

About ASBRAdvances in Social Behavior Research (ASBR) is an international peer reviewed journal hosted by Singapore International Management Research Centre (the governing body of NTU Nanyang Cultural Endowment Fund, Nanyang Technological University), published by EWA Publishing. ASBR is published monthly. ASBR publishes only original articles from a wide variety of methodological and disciplinary perspectives concerning education, psychology and communication issues. The journal aims to improve the human condition by providing a public forum for discussion and debate communication, education and psychology issues. The journal publishes articles that are research-oriented and welcomes empirical and theoretical articles concerning social activity and organizational behavior. Manuscripts that are suitable for publication in the ASBR cover domains on various perspectives of education, psychology, communication, and their impact on individuals, businesses and society.For more details of the Jasbr scope, please refer to the Aim&Scope page. For more information about the journal, please refer to the FAQ page or contact info@ewapublishing.org. |
| Aims & scope of ASBR are: ·Sociological Sciences ·Law ·Journalism & Mass Media ·Educational Studies ·Political Sciences ·Psychological Sciences |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

Birmingham, United Kingdom

Canberra, Australia

Singapore
zhao0185@e.nut.edu.sg

Sydney, Australia
Latest articles View all articles
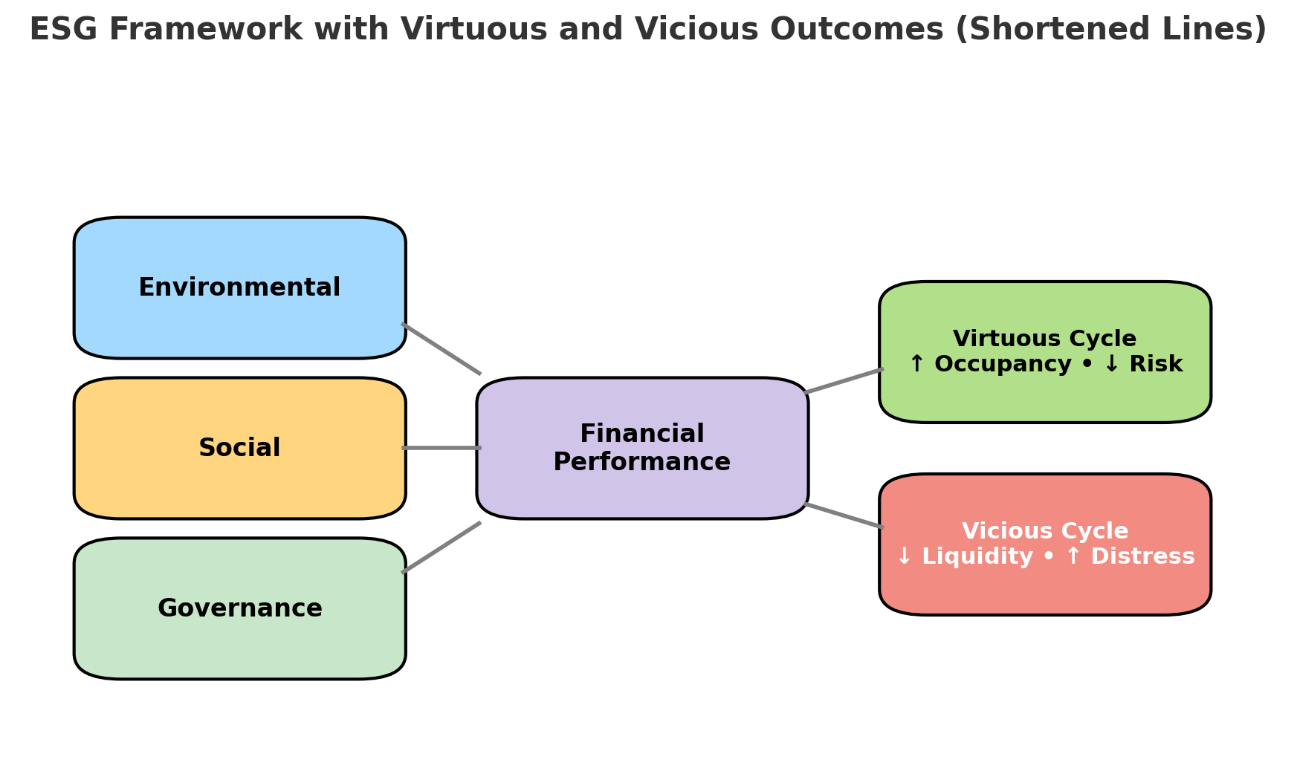
People’s dwellings, daily productive activities and access to public services pass through developers and landlords, exposing them to intense public scrutiny. This paper studies the impact of ESG on the financial outcomes of listed real estate companies. By analysing and summarising global literature, it finds that the relationship is not universally positive or negative, but depends on building age, leverage ratio, ownership structure, and regulatory shocks. It summarises three transmission paths: green energy-saving renovations increase rent and reduce vacancy rates; promoting social projects enhances tenant loyalty; and at the governance level, safeguards limit excessive debt. When these three pillars work together, ESG can compress bond spreads by 25 to 80 basis points and increase occupancy rates by 1 to 2 percentage points. In the green sector with weak governance, ESG can accelerate exit from financial distress, with targeted renovations, joint social project-oriented design, and ruling-class board committees. It ultimately calls for the establishment of unified ESG metrics to enable cross-market comparison.

 View pdf
View pdf


The advent of the Age of Intelligent Media has brought new opportunities and challenges to the international communication of Traditional Chinese Culture. This paper analyzes the new characteristics of communication in this context: the diversification of communication subjects, the precision of communication channels, and the community-based distribution of audiences. Meanwhile, the study also reveals the prominent problems currently faced: cognitive biases in the process of cultural translation weaken communication effects, technological empowerment may lead to an imbalance in the communication ecosystem, and it remains difficult to achieve in-depth cultural value identification. To address these issues, this paper proposes corresponding development strategies: establishing a precise cultural symbol translation system to bridge cognitive gaps, strengthening human-machine collaboration to optimize the communication ecosystem, and building an interactive platform with multi-subject participation. The aim is to promote the effective international communication of Traditional Chinese Culture.

 View pdf
View pdf


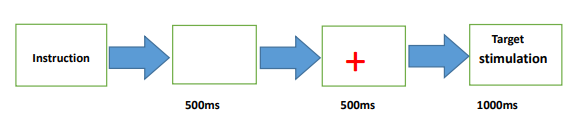
This study employed the emotional Stroop experiment from a behavioral research perspective to explore the role of the emotional Stroop effect in identifying depressive disorders among college students and to examine its correlation with the results of the Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) and the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). The results showed that the emotional Stroop effect of depressive words was significantly correlated with the scores of the depression scales, with correlations of r = 0.757 (p < 0.01) for the SDS and r = 0.739 (p < 0.01) for the PHQ-9. These findings confirm the validity of the emotional Stroop effect in identifying depressive disorders among college students, indicating that it serves as an effective supplementary method to depression scale assessments for screening depressive disorders.

 View pdf
View pdf


China's divorce rate reached 43% in 2024, significantly increasing the mental health risks faced by children from divorced families. This study investigates the complex mechanisms behind these risks and reveals that family reorganization can undermine children's sense of security, long-term parental conflict may accumulate psychological stress, and poor parenting combined with social stigma can intensify emotional problems. Nevertheless, cooperative parenting and children's psychological resilience can serve as protective factors that help mitigate these negative effects. Data show that the rates of depression and anxiety among children from divorced families are 20%–30% higher than those from intact families, with elevated SCL-90 scores indicating poorer mental health. These children also exhibit more aggressive behavior and academic difficulties, with boys showing higher levels of hostility and girls more prone to depression. Effective interventions such as school counseling, family therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and expressive art therapy have demonstrated positive outcomes. The main contribution of this study is to clarify the risk and protective mechanisms and propose a feasible framework for family-school-society collaboration, aiming to support the mental well-being of children from divorced families through conflict reduction, psychological education, and expanded social services.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
2025
Volume 16July 2025
Find articlesVolume 16April 2025
Find articlesVolume 16September 2025
Find articles2024
Volume 13December 2024
Find articlesVolume 12November 2024
Find articlesVolume 11October 2024
Find articlesAnnouncements View all announcements
Advances in Social Behavior Research
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Advances in Social Behavior Research
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Advances in Social Behavior Research (ASBR) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:





