1. Introduction
Drawing on the practical experiences of leading countries in global technological innovation, the significant improvement in enterprise innovation capabilities is often closely related to the deep integration and application of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. As the core driving force of the new technological revolution, the efficient deployment and precise application of AI within enterprises directly determine the output efficiency of enterprise innovation outcomes [1] . With the continuous maturation of AI technologies and their deep integration with the manufacturing industry, a new model of enterprise innovation development based on AI technology is gradually taking shape, attracting widespread attention in academia.
Foreign scholars primarily focus on the internal and external mechanisms of AI applications’ effects on enterprise innovation performance. Their studies have found that the intensification of external market competition and the flattening of internal organizational structures, as two important economic forms of innovation resource reallocation, significantly moderate the effectiveness of AI applications [2] . Additionally, empirical analyses by scholars point out that the application of AI is frequent and widespread throughout the innovation process, especially during the implementation phase of innovation development, where it is more prevalent than in the stages of idea generation or commercialization [3].
Domestic scholars, on the other hand, focus more on the promotion effect of AI applications on enterprise innovation performance. They argue that AI, as a key digital technology driving the intelligent transformation of the manufacturing industry, can open up new development space and opportunities for the industry, fostering new technologies, products, and models. Sun Liwen and Li Shaoshuai (2021) used fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis [4] to categorize the pathways through which AI empowers innovation performance into five types: technology-supported, data-driven, organizational transformation, service ecosystem, and marketing integration, providing diversified choices for the digital transformation and intelligent upgrading of manufacturing enterprises. The study by Li Guo and Bai Yunpu (2024) further demonstrates that dynamic capabilities play a partial mediating role in AI applications empowering manufacturing enterprise innovation performance [5] . Among the dimensions of dynamic capabilities, the mediating effect of innovation capability is the most significant, followed by absorptive capacity, while the mediating effect of adaptive capacity is relatively weak.
Although existing studies provide rich theoretical support and practical insights into the impact of AI technologies on the innovation performance of manufacturing enterprises, research in this field still requires further deepening and expansion. Firstly, current research on AI mainly focuses on its impact on economic growth, labor markets, and overall corporate performance [7], while research on the relationship between AI applications and enterprise innovation performance is still in the preliminary exploration stage. Secondly, although existing studies have preliminarily explored the mechanisms of AI applications’ effects on enterprise innovation performance from the perspectives of mediating and moderating effects, related research remains insufficiently systematic and comprehensive.
Based on this, this paper builds an AI application dictionary through the analysis of enterprise annual report texts, expanding on the previous research, and focuses on two core questions: How do AI technology applications affect the innovation performance of manufacturing enterprises? What are the underlying mechanisms? By revealing the specific pathways and inherent mechanisms through which AI technology applications enhance innovation performance in manufacturing enterprises, this paper aims to provide theoretical foundations and practical guidance for management practices in related fields.
2. Theoretical analysis and research hypotheses
2.1. Artificial intelligence applications and enterprise innovation performance
The Resource-Based Theory emphasizes the uniqueness of internal resources within enterprises and their core role in establishing and maintaining competitive advantages. Under this theoretical framework, AI applications are considered important strategic resources for enterprises. First, as a valuable resource, AI applications can significantly improve the operational efficiency and resource allocation capabilities of enterprises. Through intelligent production management systems, optimized supply chain processes, and automated customer services, AI applications help enterprises reduce operating costs, increase production efficiency, and thereby release more resources for innovation activities [9] . Furthermore, AI-driven data analysis and forecasting capabilities enable enterprises to more accurately identify market demands and technological trends [10] , optimize research and development (R&D) directions, and enhance the scientificity and effectiveness of decision-making, thereby improving the enterprise’s adaptability and competitiveness in dynamic market environments.
Second, AI applications possess rarity and inimitability, which are key characteristics for achieving sustained competitive advantage in the Resource-Based Theory. Through unique AI applications, such as customized intelligent manufacturing systems, advanced market analysis tools, and personalized customer relationship management systems [11] , enterprises can create significant differentiation advantages within their industries. These unique applications not only enhance the enterprise’s core competitiveness but also strengthen its brand influence and technological leadership in the market. At the same time, the complexity and high technological threshold of AI applications make them difficult for competitors to easily replicate or imitate, further consolidating the enterprise’s competitive advantage. Additionally, enterprises must possess corresponding organizational capabilities [12] to effectively integrate and utilize AI, including a well-developed data management system, interdepartmental collaboration mechanisms, and continuous technological innovation capabilities. These organizational capabilities ensure that AI applications can be fully leveraged to support the enterprise’s long-term strategic goals and innovation activities.
Based on the Resource-Based Theory, AI applications directly drive improvements in enterprise innovation performance by optimizing resource allocation, enhancing organizational capabilities, and promoting innovation activities. Specifically, AI applications strengthen enterprises’ knowledge management and technological integration capabilities, promote cross-disciplinary knowledge sharing and collaborative innovation, thereby accelerating new product development and technological breakthroughs. Moreover, AI-driven intelligent decision-support systems help enterprises allocate resources more effectively during the R&D process, reduce R&D risks, and increase the success rate and innovation efficiency of R&D projects [13] . This not only improves the enterprise’s exploratory innovation capacity but also strengthens its exploitative innovation capacity to optimize and improve existing resources. Through the systematic integration and optimization of AI application resources, enterprises can achieve dual improvements in innovation efficiency and quality, forming continuous innovation capabilities and competitive advantages [14] . Therefore, from the perspective of the Resource-Based Theory, AI applications are not only an important means of enhancing the value of internal resources but also a key driving force for enabling enterprises to achieve high-quality development in fierce market competition.
Based on the above analysis, Hypothesis H1 is proposed: AI applications have a promoting effect on the enhancement of enterprise innovation performance.
2.2. Mediating effect of innovation resource allocation
Based on the Dynamic Resource-Based View, AI applications promote the effective allocation of innovation resources within and outside the enterprise [15] , thereby enhancing enterprise innovation performance.
(1) R&D Human Resources
AI applications optimize and expand the allocation of R&D human resources (i.e., the size of the R&D team), establishing a mediating mechanism that affects enterprise innovation performance. AI applications improve R&D efficiency, optimize talent recruitment and management, and support the expansion of R&D activities, enabling enterprises to scientifically expand their R&D team size and enhance the team’s innovation capabilities and collaboration efficiency [16] . First, AI applications, through automation and intelligence, significantly improve the operational efficiency of enterprises in the R&D process. This improvement in efficiency helps enterprises free up more financial and time resources, enabling them to expand their R&D teams. For example, manufacturing enterprises that introduce AI automation systems reduce repetitive tasks by 50%, allowing R&D projects that previously required these resources to allocate more high-skilled R&D personnel, thereby enhancing R&D capacity and innovation potential. Second, the application of AI in talent recruitment and management significantly improves the quality and efficiency of R&D teams. By using big data analysis and machine learning algorithms, enterprises can precisely screen and assess candidates, ensuring the recruitment of R&D personnel with the necessary skills and potential. For instance, Huawei uses AI recruitment tools to analyze candidates’ skill matches and future development potential, optimizing the staffing of their R&D teams so that high-skilled talents are concentrated on key technical projects, improving overall R&D efficiency and innovation capacity. Finally, AI applications also support enterprises in expanding into new technological fields and innovation projects, which in turn require more R&D personnel. The application of AI in emerging fields such as intelligent manufacturing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics drives enterprises to explore new R&D directions, which often require expanding the R&D team to meet complex technological challenges and market demands. For example, Tencent’s AI research department, through the introduction of AI technologies, has expanded into new projects such as intelligent customer service and intelligent recommendation systems, thereby increasing the size of the R&D team and enhancing the enterprise’s technological innovation capabilities.
The expanded R&D team significantly improves enterprise innovation performance by promoting interdisciplinary collaboration, improving innovation efficiency, and enhancing the team’s overall innovation capacity. First, larger R&D teams can facilitate cross-disciplinary collaboration and knowledge sharing, improving knowledge integration and technological convergence in the innovation process. For example, Alibaba’s R&D team, with over a thousand members, fosters deep integration between big data analysis and e-commerce technologies, driving the successful implementation of multiple innovation projects and improving overall innovation performance. Second, the expanded R&D team, through rational division of labor and collaboration, can more efficiently complete R&D tasks, shorten innovation cycles, and increase innovation speed. Finally, the expanded team also brings more diverse knowledge and skills, enhancing the team’s overall innovation capacity and creativity. R&D personnel with different professional backgrounds and skills can collaborate, promoting cross-fertilization of knowledge and technological innovation. For instance, Huawei introduced experts with multidisciplinary backgrounds into its R&D team, driving deep integration of AI and communications technology, resulting in a series of innovative communication products and solutions, further enhancing the enterprise’s innovation performance.
Based on the above analysis, Hypothesis H2a is proposed: AI applications can enhance enterprise innovation performance by expanding R&D human resources.
(2) Innovation and R&D Funding
AI applications enhance resource management efficiency and optimize investment decisions, thereby releasing and optimizing research and development (R&D) funding. First, AI applications significantly improve efficiency in the resource management process through automation and intelligent methods [17] . For example, AI-driven financial management systems can monitor and optimize a company’s cash flow in real-time, reduce unnecessary spending and resource waste, and release more funds for innovative R&D activities. This optimization not only improves the efficiency of fund utilization but also strengthens the company’s control over financial resources, enabling the company to increase investment in R&D projects while maintaining stable operations. Second, AI technology helps companies scientifically assess the potential returns and risks of R&D projects through data analysis and predictive models, optimizing the allocation of R&D funds. For example, AI-driven investment analysis tools can analyze market trends, technological development paths, and competitive landscapes to identify the most strategically significant and high-return R&D projects, guiding companies to invest more funds into these projects. This precise allocation of funds not only improves the efficiency of R&D investment but also ensures that funds are directed to the most promising and innovative projects, maximizing the return on R&D investment.
Increasing investment in high-potential R&D projects can enhance the success rate and innovation performance of R&D projects [18] . First, increased R&D funding directly promotes the company’s investment in technological R&D and product innovation. Sufficient R&D funding supports the exploration and breakthroughs of cutting-edge technologies, drives the development and launch of new products, thereby improving the company’s market competitiveness and innovation performance. Second, adequate R&D funding ensures that R&D projects receive sufficient resource support, thereby improving the success rate and innovation quality of the projects. AI-driven project management systems can monitor the progress of R&D projects in real-time, identify and resolve issues promptly, ensuring that projects proceed according to plan and reducing delays and resource waste in the R&D process. This efficient fund management and project execution significantly enhance the success rate and quality of innovation outcomes, thus improving the company’s overall innovation performance. Finally, the increase in R&D funding also promotes the company’s investment in technological accumulation and continuous innovation, creating long-term competitive advantages. AI applications ensure that companies can sustain investment in core technology R&D and innovation by optimizing long-term fund planning and management.
Based on the above analysis, Hypothesis H2b is proposed: AI applications can enhance enterprise innovation performance by increasing innovative R&D funding.
3. Research design
3.1. Data sources
This study selects manufacturing companies listed on the Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share markets from 2015 to 2023 as the research objects, mainly based on the following two considerations: (1) The development process of artificial intelligence. The widespread promotion and practice of intelligent transformation began in 2015, so using 2015 as the starting year for data collection is of significant practical importance. (2) Data accessibility. Compared to non-listed companies, data from listed companies are more easily accessible, providing convenience for measuring subsequent variables. Therefore, the annual reports of the listed companies selected in this study are sourced from the official websites of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange and Shanghai Stock Exchange, while the company-level data come from the CSMAR (Guotai An) database, and patent data are sourced from the CNRDs data platform and the National Intellectual Property Administration.
In the sample selection process, the following steps were strictly followed: First, financial industry companies were excluded to ensure the focus and accuracy of the study. Second, listed companies continuously marked as ST (Special Treatment) or PT (Delisting Arrangement) during the study period were excluded to avoid the interference of abnormal data on the results. Third, samples with missing values were removed to ensure the completeness and consistency of the data. Finally, winsorization was applied to continuous variables to reduce the influence of extreme values on statistical analysis. After these steps, 10,324 valid samples were obtained.
3.2. Variable measurement
3.2.1. Core explanatory variable
The explanatory variable is artificial intelligence application (AI_apply), referring to the systematic integration and use of artificial intelligence technologies in a company’s operations and production processes to enhance automation levels, optimize decision-making processes, promote innovation, and improve overall competitiveness. This application includes not only the deployment and use of industrial robots in manufacturing but also intelligent practices in multiple functional areas such as R&D, management, market forecasting, and customer service. Existing studies measure artificial intelligence application through methods such as industrial robot penetration, the number of AI patents, and annual report text analysis, each with its strengths and limitations. Thus, this study follows the measurement method of Yao Jiaquan et al. (2024) [19] , using machine learning techniques to construct an artificial intelligence application dictionary. Based on the annual reports of listed companies, an AI application indicator was developed to accurately assess the level of AI technology application in enterprises and its role in promoting innovation performance. The specific construction process is shown in Figure 1.
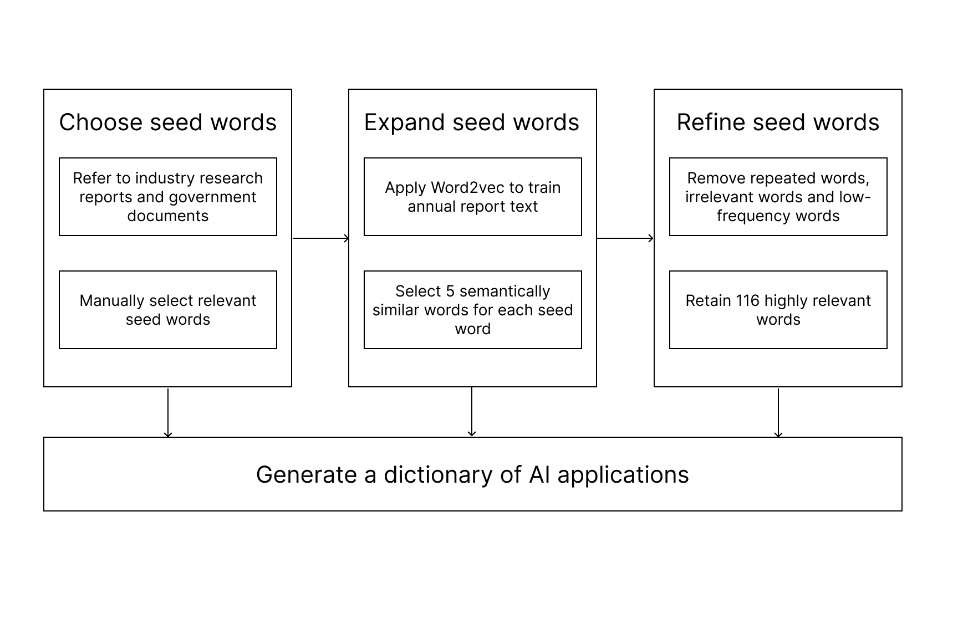
Figure 1. AI Application Dictionary Construction Process
The process of constructing the AI application dictionary includes the following steps:
(1) Seed word selection: To systematically extract keywords related to AI applications, this study integrates multiple sources and methods to obtain word roots. First, academic literature and databases (e.g., top journals, conference papers, Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore) provide the basic AI terminology, identifying high-frequency vocabulary through keyword searches and co-occurrence analysis. Second, industry reports and market research (from organizations like Gartner, IDC, McKinsey) reveal the latest AI application trends and related keywords. In addition, government and policy documents (including white papers, strategic plans, and ISO standards) offer authoritative AI terminology. Patent databases (such as WIPO, CNIPA, USPTO) extract technical terms and application field keywords through patent text analysis and patent analysis tools. Corporate annual reports and technical reports use natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze the text of listed company reports and technical white papers, extracting relevant keywords. Based on this, 52 AI-related terms, such as “image recognition,” “human-computer interaction,” “business intelligence,” and “autonomous driving,” were manually selected as seed words.
(2) Vocabulary expansion: Using the Word2Vec technology’s Skip-gram model, words in the annual report texts were trained. The cosine similarity between seed words and output words was calculated, and five semantically similar words for each seed word were selected.
(3) Vocabulary screening: Duplicate words, words unrelated to AI applications, and words with too low a frequency were removed, leaving 116 words to form the AI application dictionary used in this study.
Next, an AI application indicator was constructed based on the annual reports of listed companies. Since Chinese text lacks space separation and words are the smallest independent linguistic units, specialized word segmentation processing was required for the annual report text. This study uses the widely applied Python open-source “jieba” Chinese word segmentation module to segment the annual reports of listed companies. The constructed AI dictionary was added as a preset proprietary dictionary in the “jieba” segmentation module, and the frequency of AI-related terms appearing in the annual reports was counted. Finally, the natural logarithm of the number of AI application keywords plus one in the annual report was used as the indicator for the company’s level of AI application.
3.2.2. Dependent variable
The dependent variable in this study is corporate innovation performance (Inv). Existing research typically employs two methods for measurement: the first is to use patent data, which generally includes the total number of patent applications or patents granted by the company as an indicator; the second is to evaluate innovation performance based on the sales revenue of new products. However, since Chinese companies are not required to disclose sales revenue from new products in their annual reports, and considering the availability of data, this study chooses to measure innovation performance using patent data [20] . Compared to the number of patents granted, the number of patent applications better reflects the current level of innovation in a company, as it is not influenced by the approval process or preferences. Since invention patents represent a higher level of innovation achievements, this study uses the total number of invention patent applications by a company to measure innovation performance. To avoid the interference caused by a company having either an excessively large number of patent applications or none at all, this study, following previous research, constructs the dependent variable by taking the natural logarithm of the total number of invention patent applications plus 1. For robustness testing, the total number of all patent applications by the company is used as an alternative measure for innovation performance.
3.2.3. Mediating variables
In this study, the variable of innovation resource allocation is adapted from the research of Guan & Wang (2004), and is measured from two aspects: innovative human resources and innovation funding [21].
Innovative Human Resources Allocation (IRp): This refers to the ratio of the number of research personnel involved in innovation and R&D activities to the total number of employees in the company, reflecting the extent to which the company supports innovation activities in terms of human resources.
Innovation Funding Allocation (IRi): This refers to the ratio of the funds allocated for innovation and R&D to the company’s operating revenue, measuring the financial investment in innovation. Innovation R&D expenditures include both internal funding for technological innovation and government funding for technological innovation.
By measuring these two aspects, this study provides a comprehensive evaluation of corporate innovation resource allocation from the perspectives of human and financial resource distribution, in order to reveal the mediating role of AI applications in corporate innovation performance.
3.2.4. Control variables
To account for other possible influencing factors, this study includes several control variables. Drawing on the relevant research of Yao et al. (2024), the following control variables are included in the model: company age, return on total assets, proportion of current assets, ownership concentration, and proportion of independent directors. Detailed measurement indicators are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Variable Selection and Definitions
Category | Variable Name | Variable Symbol | Variable Definition |
Independent Variable | Artificial Intelligence Application | AI_apply | The natural logarithm of the AI composite indicator (plus 1) calculated in this study |
Dependent Variable | Corporate Innovation Performance | Inv | Ln (Total number of invention patent applications + 1) |
Mediating Variable | R&D Personnel Allocation | IRp | Number of R&D personnel involved in innovation activities / Total number of employees |
Innovation Funding Allocation | IRi | Innovation R&D expenditure / Operating revenue | |
Control Variables | Company Age | Age | Year of observation - Year of listing |
Return on Assets | Roa | Net profit / Total assets | |
Proportion of Current Assets | Cr | Current assets / Total assets | |
Ownership Concentration | Top1 | Percentage of shares held by the largest shareholder | |
Proportion of Independent Directors | Bodi | Number of independent directors / Total number of directors |
3.3. Model construction
To further examine the mediating effect, the following mediating effect model is constructed:
\( {Inv_{I,t}}={β_{0}}+{β_{1}}{{AI_{apply}}_{I,t}}+\sum {γControls_{I,t}}+\sum {Year_{t}}+\sum {Prov_{i}}+{ε_{I,t}}\ \ \ (1) \)
\( {M_{i,t}}={α_{0}}+{α_{1}}{{AI_{apply}}_{i,t}}+\sum {γControls_{i,t}}+\sum {Year_{t}}+\sum {Prov_{i}}+{ε_{i,t}}\ \ \ (2) \)
\( {Inv_{I,t}}={μ_{0}}+{μ_{1}}{{AI_{apply}}_{I,t}}+{μ_{2}}{M_{I,t}}+\sum {γControls_{I,t}}+\sum {Year_{t}}+\sum {Prov_{i}}+{ε_{I,t}}\ \ \ (3) \)
First, regression analysis is conducted using formula (1) to verify the total effect of AI applications on corporate innovation performance. Then, in the second step, formula (2) is used to examine the impact of AI applications on the mediating variable. In the final step, formula (3) is applied by introducing the mediating variable into the basic regression model to test the significance of the coefficients. The variable M includes two mediating variables: R&D personnel allocation and innovation R&D funding.
4. Empirical analysis
4.1. Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis
The results of the descriptive statistics analysis in this study are shown in Table 3, while the Pearson correlation coefficients between variables are presented in Table 4. The Pearson correlation coefficient between artificial intelligence (AI) application and enterprise innovation performance is statistically significant at the 1% level, indicating a positive correlation between the two. This finding preliminarily supports the research hypothesis H1. The correlation coefficients between enterprise innovation performance and the configuration of research and development (R&D) personnel, as well as innovation funding allocation, are all significantly positive, suggesting a positive correlation between innovation performance and the mediator variables. Moreover, there is no evident multicollinearity issue between AI application, enterprise innovation performance, and other control variables.
Table 3. Descriptive Statistics
Variable | Sample Size | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
Inv | 10324 | 0.860 | 1.450 | 0 | 8.950 |
AI_apply | 10324 | 2.370 | 1.270 | 0 | 6.930 |
IRp | 10324 | 0.170 | 0.110 | 0 | 0.920 |
IRi | 10324 | 18.13 | 1.410 | 0 | 24.12 |
Age | 10324 | 6.230 | 5.670 | -1 | 31 |
Top1 | 10324 | 31.95 | 13.74 | 2.120 | 95.50 |
Cr | 10324 | 0.620 | 0.150 | 0.0500 | 0.990 |
Roa | 10324 | 0.0500 | 0.0900 | -3.200 | 1.410 |
Bodi | 10324 | 0.460 | 0.140 | 0.220 | 1.600 |
Table 4. Correlation Analysis
Inv | AI_apply | IRp | IRi | Age | Top1 | Cr | Roa | Bodi | |
Inv | 1 | ||||||||
AI_apply | 0.119*** | 1 | |||||||
IRp | 0.165*** | 0.294*** | 1 | ||||||
IRi | 0.120*** | 0.160*** | 0.179*** | 1 | |||||
Age | -0.078*** | -0.045*** | -0.090*** | 0.300*** | 1 | ||||
Top1 | -0.00800 | -0.031*** | -0.149*** | -0.093*** | -0.237*** | 1 | |||
Cr | 0.063*** | 0.191*** | 0.291*** | -0.042*** | -0.275*** | 0.074*** | 1 | ||
Roa | 0.046*** | -0.026*** | -0.019* | 0.046*** | -0.157*** | 0.171*** | 0.174*** | 1 | |
Bodi | -0.027*** | 0.00500 | 0.018* | -0.019** | 0.0140 | -0.00500 | -0.033*** | -0.060*** | 1 |
Note: N=10324; *** p < 0.01, ** p < 0.05, * p < 0.1.
4.2. Direct effects and mediation effects test
4.2.1. Direct effects test
This study adopts a stepwise regression method, progressively adding control variables to estimate the impact of artificial intelligence on the innovation performance of manufacturing enterprises. To avoid potential issues such as omitted variables, heteroscedasticity, and serial correlation during estimation, fixed effects for year and province are introduced, along with robust standard errors to enhance the reliability of the results. The specific estimation results are shown in Table 5. Column (1) shows the regression results of the model without control variables, while column (2) presents the results with control variables. In both cases, the regression coefficient of AI application on enterprise innovation performance is significantly positive at the 1% confidence level, indicating that the higher the level of AI application, the higher the innovation performance. Thus, hypothesis H1 of this study is validated.
Table 5. Baseline Regression Analysis
(1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
Inv | Inv | Inv | Inv | Inv | Inv | |
AI_apply | 0.155*** | 0.148*** | ||||
(0.0117) | (0.0118) | |||||
IRp | 2.228*** | |||||
(0.138) | ||||||
IRi | 0.174*** | |||||
(0.0107) | ||||||
Age | -0.0136*** | -0.0114*** | -0.0279*** | -0.0121*** | -0.0152*** | |
(0.00274) | (0.00273) | (0.00285) | (0.00273) | (0.00276) | ||
Top1 | -0.00264** | -0.000289 | -0.00250** | -0.00229** | -0.00274** | |
(0.00108) | (0.00109) | (0.00108) | (0.00108) | (0.00109) | ||
Cr | 0.157 | -0.0764 | 0.337*** | 0.0501 | 0.390*** | |
(0.0986) | (0.100) | (0.0969) | (0.0984) | (0.0982) | ||
Roa | 0.702*** | 0.716*** | 0.326* | 0.557*** | 0.641*** | |
(0.169) | (0.168) | (0.169) | (0.168) | (0.170) | ||
Bodi | -0.267*** | -0.302*** | -0.223** | -0.275*** | -0.263*** | |
(0.0979) | (0.0974) | (0.0975) | (0.0973) | (0.0985) | ||
_cons | 0.499*** | 0.675*** | 0.727*** | -2.154*** | 0.770*** | 0.880*** |
(0.0310) | (0.0921) | (0.0903) | (0.210) | (0.0899) | (0.0909) | |
year | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
prov | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
N | 10324 | 10324 | 10324 | 10324 | 10324 | 10324 |
r2 | 0.0503 | 0.0567 | 0.0662 | 0.0662 | 0.0682 | 0.0448 |
Standard errors in parentheses
* p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01
4.2.2. Mediation effect test
This study discusses the mechanism through which artificial intelligence (AI) applications affect corporate innovation performance based on the model, with the specific results of the mediation effect test shown in Table 6. First, we explore how AI applications influence corporate innovation performance by affecting the configuration of research and development (R&D) personnel. In column (2) of Table 6, the regression coefficient for AI applications on R&D personnel configuration is 0.0181, which is significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that the deepening of AI applications significantly enhances the allocation of R&D personnel in enterprises. Further examination of column (3) shows the joint regression results of AI applications and R&D personnel configuration on corporate innovation performance, where the regression coefficient for AI applications is 0.113, and the regression coefficient for R&D personnel configuration is as high as 1.949. Both coefficients pass the significance test at the 1% level. Compared with the regression results in column (1), when R&D personnel configuration is included as a variable in the model, the regression coefficient for AI applications decreases but remains significantly positive at the 1% level. This phenomenon reveals that R&D personnel configuration has a partial mediation effect, confirming hypothesis H2a.
Next, we explore how AI applications influence innovation performance through the configuration of innovation funding. According to column (4) in Table 6, the regression coefficient for AI applications on innovation funding configuration is 0.162, which is significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that the enhancement of AI applications significantly promotes the proportion of investment in innovation funding. Furthermore, column (5) shows that the regression coefficient for innovation funding configuration on corporate innovation performance is significantly positive (0.157) at the 1% level, suggesting that increasing investment in innovation funding contributes to improving innovation performance. By comparing the regression coefficients for AI applications in columns (4) and (5), it is found that after adding the innovation funding configuration variable, the regression coefficient for AI applications decreases, indicating that innovation funding configuration plays a partial mediating role, thus confirming hypothesis H2b.
Table 6. Mediation Effect Test of Innovation Resource Allocation
(1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
Inv | IRp | Inv | IRi | Inv | |
AI_apply | 0.148*** | 0.0181*** | 0.113*** | 0.162*** | 0.123*** |
(0.0118) | (0.000829) | (0.0120) | (0.0107) | (0.0118) | |
Age | -0.0136*** | -0.00123*** | -0.0112*** | 0.0789*** | -0.0260*** |
(0.00274) | (0.000192) | (0.00272) | (0.00249) | (0.00284) | |
Top1 | -0.00264** | -0.00113*** | -0.000438 | -0.00186* | -0.00234** |
(0.00108) | (0.0000759) | (0.00108) | (0.000985) | (0.00107) | |
Cr | 0.157 | 0.169*** | -0.173* | -0.122 | 0.176* |
(0.0986) | (0.00691) | (0.101) | (0.0896) | (0.0976) | |
Roa | 0.702*** | -0.0370*** | 0.774*** | 1.725*** | 0.431** |
(0.169) | (0.0118) | (0.167) | (0.154) | (0.168) | |
Bodi | -0.267*** | 0.0159** | -0.298*** | -0.249*** | -0.227** |
(0.0979) | (0.00686) | (0.0970) | (0.0890) | (0.0970) | |
IRp | 1.949*** | ||||
(0.140) | |||||
IRi | 0.157*** | ||||
(0.0108) | |||||
_cons | 0.675*** | 0.0568*** | 0.564*** | 17.42*** | -2.065*** |
(0.0921) | (0.00645) | (0.0916) | (0.0837) | (0.209) | |
year | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
prov | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
N | 10324 | 10324 | 10324 | 10324 | 10324 |
r2 | 0.0567 | 0.220 | 0.0743 | 0.170 | 0.0760 |
Standard errors in parentheses
* p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01
4.3. Robustness test
To further enhance the robustness of the conclusions, this study adopts a variable substitution strategy by selecting the total number of patent applications as a new dependent variable. Column (1) of Table 7 shows the regression results, where the regression coefficient is prominently significant at the 1% level, which strongly supports the significant impact of AI applications on improving corporate innovation performance, thereby confirming the robustness of the conclusions.
Intelligent equipment and programs play an indispensable role in various processes such as R&D and manufacturing in enterprises. For large-scale, well-established listed manufacturing companies, it is rare to encounter cases where the application of such facilities is zero. However, in this study, instances with an AI application index of zero were still found, which may be attributed to the lack of explicit description of such applications in the companies’ annual reports. Therefore, for the accuracy of the research, samples with an AI application index of zero were excluded, and regression analysis was conducted based on the remaining samples, as shown in column (2) of Table 7. The regression results show that the regression coefficient for AI application technology is 0.1605, which is positively significant at the 1% level, further validating the robustness of the baseline regression results in this study.
Table 7. Robustness Test
(1) | (2) | |
Inv_sum | Inv | |
AI_apply | 0.213*** | 0.161*** |
(0.0148) | (0.0139) | |
Age | -0.0260*** | -0.0131*** |
(0.00343) | (0.00288) | |
Top1 | -0.00366*** | -0.00218* |
(0.00136) | (0.00114) | |
Cr | 0.206* | 0.168 |
(0.123) | (0.104) | |
Roa | 0.819*** | 0.805*** |
(0.211) | (0.179) | |
Bodi | -0.263** | -0.236** |
(0.123) | (0.103) | |
_cons | 0.920*** | 0.590*** |
(0.115) | (0.0985) | |
year | YES | YES |
prov | YES | YES |
N | 10324 | 9469 |
r2 | 0.0676 | 0.0563 |
Standard errors in parentheses
* p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01
5. Conclusion
This study systematically reviews existing domestic and international literature, proposes research hypotheses based on resource-based theory, dynamic resource-based view, and ambidextrous innovation theory, and empirically tests the effectiveness of these hypotheses using data from manufacturing companies listed on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges from 2015 to 2023. It analyzes the impact and mechanisms of AI technology applications on corporate innovation performance, and further conducts a heterogeneity analysis of the effects of AI applications on innovation performance. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) AI applications significantly promote the growth of innovation performance in manufacturing companies. The empirical analysis confirms the positive effect of AI applications on corporate innovation performance, which remains significant after multiple robustness tests. This shows that AI applications play a key role in promoting the effective use of production factors and are an important driver for improving corporate competitiveness and economic growth. Manufacturing companies should actively adopt AI technologies to enhance innovation capabilities and competitiveness [22] , thereby facilitating the conversion of innovative results into economic benefits.
(2) Innovation R&D resources play a significant mediating role in the process through which AI applications promote innovation performance in manufacturing companies, with varying effects across different dimensions of innovation R&D resources. Among these, the mediation effect of R&D personnel allocation is the strongest, while the mediation effect of R&D funding allocation is relatively weaker. This finding provides new insights for enterprises to further explore ways to enhance innovation R&D resources while applying AI to improve innovation performance, especially the irreplaceable role of human capital in technological innovation. By optimizing human resource allocation, the marginal benefits of AI applications can be increased, promoting the sustainable development of corporate innovation.
References
[1]. Zhang, X. (2023). The social changes that may be triggered by next-generation artificial intelligence technology (ChatGPT). Industrial Economic Review, 3, 22–30.
[2]. Liu, J., Chang, H., Forrest, J. Y. L., & Yang, B. (2020). Influence of artificial intelligence on technological innovation: evidence from the panel data of China’s manufacturing sectors. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 158, 120142.
[3]. Fadziso, T. (2018). The impact of artificial intelligence on innovation. Global Disclosure of Economics and Business, 7(2), 81–88.
[4]. Sun, L., & Li, S. (2021). Research on the influence path of artificial intelligence empowerment on innovation performance: Based on fuzzy qualitative comparative analysis. Science and Technology Management Research, 41(23), 11–19.
[5]. Li, G., & Bai, Y. (n.d.). How does the application of artificial intelligence influence innovation performance in manufacturing enterprises? Economic and Finance Review, 1–13.
[6]. Aghion, P., Jones, B. F., & Jones, C. I. (2018). Artificial intelligence and economic growth. In The Economics of Artificial Intelligence: An Agenda (pp. 237–282). University of Chicago Press.
[7]. Sun, W., & Liu, Y. (2023). A study on the impact mechanism of artificial intelligence on the labor market. East China Economic Management, 37(3), 1–9.
[8]. Mi, J., Jiang, L., & Li, Z. (2020). A study on the application of artificial intelligence technology in advancing the upgrading of China’s manufacturing industry. Humanities Journal, 9, 46–55.
[9]. Meng, F., Xu, Y., & Zhao, G. (2022). Research on the impact mechanism of “intelligent +” on innovation performance in manufacturing enterprises. Research Management, 43(9), 109–118.
[10]. Li, C., He, S., Tian, Y., Sun, S., & Ning, L. (2022). Does the bank’s FinTech innovation reduce its risk-taking? Evidence from China’s banking industry. Innovation and Knowledge, 7(3), 100219.
[11]. Zhao, L., Tao, H., & Cao, H. (2023). Empirical research on the impact of artificial intelligence technology on employment: Micro evidence from service enterprises. Information Technology and Management Applications, 2(3), 124–137.
[12]. Liu, T., Zhou, B., & Liang, B. (2024). Artificial intelligence, green innovation, and corporate carbon performance. Economic System Reform, 4, 193–200.
[13]. Liu, Q., Zhang, P., Yang, P., & Lei, Y. (2023). The impact of digital empowerment on technological innovation efficiency in manufacturing. Statistics and Decision, 23, 80–84.
[14]. Fang, H. (2024). The impact of artificial intelligence applications on corporate innovation and its mechanism: Evidence from China’s A-share listed companies. Science and Technology Management Research, 44(15), 157–167.
[15]. Li, M., & Huang, H. (2022). Industrial robot applications and innovation performance in manufacturing enterprises: The mediating effects of R&D investment and employee knowledge capabilities. Chinese Personnel Science, 3, 73–84.
[16]. Hu, S., Wang, L., & Zhao, H. (2021). The application of artificial intelligence, human-machine collaboration, and labor productivity. Chinese Population Science, 5, 48–62, 127.
[17]. Liu, B., & Liu, A. (2023). Digital transformation, factor allocation, and corporate innovation efficiency. Economic System Reform, 5, 121–128.
[18]. Xu, P., & Xu, X. (2020). The logic and analytical framework of enterprise management transformation in the era of artificial intelligence. Management World, 36(1), 122–129, 238.
[19]. Yao, J., Zhang, K., Guo, L., & Feng, X. (2024). How does artificial intelligence improve corporate production efficiency? Based on the perspective of labor force skill structure adjustment. Management World, 40(2), 101–116, 133, 117–122.
[20]. Zhu, G., & Wang, K. (2024). Artificial intelligence applications and green innovation in manufacturing enterprises. Industrial Technology Economics, 43(9), 73–81.
[21]. Guan, J. C., & Wang, J. X. (2004). Evaluation and interpretation of knowledge production efficiency. Scientometrics, 59(1), 131–155.
[22]. Roberts, D. L., & Candi, M. (2024). Artificial intelligence and innovation management: Charting the evolving landscape. Technovation, 136, 103081.
Cite this article
Zheng,R.;Yuan,C. (2025). The impact of artificial intelligence applications on enterprise innovation performance: A case study of the manufacturing industry. Advances in Operation Research and Production Management,4(1),7-17.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Operation Research and Production Management
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhang, X. (2023). The social changes that may be triggered by next-generation artificial intelligence technology (ChatGPT). Industrial Economic Review, 3, 22–30.
[2]. Liu, J., Chang, H., Forrest, J. Y. L., & Yang, B. (2020). Influence of artificial intelligence on technological innovation: evidence from the panel data of China’s manufacturing sectors. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 158, 120142.
[3]. Fadziso, T. (2018). The impact of artificial intelligence on innovation. Global Disclosure of Economics and Business, 7(2), 81–88.
[4]. Sun, L., & Li, S. (2021). Research on the influence path of artificial intelligence empowerment on innovation performance: Based on fuzzy qualitative comparative analysis. Science and Technology Management Research, 41(23), 11–19.
[5]. Li, G., & Bai, Y. (n.d.). How does the application of artificial intelligence influence innovation performance in manufacturing enterprises? Economic and Finance Review, 1–13.
[6]. Aghion, P., Jones, B. F., & Jones, C. I. (2018). Artificial intelligence and economic growth. In The Economics of Artificial Intelligence: An Agenda (pp. 237–282). University of Chicago Press.
[7]. Sun, W., & Liu, Y. (2023). A study on the impact mechanism of artificial intelligence on the labor market. East China Economic Management, 37(3), 1–9.
[8]. Mi, J., Jiang, L., & Li, Z. (2020). A study on the application of artificial intelligence technology in advancing the upgrading of China’s manufacturing industry. Humanities Journal, 9, 46–55.
[9]. Meng, F., Xu, Y., & Zhao, G. (2022). Research on the impact mechanism of “intelligent +” on innovation performance in manufacturing enterprises. Research Management, 43(9), 109–118.
[10]. Li, C., He, S., Tian, Y., Sun, S., & Ning, L. (2022). Does the bank’s FinTech innovation reduce its risk-taking? Evidence from China’s banking industry. Innovation and Knowledge, 7(3), 100219.
[11]. Zhao, L., Tao, H., & Cao, H. (2023). Empirical research on the impact of artificial intelligence technology on employment: Micro evidence from service enterprises. Information Technology and Management Applications, 2(3), 124–137.
[12]. Liu, T., Zhou, B., & Liang, B. (2024). Artificial intelligence, green innovation, and corporate carbon performance. Economic System Reform, 4, 193–200.
[13]. Liu, Q., Zhang, P., Yang, P., & Lei, Y. (2023). The impact of digital empowerment on technological innovation efficiency in manufacturing. Statistics and Decision, 23, 80–84.
[14]. Fang, H. (2024). The impact of artificial intelligence applications on corporate innovation and its mechanism: Evidence from China’s A-share listed companies. Science and Technology Management Research, 44(15), 157–167.
[15]. Li, M., & Huang, H. (2022). Industrial robot applications and innovation performance in manufacturing enterprises: The mediating effects of R&D investment and employee knowledge capabilities. Chinese Personnel Science, 3, 73–84.
[16]. Hu, S., Wang, L., & Zhao, H. (2021). The application of artificial intelligence, human-machine collaboration, and labor productivity. Chinese Population Science, 5, 48–62, 127.
[17]. Liu, B., & Liu, A. (2023). Digital transformation, factor allocation, and corporate innovation efficiency. Economic System Reform, 5, 121–128.
[18]. Xu, P., & Xu, X. (2020). The logic and analytical framework of enterprise management transformation in the era of artificial intelligence. Management World, 36(1), 122–129, 238.
[19]. Yao, J., Zhang, K., Guo, L., & Feng, X. (2024). How does artificial intelligence improve corporate production efficiency? Based on the perspective of labor force skill structure adjustment. Management World, 40(2), 101–116, 133, 117–122.
[20]. Zhu, G., & Wang, K. (2024). Artificial intelligence applications and green innovation in manufacturing enterprises. Industrial Technology Economics, 43(9), 73–81.
[21]. Guan, J. C., & Wang, J. X. (2004). Evaluation and interpretation of knowledge production efficiency. Scientometrics, 59(1), 131–155.
[22]. Roberts, D. L., & Candi, M. (2024). Artificial intelligence and innovation management: Charting the evolving landscape. Technovation, 136, 103081.









