

Volume 16 Issue 5
Published on July 2025
The increasing prevalence and number of autism (Autism Spectrum Disorder, ASD) cases worldwide in recent years have heightened awareness of the condition. Driven by concern for the well-being of children with autism and aiming to provide them with effective behavioral guidance and support, this study investigated and quantified the social cognitive characteristics and interpersonal skills of 73 autistic children. The relationship between cognitive characteristics and interpersonal skills was established using a deep learning neural network. Furthermore, multiple linear regression and grey relational analysis models were employed to explore the influence of various social cognitive characteristics on interpersonal skills. The results indicate that the cognitive representation process and behavioral motivation (attention process, cognitive representation process, behavior generation process, motivation process, motivation) in autistic children exhibit relatively stronger associations with interpersonal skills. The findings of this study provide a reference for developing targeted and effective intervention strategies for autistic children, helping them build fulfilling lives and realize their personal potential.

 View pdf
View pdf


From the theoretical perspective of the Marxist conception of space-time, this paper explores its innovative application in the practice of modern museum cultural communication. Through an in-depth interpretation of the Marxist space-time concept combined with theoretical frameworks from museology and communication studies, this study analyzes how contemporary museums employ Marxist space-time theory to innovate their cultural communication practices. The research indicates that the Marxist conception of space-time provides important guidance for exhibition design, narrative approaches, and interactive experiences in modern museums, offering new ideas and methods to enhance the effectiveness of museum cultural communication.

 View pdf
View pdf


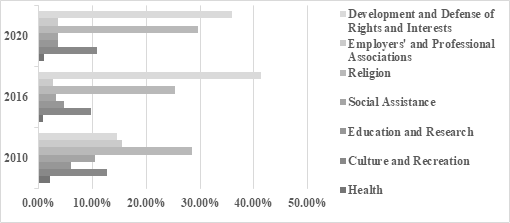
Since the establishment of the Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa (BRICS) mechanism, the imbalance between economic and trade cooperation and people-to-people and cultural exchanges has posed challenges to fostering deeper mutual understanding and political trust among member states. As BRICS countries are in their second golden decade, seeking cooperation among civil society organizations will help build a platform for people-to-people and cultural exchanges, provide a solid social foundation for economic and trade cooperation, and promote the consolidation of the “three-pillars” cooperation framework. This research focuses on Brazilian civil society organizations, examining their basic characteristics and development trends. By analyzing their regional distribution, per capita ratios, and sectoral distribution, it explores their development status and trends. Building on this foundation, the paper investigates their dual role under the BRICS mechanism: serving as a stabilizing force to ensure Brazil’s internal stability and acting as key participants in promoting people-to-people and cultural exchanges and cooperation among BRICS countries. The study aims to provide cooperation suggestions for promoting economic and trade cooperation and people-to-people and cultural exchanges among countries under the BRICS mechanism.

 View pdf
View pdf


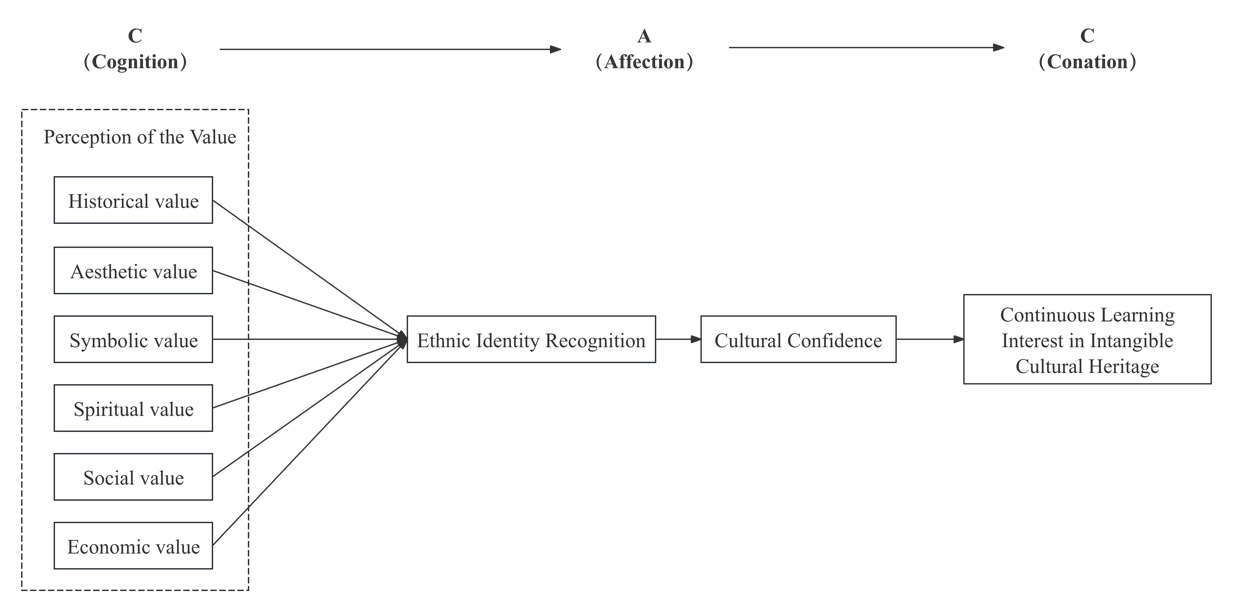
Using a sample of 605 elementary school students from grades 1 to 6 in two primary schools in Dalian, Liaoning Province, China, as the sample, this study explores the factors influencing students’ interest in continuing to learn Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) through school-based ICH activities. Grounded in the CAC theoretical model, the value theory of ICH, and ethnic identity theory, the research aims to provide fresh insights into the dissemination of ICH in schools and the development of children’s cultural education. The study categorises students’ perceived value of ICH activities into six dimensions: historical, aesthetic, symbolic, spiritual, economic, and social. It also examines a chained mediation effect composed of ethnic identity and cultural confidence. Using Structural Equation Modelling (SEM), the study empirically investigates the influencing factors and pathways. The findings reveal that all six dimensions of value significantly enhance students’ ethnic identity, which, in turn positively influences cultural confidence. Through this chained mediation effect, ethnic identity and cultural confidence play a crucial role in increasing students’ sustained interest in learning ICH.

 View pdf
View pdf


Driven by media technologies and consumerism, micro-dramas construct “simulacra subjectivity” through the symbolic portrayal of female characters, thereby obscuring the realities of women’s lived experiences. This study adopts Baudrillard’s theory of simulacra as its analytical lens and uses Lacan’s theory of the three orders as a theoretical framework to conduct textual analysis of leading female-oriented micro-dramas. The analysis reveals that female protagonists face a triple dilemma: in the Imaginary Order, they construct a “to-be-gazed” mirror self-dependent on the male gaze, intensifying anxiety over appearance and body image; in the Symbolic Order, female roles are reduced to symbols such as the “virtuous wife and good mother,” internalizing patriarchal social norms; in the Real Order, singular, pleasure-driven narratives dissolve the diversity of female subjectivities. This study argues that such simulacra subjectivity is perpetuated through a closed loop of “symbolic production—data feedback,” which not only distorts the audience’s perception of real women but also risks reinforcing existing gender power structures. To promote gender equality within media and society, micro-dramas must strike a balance between the logic of traffic and the authentic portrayal of female characters, while recognizing their role as a new media form in shaping social values.

 View pdf
View pdf


To improve the level of commentary on Chinese youth basketball games, to provide viewers with a better viewing experience, and to meet the needs of the audience for commentary on the game, the author conducted a comprehensive study to understand the audience's exposure to, evaluation and needs for youth basketball games and their comments through a questionnaire survey. The surveys included schools, Tiger Sports Forums, and social media, and collected a total of 391 valid surveys. The results of the survey show that most viewers need commentaries to help them with youth basketball games, and they have high requirements for commentaries to be professional, reflecting the greater demand for data analysis, technical and tactical analysis, and the belief that commentaries need to make a good judgment of the game. At the same time, viewers have little demand for basic qualities of commentary, such as accuracy, and different preferences for commentary style, but are less willing to respond to highly networked and emotional commentary. Based on the results of the survey, this paper proposes the following suggestions: Youth basketball game commentaries should be emphasized and popularized, traditional basketball commentaries are no longer applicable to the era of networks, and self-media commentaries should not simply pursue networks.

 View pdf
View pdf


Due to various reasons, when some people’s rights and interests are infringed, they prefer to protect their rights by petitioning, causing disturbances, conducting Internet exposure, or through other means instead of defending rights in accordance with the law through normal channels such as litigation. Although “abnormal rights protection” can protect the infringed rights and interests to some extent, it also brings a series of negative effects. Therefore, we are supposed to implement multiple strategies simultaneously and take a comprehensive approach by urging government departments to perform their duties, accelerating the modernization of the rule of law, constantly improving the petition system, strengthening social mediation, and strengthening governance at the community level.

 View pdf
View pdf


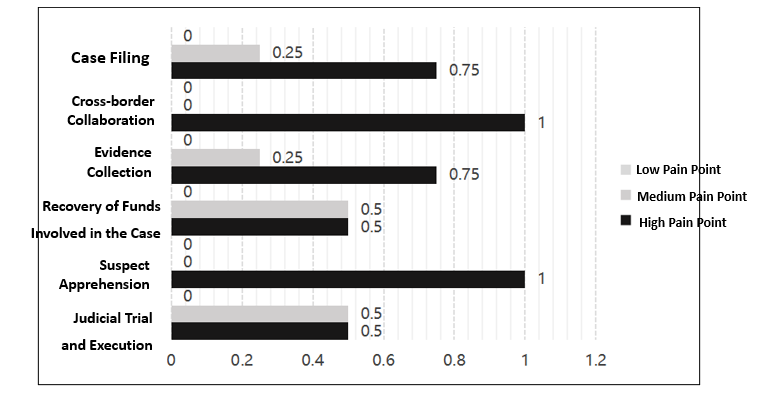
Against the backdrop of efforts to significantly enhance the modern combat capabilities of public security, this paper focuses on the interrogation challenges in cross-border telecommunication network fraud cases and explores the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology to improve interrogation efficiency and quality. It proposes the construction of an intelligent interrogation system by identifying the criminal characteristics of cross-border telecommunication fraud and analyzing the current technical and practical difficulties faced in interrogations. Focusing on AI-assisted interrogation in telecommunication fraud investigations, the study develops algorithms and models to build an intelligent interrogation system for cross-border fraud cases. The results indicate that AI-based interrogation systems can enhance the efficiency of information extraction, optimize investigative strategies, and provide technological support for the rapid resolution of cross-border telecommunication fraud cases.

 View pdf
View pdf


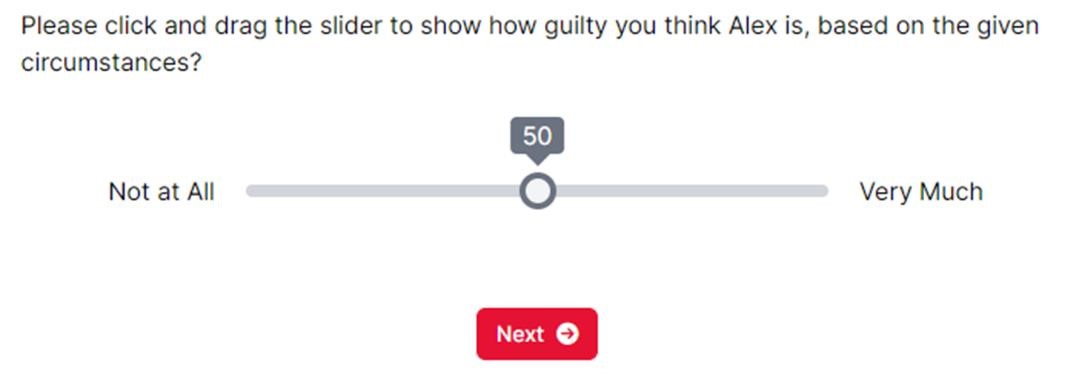
Assessing alibis within juror decision-making processes is crucial for ensuring justice, underscoring the need for research to mitigate wrongful verdicts. Building on findings that discredited alibis enhance guilt perceptions and that alibis from younger individuals are deemed more credible than those from older individuals, this study explores the impact of the age of a child giving a discredited alibi on juror guilt perceptions in a theft case. Participants were presented with a hypothetical theft case and three alibi scenarios: the absence of an alibi, a discredited alibi from a 3-year-old, and a discredited alibi from a 15-year-old, with guilt assessments conducted via a slider scale (0-100). The findings revealed increased guilt perception with the 15-year-old’s discredited alibi compared to the 3-year-old’s discredited alibi and no alibi scenarios, while an alibi from a 3-year-old did not significantly change guilt perceptions compared to no alibi scenarios. The study’s limitations, including a predominantly female and Asian subject pool, were discussed. Practical implications suggest the legal system should address age-related bias in witness credibility evaluations to influence trial outcomes. Future research directions include employing a 2x3 factorial ANOVA to further dissect guilt perceptions before and after the disclosure of an alibi’s falsehood.

 View pdf
View pdf


Humanoid robots possess technical features such as external human-like appearance, intelligence, and human-machine hybrid control. These may lead to the anthropomorphic trap, expanding the risk of infringement and complicating the attribution of liability. Different causes of infringement result in different types of infringement, which have different focuses in legal practice. Therefore, on the basis of clear classification standards, a typified discussion can be conducted. After dividing them into two major types: passive infringement and active infringement, further subdivisions can be made to clarify the nature and resolution of each type of infringement. Among the various types of infringement, the type caused by learning algorithms is the most distinctive due to its autonomous occurrence and difficulty in explanation. The method of law and economics can be utilized to allocate responsibilities among the relevant parties involved in the humanoid robot industry chain: humanoid robot manufacturers should follow the dynamic national regulations based on their development stage and different application scenarios under the guidance of the Hand Formula; users should be responsible for their negligent behavior due to failure to fulfill reasonable care obligations; and providers of general artificial intelligence models may be held jointly liable with humanoid robot product providers if they fail to fulfill the responsibility of transparency.

 View pdf
View pdf




