1.Introduction
The cross-border e-commerce platforms for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) serve as an important application carrier of new quality productivity in the new era and have significant strategic importance for promoting the high-quality development of China's cross-border e-commerce industry. In the context of current global economic integration and rapid development of internet technology, cross-border e-commerce platforms for SMEs not only provide a broader market space and more development opportunities for SMEs but also offer strong support for enhancing China's position and influence in the global value chain.
he development of cross-border e-commerce platforms for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is of great importance for promoting the high-quality development of China's cross-border e-commerce industry. It not only reflects the application of new quality productivity in the economic field but also provides more development opportunities and space for SMEs by reshaping the value chain, improving production efficiency, and economic benefits. This, in turn, offers strong support for enhancing China's position and influence in the global value chain [1].
The main purpose of this study is to conduct an in-depth analysis and discussion on cross-border e-commerce platforms for SMEs. This study aims to analyze the current operation status of cross-border e-commerce platforms for SMEs, construct the design ideas of cross-border e-commerce platforms by combining the theoretical framework of the SERVQUAL model, and explore key issues they face in the international market, such as international trade frictions and trade barriers, mismatch between trade talents and market demand, and increasingly fierce competition. Corresponding countermeasures and suggestions are proposed to address these issues. This provides practical references and insights for cross-border e-commerce platforms for SMEs. It enriches and improves the research theory in the field of cross-border e-commerce and promotes the healthy development of the cross-border e-commerce industry. The results of this study can help more cross-border e-commerce platforms for SMEs solve development problems, enhance the overall level and competitiveness of the industry, and provide consumers with more high-quality and convenient shopping choices [2].
2.Design of Cross-Border E-Commerce Platforms
2.1.Theoretical Foundation of Cross-Border E-Commerce Platform Design
Theory of the SERVQUAL Model: The SERVQUAL model, proposed by A. Parasuraman and others, evaluates service quality based on the gap between customer expectations and actual perceptions. The SERVQUAL model uses "expectation-perception" as its core formula, emphasizing the comparison between the services provided by enterprises and customer expectations. This model divides service quality into five dimensions: Tangibles, Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance, and Empathy. The evaluation structure model based on this includes two parts: one records customer expectations of high-quality companies, and the other measures customer perceptions of the evaluated company. The SERVQUAL model is widely used in service industries, especially service-oriented platforms like e-commerce platforms, to understand customer needs and perceptions, thereby optimizing service quality. Through the SERVQUAL model, enterprises can systematically understand customer expectations and perceptions of service, identify deficiencies in services, and formulate improvement measures to enhance customer satisfaction [3].
2.2.Platform Function Requirement Analysis and Design
Based on the SERVQUAL model, the requirements for cross-border e-commerce platforms are analyzed. The platform functions should be designed from the following aspects:
Logistics Service Reliability: In cross-border e-commerce platforms, the reliability of logistics services is one of the key factors for users to choose the platform. The platform needs to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of logistics services to minimize the risks of package loss, damage, and delays. This includes a strict selection mechanism for logistics service providers, covering their service history, transportation capacity, and level of informatization, as well as real-time tracking functions.
Logistics Service Responsiveness refers to the speed at which logistics service providers respond to user needs and issues. Cross-border e-commerce platforms should ensure that users can easily contact logistics service providers and receive timely feedback and solutions. The design requirements should include establishing an efficient customer service system, providing multiple contact methods, and ensuring the professionalism and responsiveness of service personnel.
Logistics Service Assurance involves the professional capability, service attitude, and credibility of logistics service providers. Cross-border e-commerce platforms need to ensure that logistics service providers can offer safe, reliable, and professional services to users. This includes a qualification review and rating system for logistics service providers so that users can choose suitable logistics services based on the ratings and evaluations of the providers.
Logistics Service Empathy emphasizes the degree of attention and understanding that logistics service providers have for user needs. Cross-border e-commerce platforms should encourage logistics service providers to offer personalized and humane services to meet users' special needs. This includes providing users with customized logistics service options, such as special packaging and expedited delivery, and encouraging logistics service providers to actively communicate with users to understand and meet their needs.
Logistics Service Tangibles mainly focus on the external performance of logistics services, such as service facilities, equipment, and employee image. Cross-border e-commerce platforms should ensure that logistics service providers maintain a good external image and professionalism. This includes setting standards and requirements for the facilities, equipment, and employee image of logistics service providers to ensure they leave a good impression on users during the service process [4].
Figure 1. Cross-Border E-Commerce Platform Structure Diagram
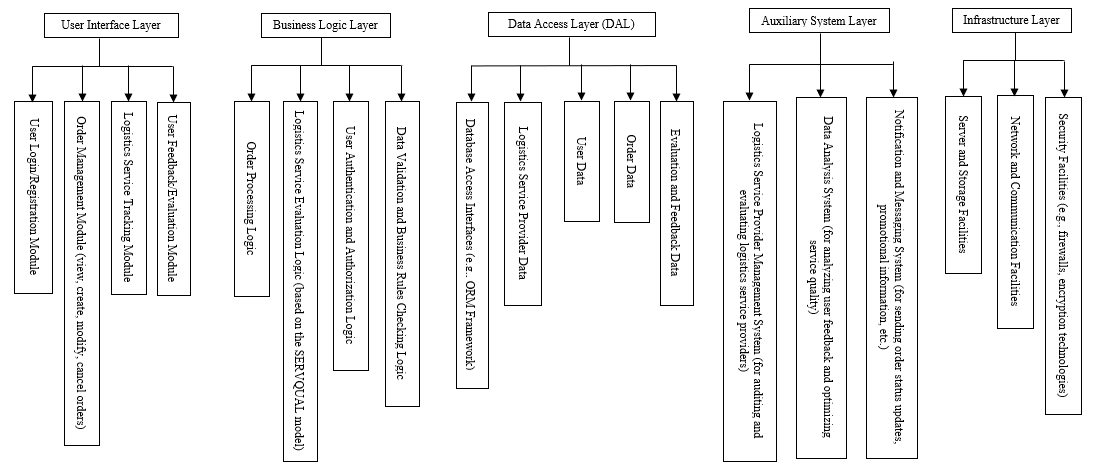
3.Challenges and Countermeasures for SMEs in Cross-Border E-Commerce Platforms
3.1.Challenges
3.1.1.International Trade Frictions and Trade Barriers
In the operation of cross-border e-commerce platforms, tangibility is directly related to the types of products and the presentation methods perceived by users. The intensification of trade frictions and trade barriers has led to rising costs of imported goods. This increase in costs not only limits the platform's ability to introduce more diverse and unique products but also potentially causes the platform to lose its price competitiveness. High costs make many products that originally had a price advantage less attractive, directly affecting the richness of the product variety on the platform, thereby limiting consumer choices. Trade frictions and barriers may also lead to restrictions or bans on the import of certain products, further reducing the diversity of products on the platform.
Assurance in cross-border e-commerce platforms manifests as the stability and reliability of product supply that the platform can provide to users. However, due to the uncertainty of international trade policies, platforms may face numerous challenges, making it difficult to ensure the stability and reliability of product supply. Changes in trade policies may result in adjustments to tariffs, import quotas, inspection standards, and other aspects, all of which can affect the platform's product supply. For example, if tariffs suddenly increase, the platform may need to bear higher costs or be unable to import certain products, leading to supply instability. Additionally, if the inspection standards for imported products change, the platform may need to reassess and adjust its supply chain, which could also lead to delays or interruptions in supply.
3.1.2.Mismatch between Trade Talents and Market Demand
In the operation of cross-border e-commerce platforms, responsiveness refers to the platform's ability to quickly respond to market changes and customer needs. However, when the platform lacks talents with expertise in international trade and cross-border e-commerce, its responsiveness will be severely affected.
The complexity and diversity of international trade require platform operators to have profound professional knowledge and keen insight to accurately judge market trends and changes in consumer demand. However, due to a lack of trade talents, the platform may fail to understand and respond to these changes in a timely manner, resulting in missed opportunities or decision-making errors.
Cross-border e-commerce platforms need to respond quickly to customer inquiries, complaints, and after-sales needs. If the platform lacks talents with relevant knowledge and experience, it will be unable to effectively handle these issues, leading to decreased customer satisfaction and damage to the brand image. This not only affects the platform's reputation and credibility but may also lead to customer attrition and a decline in market share.
In the operation of cross-border e-commerce platforms, empathy refers to the platform's ability to understand and meet the needs of local consumers. However, when the platform lacks sufficient understanding of international markets, its empathy will be severely challenged.
Consumers in different countries and regions have significant differences in culture, habits, preferences, and so on. Moreover, cross-border e-commerce platforms need to face challenges from different countries and regions, such as laws and regulations, tax policies, and payment habits. If the platform lacks an in-depth understanding of the local market and related regulations, it cannot accurately judge local consumer needs and expectations, making it difficult to provide products and services that meet their needs. This may also lead to compliance risks or operational errors, thereby affecting the platform's operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
3.1.3.Increasingly Intense Competition
As the cross-border e-commerce market continues to develop, competition is becoming increasingly intense, and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in cross-border e-commerce platforms are facing tremendous pressure.
In the fiercely competitive cross-border e-commerce market, the user experience and interface design of the platform have become key factors in attracting and retaining users [5].
3.2.Strategies and Recommendations
3.2.1.Addressing International Trade Frictions and Trade Barriers
Diversification of Supply Chain Strategy
Evaluate and expand potential suppliers globally to ensure diversity in the supply chain. Develop differentiated supply chain strategies for different countries and regions to reduce dependence on specific markets. Monitor changes in international trade policies, assess potential risks promptly, and adjust supply chain layout.
Inventory Management
Introduce advanced inventory management systems to achieve real-time updating and sharing of inventory data. Set reasonable safety stock levels to ensure stable supply of key products. Conduct regular inventory checks and audits to ensure the accuracy of inventory data.
Risk Management
Establish a dedicated risk management team responsible for identifying, assessing, and managing international trade risks. Develop contingency plans, including measures to deal with sudden events such as supply chain disruptions or tariff increases. Enhance communication with suppliers and logistics partners to collectively address trade barriers and frictions.
3.2.2.Addressing Mismatch between Trade Talents and Market Demand
Talent Cultivation and Recruitment
Regularly conduct training on international trade and cross-border e-commerce for internal staff to enhance team professional capabilities. Recruit external talents with rich experience and professional knowledge to complement team weaknesses. Establish incentive mechanisms to encourage continuous learning and self-improvement among employees.
Partnership Relations
Establish long-term partnerships with international trade consulting firms or organizations to obtain professional guidance and support. Maintain close contact with local industry associations and government departments to understand market trends and policy directions. Seek strategic partnerships with partners who share similar market goals and values.
3.2.3.Enhancing Platform Empathy
Market Research and Analysis
Conduct in-depth market research on different countries and regions to understand consumer demands, cultural habits, and legal regulations. Regularly analyze market trends, forecast future market changes, and provide data support for platform strategies. Collect user feedback, analyze user behavior data, and continuously improve products and services.
Localization Operations
Launch customized products and services according to different market characteristics to meet local consumer demands. Establish a localized customer service team to provide timely and professional after-sales support. Develop differentiated marketing strategies and promotional activities for different markets.
Addressing Intense Competition, Enhancing Platform Services and Design
Enhance platform service quality to provide more reliable and efficient services, ensuring customer satisfaction. Improve user experience to attract and retain users by continuously optimizing and improving interface design and functionality.
Continuous Improvement of Service Quality
Continuously optimize customer service processes to improve response speed and efficiency. Enhance after-sales service management to ensure customer satisfaction and loyalty. Establish a customer feedback mechanism to promptly collect and address user feedback, continuously improving service quality.
Technological Innovation
Introduce advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics to enhance platform operational efficiency and user experience. Continuously innovate business models and marketing strategies to cope with market changes and competitive pressures. Strengthen technological research and development and innovation capabilities to enhance the platform's core competitiveness.
Brand Building
Enhance brand promotion efforts to increase brand awareness and reputation. Build a unique brand image and value system to attract and retain users. Establish partnerships with other well-known brands or institutions to enhance brand influence and market competitiveness.
Optimizing User Experience
Continuously optimize platform interface design and functionality layout to enhance user experience convenience and comfort. Introduce user feedback mechanisms to promptly collect and address user feedback, continuously improving platform features and services. Strengthen user community building and management to enhance user engagement and interactivity.
References
[1]. Wang, L. (2024). Empowering new productive forces for the high-quality development of cross-border e-commerce: A perspective of value chain restructuring. Journal of Hubei University of Economics, 1-13. Retrieved from http://kns.cnki.net/kems/detail/42.1718.F.20240613.1441.002.html
[2]. Gu, J. Q. (2023). Research on the current operation status and countermeasures facing Pinduoduo's cross-border e-commerce platform. National Circulation Economy, 23, 75-79. https://doi.org/10.16834/j.cnki.issn1009-5292.2023.23.032
[3]. Gao, Y. X. (2022). Research on enhancing customer satisfaction of Company Y's cross-border e-commerce platform (Doctoral dissertation). Hebei University. https://doi.org/10.27103/d.cnki.ghebu.2022.001560
[4]. Zhang, F. X., Yang, X. R., & Wu, H. (2024). Research on strategies to improve logistics service quality based on the SERVQUAL model: A case study of Company A. China Logistics and Purchasing, 01, 118-119. https://doi.org/10.16079/j.cnki.issn1671-6663.2024.01.009
[5]. Zhang, X. Y., Liu, M., Jin, L. L. (2023). Research on the development of Xiaohongshu's metaverse cross-border e-commerce. Market Modernization, 20, 34-36. https://doi.org/10.14013/j.cnki.scxdh.2023.20.025
Cite this article
Zhang,B. (2024). Design and Operation of Cross-Border E-Commerce Platforms for SMEs. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,8,1-5.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang, L. (2024). Empowering new productive forces for the high-quality development of cross-border e-commerce: A perspective of value chain restructuring. Journal of Hubei University of Economics, 1-13. Retrieved from http://kns.cnki.net/kems/detail/42.1718.F.20240613.1441.002.html
[2]. Gu, J. Q. (2023). Research on the current operation status and countermeasures facing Pinduoduo's cross-border e-commerce platform. National Circulation Economy, 23, 75-79. https://doi.org/10.16834/j.cnki.issn1009-5292.2023.23.032
[3]. Gao, Y. X. (2022). Research on enhancing customer satisfaction of Company Y's cross-border e-commerce platform (Doctoral dissertation). Hebei University. https://doi.org/10.27103/d.cnki.ghebu.2022.001560
[4]. Zhang, F. X., Yang, X. R., & Wu, H. (2024). Research on strategies to improve logistics service quality based on the SERVQUAL model: A case study of Company A. China Logistics and Purchasing, 01, 118-119. https://doi.org/10.16079/j.cnki.issn1671-6663.2024.01.009
[5]. Zhang, X. Y., Liu, M., Jin, L. L. (2023). Research on the development of Xiaohongshu's metaverse cross-border e-commerce. Market Modernization, 20, 34-36. https://doi.org/10.14013/j.cnki.scxdh.2023.20.025









