1 Background, Objectives, and Significance of the Study
With the rapid development of the internet era, internet technology has been widely applied, bringing new vitality to the tourism industry [1]. However, along with these opportunities come challenges. Information overload and the proliferation of false information have caused many issues for consumers, who increasingly demand reliable travel reviews and recommendations. As a result, numerous scholars have begun to research and explore consumer behavior, including the extent to which reviews influence consumer decisions and choices [2-3]. Meanwhile, research on tourism focusing on university students as the primary consumer group is still in its infancy. University students represent a major consumer force in the future, and it is particularly important to tap into their potential consumption power and their role in promoting economic development [4].
Currently, sentiment analysis methods for natural language texts are mainly divided into two categories: statistical-based sentiment analysis and deep learning-based sentiment analysis. Statistical-based methods require considerable time and manpower and are easily affected by sentence ambiguity. In contrast, deep learning-based methods can effectively mitigate these issues.
In the early stages of research, the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) proposed by Zachary [5] was widely applied in various text processing domains due to its extensive applicability. However, RNNs often encounter issues such as gradient vanishing and explosion when input data exhibit long-term dependencies. Subsequently, Huang et al. [6] introduced the Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network, which effectively addresses long-term dependency issues and demonstrates better performance compared to RNNs. As research progressed, it was found that these methods struggle to accurately focus on key parts of sentences. To address this, researchers began incorporating attention mechanisms into natural language text processing. This approach aims to concentrate attention on important content within the text rather than the entire sentence. Dragoni et al. [7] thus proposed a novel sentiment analysis embedding method. Furthermore, Feng et al. [8] utilized the WordsVec model combined with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for text sentiment analysis. Building upon this, Rezaeinia's team [9] further integrated pre-trained vocabularies to deepen sentiment analysis research. However, this method did not fully consider the dependencies between past and future contexts or the varying importance of words. Xiang et al. [10] introduced a new deep learning model incorporating Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) to address intra-sentence relationships and capture dependencies between past and future contexts. This advancement has significantly pushed forward the development of sentiment analysis research.
In traditional natural language text analysis, typically only one algorithmic model is used or sentiment analysis is approached from a single perspective. However, the tourism industry is complex, requiring consideration of multiple factors, such as the influence of time [11]. To address this complexity, TF-IDF and TextRank algorithms are combined to preprocess the text. Subsequently, sentiment analysis is conducted using the SnowNLP library in Python, incorporating seasonal analysis as a manual step. The joint application of TF-IDF and TextRank enables entity recognition and extraction of overall adjectives from the text, enhancing the granularity of text processing. Simultaneously, by integrating time factors and incorporating manual analysis, the study aims to comprehensively summarize sentiment patterns in text over time, thereby enhancing the authority and accuracy of sentiment analysis research.
2 Research Methodology
2.1 Sentiment Analysis Research Process
First, tourist attractions are selected, focusing on those near Wenzhou University Town as the research subjects. Comment data is then acquired using Python technology. Subsequently, the influence of time factors on tourism sentiment is analyzed, followed by sentiment analysis of the comment data. The analysis results incorporate the influence of comprehensive factors on tourism sentiment, leading to the provision of enhancement strategies. The specific process is illustrated in Figure 1.
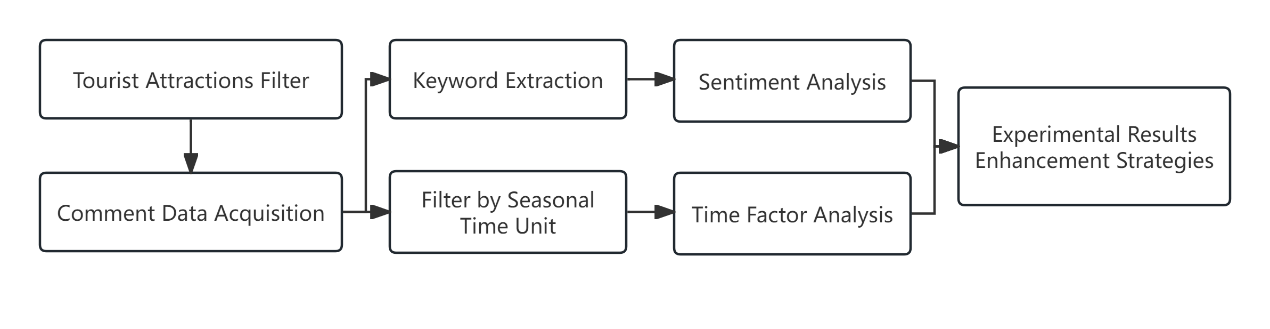
Figure 1. Analysis flow chart
2.2 Data Collection and Preprocessing
In this study, data was collected using Python technology and the Octoparse data extractor from various tourism websites and map navigation software, including Ctrip, Tongcheng Travel, Meituan, Tuniu, Qunar, Amap, and Tencent Maps. Centering on the South Campus of Wenzhou Business College, the distance filtering function within the software was employed to set range boundaries of 5 kilometers, 10 kilometers, and 15 kilometers. Several tourist attractions within these ranges were selected as research subjects, including Wenzhou Paradise, Wenzhou Polar Ocean World, Wenzhou Museum, Sanyang Wetland Reserve, Jiangxin Island, and Wenzhou Zoo.
Subsequently, the data was filtered to remove fraudulent reviews and duplicate comments. The results of the data processing are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Comment Data
Target Distance |
Tourist Attraction |
Total Number of Online Reviews |
Within 5 km |
Wenzhou Paradise |
9273 |
Within 5 km |
Wenzhou Polar Ocean World |
9414 |
Within 10 km |
Wenzhou Museum |
7006 |
Within 10 km |
Sanyang Wetland Reserve |
7115 |
Within 15 km |
Jiangxin Island |
8437 |
Within 15 km |
Wenzhou Zoo |
6204 |
2.3 Introduction to Time and Fine-Grained Sentiment Analysis Methods
Time has a significant impact on the tourism industry, influencing factors such as seasonal demand, differences between peak and off-peak seasons, the concentration of holidays and long vacations, and the timeliness of tourism activities.
This study divides time into quarters of three months each (March-May as spring, June-August as summer, September-November as autumn, and December-February as winter) and aggregates the reviews for each month. Each review is scored on a scale of 1 to 5, with reviews scoring below 3 classified as indicating a poor travel experience and negative sentiment, while reviews scoring above 3 indicate positive sentiment. The influence of time intervals on sentiment is also considered in the evaluation [12].
2.4 Keyword Extraction Using TF-IDF and TextRank Algorithms
In the keyword extraction process, this study employs a combined method of TF-IDF and TextRank algorithms.
TF-IDF Algorithm (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency):
• Term Frequency (TF): Measures the frequency of a term within a single document. The calculation formula is:
\( TF(t,d)=\frac{The number of occurrences of term t in document d}{Total number of terms in document d}\ \ \ (1.1) \)
• Inverse Document Frequency (IDF): Measures the rarity of a term, i.e., the frequency of its occurrence across the entire document collection. The calculation formula is:
\( IDF(t,D)=log{(\frac{|D|}{\lbrace d∈D:t∈d\rbrace })}\ \ \ (1.2) \)
• TF-IDF (Value): The product of term frequency and inverse document frequency, representing the importance of term \( t \) in document d
\( TF-IDF(t,d,D)=TF(t,d)×IDF(t,D)\ \ \ (1.3) \)
TextRank Algorithm (TextRank: Bringing Order into Texts) Formula:
• Graph Construction:
• Split the text to be processed into sentences or words, which serve as nodes.
• Add edges between nodes based on certain conditions (e.g., co-occurrence relationships, part of speech).
• Iterative Calculation of Each Node's Weight:
• Initialize the weight of each node to 1.
• Iteratively calculate the weight of each node until convergence.
• For each node, calculate its weight using the following formula:
\( Score(i)= (1-d)+ d * Σ(w(i, j)/Σ(w(j, k)))* Score(j)\ \ \ (1.4) \)
• Score(i)represents the weight of node i.
• d is the damping factor, typically set to 0.85.
• w(i,j) represents the weight of the edge from node i to node j.
• Σ(w(j, k)) represents the sum of the weights of all outgoing edges from node j.
• Sort Nodes by Weight:
• Sort the nodes based on their weights.
• Select the nodes with the highest weights as key sentences or keywords.
The combination of the TF-IDF algorithm and the TextRank algorithm effectively extracts the most representative and information-rich keywords from review texts. The TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) algorithm is utilized to extract important nouns and adjectives from reviews. This algorithm considers the frequency of words in the review text and their importance in the entire corpus, thereby identifying words that significantly contribute to the content of the reviews. The TextRank algorithm is used to find adjectives that provide a summary of the attractions or themes mentioned in the reviews, thereby offering key insights into the sentiment and themes of the reviews.
2.5 Sentiment Analysis Based on SnowNLP Library in Python
SnowNLP is a Chinese natural language processing library based on Python, which utilizes advanced deep learning techniques in its sentiment analysis model. This model is trained on a large corpus of text data, enabling it to recognize and classify sentiments within Chinese text. Its main functionalities include sentiment polarity classification, sentiment intensity evaluation, and sentiment theme identification. Additionally, SnowNLP is optimized for the unique characteristics of the Chinese language, enhancing the accuracy of sentiment analysis. Beyond sentiment analysis, SnowNLP also offers other NLP functions such as word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging.
3 Understanding Research Results
3.1 Understanding the Impact of Time Factors on Online Reviews of Tourist Attractions
To more fully demonstrate the impact of time factors on tourist attractions, the research selects one attraction from each group of tourist spots to present the analysis results. This approach effectively displays the research findings within a limited space while maintaining the credibility and completeness of the information. The analysis data is shown in Tables 2, 3, and 4.
Table 2. Wenzhou Paradise
Tourist Attraction Name |
Review Period |
Average Rating |
Wenzhou Amusement Park |
March-May (Spring) |
5.00 |
June-August (Summer) |
5.00 |
|
September-November (Autumn) |
4.20 |
|
December-February (Winter) |
3.78 |
Table 3. Wenzhou Museum
Attraction Name |
Review Time |
Average Rating |
Wenzhou Museum |
March-May (Spring) |
4.64 |
June-August (Summer) |
4.87 |
|
September-November (Autumn) |
4.69 |
|
December-February (Winter) |
4.12 |
Table 4. Jiangxin islet
Attraction Name |
Review Time |
Average Rating |
Jiangxin islet |
March-May (Spring) |
4.59 |
June-August (Summer) |
4.41 |
|
September-November (Autumn) |
4.54 |
|
December-February (Winter) |
4.57 |
From Tables 2 and 3, it can be seen that during the winter season (September-November), the ratings for some attractions are at their lowest, approaching or even below 4. This may be due to climatic conditions and a decrease in seasonal tourism activities. However, as the season transitions into spring (March-May) and summer (June-August), the ratings for the attractions show a significant increase, only to decline again in autumn (December-February).
From Table 4, it is evident that the quarterly average rating for Jiangxin Islet remains relatively stable at around 4.5. Unlike other attractions, the ratings for Jiangxin Islet are relatively unique in that they are hardly affected by seasonal factors. According to the inspection of the attraction, Jiangxin Islet is classified as a "comprehensive cultural tourism destination." The appeal of such attractions mainly stems from visitors' personal interests and preferences related to specific environments, cultures, and histories, resulting in relatively consistent ratings throughout the year.
3.2 Perception Study of Scenic Spots' Emotional Image Based on Tourist Reviews
Using a combination of TF-IDF and TextRank algorithms, different vocabulary was extracted from the review data, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Keyword extraction case of Wenzhou Paradise Attractions
Review Number |
TF-IDF |
TextRank |
1 |
Very cool, Great reviews, Wonderful performance, Kids |
Not bad |
2 |
High cost performance, Inspiring, Convenient, Transportation |
Convenient |
3 |
Project maintenance, Staff, Average, Few people |
Happy |
4 |
Roller coaster, Exciting feeling |
Cheap |
5 |
Many projects, Too many people, Long queues |
Quite fun |
After keyword extraction, sentiment analysis was performed using the SnowNLP library in Python. Additionally, to gain a more intuitive understanding of the overall distribution of the comments, a sentiment analysis chart of the reviews was created at the end of the data analysis, as shown in Figure 2.
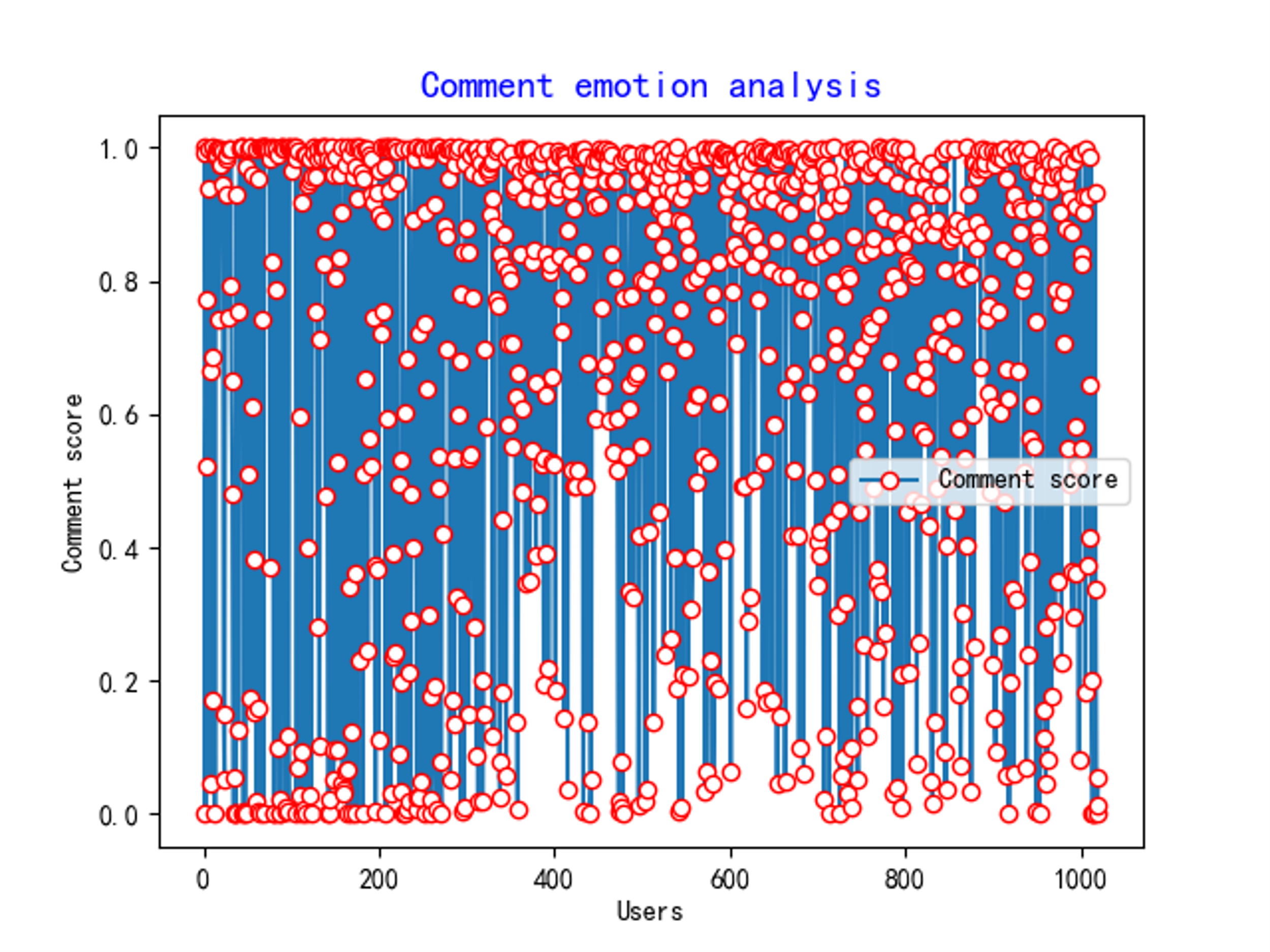
Figure 2. Wenzhou Paradise Review Emotional Scatter Distribution Map
Sentiment analysis keywords were extracted in increasing monthly order. As shown in Figure 2, points with lower review scores are located on the left side of the chart, gradually decreasing towards the right. It can be seen that the combined use of TF-IDF and TextRank algorithms offers higher accuracy. Additionally, Figure 2 visually matches the data in Table 2, showing lower review scores during the winter months (December to February), indicating higher reliability.
4 Conclusion
The combination of algorithms enhances the accuracy of natural language text analysis, and the incorporation of visualization makes the results more intuitive. Through the analysis of time factors, it is evident that most scenic spots are significantly affected by seasonal factors. Sentiment and evaluations of scenic spots cannot solely rely on textual analysis and scores. When analyzing tourist attractions, multiple factors should be considered. Current studies predominantly focus on single factors, failing to integrate multiple influencing factors. For example, Jiangxin Island is categorized as a "comprehensive cultural tourism site," which shows less correlation with time factors. Future research should attempt to combine other influencing factors such as the type of scenic spot for more effective analysis.
Acknowledgment
We appreciate the support from the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students at Wenzhou Business College for this research. The project title is " A Study on the Evaluation of Tourist Attractions Around Wenzhou University Town Based on Big Data Analysis," and the project number is 202313637017.
References
[1]. Xiong, D. (2021). Theoretical and empirical research on the impact of the Internet on the development of China's tourism industry (Doctoral dissertation). East China Normal University. https://doi.org/10.27149/d.cnki.ghdsu.2021.002002 (pp. 12-17)
[2]. Sunyoung, H., Hanna, L., & Chulmo, K. (2018). Hospitality and Tourism Online Review Research: A Systematic Analysis and Heuristic-Systematic Model. Sustainability, 10(4), 1141-1141. https://doi.org/10.4(2018):1141-1141
[3]. Liu, Y., & Hu, F. H. (2021). Online review helpfulness: the moderating effects of review comprehensiveness. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 33(2), 534-556.
[4]. Zheng, Y., & Wang, X. S. (2016). Review and prospect of domestic college students' tourism research. Economic Research Guide, (06), 131+146.
[5]. Lipton, C. Z. (2015). A Critical Review of Recurrent Neural Networks for Sequence Learning. CoRR, abs/1506.00019.
[6]. Huang, Z., Xu, W., & Y K 0001. (2015). Bidirectional LSTM-CRF Models for Sequence Tagging. CoRR, abs/1508.01991.
[7]. Mauro, D., & Giulio, P. (2017). A Neural Word Embeddings Approach for Multi-Domain Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 8(4), 457-470.
[8]. Feng, X. J., Zhang, Z. W., & Shi, J. C. (2018). Text sentiment analysis based on convolutional neural networks and attention models. Computer Application Research, 35(05), 1434-1436.
[9]. Rezaeinia, M. S., Rahmani, R., Ghodsi, A., et al. (2018). Sentiment Analysis based on Improved Pre-trained Word Embeddings. Expert Systems With Applications, 117, 139-147.
[10]. Xiang, R. L., Li, Z. Y., & Sun, P. (2023). Research on sentiment analysis of scenic spot reviews based on RoBerta-BiGRU-Attention. Data Mining, 13(4), 312-316.
[11]. Li, Y. Q., & Jiang, Q. M. (2023). Tourism research under psychological time framework: current situation and prospects. Tourism Tribune, 38(06), 53-62. https://doi.org/10.19765/j.cnki.1002-5006.2023.00.007
[12]. Zhu, H. W., Xu, J. J., & Tang, D. H. (2017). The interactive effects of time intervals and product types on the extremity of review efficacy. Journal of Marketing Science, 13(03), 98-112.
Cite this article
Zhou,R.;Xu,Y.;Zou,X. (2024). A study on the evaluation of tourist attractions around Wenzhou University Town based on big data analysis. Advances in Operation Research and Production Management,2,22-27.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Operation Research and Production Management
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Xiong, D. (2021). Theoretical and empirical research on the impact of the Internet on the development of China's tourism industry (Doctoral dissertation). East China Normal University. https://doi.org/10.27149/d.cnki.ghdsu.2021.002002 (pp. 12-17)
[2]. Sunyoung, H., Hanna, L., & Chulmo, K. (2018). Hospitality and Tourism Online Review Research: A Systematic Analysis and Heuristic-Systematic Model. Sustainability, 10(4), 1141-1141. https://doi.org/10.4(2018):1141-1141
[3]. Liu, Y., & Hu, F. H. (2021). Online review helpfulness: the moderating effects of review comprehensiveness. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 33(2), 534-556.
[4]. Zheng, Y., & Wang, X. S. (2016). Review and prospect of domestic college students' tourism research. Economic Research Guide, (06), 131+146.
[5]. Lipton, C. Z. (2015). A Critical Review of Recurrent Neural Networks for Sequence Learning. CoRR, abs/1506.00019.
[6]. Huang, Z., Xu, W., & Y K 0001. (2015). Bidirectional LSTM-CRF Models for Sequence Tagging. CoRR, abs/1508.01991.
[7]. Mauro, D., & Giulio, P. (2017). A Neural Word Embeddings Approach for Multi-Domain Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 8(4), 457-470.
[8]. Feng, X. J., Zhang, Z. W., & Shi, J. C. (2018). Text sentiment analysis based on convolutional neural networks and attention models. Computer Application Research, 35(05), 1434-1436.
[9]. Rezaeinia, M. S., Rahmani, R., Ghodsi, A., et al. (2018). Sentiment Analysis based on Improved Pre-trained Word Embeddings. Expert Systems With Applications, 117, 139-147.
[10]. Xiang, R. L., Li, Z. Y., & Sun, P. (2023). Research on sentiment analysis of scenic spot reviews based on RoBerta-BiGRU-Attention. Data Mining, 13(4), 312-316.
[11]. Li, Y. Q., & Jiang, Q. M. (2023). Tourism research under psychological time framework: current situation and prospects. Tourism Tribune, 38(06), 53-62. https://doi.org/10.19765/j.cnki.1002-5006.2023.00.007
[12]. Zhu, H. W., Xu, J. J., & Tang, D. H. (2017). The interactive effects of time intervals and product types on the extremity of review efficacy. Journal of Marketing Science, 13(03), 98-112.









