1. Introduction
As one of the most influential global sports events, the FIFA World Cup exerts extensive and diverse effects on the host nation. The 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia and the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar serve as exemplary instances for examining this issue. The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic introduced a unique context for the 2022 World Cup. The 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia and the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar provide excellent cases for studying this phenomenon. The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has added a special background to the 2022 World Cup.
This study fills a gap in the existing literature by conducting a scoping review of Google Scholar (2017-2024). It investigates the impacts of the 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia and the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar. Prior research has not thoroughly explored these events. The goal is to examine the economic, cultural, infrastructure, tourism, and hotel-related effects of the World Cups on Russia and Qatar. Consequently, it will advance the knowledge in this area. By applying the scoping review method, the goals were defined, Google Scholar was selected, search terms were set, literature was screened, data was extracted and verified, and then analyzed. The results indicate that 14 publications were discovered, comprising 5 pertaining to the 2018 World Cup and 9 related to the 2022 World Cup, with publishing surges occurring in 2019 and 2023. The effects include economic factors like Qatar's GDP growth, cultural transformations, and infrastructure advancements. The economic consequences encompass all dimensions, with the tourism and hospitality sectors witnessing growth and enhancements. These findings provide valuable insights for future studies on the World Cup and its implications for the 2026 host.
In the early 20th century, due to the restrictions on professional players’ participation in the Olympic Games, FIFA decided to launch a world-class football event, which is independent of the Olympics, in 1928. The first FIFA World Cup was held in Uruguay in 1930. The purpose of the World Cup is to promote the football spirit, facilitate football cultural integration among countries and display the cultural features of the host country.
To achieve these objectives, FIFA has established stringent criteria for the selection of host countries. National football associations submit applications to FIFA. After evaluation of FIFA, all member countries vote to select the host country. The host country must be a member of FIFA. They must have event-organizing capabilities and provide the sufficient stadium facilities. Security guarantees and financial support are the keys to ensure the smooth holding of the event and the reception of fans.
The World Cup offers the host country a prime chance to show its national image and drive economic growth. It draws global football fans and tourists, spurring the hotel and tourism industries. This event is crucial for enhancing the host country’s international standing and domestic development in the economy, tourism, and hotel industry.
1.1. The impacts of the 2018 & 2022 FIFA World Cup
On December 2, 2010, Russia and Qatar obtained the hosting rights for the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cups, respectively. In contrast to previous FIFA World Cups, the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar occurred under a markedly distinct context. The worldwide epidemic brought major difficulties and adjustments in many spheres of the event. However, the context of the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar was markedly different from previous tournaments, as the COVID-19 pandemic presented unprecedented challenges to both the organization of the event and its economic impacts. The analysis included consumer buying patterns, developing plans, and the health of the world economy. This framework provides a unique approach to look at the financial consequences of hosting the major international athletic events.
The 2018 World Cup has a substantial impact on the Russian economy. The influx of fans prompted growth in accommodation, dining, and shopping, leading to heightened sales. Simultaneously, investment in infrastructure improved domestic amenities and invigorated construction-related industries. Moreover, it enhanced Russia's global stature, attracted foreign investment, promoted sustainable economic development, and alleviated specific economic challenges. Likewise, the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar stimulated investment, invigorating the building and engineering industries and generating a multitude of employment opportunities. During the event, tourism reached its zenith, enhancing associated income and fostering economic diversity. It also progressed financial and logistical services, augmenting Qatar’s global economic stature and supplying expertise and capital for future economic transformation.
The FIFA World Cup profoundly influenced the societies of both Russia and Qatar as citizens participated in event-related activities. The arrival of foreign tourists elevated international attitudes, and expanded global knowledge among residents. It brought the enhancements of urban environments, the development of public facilities, and the upgrading of social services. Consequently, it not only enhanced the quality of life for residents but also enhanced their cultural experiences.
1.2. The gap of previous studies
In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on the economic impacts of hosting the FIFA World Cup. This event yields significant economic advantages. It promotes tourism, stimulates infrastructural development, and enhance a nation's global reputation. However, the unique circumstances of the pandemic have introduced new complexities to these economic effects. While prior studies have examined the broad economic advantages, there remains a gap in understanding how the pandemic has specifically influenced the economic outcomes for host countries. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the economic impacts of the FIFA World Cup were relatively predictable. It was marked by a surge in the international tourists, numerous offline events, and the active business participation and the vibrant economic scene. However, the pandemic disrupted this. It severely damaged global tourism and slashed tourist flows. Stadium capacities were strictly limited for epidemic prevention, and the public gatherings were greatly restricted. Consumer behavior patterns fundamentally changed, especially in consumption decision-making, methods, and preferences.
With an in-depth review of available literature and data, this review aims to study the impacts of the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cups on Russia and Qatar, their economic impacts on these two countries, and their influences on the tourism and hotel industries in Russia and Qatar. Hence, the research questions are as follows:
• What are the documented impacts of hosting the 2018, 2022 FIFA World Cup on the host country?
• What are the economic impacts of hosting the 2018, 2022 FIFA World Cup on the host country's economy?
• How has hosting the 2018, 2022 FIFA World Cup influenced the tourism and hospitality industries in the host countries?
2. Methods
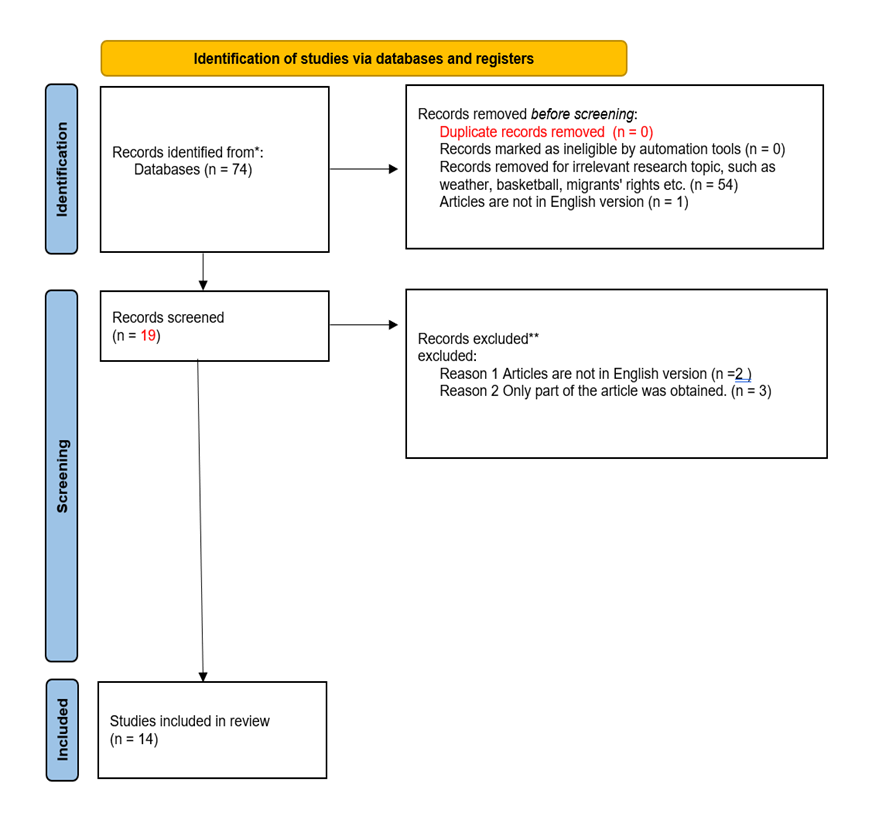
Figure 1. Study flow diagram
This study (see Figure 1) adopted the scoping review method to comprehensively sort out the impacts of the 2018 FIFA World Cup and the 2022 FIFA World Cup on the host countries, with a particular focus on the fields of economy, tourism, and the hotel industry. The specific steps are as follows:
2.1. Definition and goal clarification
In accordance with the requirements of the scoping review, the research goal was precisely defined as systematically exploring the multi-faceted impacts of the two World Cups on the host countries, especially in terms of economy, tourism, and the hotel industry. Through a comprehensive analysis of these impacts, this study provides a holistic perspective for research in related fields, facilitating the in-depth development of subsequent studies.
2.2. Literature retrieval
• Database Selection: Google Scholar.
• Combined with the research theme, detailed search terms were determined. For World Cup-related content, terms such as “2018 FIFA World Cup,” “2022 FIFA World Cup,” and “FIFA World Cup” were used; for the host countries, the specific names of the host countries were included; in terms of economic impacts, words like “economic impact,” “GDP growth,” and “employment” were employed; Tourism-related search terms included “tourism industry,” “tourist arrivals,” and “travel and tourism,” etc.; for the hotel industry, there were terms such as “hotel industry,” “hotel occupancy,” and “accommodation sector,” etc. Boolean logic operators “AND” and “OR” were used to connect the search terms to construct a comprehensive and effective retrieval strategy.
• Time Range: The publication time of the retrieved literature was limited to the period from 2017 (covering studies related to pre-event preparations) to 2024 to obtain research results that were closely related to the two World Cups and had relatively strong timeliness.
2.3. Literature screening
• Inclusion Criteria: The research literature focusing on the impacts of the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cups on the host countries was included, including but not limited to academic journal papers, dissertations, and research reports. Studies that explicitly addressed at least one aspect of the impacts on the economy, tourism, or the hotel industry were included to ensure relevance to the theme.
• Exclusion Criteria: Literature that was irrelevant to the theme, with unclear research content or lacking substantial data support was excluded. Duplicate publications and non-English literature were excluded (due to language proficiency limitations and to ensure the consistency of research resources).
2.4. Data extraction
• Design of Extraction Table: A standardized data extraction table was created, covering basic information of the literature (such as authors, year, source of the literature, etc.), research methods (research types, data collection methods, etc.), information related to the host countries, economic impact indicators (such as economic growth data, employment situation, etc.), tourism-related data (number of tourists, tourism revenue, improvement of infrastructure etc.), and hotel industry-related data (hotel occupancy rate, long-term impacts on hotel industry, etc.).
• Double Extraction and Verification: Two researchers independently extracted data from the included literature, and after the extraction was completed, cross-checking was carried out. For discrepancies arising during the data extraction process, in-depth discussions or reference to third-party authoritative materials were used to resolve them to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data extraction.
2.5. Data synthesis and analysis
Descriptive statistical analysis was applied. The extracted data were classified and sorted, and descriptive statistical methods, such as frequency analysis and mean calculation, were used to present the overall situation of the impacts of the two World Cups on the host countries in terms of economy, tourism, and the hotel industry, including the distribution and changing trends of various indicators.
In the thematic induction and summary, the data were analyzed in depth to summarize the key themes and common findings in different impact areas. For example, in terms of economic impacts, the impacts on macroeconomic indicators and industrial structure adjustment were summarized; in the tourism aspect, themes such as changes in tourist flows and the shaping of the image of tourist destinations were sorted out; in the hotel industry aspect, points such as fluctuations in occupancy rates and improvements in service quality were summarized to comprehensively and systematically elaborate on the comprehensive impacts of the World Cup on the host countries. Meanwhile, the limitations in the research, such as the completeness of data and the limitations of research methods, were explored to provide directions for improvement in future studies.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive results
In this section, the research questions will be explained in detail through text and charts.
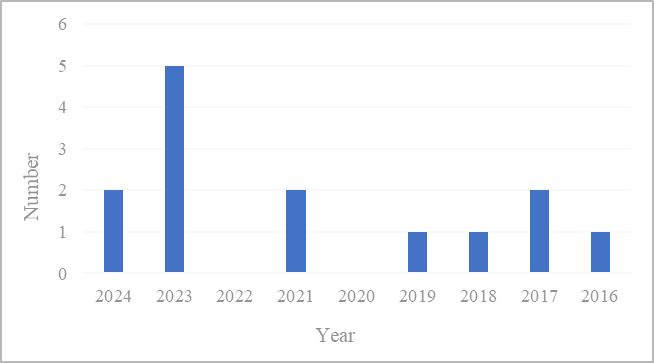
Figure 2. Number of articles
Figure 2 presents the number of articles centered on the themes of the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cups. A total of 14 articles relevant to the research questions were identified within the literature. Among these, no articles were published in 2020 and 2022, while the year 2023 witnessed the highest number of publications, with a total of 5 articles. It is likely that certain commercial activities and transfer-related news associated with the 2022 FIFA World Cup exerted a continued influence on the football domain in 2023. For example, an outstanding performance by a star player in the 2022 FIFA World Cup instigated a series of transfer rumors and discussions in 2023, thereby stimulating the generation of articles concerning the 2022 FIFA World Cup during that year. Additionally, some players who emerged during the 2018 FIFA World Cup might have evolved into football superstars or undergone substantial career transitions in 2023. This could have prompted retrospective analyses of their performances in the 2018 FIFA World Cup and examinations of their growth trajectories. Take Kylian Mbappé as an example; he performed remarkably in the 2018 FIFA World Cup and maintained his prominent status in subsequent years. In 2023, there were articles making comparisons between his standing then and that in the present.
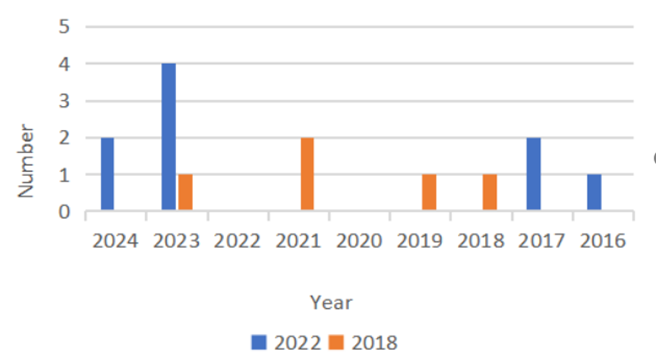
Figure 3. Annual quantity of articles
Figure 3 depicts the annual quantity of articles focusing on the 2018 or 2022 FIFA World Cup. It visually illustrates the number of articles related to the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cups across different years. Evidently, the blue bar, which represents articles on the 2022 FIFA World Cup, in 2023 is conspicuously taller than those in other years, with a count of four articles.
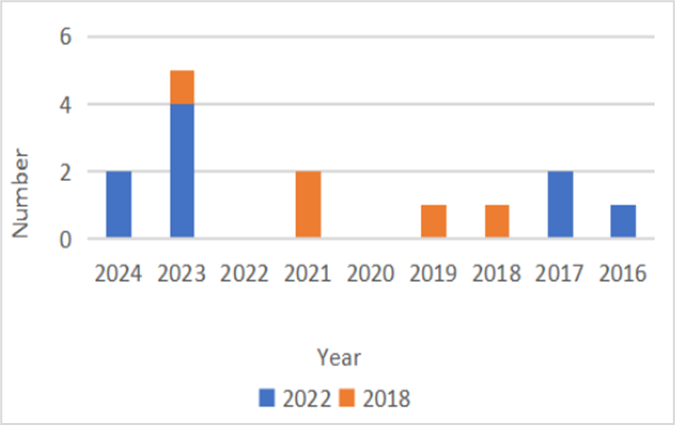
Figure 4. Comparison of article distribution
Figure 4 features a a stacked bar chart that is similar to the bar chart in Figure 3. Although there are slight differences in data presentation and proportion between these two charts, both clearly indicate that 2023 represents the peak year for the number of articles related to the 2022 FIFA World Cup, while 2019 is the peak year for articles concerning the 2018 FIFA World Cup.
There are 5 articles studying the 2018 FIFA World Cup and 9 articles studying the 2022 FIFA World Cup. Relatively speaking, the difference in the number of articles is not significant, which is conducive to research.
As previously stated, 2023 could potentially be a period conducive to the comprehensive summarization, analysis, and review of the 2022 FIFA World Cup. This may account for the relatively large number of articles published during this year. In the case of the 2018 FIFA World Cup, 2019 might have been a time when topics such as its subsequent impacts and player development were extensively debated, thereby resulting in a peak in the quantity of related articles. The distribution of the number of articles in other years may be associated with factors including football-related trending topics, event-commemorative activities, and player-specific news prevalent at that time. However, compared with 2023 and 2019, the concentration of article publication in these other years is relatively lower.
3.2. What are the documented impacts of hosting the FIFA World Cup on the host country?
Based on the analysis of 14 relevant documents, the impacts of the FIFA World Cup on the host country can be divided into three main aspects: economic impact, cultural impact, and infrastructure-building impact. The following is a detailed discussion of these three aspects.
3.2.1. Economic impact
12 out of 14 articles focus on the economy, 1 article studies culture, and 1 article examines infrastructure. These 12 articles explore the specific economic impacts of the FIFA World Cup on the host country from different perspectives.
Economy refers to the activities in which humans allocate scarce resources to meet survival needs under a specific social organization and order, covering the cycle of production, exchange, distribution, and consumption. For example, society needs to decide the direction of resource allocation, and families need to distribute their incomes. Enterprises produce products, which are exchanged and then distributed by society for consumers to use, thus completing the economic cycle. At the same time, economics, as a social science, studies the economic activities, economic relations, and their operational and development laws of humans at different development stages. Macroeconomics focuses on national-level economic indicators, while microeconomics focuses on the behaviour of individual economic units.
The analysis of 12 articles demonstrates that hosting the 2022 FIFA World Cup has significantly benefited Qatar's economy across various dimensions. A particularly noticeable aspect is the growth of the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) alongside the expansion of the retail and hospitality industries. This growth has, in turn, generated a substantial number of employment and investment opportunities. “In 2022, Qatar's GDP increased by approximately 4%, a significant improvement from the 1.5% growth in 2021 [1].” The description of the positive economic impact of hosting the 2022 FIFA World Cup is reasonable. Hosting a large-scale international sports event like the FIFA World Cup usually drives the development of industries such as retail and hotels in the host country, thereby promoting GDP growth and creating employment and investment opportunities. The comparison of Qatar’s GDP data in 2021 and 2022 mentioned also provides certain data support for the argument, enhancing the credibility of the content.
However, they applied different indicators to make studies. Al Refai & Eissa and Chancharat & Sangchan focus more on stock-market data, paying attention to changes in stock prices and trading volumes [2,3]. AL-MOHANNADI and Nikolaou et al., focus more on the comprehensive impact on the social economy, including various economic indicators [4,5]. Andersson et al., focus more on the enhancement of the destination image and its indirect impact on the economy [6]. Bibolov et al., focus more on the regional spill-over effect [7]. Averin & Kuznetsov and Bashkova focus more on specific economic indicators such as tourism revenue and hotel occupancy rates [8,9]. Kaplanidou et al., pay more attention to tourism willingness and potential tourism revenue [10]. Karamanaga and Rozhda & Sheresheva focus more on the enhancement of the tourism image and its indirect impact on the economy [11,12].
These research methods also differ. Al Refai & Eissa and Chancharat & Sangchan mainly use stock-market data [2,3]. AL-MOHANNADI and Nikolaou et al., mainly use official reports and statistical data [4,5]. Andersson et al., use questionnaires and social media analysis [6]. For tourism-related literature, Averin & Kuznetsov and Bashkova mainly use official statistical data [8,9]. Kaplanidou et al., and Karamanaga mainly use questionnaires [10,11]. Rozhda & Sheresheva use more questionnaires and social media analysis [12].
3.2.2. Cultural impact
Of the 14 articles, one delves into the cultural impacts of hosting the FIFA World Cup. Culture is the sum of material and spiritual wealth created in the historical development of human society. Material culture includes buildings like the pyramids, and spiritual culture encompasses religion, customs, knowledge, art, and many other aspects. Culture is also reflected in all aspects of life, such as diet, language, and clothing. Different cuisines, language dialects, and clothing styles all showcase cultural differences.
The 2022 FIFA World Cup attracted nearly a million spectators to the region, marking a significant cultural exchange event. This event offered many their initial encounter with Arab culture. In Qatar, the locals typically wear their traditional clothing with their long-standing cultural identity, while tourists wear a diverse range of clothes. More interesting, tourists are welcome to wear traditional Qatari clothing. In Qatari culture, strong and stable families are highly valued, forming the bedrock of society and influencing all aspects of daily life [13].
In the article of Yasir [13], culture is defined as the sum of the values, beliefs, customs, traditions, arts, languages, and lifestyles of a country or region. More specifically, culture encompasses the following dimensions:
• Values and beliefs
They refer to the commonly accepted codes of conduct and moral concepts. These values and beliefs largely shape the behaviour and interactions in society.
• Customs and traditions
They include festival celebrations, religious ceremonies, social customs, and traditional activities, which reflect the historical and cultural background of society.
• Arts and literature
They include music, dance, painting, sculpture, literary works, etc., which are important forms of cultural expression.
• Language
Language is not only a tool for communication but also an important carrier of cultural inheritance, reflecting the historical and cultural characteristics of a nation.
• Lifestyle
It includes eating habits, clothing, living styles, and social interaction styles, which reflect people's attitudes towards life and cultural characteristics.
The main research question of Yasir is to explore the impact of the 2022 FIFA World Cup on Qatar's culture and international image [13]. It mainly focuses on three aspects:
• The impact of the World Cup on the dissemination and promotion of Qatari culture.
• How the World Cup had changed the international community’s perception and evaluation of Qatar.
• Whether the World Cup had promoted cultural diversity and inclusivity in Qatar.
Regarding cultural dissemination and promotion, the study revealed that the 2022 FIFA World Cup substantially augmented the international visibility of Qatari culture. Through media reports, event broadcasts, and tourist experiences, Qatari traditional arts, music, cuisine, and lifestyle were extensively presented and diffused. In terms of international perception and evaluation, the World Cup enhanced the international community’s perspective on Qatar. Many countries and regions highly commended Qatar’s modernization process, infrastructure construction, and event-organizing capabilities, thereby elevating Qatar’s international image. Concerning cultural diversity and inclusivity, during the World Cup, Qatar implemented a series of measures to foster cultural diversity and inclusivity, such as organizing multicultural activities, offering multilingual services, and establishing cultural exchange platforms. These measures contributed to enhancing Qatar’s image as an open and inclusive nation.
The study acknowledges several limitations that may affect the generalization and accuracy of the findings. In terms of sample representativeness, its heavy reliance on media reports and tourist surveys means the sample might lack extensiveness and full representativeness, thus hampering the comprehensive reflection of the views and feelings of all groups. Due to the primary focus on data during and shortly after the World Cup, the evaluation of long-term impacts remains relatively restricted. The research data, predominantly derived from secondary sources such as media reports and online surveys, may be subject to biases and inaccuracy. Finally, the measurement methods for cultural diversity and exclusivity are highly subjective, lacking unified standards and indicators, which could introduce uncertainties when interpreting the research results.
3.2.3. Infrastructure-building impact
One article out of 14 articles specifically explores the impact of infrastructure-building, that is, “2022 FIFA World Cup and its Effect on the Urban Development of the City of Doha and its Infrastructure: A Three-Dimensional Impact Assessment Model, 3D IAM” by Al-Qahtani [14].
Generally, infrastructure refers to the basic physical and organizational structures. These structures and services are an indispensable part of social operation and development, providing necessary support for daily life, business activities, and public services. To prepare for the 2022 FIFA World Cup, Qatar spent around $200 billion on infrastructure, including railways, hotels, and roads [14].
In the study by Al-Qahtani, infrastructure-building supports urban operation and development [14]. Specifically, infrastructure includes transportation systems, communication systems, public service facilities, public buildings, and facilities, as well as urban planning and land development.
Research results of this article are that the World Cup significantly promoted the urban infrastructure construction of Doha, including the improvement of transportation, communication, and public service facilities. The 3D-IAM model effectively evaluated the multi-faceted impacts of the World Cup on urban development. This evaluation spanned multiple dimensions, namely economic, social, and environmental aspects. The World Cup promoted the urban modernization and sustainable development of Doha.
However, the applicability and accuracy of the model need to be further verified. The research mainly focuses on the city of Doha and fails to fully cover the infrastructure development of other regions in Qatar. The data sources mainly rely on official reports and planning documents, which may lack verification of actual effects.
3.3. What are the economic impacts of hosting the FIFA World Cup on the host country's economy?
3.3.1. Stock market performance
Two articles study the stock market. The stock market is an important part of the financial market. In terms of functions, it has a resource-allocation function, which can direct funds to high-quality enterprises, and a price-discovery function. Stock prices are determined by supply and demand and reflect the expected value of enterprises. From the perspective of participants, enterprises raise funds by issuing stocks, investors buy and sell stocks to obtain returns, securities intermediary institutions provide services, and stock exchanges supervise transactions.
Two articles, namely Al Refai & Eissa focus on the performance of the stock market [2,3]. Al Refai & Eissa analyzed the Qatari stock market data [2]. After Qatar was officially declared the host of the 2022 FIFA World Cup, an interesting phenomenon emerged in the stock market. There was a remarkable positive response, characterized by the rise in both stock prices and trading volumes. Chancharat & Sangchan focus analyzed the French stock market data and evaluated the short-term impact of the results of the 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia on the French stock market [3]. It was found that the game results had a significant short-term impact on the stock market.
These two articles on the impact of the FIFA World Cup on the stock market lack detailed data and materials, which limits our understanding of the specific mechanisms through which the World Cup affects the stock market.
3.3.2. Impact on the tourism and hotel industries
Five articles spotlight the FIFA World Cup's effects on these two sectors. It provided fresh insights that contribute to theoretical development.
Averin & Kuznetsov [8] assessed the 2018 Russia World Cup's effect on the country's tourism. Using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods, analyzing official stats, tourism firm data, and field research, they found it greatly boosted Russia's international tourism appeal. Tourist arrivals and revenue surged, particularly in host cities, underscoring the event's significant impact on the host country's tourism economy. In the related study, Bashkova [9] centered on the 2018 World Cup's impact on the Kaliningrad region's tourism. Via case studies and comparative analysis of key data like tourist flow, consumption structure, and infrastructure use, it showed the World Cup powerfully spurred local tourism. Tourist numbers and revenue rose markedly, spurring accommodation, catering, and transportation industries and energizing the regional economy. Similarly, Rozhda & Sheresheva [12] probed the 2018 Russia World Cup's influence on tourism destination image. Using surveys, interviews, and content analysis, gathering data from international tourists, insiders, and social media, they found the World Cup significantly enhanced Russia's international tourism image. Host cities' popularity and reputation grew a lot, forming a modern, international, and culturally-attractive urban image and building a solid brand base for Russia's tourism sustainability.
In addition to studying the favorable effect on the U.S. tourism sector, Kaplanidou et al., [10] looked into the popularity of the 2022 FIFA World Cup. The results suggested that the event had a substantial impact on Qatar's visibility in the U.S. tourism market. Karamanaga [11] delved deep into how the 2022 FIFA World Cup influenced Qatar's image as a tourist destination. The research showed that the event significantly enhanced people's perception of Qatar as a tourist spot. This, in turn, spurred the growth of tourism-related revenues. These studies highlight the substantial benefits of hosting the FIFA World Cup. These include increased tourism attractiveness, an improved destination image, and greater economic gains.
3.3.3. Other impacts on economy
Five studies present diverse perspectives on the economic impacts. Specifically, AL-MOHANNADI and Nikolaou et al., adopted a comprehensive socio-economic methodology [4,5]. By making use of official reports and statistical data, AL-MOHANNADI assessed the socio-economic impacts of the 2022 FIFA World Cup on Qatar [4]. This study investigated various aspects, including economic growth, employment, infrastructure development, and tourism revenue. The research findings of Nikolaou et al., emphasized that the World Cup remarkably enhanced Qatar's economic growth, especially in aspects such as infrastructure development, employment, and tourism revenue [5].
Andersson et al., investigated the impact of major football events on destination perception by employing questionnaires and social media analysis [6]. Their findings indicated that the World Cup significantly enhanced the international image of the host city. It also boosted tourism and investment.
Bibolov et al., further examined the regional spillover effects of the 2022 FIFA World Cup [7]. Their study focused on understanding how the event influenced surrounding areas, particularly in terms of economic and social impacts. By analyzing various data sources, the authors identified significant trends and patterns. Specifically, they found that the World Cup generated substantial economic activity in host cities, which extended to neighboring regions. Additionally, the event fostered increased social cohesion and cultural exchange across these areas. These findings underscore the broader implications of hosting large-scale international events, indicating that the benefits frequently extend beyond the immediate host locations.
3.4. How has hosting the FIFA World Cup influenced the tourism and hospitality industries in the host countries?
Five articles focused on the tourism and hospitality industry, which is a comprehensive industrial activity. Hosting the FIFA World Cup has a profound impact on the tourism and hospitality industries. It influenced the various sectors, for instance, transportation, accommodation, catering, and entertainment. These studies examine the effects of the World Cup on these industries with key indicators such as tourist numbers, revenue generation, and infrastructure improvements.
3.4.1. Tourism industry indicators
• Growth in the Number of Tourists
Studies indicate the great increases in tourist numbers while hosting the FIFA World Cup. According to Averin & Kuznetsov, the global interest in the 2018 World Cup in Russia resulted in a notable increase in international tourist arrivals [8]. Bashkova pointed out a notable increase in the Kaliningrad region, particularly in terms of tourist numbers and hotel occupancy rates [9]. Karamanaga also observed that the 2022 World Cup in Qatar not only boosted international arrivals but also enhanced the country's destination image, potentially drawing more visitors in the future [11].
• Increase in Tourism Revenue
The FIFA World Cup serves as a major driver of tourism revenue. It was reported that Russia experienced a significant rise in tourism revenue during the 2018 World Cup [8]. Bashkova also demonstrated revenue growth in the Kaliningrad region, resulting in the financial gains at both national and regional levels [9]. These findings demonstrate the World Cup's role in stimulating the tourism economy.
• Improvement of Infrastructure
To accommodate the large number of incoming visitors, host countries invest heavily in infrastructure development. Averin & Kuznetsov detailed Russia's investments in transportation, accommodation, and public facilities in the 2018 World Cup [8]. These enhancements not only facilitated tourism during the event but also provided a solid groundwork for the long-term growth of sustainable tourism after the World Cup.
3.4.2. Hospitality industry indicators
• Increase in Hotel Occupancy Rate
The World Cup led to a surge in hotel occupancy in host cities. Bashkov observed that major cities like Kaliningrad experienced occupancy rates exceeding 90%, indicating high demand for accommodations [9]. Averin & Kuznetsov documented elevated occupancy rates in Russian host cities, highlighting the event's influence on the hotel sector [8]. This increase in occupancy rates is directly linked to a notable rise in hotel revenues. Although regional figures differ, the overarching trend demonstrates substantial financial benefits for the hospitality industry during World Cup events.
• Long-term Impacts on the Hotel Industry
The World Cup not only provides immediate financial gains but also fosters long-term benefits in the hospitality sector. It is observed that improved infrastructure and enhanced destination images continue to benefit hotels in Russia. This suggested the sustained growth in the sector [12].
Hosting the FIFA World Cup yields multifaceted benefits for the tourism and hospitality industries by increasing the tourist numbers, financial revenue, and infrastructure enhancements. These impacts vary across countries and regions, necessitating further research to explore their depth and duration. Drawing on insights from these five studies, policymakers and industry stakeholders can develop a clearer understanding of the transformative potential associated with hosting the global events. This knowledge enables them to strategically leverage the opportunities such events present.
4. Conclusion
This article explores the various impacts of the World Cup on host nations, mainly focusing on infrastructure, culture, and the economy. Using a comprehensive scoping review method, the study systematically evaluates 14 relevant articles. It aims to comprehensively understand the World Cup's influences. These articles investigate the World Cup's effects on the economies, cultural dynamics, and urban infrastructure development of host countries from diverse perspectives. Through a detailed analysis, the study provides a deeper understanding of more profound implications that is associated with the international sporting event.
Hosting the FIFA World Cup undeniably generates a wide range of positive impacts. From economic perspective, it drives growth across multiple sectors, including the stock market, tourism, and hospitality industries. Studies have shown that host countries often experience a significant increase in stock market indices and tourism revenues. In the stock market, the announcement of a host country often leads to positive reactions in stock prices and trading volumes. The tourism and hotel industries experience substantial growth, with increased tourist arrivals, higher tourism revenues, and elevated hotel occupancy rates and revenues. This economic boost also has a spillover effect on neighboring regions, and the long-term enhancement of the host country’s destination image continues to attract investment and tourists.
Culturally, although the research on this aspect is relatively scarce, the FIFA World Cup plays a crucial role in promoting the host country's culture, altering international perceptions, and fostering cultural diversity and inclusivity. However, the existing research on cultural impacts has limitations, including issues with sample representativeness, a narrow focus on short-term data, and subjective measurement methods.
In terms of infrastructure building, the event serves as a powerful driver for urban infrastructure development in the host city, covering transportation, communication, and public service facilities, which in turn promotes urban modernization and sustainable development. However, it is important to note that such rapid development can also lead to challenges, including cost overruns, underutilization of facilities post-event, and environmental concerns. But the evaluation models used in this area require further verification of their applicability and accuracy, and there are limitations in data sources and regional coverage.
Our study also made unique discoveries, such as the innovative and sustainable renovation and utilization of stadiums in the Qatar World Cup. This not only provides a model for resource-friendly stadium management but also indicates the need for future research. Future studies should address the limitations identified in this research, such as obtaining more granular economic data through longitudinal studies, employing mixed-methods approaches to improve cultural impact assessments, and utilizing advanced modeling techniques to verify infrastructure development outcomes. Additionally, research should focus on stadium-related issues, including strategies for sustainable construction waste management and the adaptive reuse of stadiums to prevent post-event underutilization. This includes exploring how to scientifically manage the large amount of construction waste generated during World Cup preparation, especially in stadium construction, and studying the diverse reuse strategies for stadiums that may become idle after the event.
The findings of this research not only contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the FIFA World Cup but also offer practical guidance for future host countries. They can assist the host countries of the upcoming 2026 World Cup in aspects such as event preparation, hosting, and post-event stadium utilization, promoting the harmonious integration of sports events and sustainable development. Policymakers and stakeholders can utilize these findings to make more informed decisions regarding the hosting of the FIFA World Cup, maximizing the benefits while minimizing potential negative impacts.
References
[1]. Zhang, C. (2024). Impact of the 2022 FIFA World Cup on Qatar. International Journal of Social Science and Humanity, 14(5).
[2]. Al Refai, H., & Eissa, M. A. (2017). The impact of FIFA’s official announcements on the stock market of Qatar: The case of the 2022 World Cup. Research in International Business and Finance, 41, 347–353.
[3]. Chancharat, S., & Sangchan, S. (2023). THE EFFECT OF THE 2018 FIFA WORLD CUP COMPETITION RESULTS ON STOCK RETURN IN FRANCE. Srinakharinwirot Research and Development Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 15(29, January-June), 266226–1.
[4]. AL-MOHANNADI, S. A. (2023). SOCIO-ECONOMIC IMPACT OF THE FIFA WORLD CUP QATAR 2022.
[5]. Nikolaou, E. E., Konteos, G., Kalogiannidis, S., & Syndoukas, D. (2023). Mega sporting events and their socio-economic impact: Case study of the 2022 FIFA World Cup. Journal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development, 7(2), 2158.
[6]. Andersson, S., Bengtsson, L., & Svensson, Å. (2021). Mega-sport football events’ influence on destination images: A study of the of 2016 UEFA European Football Championship in France, the 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia, and the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 19, 100536.
[7]. Bibolov, A., Miyajima, M. K., Rehman, S., & Yuan, T. (2024). 2022 FIFA World Cup: Economic Impact on Qatar and Regional Spillovers. International Monetary Fund.
[8]. Averin, A., & Kuznetsov, E. (2018). EVALUATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE WORLD CUP IN 2018 ON THE TOURIST ATTRACTIVENESS OF RUSSIA. Потенциал Роста Современной Экономики: Возможности, Риски, Стратегии, 23–27.
[9]. Bashkova, A. A. (2019). INFLUENCE OF THE 2018 FIFA WORLD CUP ON TOURISM IN THE KALININGRAD REGION. Энигма, 1(3–1), 54–57.
[10]. Kaplanidou, K. K., Al-Emadi, A., Triantafyllidis, S., Sagas, M., & Diop, A. (2016). Qatar World Cup 2022: Awareness of the event and its impact on destination and country character perceptions in the US tourism market. Tourism Review International, 20(2–3), 143–153.
[11]. Karamanaga, A. (2023). The Impact of the 2022 FIFA World Cup on the Destination Image of Qatar [PhD Thesis]. RIT Croatia.
[12]. Rozhda, Y., & Sheresheva, M. (2021). Impact of a sports mega-event on the perception of the image of a tourist destination: The case of the 2018 FIFA World Cup. BRICS Journal of Economics, 2(2), 53–83.
[13]. Yasir, A. L. H. H. (2023). The cultural impact of the world cup competition in Qatar 2022. Journal of Imam Al-Kadhum College, 7(2).
[14]. Al-Qahtani, A. M. (2017). 2022 FIFA World Cup and its Effect on the Urban Development of the City of Doha and its Infrastructure: A Three-Dimensional Impact Assessment Model, 3D-IAM.
Cite this article
He,M.H.;Yu,X. (2025). Impacts of the 2018 & 2022 FIFA World Cups: a scoping review of the current literature. Advances in Social Behavior Research,16(1),23-33.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Social Behavior Research
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhang, C. (2024). Impact of the 2022 FIFA World Cup on Qatar. International Journal of Social Science and Humanity, 14(5).
[2]. Al Refai, H., & Eissa, M. A. (2017). The impact of FIFA’s official announcements on the stock market of Qatar: The case of the 2022 World Cup. Research in International Business and Finance, 41, 347–353.
[3]. Chancharat, S., & Sangchan, S. (2023). THE EFFECT OF THE 2018 FIFA WORLD CUP COMPETITION RESULTS ON STOCK RETURN IN FRANCE. Srinakharinwirot Research and Development Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 15(29, January-June), 266226–1.
[4]. AL-MOHANNADI, S. A. (2023). SOCIO-ECONOMIC IMPACT OF THE FIFA WORLD CUP QATAR 2022.
[5]. Nikolaou, E. E., Konteos, G., Kalogiannidis, S., & Syndoukas, D. (2023). Mega sporting events and their socio-economic impact: Case study of the 2022 FIFA World Cup. Journal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development, 7(2), 2158.
[6]. Andersson, S., Bengtsson, L., & Svensson, Å. (2021). Mega-sport football events’ influence on destination images: A study of the of 2016 UEFA European Football Championship in France, the 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia, and the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 19, 100536.
[7]. Bibolov, A., Miyajima, M. K., Rehman, S., & Yuan, T. (2024). 2022 FIFA World Cup: Economic Impact on Qatar and Regional Spillovers. International Monetary Fund.
[8]. Averin, A., & Kuznetsov, E. (2018). EVALUATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE WORLD CUP IN 2018 ON THE TOURIST ATTRACTIVENESS OF RUSSIA. Потенциал Роста Современной Экономики: Возможности, Риски, Стратегии, 23–27.
[9]. Bashkova, A. A. (2019). INFLUENCE OF THE 2018 FIFA WORLD CUP ON TOURISM IN THE KALININGRAD REGION. Энигма, 1(3–1), 54–57.
[10]. Kaplanidou, K. K., Al-Emadi, A., Triantafyllidis, S., Sagas, M., & Diop, A. (2016). Qatar World Cup 2022: Awareness of the event and its impact on destination and country character perceptions in the US tourism market. Tourism Review International, 20(2–3), 143–153.
[11]. Karamanaga, A. (2023). The Impact of the 2022 FIFA World Cup on the Destination Image of Qatar [PhD Thesis]. RIT Croatia.
[12]. Rozhda, Y., & Sheresheva, M. (2021). Impact of a sports mega-event on the perception of the image of a tourist destination: The case of the 2018 FIFA World Cup. BRICS Journal of Economics, 2(2), 53–83.
[13]. Yasir, A. L. H. H. (2023). The cultural impact of the world cup competition in Qatar 2022. Journal of Imam Al-Kadhum College, 7(2).
[14]. Al-Qahtani, A. M. (2017). 2022 FIFA World Cup and its Effect on the Urban Development of the City of Doha and its Infrastructure: A Three-Dimensional Impact Assessment Model, 3D-IAM.









