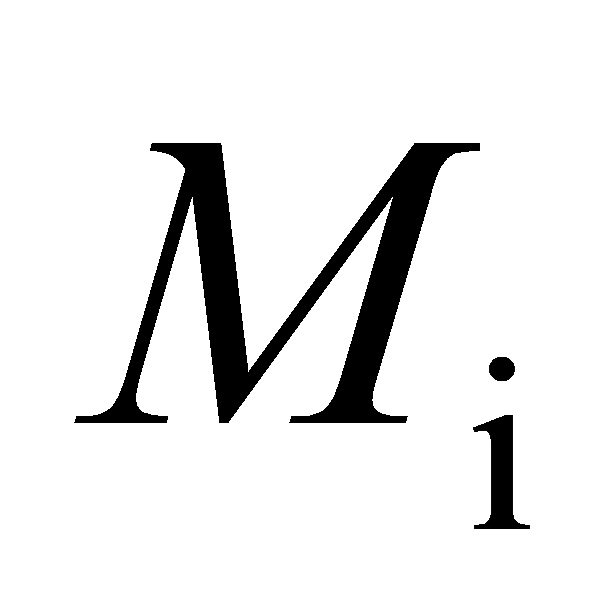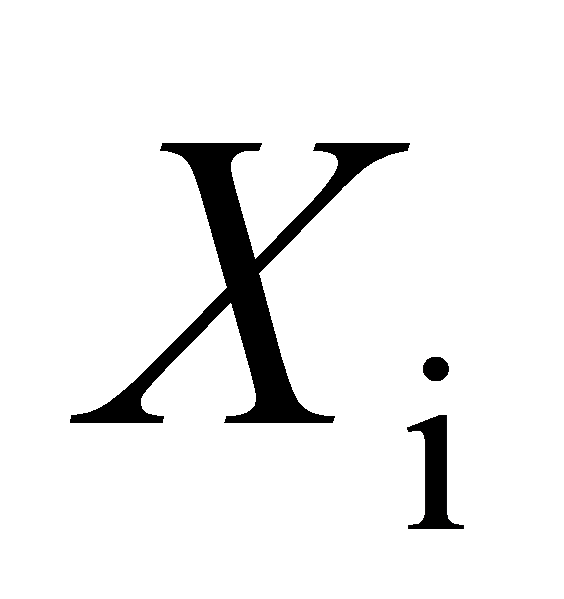1 Introduction
A review of domestic scholars' research on FlexSim simulation software reveals that their focus has primarily been on optimizing and improving warehousing systems, pharmaceutical logistics systems, and express sorting systems, with less attention paid to the issue of resource allocation in shuttle transport. In the field of shuttle transport, the selection and configuration of car transporters urgently need to be addressed due to the pressing need for efficient utilization of transport capacity and minimization of transport costs. This paper, in conjunction with the fixed daily shuttle transport volume of 2880 units for automobile companies, uses FlexSim simulation software to model and simulate the 8-kilometer shuttle transport process of three types of car transporters. The selection and resource allocation of the three types of car transporters were derived through mathematical calculations. This method is more convenient and practical compared to other methods in solving such issues.
2 Problem Description and Optimization Objectives
2.1 Problem Description
This study focuses on the 8-kilometer shuttle transport segment from the vehicle loading area in a smart logistics park of an automobile company to the railway freight station. The annual shuttle transport volume of this automobile company in the Changchun area is 720,000 units, with 250 working days per year and a single day shift of 10 hours per day. It can be calculated that the dedicated channel in the Changchun area needs to complete the shuttle transport of 288 vehicles per hour. The specific transportation business model is shown in Figure 1:

Figure 1. Overall Process of Vehicle Transport
This paper designs three transportation schemes for this segment to explore the goal of minimizing costs under the condition of maximizing transport capacity. The first scheme involves L3-level automated heavy trucks with double-deck trailers, referred to as DMU1. The second scheme also involves L3-level automated heavy trucks with double-deck trailers, referred to as DMU2. The third scheme involves L4-level automated tractors with single-deck flatbeds, referred to as DMU3 [3]. The specific parameters of the three schemes are compared in Table 1.
Table 1. Comparison of Environmental Parameters for Three Schemes
Environmental Parameter |
DMU1 |
DMU2 |
DMU3 |
Car Transporter Speed |
40km/h |
30km/h |
15km/h |
Loading Capacity |
6 vehicles |
9 vehicles |
6 vehicles |
Round-trip Distance |
16km |
16km |
16km |
Round-trip Time |
24min |
32min |
64min |
Loading Time |
45min |
68min |
45min |
Unloading Time |
15min |
23min |
15min |
Car Transporter Price |
1.2 million CNY |
1.5 million CNY |
1 million CNY |
2.2 Model Assumptions and Optimization Objectives
To simulate the shuttle transport process of this automobile company, the model will equivalently represent the car transporter’s driving speed over a certain distance as the time taken during the shuttle transport process [1]. The total operation time of the three schemes will be obtained through model simulation. By calculating the transportation cost of the three schemes and comparing these costs, the optimal car transporter resource allocation strategy will be explored. Before constructing the model, the following assumptions were made to eliminate interfering factors:
(1) Each car transporter is assumed to be fully loaded during transport to achieve the model’s goal of maximizing transport capacity.
(2) The traffic conditions on the transport path are assumed to be stable, and vehicle transport is stable, with no consideration of unexpected situations [5].
(3) The vehicle purchase cost is assumed to remain unchanged, not fluctuating with market supply and demand or over time.
(4) The efficiency of loading and unloading is assumed to be stable, with the time required to load and unload the same type of car transporter remaining fixed.
3 Simulation Model Approach and Steps
Combining the actual business needs of FAW Logistics Company, this study uses FlexSim software to construct a simulation model that can adapt to changes in transport volume and sets operational parameters to accurately simulate the results of shuttle transport. The steps to build the model are as follows:
1) Constructing the Model Layout
This paper constructs a simulation model including key elements such as generators, synthesizers, processors, and decomposers. Based on the company's fixed daily shuttle transport volume, three different types of car transporter data were selected for simulation [8]. The specific number of transport tasks was set, and the simulation model layout was built by combining the loading and unloading efficiency of different types of car transporters [9].
2) Defining the Model Operating Process
The model simulates the entire shuttle transport process from the Changchun main plant to the railway freight station, including vehicle storage, loading, and unloading. Based on the object entity logical relationships provided by FlexSim software, the model operating process was meticulously defined, and input and output ports were reasonably set to improve the reliability of the simulation results.
3) Editing Entity Parameters
During model construction, based on the selected three different types of car transporters, and the collected key data such as loading and unloading time, transport time, and loading capacity, the entity parameters of dispatching, preparing vehicles, loading, transporting, and unloading were meticulously set in the FlexSim model to fully reflect the model's realism.
4) Running the Simulation
After completing the model construction and parameter setting, the simulation was run. Each of the three simulation schemes was simulated multiple times, recording the total running time at the end of each model run, and the average running time was taken to provide strong data support for subsequent result analysis.
5) Analyzing Simulation Results
The average running time obtained during the shuttle transport process was analyzed using mathematical formulas to derive the vehicle purchase cost for each scheme under the condition of maximizing daily shuttle transport volume. Comparative analysis was conducted, and the car transporter transport scheme with the lowest vehicle purchase cost was gradually selected [2].
4 Simulation Example and Analysis
4.1 Model Case
The parameters required for the constructed model are shown in Table 2:
Table 2: Parameter Definitions for the Model
Parameter |
Meaning |
|
Unit Price (yuan) |
Q |
Total Transport Volume (vehicles) |
|
Equivalent Operating Hours (hours) |
|
Loading Capacity (vehicles) |
|
Hourly Transport Volume after Loading (vehicles) |
|
Total Transport Volume after Loading (vehicles) |
|
Vehicle Purchase Cost (yuan) |
|
Number of Car Transporters (vehicles) |
|
Scheme 1, 2, 3 |
With the objective of minimizing transport costs, the mathematical model for shuttle transport costs is established as follows:
(1) Hourly Transport Volume after Loading:
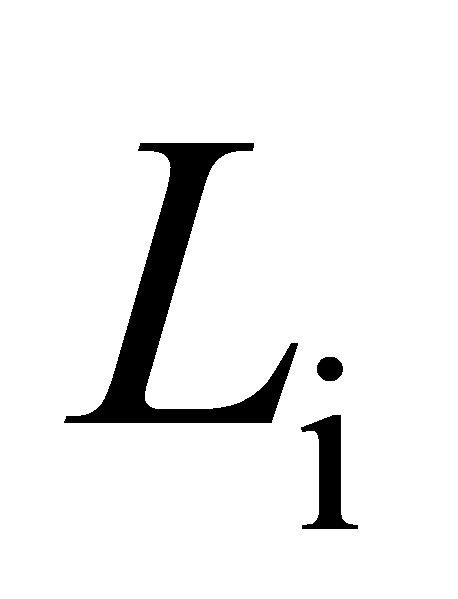
\( M_{i}=\frac{Q}{T_{i}∙L_{i}} \ \ \ (1) \ \ \ \)
(2) Transport Volume after Loading:
\( N_{i}=\frac{Q}{L_{i}} \ \ \ (2) \)
(3) Number of Transport Vehicles:
\( X_{i}=\frac{N_{i}}{M_{i}} \ \ \ (3) \)
(4) Vehicle Purchase Cost:
\( Y_{i}=X_{i}∙P_{i} \ \ \ (4) \)
Where: \( P_{i} \) is the unit price, indicating the price per unit of each type of car transporter. \( P_{1}=120 \) , \( P_{2}=150 \) , \( P_{3}=100 \) . \( Q \) is the total transport volume, indicating the actual number of vehicles transported by the car transporter in one hour, \( Q=288 \) . \( L_{i} \) is the loading capacity, indicating the actual cargo load of the car transporter in each transport, \( L_{1}=6 \) , \( L_{2}=9 \) , \( L_{3}=6 \) . \( T_{i} \) is the equivalent operating hours, converting the model operating time to hours. \( M_{i} \) is the hourly transport volume after loading, indicating the number of vehicles the car transporter can load and transport in one hour. \( N_{i} \) is the total transport volume after loading, indicating the total number of vehicles transported by a specific car transporter after loading. \( X_{i} \) is the number of car transporters, indicating the number of vehicles required to complete the total transport volume in one hour. \( Y_{i} \) is the vehicle purchase cost, indicating the cost required for the corresponding number of car transporters to complete the shuttle transport.
By substituting the above parameter data into the formulas, the costs for the DMU1, DMU2, and DMU3 schemes are calculated.
4.2 Establishing the Simulation Model
The simulation model for selecting and allocating car transporter resources in the shuttle transport process of a FAW Logistics Company is shown in Figure 2. First, vehicles are taken offline at the Changchun main plant, inspected, and placed in the on-site buffer zone. The vehicle handler, via the task dispatcher, moves the vehicles to the designated location in the Changchun Smart Logistics Park. According to the order instructions, the car transporter retrieves the outbound vehicles from various storage locations in the logistics park and transports them to the Changchun railway freight station, where they are unloaded and the transporter returns [6].
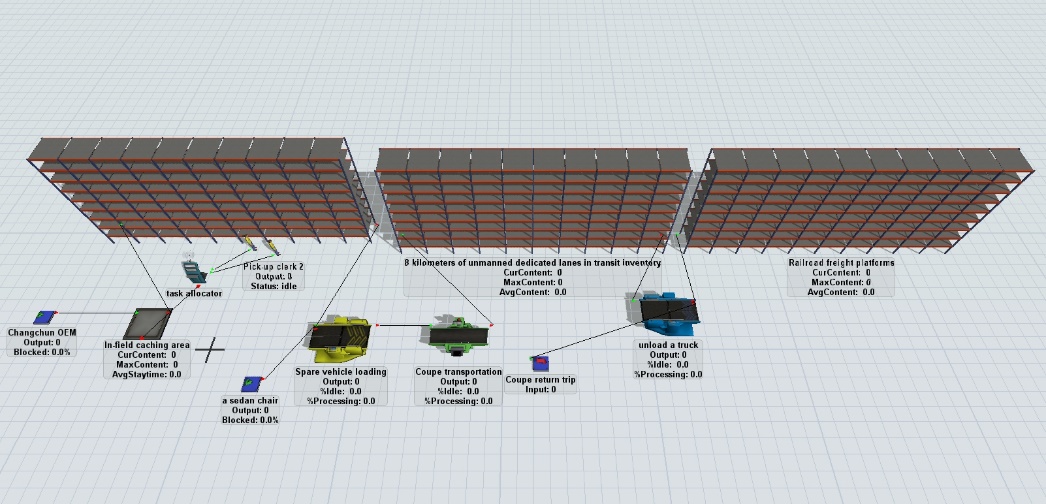
Figure 2. Simulation Model for Selecting and Allocating Car Transporter Resources
For such a complex shuttle transport optimization problem, many parameters and variables must be resolved by setting the entity object label values. The specific settings for the label values required in the simulation are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Labels for Each Entity Object and Their Functions
Entity Object |
Label |
Function |
Cargo |
Product |
Simulate the vehicle |
Generator—Changchun Main Plant |
Quantity |
Record total transport volume |
Synthesizer—Vehicle Loading |
Target Quantity |
Record loading capacity under three schemes |
Processor—Car Transporter |
Processing Time |
Record vehicle preparation time under three schemes |
Decomposer—Unload Vehicles |
Processing Time |
Record vehicle unloading time under three schemes |
4.3 Simulation Experiment
To rigorously study the temporary entity operation route simulating the vehicle shipping route, each of the three simulation schemes was run multiple times, and the average running time was taken to obtain a specific running time [7].
The experimental process is described as follows:
(1) Changchun Main Plant Shipping Setup
Set the generator as the Changchun main plant to simulate the shipping process. Click on the "Generator" label and set the arrival mode to "Arrival Schedule". Set "Quantity", the total transport volume \( Q \) , to 288 vehicles.
(2) Vehicle Preparation and Loading
Set the synthesizer to simulate the vehicle preparation and loading process, ensuring vehicle capacity is met. Click the "Processing Time" label in the "Synthesis Mode" and set it to "Packaging". Then set "Target Quantity" to 6, 9, and 6 respectively, representing the loading capacity of each vehicle for DMU1, DMU2, and DMU3 schemes [10].
(3) Loading Process
Set the generator to simulate the loading process during the 8 km shuttle transport. Click the "Processor" label, and set "Processing Time" to 45, 68, and 45 minutes respectively for DMU1, DMU2, and DMU3 based on the loading times of the vehicles in each scheme.
(4) Transport Process
Set the processor to simulate the transport process of the car transporter. Click the "Processor" label, and set "Processing Time" to 24, 32, and 64 minutes respectively for DMU1, DMU2, and DMU3 based on the round-trip driving times of the vehicles in each scheme.
(5) Unloading Process
Set the decomposer to simulate the unloading process. Click the "Processing Time" label, and set "Processing Time" to 15, 23, and 15 minutes respectively for DMU1, DMU2, and DMU3 based on the unloading times of the vehicles in each scheme.
4.4 Simulation Experiment Results and Analysis
Due to the different loading capacities, driving speeds, loading times, and unloading times of the vehicles chosen under the three schemes, the round-trip driving time and simulation running time during the shuttle transport process also differ. The simulation results were organized, and the model running time was converted into equivalent operating hours as shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Summary of Simulation Model Running Times
Scheme |
Running Time (min) |
Equivalent Operating Hours (h) |
DMU1 |
2207.60 |
36.79 |
DMU2 |
2243.70 |
37.40 |
DMU3 |
3140.60 |
52.34 |
Substituting the above formulas, the transport costs for the three schemes were obtained as shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Solution Results for Shuttle Transport Cost Model of an Automobile Company
Parameter Scheme |
DUM1 |
DUM2 |
DUM3 |
Hourly Volume |
7.83 |
7.70 |
5.50 |
Hourly Volume after Loading |
1.30 |
0.86 |
0.92 |
Total Volume after Loading |
48 |
32 |
48 |
Number of Vehicles |
36.79 |
37.395 |
52.34 |
Rounded Number of Vehicles |
37 |
38 |
53 |
Unit Price (100,000 yuan) |
120 |
150 |
100 |
Total Price (100,000 yuan) |
4440 |
5700 |
5300 |
In summary, through the simulation calculations of the 8 km shuttle transport process for the three car transporters and the comparative analysis of the simulation results of the three transport schemes, it can be seen that the transport cost of the DMU1 scheme is the lowest. Based on the goal of achieving the lowest total transport cost and shortest total time in the shuttle transport process, the optimal transport scheme selected is DMU1, which uses L3-level automated heavy trucks with double-deck trailers. A total of 37 vehicles are required to complete the target shuttle transport [4].
5 Conclusion
This paper focuses on the 8-kilometer shuttle transport of an automobile company in the Changchun area with the aim of solving practical problems. For the issue of selecting and allocating resources for 8-kilometer car transporters, an optimization goal of minimizing vehicle purchase costs was proposed. FlexSim software was used to simulate the shuttle transport process for three car transporter schemes, and the operation results were mathematically analyzed. It was found that deploying 37 L3-level automated heavy trucks with double-deck trailers to complete the shuttle transport can achieve the optimization goal of minimizing vehicle purchase costs. This further optimizes the car transporter selection and resource allocation for the automobile company. The automobile company can adopt the approach presented in this paper and select the appropriate vehicle models and corresponding resource allocation schemes based on its own situation.
Authors’ Contributions
Wang Lianfan and Li Yanyi: Writing the First Draft, Data Investigation and Sorting, Software Simulation, Mathematical Analysis, and Paper Revision. Both authors contributed equally to the article.
References
[1]. Zhang, H. H., Huang, F., Cao, Y. L., Yang, J. X., & Ma, B. R. (2009). Simulation analysis of an automated three-dimensional warehouse system based on Flexsim. Hoisting and Conveying Machinery, (1), 76.
[2]. Marek, K. (2023). Optimizing supply chain in a foundry through computer simulation using Flexsim – A case study. System Safety: Human - Technical Facility - Environment, 5(1), 172-181.
[3]. Chen, Y. W., Wu, X. B., Sun, Y. L., & Chen, F. M. (2013). Research on cargo space optimization of automated three-dimensional warehouses for the military based on Flexsim. Packaging Engineering, 34(19), 74-77.
[4]. Lendjel, E., & Fischman, M. (2015). Innovations in barge transport for supplying French urban dense areas: A transaction costs approach. Supply Chain Forum: An International Journal, 15, 16-27.
[5]. Wu, D. L., & Wang, X. Q. (2020). Simulation and optimization of the main production logistics system of coal based on the Flexsim model. China Mining Magazine, 29(9), 76-81.
[6]. Wei, L., Qin, X. B., & Meng, L. G. (2009). Modeling and simulation of logistics warehousing systems based on Flexsim. Hoisting and Conveying Machinery, (10), 57-60.
[7]. Zhu, X. R. (2012). Simulation and optimization of warehousing operation systems based on Flexsim. Logistics Technology, (3), 135-137.
[8]. Zhang, W. F. (2018). Simulation research on intermodal transportation path optimization based on Flexsim. Journal of Hubei University of Automotive Technology, 32(3), 55-59.
[9]. Xia, Q. (2014). Simulation planning of short-distance transshipment resource allocation for railway-road intermodal logistics of commercial vehicles based on Flexsim. Logistics Technology, (11), 441-442, 445.
[10]. T O V, V E M, & E S L. (2023). Simulation of the production and transport problem in the FlexSim environment. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1277(1).
Cite this article
Wang,L.;Li,Y.;Wu,Y.;Sun,W. (2024). Selection and Research of Resource Allocation Scheme for Shuttle Transport Based on FlexSim. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,6,12-17.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhang, H. H., Huang, F., Cao, Y. L., Yang, J. X., & Ma, B. R. (2009). Simulation analysis of an automated three-dimensional warehouse system based on Flexsim. Hoisting and Conveying Machinery, (1), 76.
[2]. Marek, K. (2023). Optimizing supply chain in a foundry through computer simulation using Flexsim – A case study. System Safety: Human - Technical Facility - Environment, 5(1), 172-181.
[3]. Chen, Y. W., Wu, X. B., Sun, Y. L., & Chen, F. M. (2013). Research on cargo space optimization of automated three-dimensional warehouses for the military based on Flexsim. Packaging Engineering, 34(19), 74-77.
[4]. Lendjel, E., & Fischman, M. (2015). Innovations in barge transport for supplying French urban dense areas: A transaction costs approach. Supply Chain Forum: An International Journal, 15, 16-27.
[5]. Wu, D. L., & Wang, X. Q. (2020). Simulation and optimization of the main production logistics system of coal based on the Flexsim model. China Mining Magazine, 29(9), 76-81.
[6]. Wei, L., Qin, X. B., & Meng, L. G. (2009). Modeling and simulation of logistics warehousing systems based on Flexsim. Hoisting and Conveying Machinery, (10), 57-60.
[7]. Zhu, X. R. (2012). Simulation and optimization of warehousing operation systems based on Flexsim. Logistics Technology, (3), 135-137.
[8]. Zhang, W. F. (2018). Simulation research on intermodal transportation path optimization based on Flexsim. Journal of Hubei University of Automotive Technology, 32(3), 55-59.
[9]. Xia, Q. (2014). Simulation planning of short-distance transshipment resource allocation for railway-road intermodal logistics of commercial vehicles based on Flexsim. Logistics Technology, (11), 441-442, 445.
[10]. T O V, V E M, & E S L. (2023). Simulation of the production and transport problem in the FlexSim environment. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1277(1).