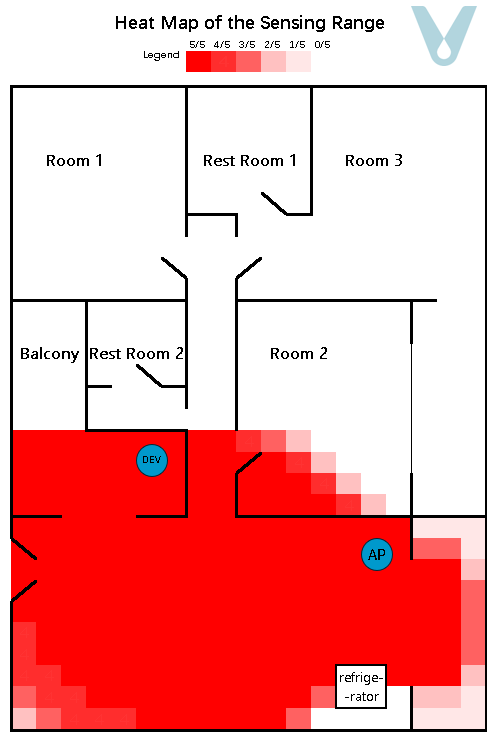
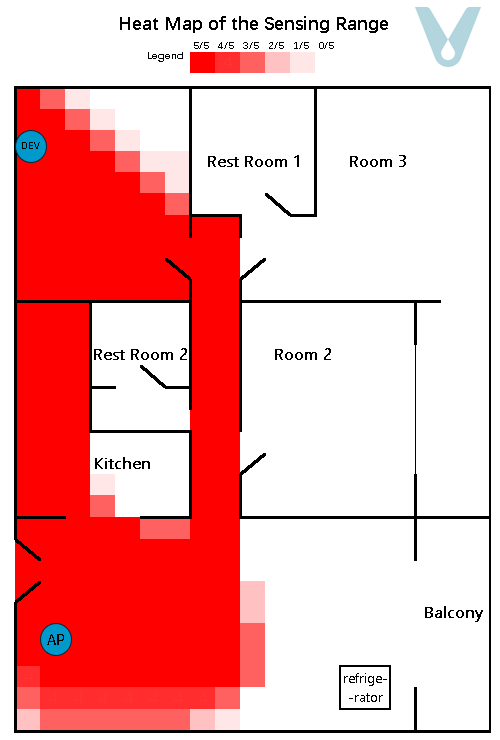
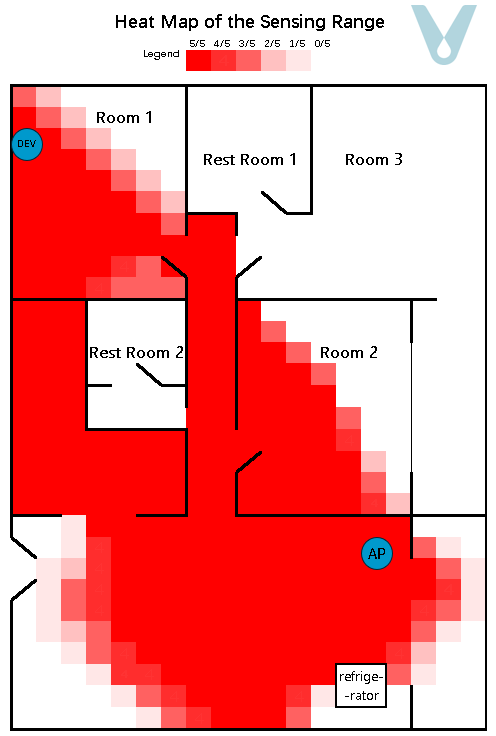
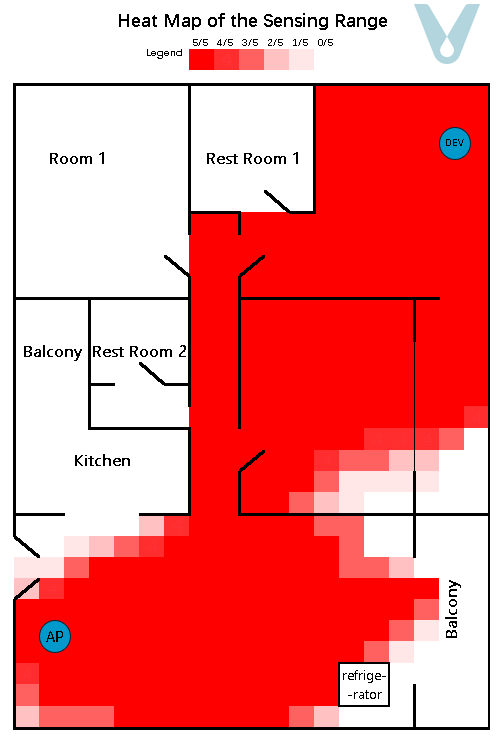
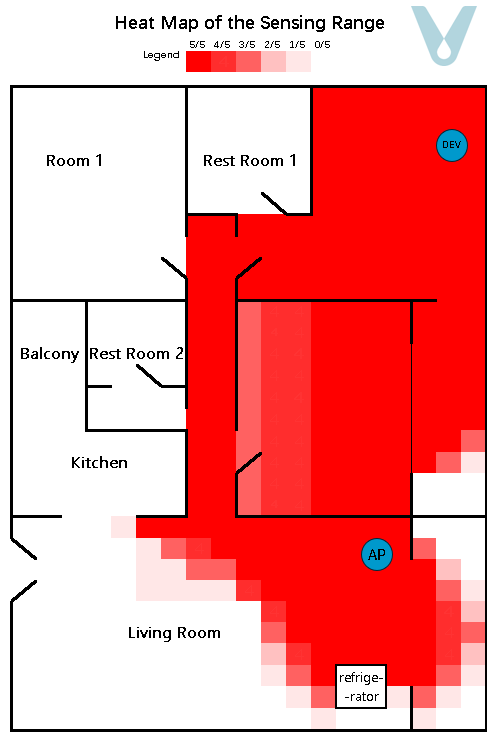
Figure 11. Sensing heat map of the multipath fading scenario (single terminal)
From the experimental outcomes, it is evident that when a single terminal device is made to be compatible with the router so as to cover a particular living space, it can generally attain full sensing coverage of the space in which the terminal is situated. Nevertheless, as the distance between the terminal device and the router grows, the proportion of the direct wave in the signal diminishes, while the proportions of the reflected and transmitted waves increase. Consequently, the sensing range exhibits unanticipated “overflow” phenomena, such as the signal passing through walls and having an overly extensive range.
4.4.2. Long-term hanging test experiment
A long-term hanging test is conducted, along with the collection of raw CSI data, with a working day serving as the unit of measurement.
On one hand, the sensing judgment results of the terminal device and the raw CSI data are synchronized along the time axis. By verifying the format of the raw data, random interferences or alterations in the channel state that occur during the hanging period are effectively mitigated. This synchronization and verification process helps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data, enabling a more precise analysis of the system's performance under real-world conditions.
On the other hand, certain key technologies are deactivated through a post-processing approach. The resulting outcome is then utilized as a comparative baseline. This allows for a clear assessment of the impact and effectiveness of these key technologies. By comparing the performance of the system with and without the key technologies, it becomes possible to determine their significance in enhancing the overall sensing capabilities, such as improving detection accuracy, reducing false alarms, and optimizing the sensing range.
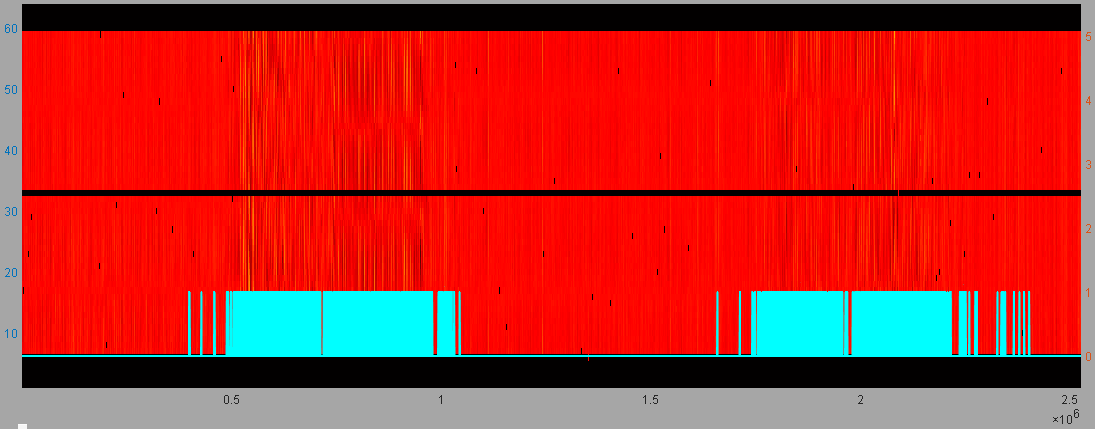
Figure 12. Raw data of a certain router and the terminal judgment results
(48 hours, with mode filtering)
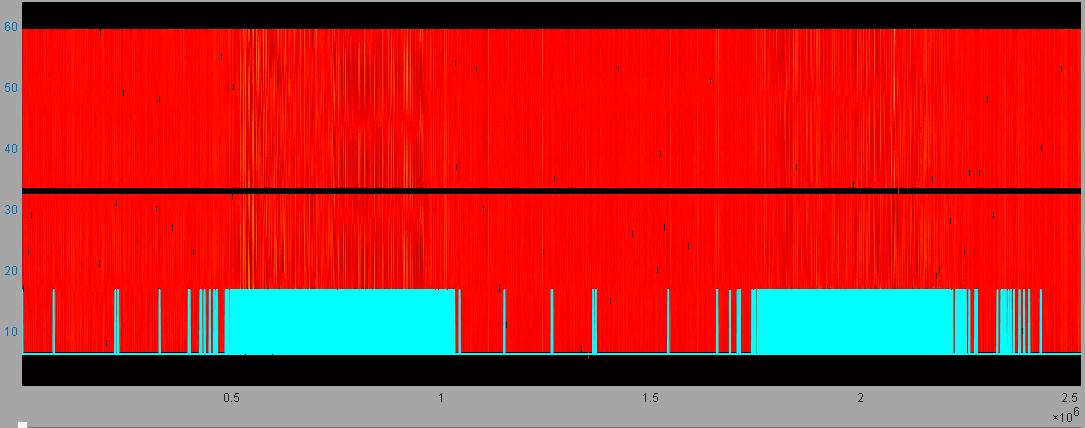
Figure 13. Raw data of a certain router and the terminal judgment results
(48 hours, without mode filtering)
The findings of the hanging test experiment, which spanned nearly 200 working days, indicate that upon the application of the key technology of adaptive Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) enhancement, the mis-identification rate of the communication sensing terminal during the period when it is confirmed that there is no human activity is effectively decreased to a level close to zero (see Figure 12). Conversely, when only the mode filtering technology is disabled, the mis-identification rate experiences a substantial increase (see Figure 13). This clearly demonstrates the crucial role played by the adaptive SNR enhancement technology in improving the accuracy of the communication sensing terminal in distinguishing the absence of human activity, while also highlighting the significance of the mode filtering technology in maintaining a low mis-identification rate. The results provide strong evidence for the effectiveness and indispensability of these key technologies in enhancing the performance of the communication sensing system (see Table 2).
Table 2. Average daily mis-identification times during periods without people vs RSSI
Model of Router * | B-manufacture AX3000 | C-manufacture AX3000 | D-manufacture AX3Pro | E-manufacture AX3000 | F-manufacture AC1200 | G-manufacture AC10 | D-manufacture AX2 Pro | E-manufacture AX1800 | I-manufacture AC1900 | ||
Test Case | RSSI | Filter Mode | |||||||||
Average mis-identification times, in no human presence duration. | -30dBm | on | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
off | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 13 | ||
-50dBm | on | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
off | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 18 | ||
-60dBm | on | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
off | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 19 | 0 | 30 | ||
-70dBm | on | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
off | 5 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 22 | 8 | 20 | ||
-75dBm | on | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
off | 5 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 12 | 8 | 18 | 5 | 20 | ||
(* The company name has been replaced with a code.)
4.4.3. Multi-device and multi-region division experiment
Upon the activation of the spatial granularity refinement technology, the primary task entails evaluating the correctness of the dynamically established point-to-point channels. Subsequently, a partition sensing heat map is constructed in accordance with the sensing range.
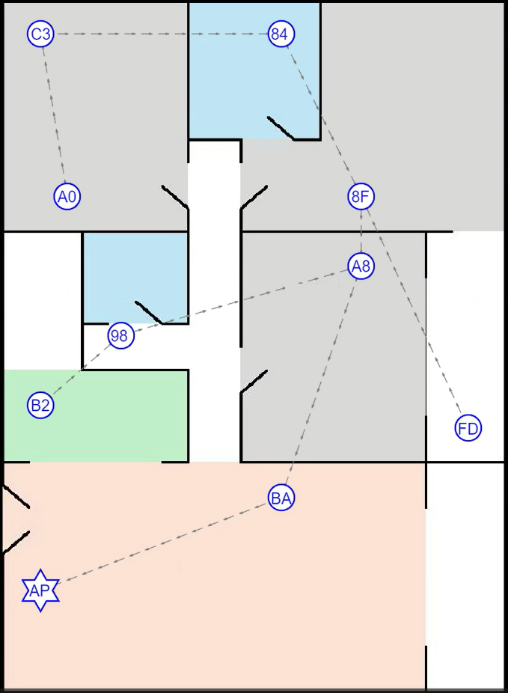
Figure 14. Point-to-point information channels between terminal devices
As depicted in Figure 14, after the commencement of the test, with the support of the cloud, all terminal devices dynamically establish point-to-point channels grounded in the principle of proximity and the spanning-tree algorithm. Following the first spatial granularity division, the sensing range is narrowed down to the region between the Fresnel ellipses formed by two adjacent terminals (see Figure 15). The subsequent tests predominantly assess the accuracy of granular sensing.
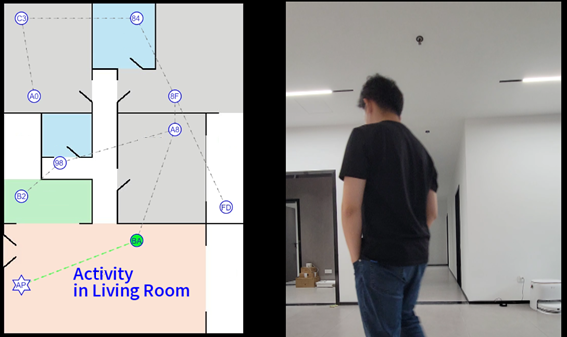
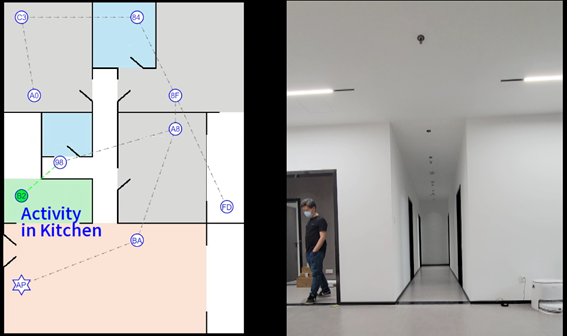
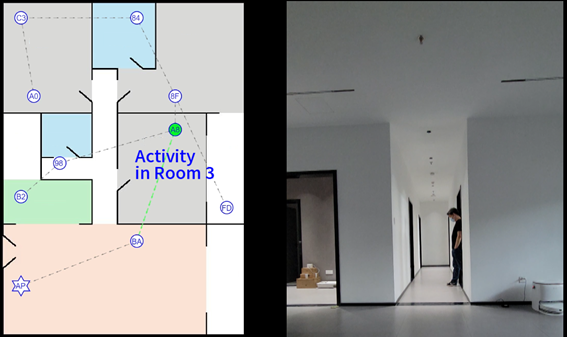
Figure 15. Sensing range converges significantly, after spatial granularity division
5. Implementation applications and main achievements
The technical methods expounded in this article have been implemented on over 15,000 actual user devices. These methods are primarily utilized for the “energy-saving reminder” function in the absence of occupants. Through comprehensive data analysis, the efficacy of the Wi-Fi CSI sensing algorithm proposed herein attains a level exceeding 90% (see Figure 16).
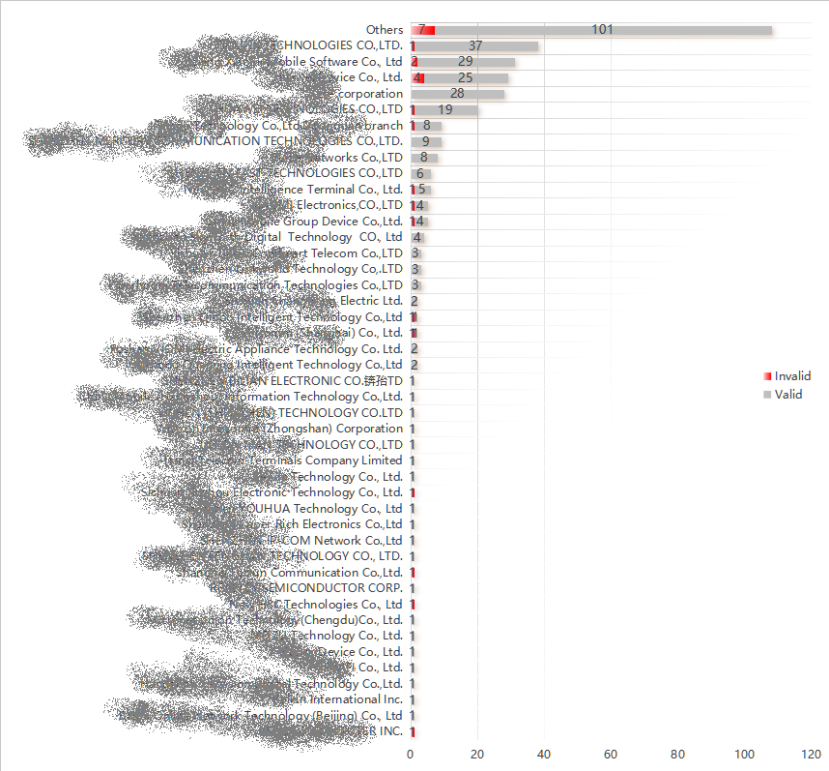
Figure 16. Statistical data on sensing effectiveness
(Valid 91.82%, while Invalid is 7.18%)
6. Conclusion
This article puts forward a technical approach for achieving region-specific human activity detection by leveraging Wi-Fi CSI. The approach encompasses the following key components:
a) Adaptive Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) enhancement.
b) Adversarial sample training.
c) Method of refined spatial granularity.
d) Edge-side model lightweighting method.
Through experimental validations and real-user applications, the adaptability and effectiveness of this proposed approach have been demonstrated. It holds the potential to be applied in enhancing the human activity sensing capabilities of smart home appliances equipped with Wi-Fi networking functionality.
7. Future perspectives
Looking ahead, prospective research on Wi-Fi CSI sensing technology can be conducted along the following dimensions:
7.1. Algorithm optimization and hardware upgrading
In view of the intricacy associated with the processing of CSI data, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can be employed to boost the efficiency and accuracy of data analysis. Simultaneously, through the development of hardware devices with superior performance, such as high-precision CSI acquisition chips, the practicality and reliability of this technology can be further augmented. This would not only expedite the data processing workflow but also enable more precise interpretations of the CSI data, leading to enhanced performance in various applications that rely on Wi-Fi CSI sensing. Additionally, the advanced hardware can better withstand the rigors of real-world environments, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the overall stability of the system.
7.2. Anti-interference and robustness enhancement
In complex wireless environments, CSI technology is highly susceptible to the impacts of multipath effects, noise, and other interfering factors. Looking ahead, advancements in signal processing algorithms or the introduction of multi-frequency band joint sensing methods can be pursued to enhance the adaptability of this technology across diverse environments.
Signal processing algorithm improvements may involve developing more sophisticated techniques for filtering out noise, mitigating multipath distortions, and extracting more accurate CSI features. For instance, novel adaptive filtering algorithms could be designed to adjust in real-time to changing interference levels. On the other hand, multi-frequency band joint sensing holds promise as it allows for the exploitation of information from different frequency bands. By combining the CSI data obtained from multiple frequency bands, the technology can potentially overcome the limitations imposed by interference in a single band, thereby achieving more reliable and consistent performance in various wireless scenarios.
7.3. Privacy protection and ethical norms
CSI data has the potential to encompass users' location and behavioral information. Consequently, it is of paramount importance to institute rigorous privacy protection mechanisms. For instance, by implementing data desensitization techniques, which involve the removal or alteration of sensitive details within the data, and anonymization processes that render individual users unidentifiable, the integrity of user privacy can be safeguarded. Additionally, the establishment of user authorization mechanisms is crucial. These mechanisms ensure that users have control over how their CSI data is accessed and utilized. Through such comprehensive measures, it can be guaranteed that the application of CSI sensing technology adheres to stringent privacy and security regulations, thereby fostering user trust and enabling the responsible deployment of this technology in various contexts.
7.4. Interdisciplinary integration and exploration of novel scenarios
The application scope of CSI technology should not be confined to traditional domains; instead, it can be further extended to emerging areas like smart healthcare and smart agriculture. Through in-depth integration with other cutting-edge technologies, such as 5G/6G communication, edge computing, and blockchain, CSI sensing technology is anticipated to assume a significant role in an even broader spectrum of scenarios.
Furthermore, as the price of commercial chip solutions continues to decline, their performance steadily improves, and multi-antenna Wi-Fi 6 and even Wi-Fi 7 communication chips become more prevalent, the CSI communication and sensing integration technology will be able to glean more information through phase fusion and angle-of-arrival analysis. As a result, capabilities such as precise azimuth determination, gesture and posture recognition [11-12], and respiration measurement can be developed. At that juncture, smart homes will be capable of deeply perceiving the real world, propelling smart home applications to a more advanced stage.
In summary, CSI sensing technology holds vast development potential in the future. However, it is imperative to surmount the current technical hurdles and address the challenges encountered in practical applications. With the unceasing advancements in algorithms, hardware, and privacy protection technologies, CSI technology will offer more robust technical support for an intelligent society and the era of the Internet of Everything.
References
[1]. Jiao, W., Zhang, C., Du, W., & Ma, S. (2025). WiSDA: Subdomain Adaptation Human Activity Recognition Method Using Wi-Fi Signals. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 24(4).
[2]. Tian, L., Chen, L., Xu, Z., & Chen, Z. D. (2021). A People-Counting and Speed-Estimation System Using Wi-Fi Signals. Sensors, 21(10), 3472.
[3]. Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Wen, J., & Zhu, X. (2024). WiFi-based non-contact human presence detection technology. Scientific Reports, 14, 3605.
[4]. Huang, J. (n.d.). Tackling the challenges of wireless interference and coexistence. Michigan State University.
[5]. Wang, X., Niu, K., Xiong, J., Qian, B., Yao, Z., Lou, T., & Zhang, D. (2022). Placement matters: understanding the effects of device placement for wifi sensing. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 6(1), 1–25.
[6]. LAIC-P., & NARAYANAN, R. M. (2005). Through-wall imaging and characterization of human activity using ultrawide-band (UWB) random noise radar. In Defense and Security (pp. 186–195). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
[7]. POSTOLACHEO., GIRÃOPS., POSTOLACHEG., et al. (2011). Cardio-respiratory and daily activity monitor based on FMCW Doppler radar embedded in a wheelchair. In 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (pp. 1917–1920). IEEE.
[8]. SCHÖLKOPFB., PLATTJC., SHAWE-TAYLORJ., et al. (2001). Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural Computation, 13(7), 1443–1471.
[9]. BAHLP., & PADMANABHAN, V. N. (2000). RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In 19th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (pp. 775–784). IEEE.
[10]. NIU, K., ZHANG, F., WU, D., & ZHANG, D. Exploring Stability in WiFi Sensing System Based on Fresnel Zone Model.
[11]. Ahmad, I., Ullah, A., & Choi, W. (2022). WiFi-Based Human Sensing with Deep Learning: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 5.
[12]. Wang, F., Zhou, S., Panev, S., Han, J., & Huang, D. (2019). Person-in-WiFi: Fine-Grained Person Perception Using WiFi. In 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
Cite this article
Zhang,F.;Huang,X.;Chen,Z.;Duan,E. (2025). Research and application of human activity detection technology based on Wi-Fi sensing for home environment adaptation. Advances in Engineering Innovation,16(2),44-60.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Engineering Innovation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Jiao, W., Zhang, C., Du, W., & Ma, S. (2025). WiSDA: Subdomain Adaptation Human Activity Recognition Method Using Wi-Fi Signals. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 24(4).
[2]. Tian, L., Chen, L., Xu, Z., & Chen, Z. D. (2021). A People-Counting and Speed-Estimation System Using Wi-Fi Signals. Sensors, 21(10), 3472.
[3]. Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Wen, J., & Zhu, X. (2024). WiFi-based non-contact human presence detection technology. Scientific Reports, 14, 3605.
[4]. Huang, J. (n.d.). Tackling the challenges of wireless interference and coexistence. Michigan State University.
[5]. Wang, X., Niu, K., Xiong, J., Qian, B., Yao, Z., Lou, T., & Zhang, D. (2022). Placement matters: understanding the effects of device placement for wifi sensing. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 6(1), 1–25.
[6]. LAIC-P., & NARAYANAN, R. M. (2005). Through-wall imaging and characterization of human activity using ultrawide-band (UWB) random noise radar. In Defense and Security (pp. 186–195). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
[7]. POSTOLACHEO., GIRÃOPS., POSTOLACHEG., et al. (2011). Cardio-respiratory and daily activity monitor based on FMCW Doppler radar embedded in a wheelchair. In 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (pp. 1917–1920). IEEE.
[8]. SCHÖLKOPFB., PLATTJC., SHAWE-TAYLORJ., et al. (2001). Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural Computation, 13(7), 1443–1471.
[9]. BAHLP., & PADMANABHAN, V. N. (2000). RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In 19th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (pp. 775–784). IEEE.
[10]. NIU, K., ZHANG, F., WU, D., & ZHANG, D. Exploring Stability in WiFi Sensing System Based on Fresnel Zone Model.
[11]. Ahmad, I., Ullah, A., & Choi, W. (2022). WiFi-Based Human Sensing with Deep Learning: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 5.
[12]. Wang, F., Zhou, S., Panev, S., Han, J., & Huang, D. (2019). Person-in-WiFi: Fine-Grained Person Perception Using WiFi. In 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).









