1. Introduction
The Outline of the 14th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and Long-Range Objectives for 2035 of the People's Republic of China clearly proposes that China will "implement a strategy for the digitalization of the cultural industry, accelerate the development of new types of cultural enterprises, cultural formats, and cultural consumption models, and expand industries such as digital creativity, online audiovisual services, digital publishing, digital entertainment, and online performances" [1]. In recent years, the public's enthusiasm for spiritual and cultural enrichment has been growing, continuously advancing the development and prosperity of China's gaming industry. To date, the gaming industry in China has surpassed 260 billion RMB in revenue, with over 668 million users . As a new form of cultural product that integrates audio-visual languages such as sound, images, and text, games have been hailed as the "ninth art" [2, 3]. In recent years, the social perception of the gaming industry has steadily improved, and its value has extended to other fields. For example, the game Black Myth: Wukong collaborated with the Shanxi Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism to digitally recreate two precious Tang Dynasty wooden structures, Foguang Temple and Nanchan Temple, within the game. This digital preservation of traditional culture has significantly promoted it both domestically and internationally, and the game’s virtual experience has encouraged people to engage with physical manifestations of Chinese cultural heritage. Based on the game, the Shanxi Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism launched the Black Myth: A Tour of Ancient Shanxi Architecture tourism project, attracting the attention of numerous gamers. As a comprehensive industry with value potential across multiple sectors, studying the primary stakeholders in the gaming industry—game consumers—is crucial for the digitalization of China’s cultural industries. This study focuses on mobile shooting games, which rank second in terms of monthly revenue and active users among all game categories in China. The consumer behavior of players in this category holds significant reference value, as their behavior primarily involves purchasing value-added services or virtual items within the game. The consumption process is mainly driven by marketing information released by game developers, which stimulates players to make consumption decisions based on their individual characteristics. This study investigates the impact of the quality of marketing information on players’ perceptions, ambivalent attitudes, and purchase intentions, providing empirical support for setting marketing strategies from the perspective of consumer ambivalence.
The significance of this research lies in three key areas: (1) Current research on ambivalent attitudes mainly focuses on policy acceptance, green ecological products, and e-commerce. This study introduces ambivalent attitude research into the field of game consumption, enriching the application scenarios of ambivalence theory. (2) This study analyzes the mechanisms by which marketing information quality, player perceptions, ambivalent attitudes, and purchase intentions influence one another, supplementing the existing understanding of how these factors interact. (3) By integrating the TAM model, S-O-R model, and the concept of consumer ambivalence, this study proposes a new theoretical model for research on purchase intentions. The content of this study is structured as follows: Chapter 2 provides a literature review. Chapter 3 constructs the theoretical model and proposes research hypotheses. Chapter 4 presents the empirical research. Chapter 5 concludes the study and offers marketing recommendations.
2. Literature Review
Current research on game consumption behavior by scholars is primarily based on different perspectives and theories, including the TAM (Technology Acceptance Model) and S-O-R (Stimulus-Organism-Response) models. These models are used to empirically examine the various factors that might influence the consumption behavior of game consumers. In studies on online game consumers, the TAM model has been widely applied. The TAM model, rooted in the Theory of Reasoned Action, was proposed by Davis [4] in 1989, building on previous scholars’ research [5]. It explains and predicts individuals' acceptance of new information technologies through a causal chain of belief-attitude-intention-behavior.
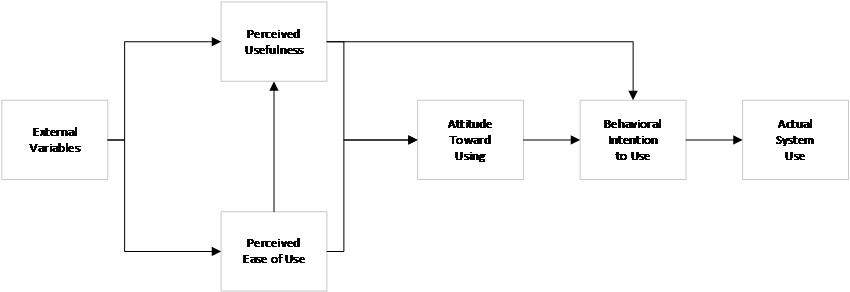
Figure 1. TAM Model
Scholars using the TAM model primarily explore the influence of external environmental factors, product attributes, and social-entertainment value on game consumption intentions. Zhou Hui’s [6] research found that external stimuli, performance expectations, social influence, facilitating conditions, and perceived value all positively impact mobile game players’ consumption intentions. Shi Jianan's [7] empirical findings suggest that the most substantial positive influence on consumption intention comes from facilitating conditions. The empirical results of Cao Shujin and Lu Taihong [8] show that entertainment experiences indirectly influence players' consumption intentions by positively affecting their consumption attitudes. Wen Lu’s [9] research concluded that “entertainment-sociality,” “game product innovation,” “perceived ease of use,” and “external environment” all have a positive impact on online game consumption behavior.
Regarding the system perception variables in the TAM model, earlier scholars primarily investigated game consumers' perceptions of usefulness, ease of use, entertainment, and value. Xia Ting's [10] empirical results show that perceived usefulness is significantly positively correlated with spending behavior in games. Furthermore, perceived usefulness positively influences spending behavior through consumption attitudes. Guo Le's [11] empirical findings suggest that perceived usefulness positively influences consumption intention. Wen Lu [9] also found that entertainment-sociality and perceived ease of use significantly influence consumption behavior. Similar conclusions were drawn by Wang Yamin, Wang Linlin [12], and Shi Jianan [7].
Beyond the TAM model, the S-O-R model proposed by Mehrabian & Russell in 1974 is another widely applied model in game consumption behavior research. The model consists of three parts: external stimulus factors, internal emotional cognition of the organism, and the behavioral or emotional outcomes of the organism. Chen Mei et al.'s [13] research indicates that esports users' consumption intentions are primarily influenced by external factors, including consumption cognition, consumption motivation (game experience, emotional needs, social needs), external stimuli, and product attributes. The magnitude of these influences, in descending order, are: external stimuli, consumption motivation, consumption cognition, and product attributes. Chen Zhigang and Pan Fan's [14] research shows that the sociability and interactivity of short videos can significantly positively influence players' willingness to purchase game items through pleasure and perceived value differences.

Figure 2. S-O-R Model
Additionally, some scholars, based on Robert Slavin’s [15] motivation theory, conducted empirical studies on the individual reasons for players' game consumption. These studies partially explain the types of utility that players focus on during game consumption, primarily including achievement, entertainment, and socialization. Wu Xiaowei et al. [16] found that entertainment motivation had the strongest correlation with female college students' online game consumption. Guo Miaomiao and Huang Xiaohong's [17] research demonstrated that entertainment motivation has the most significant positive influence on college students' online game consumption behavior. Zhang Ziyan [18] found that achievement motivation significantly influences paid, learning, and competitive game behaviors. Li Xianguo and Xu Huawei [19] concluded that the primary motivations for players consuming virtual items in online games include comparison, achievement, leadership, utility, convenience, and immersion. Yueh-Tung Hua et al. [20] found that comprehensive social motivation positively influences consumption behavior across different game types. Felipe et al. [21] discovered through their research on card game players that the motivation to pay was driven by the desire to win in the game.
Regarding the relationship between consumption attitude and purchase intention, some empirical studies suggest a positive correlation. The research by Won, Jessica, and Kim, Bo-Young [22] revealed a positive correlation between consumers' hedonic and ecological motivations and favorable consumption attitudes, which in turn positively correlated with purchase intention. Seo Hyeon-Gyeom and Yoo Tai-Soon's [23] study indicated that information about cosmetics on Instagram (including the amount and authenticity of information) and the usefulness and consumer attitudes towards it directly and indirectly influence purchase intentions. These studies examined the attitude variable from a single dimension. However, in real-world consumption scenarios, consumers often form attitudes toward a product based on multiple aspects, generating both positive and negative evaluations simultaneously. From March to June 2023, W company conducted interviews with several core players of a shooting game. Players exhibited ambivalence when evaluating a new game product. They praised the skin's appearance and visual effects but also expressed concerns that overly flashy effects might negatively impact their performance in battle. When these opposing evaluations reach a certain intensity, it becomes challenging for consumers to make purchase decisions. This ambivalence is influenced by both internal factors and external stimuli. In the case of H game's skin, players are simultaneously attracted to its flashy appearance and special effects, while also holding lower evaluations due to its lack of enhancement to in-game abilities and potential negative impact on performance. This leads to what is known as consumer ambivalence [24].
The main research directions on consumer ambivalence by scholars at home and abroad include: the specific pathways or mechanisms by which reviews or word-of-mouth marketing information influence consumer decision-making through ambivalent attitudes [25-28], the changes in consumer ambivalence over time [29-33], and other research directions such as methods of measuring consumer ambivalence [36].
Regarding the impact of consumer ambivalence on consumption behavior, scholars have mainly focused on three dimensions: consumer cognition, consistency, and the quality of marketing information. Tudoran et al.'s [39] research found that ambivalent attitudes weaken the relationship between satisfaction and purchase intention, with the importance of ambivalent attitudes acting as a mediator in this relationship. Jiang et al.'s [40] study confirmed that positive emotions have a direct positive impact on attitude-behavior consistency in individuals with ambivalent attitudes. Lian Yizhen et al.'s [41] research indicated that the perception of authenticity in products reduces ambivalence by lowering perceived risk. Chen Jieqi et al.'s [42] findings suggest that the higher the perceived authenticity of tourist souvenirs, the lower the consumer ambivalence, and the stronger the purchase intention. Consumer ambivalence plays a mediating role in the influence of souvenir authenticity and aesthetics on purchase intention.
In conclusion, existing research provides a foundation of factors and theoretical support for constructing a model of the impact of ambivalent attitudes and consumption intention. However, there are still some gaps in the current research that need further exploration. First, while scholars have validated the influence of external marketing information on consumer perception and consumption intention, few have studied how marketing information affects consumer ambivalence. Second, most studies on ambivalent attitudes have focused on policy acceptance, green ecological products, and e-commerce, with little research conducted in the context of game consumption. Therefore, this study introduces consumer ambivalence into the field of game consumer research to construct a theoretical model that explores the relationships and specific pathways between marketing information quality, consumer perception, ambivalent attitudes, and purchase intention.
3. Model Construction and Hypothesis
In the context of game consumption, marketing information mainly refers to the promotional descriptive information provided by game developers about a product. Based on a review of prior research, high-quality marketing information positively influences players' willingness to purchase [43, 44]. This study focuses on three aspects of product descriptive information: authenticity, clarity, and the amount of text describing a single product.
Based on previous studies, this paper posits that the higher the authenticity of the product image in marketing information, the higher the consumer's perception of authenticity, which lowers perceived risk and may reduce ambivalent attitudes [41]. The authenticity of the product image also affects the player’s perception of the product's usefulness [45]. The clearer the product information is described, the less confusion the player experiences, making it easier for them to confirm the utility of the product, which increases perceived ease of use and lowers perceived risk. This, in turn, reduces ambivalent attitudes and enhances purchase intentions [46]. The clearer the product description, the more explanatory text it contains, which increases the total information volume. As consumers process the information, the mental effort required rises, which decreases perceived ease of use. The larger the amount of irrelevant information, the higher the perceived risk for the player. Additionally, the more information unrelated to the product attributes, the more processing is required by the player, reducing the proportion of useful information extracted within the same time frame and decreasing the perceived usefulness of the product.
Based on this, the hypotheses regarding marketing information quality variables are proposed as follows:
H1.1: The authenticity of product images in marketing information positively influences perceived ease of use.
H1.2: The authenticity of product images in marketing information positively influences perceived usefulness.
H1.3: The authenticity of product images in marketing information positively influences perceived risk.
H1.4: The clarity of product descriptions in marketing information positively influences perceived ease of use.
H1.5: The clarity of product descriptions in marketing information positively influences perceived usefulness.
H1.6: The clarity of product descriptions in marketing information positively influences perceived risk.
H1.7: The volume of product description negatively influences perceived ease of use.
H1.8: The volume of product description negatively influences perceived usefulness.
H1.9: The volume of product description positively influences perceived risk.
Scholars generally believe that perceived usefulness has a positive effect on consumers' purchase intentions [6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 51]. Drawing from prior research, this paper focuses on three dimensions of perceived usefulness: achievement utility [6, 12], social utility [6, 10], and entertainment utility [7, 9, 12, 51]. The following hypotheses on perceived usefulness are proposed:
H2.1: The higher the consumer’s perceived achievement utility of the product, the higher the consumer’s positive evaluation of the product, and the lower the strength of ambivalent attitudes.
H2.2: The higher the consumer’s perceived social utility of the product, the higher the consumer’s positive evaluation of the product, and the lower the strength of ambivalent attitudes.
H2.3: The higher the consumer’s perceived entertainment utility of the product, the higher the consumer’s positive evaluation of the product, and the lower the strength of ambivalent attitudes.
H2.4: The higher the consumer’s perceived achievement utility of the product, the higher the consumer’s purchase intention.
H2.5: The higher the consumer’s perceived social utility of the product, the higher the consumer’s purchase intention.
H2.6: The higher the consumer’s perceived entertainment utility of the product, the higher the consumer’s purchase intention.
Perceived ease of use traditionally reflects how easily a technology user perceives using a system [4, 5]. It can directly influence purchase intention and indirectly affect intention through perceived usefulness and consumer attitudes [8, 47, 51]. This study defines perceived ease of use as the extent to which players find it easy to accept product information. We believe that the lower the difficulty of the decision-making process, the less effort consumers perceive to spend, and the lower their perceived risk of consumption. Therefore, we hypothesize that perceived ease of use positively influences perceived usefulness, perceived risk, and consumer ambivalence:
H2.7: The higher the consumer’s perceived ease of use of the product, the higher the perceived social utility of the product.
H2.8: The higher the consumer’s perceived ease of use of the product, the higher the perceived entertainment utility of the product.
H2.9: The higher the consumer’s perceived ease of use of the product, the higher the perceived achievement utility of the product.
H2.10: The higher the consumer’s perceived ease of use of the product, the lower the consumer’s perceived risk.
H2.11: The higher the consumer’s perceived ease of use of the product, the lower the strength of consumer ambivalence.
H2.12: The higher the consumer’s perceived ease of use of the product, the higher the consumer’s purchase intention.
H2.13: Perceived ease of use affects ambivalent attitudes through perceived usefulness.
H2.14: Perceived ease of use affects ambivalent attitudes through perceived risk.
H2.15: Perceived ease of use affects purchase intention through perceived usefulness.
H2.16: Perceived ease of use affects purchase intention through perceived risk.
Raymond Bauer [48] defined perceived risk from two angles: its negative impact and uncertainty. It refers to both the uncertainty of the outcomes generated by purchase decisions and the uncertainty of satisfaction with the outcomes. Reviewing prior studies on perceived risk and consumer attitudes from different perspectives, scholars have commonly found that perceived risk negatively impacts consumer attitudes [47, 49, 50]. This study suggests that perceived risk negatively impacts consumer ambivalence. In other words, the higher the uncertainty regarding the outcomes of purchase decisions and satisfaction, the higher the ambivalence.
Based on previous research results, this paper proposes the following hypotheses:
H2.17: The higher the consumer’s perceived risk, the lower the strength of consumer ambivalence.
H2.18: The higher the consumer’s perceived risk, the lower the consumer’s purchase intention.
Previous research confirmed that ambivalent attitudes weaken the consistency between external stimuli and consumer intention [39]. Therefore, we propose that consumer ambivalence negatively impacts purchase intention. Furthermore, scholars have demonstrated that ambivalent attitudes mediate the effects of external variables on purchase intention [42]. Thus, this study hypothesizes that consumer ambivalence plays a mediating role in the pathway between external variables and purchase intention:
H3.1: The higher the consumer’s ambivalence, the lower the consumer’s purchase intention.
H3.2: Social utility influences purchase intention through consumer ambivalence.
H3.3: Entertainment utility influences purchase intention through consumer ambivalence.
H3.4: Achievement utility influences purchase intention through consumer ambivalence.
H3.5: Perceived ease of use influences purchase intention through consumer ambivalence.
H3.6: Perceived risk influences purchase intention through consumer ambivalence.
The theoretical model proposed in this study is based on the TAM and S-O-R models and draws on previous research on game consumer behavior, gaming motivation, and consumer ambivalence. The model is divided into three parts: stimulus, organism cognition, and emotional cognitive outcomes. The stimulus includes the quality of the marketing information about a specific game product. The organism cognition includes the perceptual factors resulting from players' acceptance of marketing information and consumer ambivalence. The emotional cognitive outcomes refer to the game players’ purchase intention towards the product. Perceptual factors directly influence players' ambivalent attitudes and purchase intention after receiving marketing information. Perceived ease of use partially mediates the effect of perceived usefulness on purchase intention. Perceptual factors mediate the effect of marketing information quality on ambivalent attitudes and purchase intention. The specific model is shown in Figure 3.
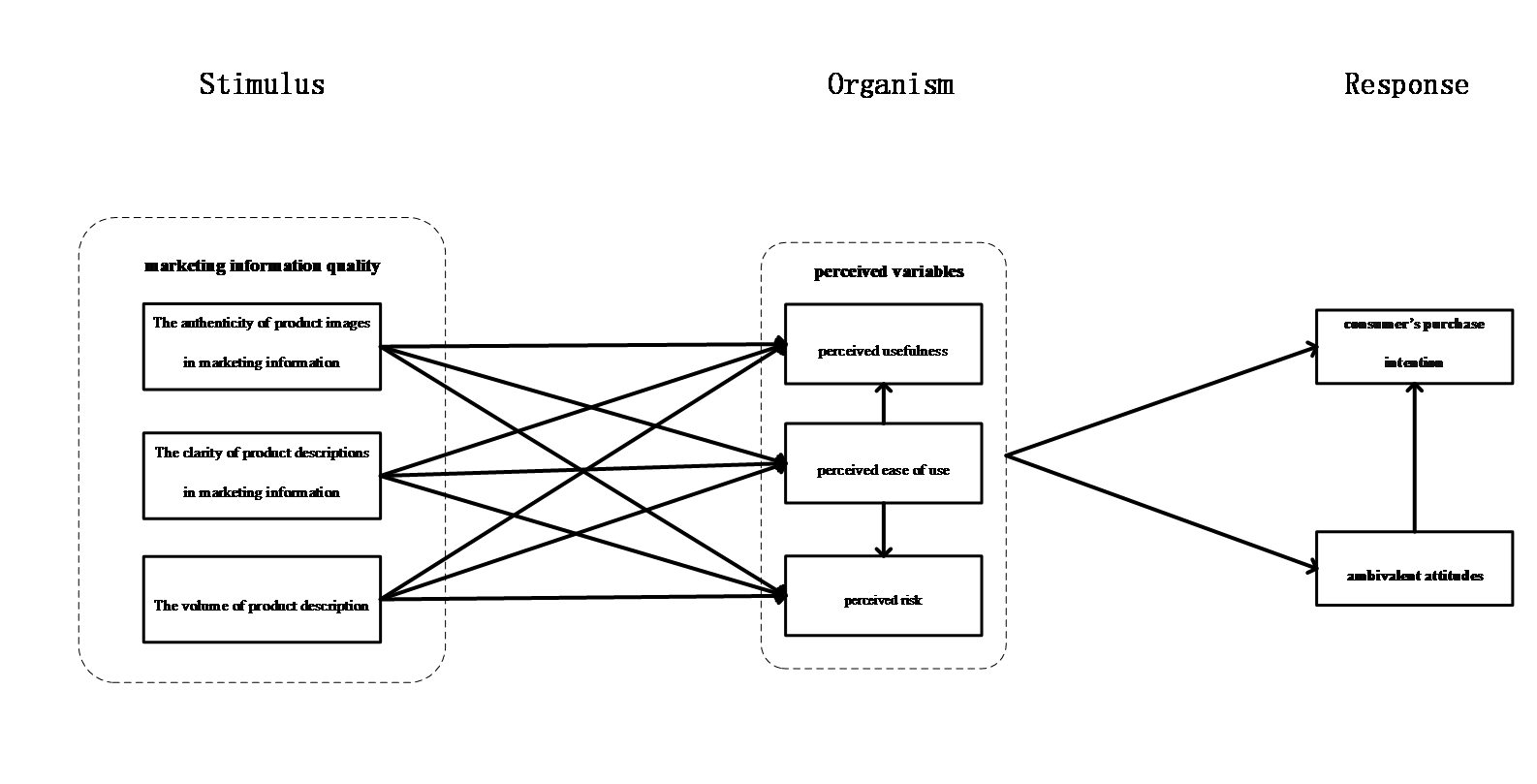
Figure 3. Theoretical Model
4. Empirical Study and Hypothesis Testing
This chapter conducts an empirical analysis and hypothesis testing using a questionnaire survey based on the theoretical model constructed in Chapter 3. The questionnaire uses a Likert 5-point scale, with responses ranging from "strongly disagree," "disagree," "neutral," "agree," to "strongly agree," which are scored from 1 to 5, respectively, for data collection. The data is analyzed and verified using SPSS 26.0 and AMOS 26.0 software to validate the structural equation model.
4.1. Questionnaire Design
The independent variables in this survey include product information authenticity, clarity, and information volume. The variables measured by the follow-up questions include perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived risk, consumer ambivalence, and purchase intention. To ensure the reliability and validity of the measurement results, all variables in this study were measured using well-established scales from previous scholars. The descriptions of each item were adjusted to match the actual content of the game type studied in this research. Specific items are listed in Tables 1 to 8.
Table 1. Perceived Social Usefulness Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Perceived Social Usefulness |
PSU1 |
I think purchasing this product helps me gain social capital. |
Davis [5]; Cao Shule & Xu Xinyi [52] |
PSU2 |
I think purchasing this product helps me attract others' attention. |
||
PSU3 |
I think purchasing this product helps me gain recognition from peers and friends. |
||
PSU4 |
Overall, I believe purchasing this product improves my social performance. |
Table 2. Perceived Entertainment Usefulness Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Perceived Entertainment Usefulness |
PEU1 |
I think purchasing this product enhances my visual appeal in the game. |
Guo Le [7]; Zhou Hui [6]; Shi Jianan [11]; Guo Miaomiao & Huang Xiaohong [17] |
PEU2 |
I think purchasing this product makes the gaming experience more fun. |
||
PEU3 |
I think purchasing this product brings surprises. |
||
PEU4 |
I think purchasing this product helps relieve negative emotions. |
||
PEU5 |
Overall, I believe purchasing this product makes me happier when playing the game. |
Table 3. Perceived Achievement Usefulness Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Perceived Achievement Usefulness |
PAU1 |
I think purchasing this product improves my in-game performance. |
Davis [5]; Xia Ting [37]; Zhou Hui [6]; Shi Jianan [11]; Zhang Ziyan [18] |
PAU2 |
I think purchasing this product helps me achieve a higher game ranking. |
||
PAU3 |
I think purchasing this product lowers the difficulty of winning the game. |
||
PAU4 |
I think purchasing this product enhances my control over game outcomes. |
||
PAU5 |
Overall, I think purchasing this product helps me achieve in-game accomplishments. |
Table 4. Perceived Ease of Use Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Perceived Ease of Use |
PE1 |
I find the product description easy to understand. |
Davis [5]; Guo Le [7]; Zhou Hui [6] |
PE2 |
It doesn't take much time to fully read the product description. |
||
PE3 |
It's easy to determine the product’s usefulness to me. |
||
PE4 |
Overall, the process of deciding whether to purchase this product is easy. |
Table 5. Perceived Risk Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Perceived Risk |
PR1 |
I am worried that the actual performance of the product in the game may not match its description. |
Jacoby [54]; Wang Yuan [55] |
PR2 |
I am concerned that purchasing the item may not be approved by my friends. |
||
PR3 |
I am worried that reading too much product information will waste my time. |
Table 6. Positive Consumer Ambivalence Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Positive Attitude |
PA1 |
Considering only the positive aspects, I believe the product is good. |
Jonas et al [53]; Chen Jieqi et al [42] |
PA2 |
Considering only the positive aspects, I believe the product meets all my needs. |
||
PA3 |
Considering only the positive aspects, I believe purchasing this product will yield good results. |
Table 7. Negative Consumer Ambivalence Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Negative Attitude |
NA1 |
Considering only the negative aspects, I believe the product is bad. |
Jonas et al [53]; Chen Jieqi et al [42] |
NA2 |
Considering only the negative aspects, I believe the product cannot meet all my needs. |
||
NA3 |
Considering only the negative aspects, I believe purchasing this product will lead to bad outcomes. |
Table 8. Consumer Sentiment Measurement Scale
Variable Name |
Item No. |
Measurement Items |
Source |
Consumer Sentiment |
CS1 |
I am willing to learn more about the product. |
Zhou Hui [6]; Shi Jianan [7] |
CS2 |
I am willing to purchase this product. |
||
CS3 |
I am willing to recommend this product to others. |
4.2. Data Collection
This study employed the snowball sampling method to collect questionnaire data, using self-reported responses from players. The data collection was conducted through both online and offline channels, ensuring that respondents were somewhat concentrated in specific groups while controlling the time and cost of the survey. The formal data was gathered using two methods: via the Tencent Questionnaire platform and through the distribution of paper questionnaires in concentrated areas of university campuses, such as dormitories and libraries. The electronic questionnaires were primarily distributed through fan groups of game streamers, major gaming forums, and various gaming communities by providing a link to the questionnaire. The paper questionnaires were distributed mainly in concentrated areas on university campuses, such as dormitories and libraries. In total, 1,034 formal responses were collected, including 874 electronic responses and 160 paper responses. After screening, 298 questionnaires were excluded due to abnormal response times or illogical answers. Additionally, 20 questionnaires from non-core players (those who had not played mobile battle royale games in the past year or had too little playtime) were removed. Ultimately, 716 valid questionnaires were obtained, with an effective response rate of 69.2%, meeting the requirements for questionnaire recovery.
4.3. Data Analysis
To assess the validity and reliability of the formal questionnaire, this study used SPSS 26.0 software to conduct sample characteristic analysis, descriptive analysis, and reliability analysis on the 716 valid responses. AMOS 26.0 was employed to test the convergent and discriminant validity of the formal questionnaire, to build the structural equation model, and to examine the direct effects and mediating effects within the model. This process was carried out to validate the theoretical model constructed in this study. Among the 716 valid responses, the majority of respondents were male, accounting for 79.2%, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 4:1. Most players were aged between 18 and 30, representing 87.3% of the sample. In terms of educational background, most core players had undergraduate or higher degrees, which aligns with the user profile of mobile battle royale game players.
The study used Cronbach's α to measure reliability. SPSS 26.0 was employed to conduct internal consistency tests for both the overall questionnaire and the various dimensions. The overall Cronbach's α value for the scale was 0.771, with the Cronbach’s α values for each subscale being greater than 0.7. Additionally, removing any individual item did not improve the Cronbach’s α value, indicating that the formal questionnaire had good consistency and stability, and that all items could be retained for further analysis.
First, the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) and Bartlett’s sphericity tests were conducted to assess the validity of the questionnaire. In the exploratory factor analysis (EFA), the KMO coefficient was 0.934, and Bartlett’s sphericity test was significant (p < 0.001), suggesting that the model was suitable for factor analysis. Furthermore, the standard loading coefficients for each factor were all above 0.5, with the lowest composite reliability (CR) being 0.802, exceeding the threshold of 0.7. The average variance extracted (AVE) was above 0.5 for all dimensions except for perceived entertainment usefulness and perceived achievement usefulness, demonstrating a high level of internal consistency and good convergent validity of the model, allowing for further analysis. The Cronbach’s α values, composite reliability (CR), and average variance extracted (AVE) for each subscale are shown in Table 9.
Table 9. Reliability and Validity Results of the Formal Research Scale
Measurement Variables |
Items |
Cronbach's α |
Corrected Item-Total Correlation |
α After Item Deletion |
Loading Coefficient |
CR |
AVE |
Perceived Ease of Use |
PE1 |
0.79 |
0.707 |
0.683 |
0.780 |
0.807 |
0.512 |
PE2 |
0.523 |
0.779 |
0.692 |
||||
PE3 |
0.555 |
0.759 |
0.677 |
||||
PE4 |
0.621 |
0.726 |
0.709 |
||||
Perceived Social Usefulness |
PSU1 |
0.759 |
0.529 |
0.717 |
0.751 |
0.800 |
0.501 |
PSU2 |
0.534 |
0.715 |
0.702 |
||||
PSU3 |
0.527 |
0.718 |
0.675 |
||||
PSU4 |
0.64 |
0.657 |
0.701 |
||||
Perceived Entertainment Usefulness |
PEU1 |
0.794 |
0.576 |
0.754 |
0.722 |
0.809 |
0.459 |
PEU2 |
0.599 |
0.747 |
0.687 |
||||
PEU3 |
0.535 |
0.767 |
0.595 |
||||
PEU4 |
0.561 |
0.759 |
0.680 |
||||
PEU5 |
0.598 |
0.747 |
0.696 |
||||
Perceived Achievement Usefulness |
PAU1 |
0.821 |
0.637 |
0.778 |
0.749 |
0.824 |
0.484 |
PAU2 |
0.596 |
0.791 |
0.623 |
||||
PAU3 |
0.569 |
0.799 |
0.663 |
||||
PAU4 |
0.598 |
0.791 |
0.702 |
||||
PAU5 |
0.672 |
0.769 |
0.734 |
||||
Perceived Risk |
PR1 |
0.862 |
0.711 |
0.831 |
0.826 |
0.876 |
0.703 |
PR2 |
0.745 |
0.8 |
0.852 |
||||
PR3 |
0.759 |
0.786 |
0.837 |
||||
Ambivalent Attitude |
AA1 |
0.927 |
0.845 |
0.9 |
0.904 |
0.921 |
0.795 |
AA2 |
0.843 |
0.902 |
0.893 |
||||
AA3 |
0.868 |
0.882 |
0.877 |
||||
Purchase Intention |
CS1 |
0.967 |
0.924 |
0.954 |
0.779 |
0.831 |
0.622 |
CS2 |
0.938 |
0.944 |
0.787 |
||||
CS3 |
0.924 |
0.954 |
0.799 |
4.4. Structural Equation Model Testing
4.4.1. Structural Equation Model Construction
This study employed AMOS 26.0 software to build a structural equation model (SEM) with the following variables: independent variables—authenticity of product images, clarity of product information descriptions, and total volume of product description information; intermediary variables—perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived risk, and consumer ambivalence; and outcome variable—purchase intention of mobile battle royale game players. The model is based on the framework of "Purchase Intention of Mobile Battle Royale Game Players from the Perspective of Consumer Ambivalence."
The study used several fit indices to evaluate the model, including relative chi-square (CMIN/DF), goodness of fit index (GFI), adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI), normed fit index (NFI), comparative fit index (CFI), and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA). These indicators were used to assess the model’s fit. The results of the model fit are presented in Table 10, where all the fit indices meet the required standards, indicating that the structural equation model has a good fit and the theoretical model constructed in this study is acceptable.
Table 10. Fit Results of the Formal Questionnaire Data
Fit Index |
Evaluation Criteria |
Actual Value |
|
Acceptable Standard |
Good Standard |
||
Relative Chi-square (CMIN/DF) |
<3.0 |
2.835 |
|
Goodness of Fit Index (GFI) |
[0.7,0.9) |
>0.9 |
0.937 |
Adjusted Goodness of Fit (AGFI) |
[0.7,0.9) |
>0.9 |
0.911 |
Normed Fit Index (NFI) |
[0.7,0.9) |
>0.9 |
0.949 |
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) |
[0.7,0.9) |
>0.9 |
0.966 |
Root Mean Square Error (RMSEA) |
<0.08 |
<0.05 |
0.051 |
4.4.2. Direct Effects Test
In the structural equation model (SEM) constructed in this study, the path coefficients of observed variables to their latent variables are all above 0.6, indicating high support for each variable’s measurement items. The maximum likelihood method was used to estimate the parameters of the SEM and assess the significance of each path by examining the p-values. The results are shown in Table 11.
Table 11. Direct Effects Test Results for Model Variables (N=716)
Variable Relationship |
Estimate |
S.E. |
C.R. |
Result |
Product Authenticity ---> Perceived Ease of Use |
0.098* |
0.50 |
1.975 |
Significant |
Product Authenticity ---> Perceived Social Usefulness |
0.055 |
0.045 |
1.209 |
Not significant |
Product Authenticity ---> Perceived Entertainment Usefulness |
0.042 |
0.029 |
1.477 |
Not significant |
Product Authenticity ---> Perceived Achievement Usefulness |
0.145*** |
0.038 |
3.787 |
Significant |
Product Authenticity ---> Perceived Risk |
-0.191** |
0.072 |
-2.66 |
Significant |
Clarity of Product Description ---> Perceived Ease of Use |
-0.006 |
0.076 |
-0.085 |
Not significant |
Clarity of Product Description ---> Perceived Social Usefulness |
0.269*** |
0.068 |
3.928 |
Significant |
Clarity of Product Description ---> Perceived Entertainment Usefulness |
0.159*** |
0.045 |
3.56 |
Significant |
Clarity of Product Description ---> Perceived Achievement Usefulness |
0.247*** |
0.058 |
4.241 |
Significant |
Clarity of Product Description ---> Perceived Risk |
-0.37*** |
0.109 |
-3.404 |
Significant |
Total Volume of Product Description ---> Perceived Ease of Use |
-0.013 |
0.05 |
-0.257 |
Not significant |
Total Volume of Product Description ---> Perceived Social Usefulness |
-0.121** |
0.046 |
-2.613 |
Significant |
Total Volume of Product Description ---> Perceived Entertainment Usefulness |
-0.035 |
0.029 |
-1.225 |
Not significant |
Total Volume of Product Description ---> Perceived Achievement Usefulness |
-0.114** |
0.038 |
-2.967 |
Significant |
Total Volume of Product Description ---> Perceived Risk |
-0.37*** |
0.109 |
-3.404 |
Significant |
Perceived Ease of Use ---> Perceived Social Usefulness |
0.705*** |
0.052 |
13.619 |
Significant |
Perceived Ease of Use ---> Perceived Entertainment Usefulness |
0.605*** |
0.048 |
13.96 |
Significant |
Perceived Ease of Use ---> Perceived Achievement Usefulness |
0.735*** |
0.053 |
13.792 |
Significant |
Perceived Ease of Use ---> Perceived Risk |
-0.56*** |
0.065 |
-8.544 |
Significant |
Perceived Ease of Use ---> Consumer Ambivalence |
0.503 |
0.174 |
2.896 |
Not significant |
Perceived Ease of Use ---> Purchase Intention |
0.717* |
0.103 |
10.05 |
Significant |
Perceived Social Usefulness ---> Consumer Ambivalence |
-0.358*** |
0.82 |
-4.391 |
Significant |
Perceived Social Usefulness ---> Purchase Intention |
0.240* |
0.53 |
1.45 |
Significant |
Perceived Entertainment Usefulness ---> Consumer Ambivalence |
-0.428** |
0.162 |
-2.638 |
Significant |
Perceived Entertainment Usefulness ---> Purchase Intention |
0.108* |
0.31 |
3.157 |
Significant |
Perceived Achievement Usefulness ---> Consumer Ambivalence |
-0.094 |
0.092 |
-1.021 |
Not significant |
Perceived Achievement Usefulness ---> Purchase Intention |
0.016 |
0.031 |
0.23 |
Not significant |
Perceived Risk ---> Consumer Ambivalence |
1.528*** |
0.060 |
25.562 |
Significant |
Perceived Risk ---> Purchase Intention |
-0.969* |
0.49 |
-2.60 |
Significant |
Consumer Ambivalence ---> Purchase Intention |
-0.58*** |
0.232 |
-3.871 |
Significant |
Note: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001
Summary of Direct Path Analysis Results: The positive effects of product authenticity on perceived ease of use and perceived achievement usefulness were significant. The negative effect of product authenticity on perceived risk was also significant. However, the positive effects of product authenticity on perceived social usefulness and perceived entertainment usefulness were not significant. Hypotheses H1.1 and H1.3 were supported, while H1.2 was partially supported. The positive effect of clarity of product description on perceived ease of use was not significant. However, its positive effects on the three dimensions of perceived usefulness and perceived risk were significant. Hypotheses H1.5 and H1.6 were supported. The negative effects of total volume of product description on perceived ease of use and perceived entertainment usefulness were not significant. However, its positive effects on perceived achievement usefulness and perceived risk were significant. Hypothesis H1.8 was partially supported, and H1.9 was supported. The positive effects of perceived social usefulness and perceived entertainment usefulness on consumer ambivalence and purchase intention were significant. However, the effects of perceived achievement usefulness on consumer ambivalence and purchase intention were not significant. Hypotheses H2.2, H2.3, H2.5, and H2.6 were supported. The positive effects of perceived ease of use on the three dimensions of perceived usefulness, perceived risk, and purchase intention were significant. However, its effect on consumer ambivalence was not significant. Hypotheses H2.7, H2.8, H2.9, H2.10, and H2.11 were supported. The negative effects of perceived risk on consumer ambivalence and purchase intention were significant, supporting H2.17 and H2.18. The negative effect of consumer ambivalence on purchase intention was significant, supporting H3.1.
Based on the path analysis results, the validated model and path coefficients are shown in Figure 4:
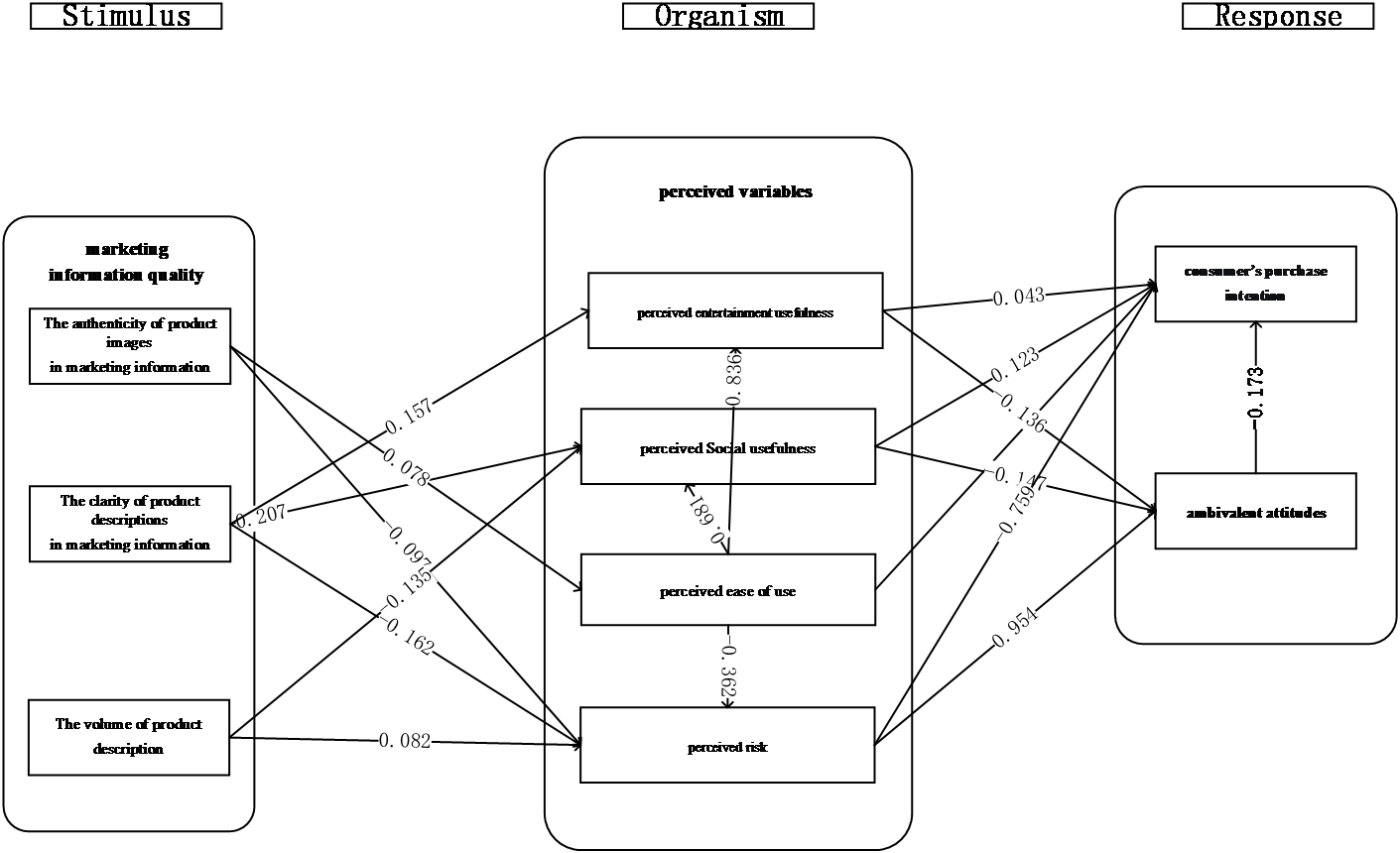
Figure 4. Verified consumer ambivalence model of game players and path coefficient
4.4.3. Mediation Effects Analysis
Based on the hypotheses and the results of the structural equation model, it is evident that perceived ease of use not only directly influences players' purchase intention but also affects consumer ambivalence and purchase intention through perceived usefulness and perceived risk. Additionally, perceived usefulness and perceived risk directly impact players' purchase intention and indirectly influence purchase intention through consumer ambivalence. Therefore, this section examines the mediation effects among perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness, perceived risk, consumer ambivalence, and purchase intention.
To explore the mechanisms through which perceived ease of use affects players' ambivalence and purchase intention, we used perceived ease of use as the independent variable, and consumer ambivalence and purchase intention as the dependent variables, constructing a chain mediation model with perceived usefulness and perceived risk as mediators. The Bootstrap method (sample size set at 5,000) was employed to test the mediation effects between perceived ease of use and purchase intention. If the indirect effect does not include 0 within the 95% confidence interval, the mediation effect is considered significant. The results showed that under both methods, the mediation effects of perceived ease of use on consumer ambivalence through perceived social usefulness and perceived risk were significant. However, the mediation effects of perceived ease of use on consumer ambivalence through perceived entertainment usefulness and perceived achievement usefulness were not significant. H2.13 was partially supported, and H2.14 was supported. The mediation effects of perceived ease of use on purchase intention through consumer ambivalence were not significant. The mediation effects of perceived ease of use on purchase intention through perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, and perceived risk were significant, but through perceived achievement usefulness were not. H2.15 was partially supported, and H2.16 was supported. Specific paths and related parameters are shown in Table 12.
Table 12. Standardized Bootstrap Mediation Effects of Perceived Ease of Use (N=716)
Path |
Effect Value |
S.E. |
Bias-corrected 95%CI |
Percentile 95%CI |
||||
Lower |
Upper |
P |
Lower |
Upper |
P |
|||
PE->PSU->AA |
-0.153 |
0.046 |
-0.255 |
-0.069 |
0.001 |
-0.250 |
-0.066 |
0.001 |
PE->PEU->AA |
-0.088 |
0.059 |
-0.198 |
0.037 |
0.148 |
-0.200 |
0.034 |
0.136 |
PE->PAU->AA |
-0.104 |
0.129 |
-0.385 |
0.130 |
0.363 |
-0.369 |
0.147 |
0.426 |
PE->PR->AA |
-0.785 |
0.109 |
-0.1010 |
-0.574 |
0.000 |
-1.016 |
-0.577 |
0.000 |
PE->PSU->CS |
0.150 |
0.043 |
0.072 |
0.247 |
0.001 |
0.069 |
0.241 |
0.002 |
PE->PEU->CS |
0.189 |
0.058 |
0.079 |
0.309 |
0.003 |
0.075 |
0.303 |
0.004 |
PE->PAU->CS |
-0.055 |
0.129 |
-0.341 |
0.156 |
0.656 |
-0.362 |
0.145 |
0.590 |
PE->PR->CS |
0.455 |
0.121 |
0.174 |
0.675 |
0.010 |
0.208 |
0.698 |
0.006 |
PE->PSU->AA->CS |
0.010 |
0.028 0.0 |
-0.020 |
0.119 |
0.353 |
-0.038 |
0.076 |
0.684 |
PE->PEU->AA->CS |
0.010 |
0.031 |
-0.018 |
0.144 |
0.327 |
-0.044 |
0.084 |
0.686 |
PE->PAU->AA->CS |
-0.025 |
0.044 |
-0.170 |
0.25 |
0.288 |
-0.129 |
0.039 |
0.475 |
PE->PR->AA->CS |
-0.037 |
0.103 |
-0.073 |
0.418 |
0.363 |
-0.149 |
0.282 |
0.684 |
PE->AA->CS |
0.17 |
0.051 |
-0.240 |
0.032 |
0.335 |
-0.138 |
0.073 |
0.685 |
To explore the mechanisms by which perceived usefulness and perceived risk affect players' purchase intention, we used perceived usefulness and perceived risk as the independent variables and purchase intention as the dependent variable, constructing a mediation model with consumer ambivalence as the mediator. The Bootstrap method (sample size set at 5,000) was used to test the mediation effects of ambivalence on the relationships among perceived usefulness, perceived risk, and purchase intention. If the indirect effect does not include 0 within the 95% confidence interval, the mediation effect is considered significant. The results showed that under both methods, the mediation effects of perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, and perceived risk on purchase intention through consumer ambivalence were significant. However, the mediation effect of perceived achievement usefulness on purchase intention through consumer ambivalence was not significant. H3.2, H3.3, and H3.6 were supported. Specific paths and related parameters are shown in Table 13.
Table 13. Standardized Bootstrap Mediation Effects of Perceived Usefulness and Perceived Risk (N=716)
Path |
Effect Value |
SE |
Bias-corrected 95%CI |
Percentile 95%CI |
||||
Lower |
Upper |
P |
Lower |
Upper |
P |
|||
PSU->AA->CS |
0.185 |
0.077 |
0.356 |
0.047 |
0.008 |
0.34 |
0.038 |
0.011 |
PEU->AA->CS |
0.148 |
0.085 |
0.224 |
0.116 |
0.009 |
0.217 |
0.119 |
0.009 |
PAU->AA->CS |
-0.029 |
0.050 |
-0.614 |
0.514 |
0.895 |
-0.681 |
0.460 |
0.804 |
PR->AA->CS |
-0.917 |
0.237 |
-0.227 |
-1.296 |
0.017 |
-0.327 |
-1.376 |
0.010 |
4.4.4. Results Analysis and Discussion
Based on the relevant output results from Sections 4.4.2 and 4.4.3, the validation of the research hypotheses is summarized in the following table:
Table 14. Supported Hypotheses
Hypothesis |
Relationship Between Variables |
Result |
H1.1 |
PE<---API |
Supported |
H1.2 |
PAU<---API |
Supported |
H1.3 |
PR<---API |
Supported |
H1.5 |
PSU<---CPI |
Supported |
PEU<---CPI |
Supported |
|
PAU<---CPI |
Supported |
|
H1.6 |
PR<---CPI |
Supported |
H1.8 |
PSU<---VPI |
Supported |
PAU<---VPI |
Supported |
|
H1.9 |
PR<---VPI |
Supported |
H2.2 |
AA<--- PSU |
Supported |
H2.3 |
AA<--- PEU |
Supported |
H2.5 |
CS<--- PSU |
Supported |
H2.6 |
CS<--- PEU |
Supported |
H2.7 |
PSU<---PE |
Supported |
H2.8 |
PEU<---PE |
Supported |
H2.9 |
PAU<---PE |
Supported |
H2.10 |
PR<---PE |
Supported |
H2.12 |
CS<---PE |
Supported |
H2.13 |
AA<---PSU<---PE |
Supported |
H2.14 |
AA<---PR<---PE |
Supported |
H2.15 |
CS<---PSU<---PE |
Supported |
CS<---PEU<---PE |
Supported |
|
H2.16 |
CS<---PR<---PE |
Supported |
H2.17 |
AA<---PR |
Supported |
H2.18 |
CS<---PR |
Supported |
H3.1 |
CS<---AA |
Supported |
H3.2 |
CS<---AA<---PSU |
Supported |
H3.3 |
CS<---AA<---PEU |
Supported |
Analysis of the Model Based on the Hypothesis Validation Results:
(1) The Effect of Marketing Information on Players' Perceptions of Different Product Dimensions
The results show that the authenticity of the product image, clarity of the product description, and the total amount of product information can all affect players’ perceptions, but the influence varies in terms of the target and strength. The authenticity of the product image has a positive effect on perceived ease of use and perceived risk. Additionally, the positive influence of product image authenticity on perceived achievement usefulness is significant, suggesting that when promoting a product, using images that realistically reflect the product’s value and effects can help players perceive the product's utility in achieving goals. The clarity of the product description has a significant positive impact on perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, perceived achievement usefulness, and a significant positive impact on perceived risk. As for the total volume of product information, its impact on perceived ease of use is not significant, while it has a significant negative impact on perceived social usefulness and perceived achievement usefulness. The total volume of product information also has a significant negative impact on perceived risk.
(2) The Influence of Players' Perceptions of Product Dimensions on Consumer Ambivalence
The results indicate that perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, and perceived risk all significantly influence players' consumer ambivalence, in the following order: perceived risk, perceived social usefulness, and perceived entertainment usefulness.
(3) The Influence of Different Perceptions on Players' Purchase Intention
The results show that perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived risk, and consumer ambivalence all have significant effects on players' purchase intention.
(4) The Mediating Effect of Perceived Ease of Use
The results demonstrate that perceived ease of use not only directly affects consumer ambivalence but also indirectly influences consumer ambivalence through its effect on perceived entertainment usefulness and perceived risk. In addition to its direct impact on purchase intention, perceived ease of use also indirectly influences purchase intention through its effects on perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, and perceived risk.
(5) The Mediating Role of Consumer Ambivalence
The results show that perceived entertainment usefulness and perceived social usefulness significantly affect purchase intention through their impact on consumer ambivalence. Moreover, perceived ease of use influences consumer ambivalence through perceived risk, which in turn affects purchase intention.
5. Research Conclusions and Recommendations
This study, based on the TAM model, S-O-R model, and the perspective of ambivalent attitudes, explores the impact of marketing information quality, player perception, ambivalent attitudes, and purchase intentions. In light of the research findings, the following three marketing recommendations are proposed:
(1) Clarity of Marketing Information: When designing product marketing information for mobile shooting games, developers should focus on the clarity of the textual content. The empirical results show that the clarity of product descriptions significantly influences perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, and perceived risk, all of which, in turn, have a significant effect on players' purchase intentions. Therefore, providing clear and concise product descriptions can enhance the social and entertainment utility perceived by players and reduce their perceived risks, ultimately increasing their likelihood of making a purchase.
(2) Minimizing Irrelevant Information: Developers should strive to minimize the inclusion of irrelevant information in product descriptions. The total volume of product information negatively affects perceived social usefulness, perceived achievement usefulness, and perceived risk. Non-utility-related descriptions significantly reduce players' perceptions of a product's social and achievement utility, while increasing their uncertainty and confusion about the product. Thus, irrelevant information should be limited to improve the effectiveness of marketing communications and enhance players' confidence in the product.
(3) Focusing on Social and Entertainment Utility: When designing products, mobile shooting game developers should prioritize the product's social and entertainment utility. The empirical findings indicate that perceived social usefulness, perceived entertainment usefulness, and perceived risk significantly influence players' ambivalent attitudes. This suggests that when players consider a product from different perspectives, higher perceived social and entertainment utility reduces the intensity of ambivalent attitudes, leading to a more positive overall attitude and an increased likelihood of purchase intention.
References
[1]. People's Republic of China. (n.d.). The 14th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and the Long-Range Objectives Through the Year 2035 [Monograph]. Beijing: People's Publishing House.
[2]. Yu, H. D. (2018). From "Electronic Heroin" to "The Ninth Art": The evolution of Chinese video game imagery from the perspective of media criticism. New Media Research, 4(10), 122–123.
[3]. Wang, X. H., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Viewing the ninth art from an art appreciation perspective. Art and Design (Theory), 2(09), 122–123.
[4]. Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35(8), 982–1003.
[5]. Davis, F. (1985). A technology acceptance model for empirically testing new end-user information systems [Monograph].
[6]. Zhou, H. (2019). Research on factors influencing consumer willingness in mobile games [Master’s thesis, Jinan University].
[7]. Shi, J. N. (2018). Research on factors influencing in-app purchase intentions in mobile games [Master’s thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology].
[8]. Cao, S. J., & Lu, T. H. (2006). Empirical research on attitudes and behaviors of online game consumption [Technical report]. Beijing, China.
[9]. Wen, L. (2019). Analysis of factors influencing online game consumption behavior: An empirical study based on Nanjing college students [Master’s thesis, Nanjing University of Finance & Economics].
[10]. Xia, T. (2021). Research on factors influencing college students' spending behavior in video games based on the Technology Acceptance Model [Master’s thesis, Shanghai Normal University].
[11]. Guo, L. (2015). Research on factors influencing online game consumption behavior intention [Master’s thesis, Lanzhou University].
[12]. Wang, Y. M., & Wang, L. L. (2017). Research on factors influencing willingness to consume mobile games. E-Commerce, (11), 17–20.
[13]. Chen, M., Wang, P., & Zhang, C. Y. (2021). Empirical research on factors influencing e-sports user consumption behavior: Based on the SOR theory perspective. Journal of Adult Physical Education, 37(05), 23–31.
[14]. Chen, Z. G., & Pan, F. (2023). Research on factors influencing the willingness to purchase virtual items in games based on the SOR model. Business Management, (03), 67–75.
[15]. Slavin, W. B. (2004). Educational psychology: Theory and practice [Monograph]. Beijing: People's Posts and Telecommunications Press.
[16]. Wu, X. W., Kang, X. H., & Lin, Q. F. (2020). Female college students' motivations and online game consumption. Journal of China Women's University, 32(04), 37–46.
[17]. Guo, M. M., & Huang, X. H. (2020). Empirical analysis of college students' online game consumption motives and behavior. Fujian Quality Management, (12), 96.
[18]. Zhang, Z. Y. (2020). The impact of achievement motivation on competitive online game player behavior: A case study of "League of Legends" [Master’s thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University].
[19]. Li, X. G., & Xu, H. W. (2010). Measurement of motivations for purchasing virtual items online. China Soft Science, (4), 135–145.
[20]. Liuhsien-Che, Y. H. (2023). Testing variation in esports spectators’ motivations in relation to consumption behavior. Sustainability, 3(15), 2028.
[21]. Paiva, F., Franco, A., Mendonça Junior, G., et al. (2018). Analyzing player profiles in collectible card games [Monograph].
[22]. Won, J., & Kim, B. (2020). The effect of consumer motivations on purchase intention of online fashion-sharing platforms. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(6), 197–207.
[23]. Seo, H., & Yoo, T. (2017). Structural relationship among informativeness, usefulness, consumer attitude, and purchase intention of cosmetics on Instagram. Journal of Korea Design Forum, 55, 183–194.
[24]. Huang, M. X., Feng, X. L., & Xie, T. T. (2010). A new understanding of consumer attitudes: Dualistic contradictory attitudes. Advances in Psychological Science, 18(06), 987–996.
[25]. Wang, Y. B., Min, Q. F., & Lin, Z. K. (2020). The consistency of attitude and purchase intention in peer response conflicts in online reviews. Science Research Management, 41(11), 173–181.
[26]. Shi, W. H., Zhang, Q., & Cai, J. L. (2018). Research on the impact of contradictory online reviews on consumer attitudes and purchase intentions. Management Review, 30(7), 77–88.
[27]. Cao, Y., Li, Q. S., & Wan, G. Y. (2020). Research on the impact of online reviews on consumer snack purchase decisions. Management Review, 32(03), 157–166.
[28]. Wang, D. H., Yao, T., & Yao, F. (2015). To buy or not to buy: Research on ecological product purchase intentions from the perspective of contradictory attitudes. Nankai Business Review, 18(02), 136–146.
[29]. Ma, Y. L., & Hu, Z. M. (2013). Research on factors influencing and mechanisms of contradictory online reviews. Yunnan Social Sciences, (5), 78–81, 95.
[30]. Yue, X. (2022). Research on the impact of review information on consumers' contradictory attitudes from the perspective of Hovland's attitude change theory. Journal of Management Engineering, 36(04), 36–49.
[31]. Yue, X., & Wan, C. R. (2021). Research on consumer contradictory attitudes under the combined influence of personal, product, and situational factors. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Social Sciences Edition), 23(04), 19–27.
[32]. Cheng, B., & Gao, S. G. (2020). Research on the impact of the contradiction between initial and follow-up reviews on consumer contradictory attitudes. E-Commerce, (06), 43–44.
[33]. Ma, Y. L. (2014). The impact of conflicting online reviews on consumer attitudes. Economic Issues, (03), 37–40.
[34]. Xu, H. N. (2022). Research on factors influencing mobile game consumer loyalty and spending based on grounded theory [Master’s thesis, Beijing Foreign Studies University].
[35]. Gao, H. X., Sun, S. F., & Zhang, M. (2016). The impact of online word of mouth on consumer brand-switching behavior from a contradictory attitude perspective. Productivity Research, (10), 134–138.
[36]. Mo, X. Y. (2021). Research on methods for measuring contradictory attitudes based on eye-tracking experiments [Master’s thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications].
[37]. Maio, G., Esses, V., & Bell, D. (2000). Examining conflict between components of attitudes: Ambivalence and inconsistency are distinct constructs. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue canadienne des sciences du comportement, 32, 71–83.
[38]. Priester, J., & Petty, R. (1996). The gradual threshold model of ambivalence: Relating the positive and negative bases of attitudes to subjective ambivalence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 71, 431–449.
[39]. Tudoran, A., Olsen, S., & Dopico, D. (2012). Satisfaction strength and intention to purchase a new product. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 11.
[40]. Jiang, H., Liang, J., Wang, H., et al. (2015). The interplay of emotions, elaboration, and ambivalence on attitude–behavior consistency. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 15.
[41]. Lian, Y. Z., Li, X. X., & Shen, H. (2022). The mediating mechanism of consumer perceived authenticity on the impact of contradictory attitudes in marketing: Heterogeneity in analog and index marketing contexts. Journal of Central University of Finance & Economics, (12), 111–122.
[42]. Chen, J. Q., Li, G. S., & Lu, L. (2021). Souvenirs: To buy or not to buy? A study of consumer purchase intentions based on contradictory attitude theory. Tourism Science, 35(04), 108–127.
[43]. Xue, T. (2021). Research on purchase intentions of virtual goods based on the Technology Acceptance Model. China Business Review, No.843(20), 43–45.
[44]. Qu, Q. S. (2021). Research on factors influencing the willingness to quit mobile online games based on the SOR perspective. Knowledge Management Forum, 6(01), 56–65.
[45]. Zhang, B. S., Zhang, Q. P., & Zhao, C. G. (2021). Research on the impact of live streaming features on consumer purchase intentions in e-commerce: The mediating role of consumer perception. China Circulation Economy, 35(06), 52–61.
[46]. Zhang, Q. Y., & Sun, X. X. (2018). Research on the impact of consumer confusion on green brand purchase intentions: The mediating role of contradictory attitudes. Consumption Economics, 34(03), 80–87.
[47]. Chen, G. Q. (2020). Research on factors influencing the intention to purchase electric vehicles based on the Technology Acceptance Model [Master’s thesis, Yunnan University of Finance & Economics].
[48]. A. B. R. (1960). Consumer behavior as risk-taking. Chicago IL, 384–398.
[49]. Xia, X. Q., & Du, Z. L. (2014). Research on factors influencing consumer intentions to purchase internet financial products. Finance & Economics, (20), 55–201.
[50]. Shi, F., Meng, C., & Li, X. F., et al. (2017). Research on factors influencing online group-buying consumers' purchase intentions based on the SOR model. Business Economics Research, No.735(20), 53–55.
[51]. Lee, Y., 장세윤, & 양희순, et al. (2010). The difference of TAM according to purchase intention of customized golf gloves. Journal of the Korean Society of Clothing and Textiles, 34(7), 1100–1110.
[52]. Cao, S. L., & Xu, X. Y. (2020). Research on the monetization mechanism and players’ motivations in the mobile game "Onmyoji". Journalist, (07), 27–37.
[53]. Jonas, K., Diehl, M., & Brömer, P. (1997). Effects of attitudinal ambivalence on information processing and attitude-intention consistency. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 33(2), 190–210.
[54]. Jacoby, J., & Kaplan, L. B. (1972). The components of perceived risk [Monograph].
[55]. Wang, Y. (2021). Research on the impact of consumers' perceptions of online cultural products on consumption intentions [Master’s thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology].
Cite this article
Chen,Y. (2024). Research on Game Players' Willingness to Purchase Based on the Perspective of Ambivalent Attitudes. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,11,10-24.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. People's Republic of China. (n.d.). The 14th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and the Long-Range Objectives Through the Year 2035 [Monograph]. Beijing: People's Publishing House.
[2]. Yu, H. D. (2018). From "Electronic Heroin" to "The Ninth Art": The evolution of Chinese video game imagery from the perspective of media criticism. New Media Research, 4(10), 122–123.
[3]. Wang, X. H., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Viewing the ninth art from an art appreciation perspective. Art and Design (Theory), 2(09), 122–123.
[4]. Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35(8), 982–1003.
[5]. Davis, F. (1985). A technology acceptance model for empirically testing new end-user information systems [Monograph].
[6]. Zhou, H. (2019). Research on factors influencing consumer willingness in mobile games [Master’s thesis, Jinan University].
[7]. Shi, J. N. (2018). Research on factors influencing in-app purchase intentions in mobile games [Master’s thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology].
[8]. Cao, S. J., & Lu, T. H. (2006). Empirical research on attitudes and behaviors of online game consumption [Technical report]. Beijing, China.
[9]. Wen, L. (2019). Analysis of factors influencing online game consumption behavior: An empirical study based on Nanjing college students [Master’s thesis, Nanjing University of Finance & Economics].
[10]. Xia, T. (2021). Research on factors influencing college students' spending behavior in video games based on the Technology Acceptance Model [Master’s thesis, Shanghai Normal University].
[11]. Guo, L. (2015). Research on factors influencing online game consumption behavior intention [Master’s thesis, Lanzhou University].
[12]. Wang, Y. M., & Wang, L. L. (2017). Research on factors influencing willingness to consume mobile games. E-Commerce, (11), 17–20.
[13]. Chen, M., Wang, P., & Zhang, C. Y. (2021). Empirical research on factors influencing e-sports user consumption behavior: Based on the SOR theory perspective. Journal of Adult Physical Education, 37(05), 23–31.
[14]. Chen, Z. G., & Pan, F. (2023). Research on factors influencing the willingness to purchase virtual items in games based on the SOR model. Business Management, (03), 67–75.
[15]. Slavin, W. B. (2004). Educational psychology: Theory and practice [Monograph]. Beijing: People's Posts and Telecommunications Press.
[16]. Wu, X. W., Kang, X. H., & Lin, Q. F. (2020). Female college students' motivations and online game consumption. Journal of China Women's University, 32(04), 37–46.
[17]. Guo, M. M., & Huang, X. H. (2020). Empirical analysis of college students' online game consumption motives and behavior. Fujian Quality Management, (12), 96.
[18]. Zhang, Z. Y. (2020). The impact of achievement motivation on competitive online game player behavior: A case study of "League of Legends" [Master’s thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University].
[19]. Li, X. G., & Xu, H. W. (2010). Measurement of motivations for purchasing virtual items online. China Soft Science, (4), 135–145.
[20]. Liuhsien-Che, Y. H. (2023). Testing variation in esports spectators’ motivations in relation to consumption behavior. Sustainability, 3(15), 2028.
[21]. Paiva, F., Franco, A., Mendonça Junior, G., et al. (2018). Analyzing player profiles in collectible card games [Monograph].
[22]. Won, J., & Kim, B. (2020). The effect of consumer motivations on purchase intention of online fashion-sharing platforms. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(6), 197–207.
[23]. Seo, H., & Yoo, T. (2017). Structural relationship among informativeness, usefulness, consumer attitude, and purchase intention of cosmetics on Instagram. Journal of Korea Design Forum, 55, 183–194.
[24]. Huang, M. X., Feng, X. L., & Xie, T. T. (2010). A new understanding of consumer attitudes: Dualistic contradictory attitudes. Advances in Psychological Science, 18(06), 987–996.
[25]. Wang, Y. B., Min, Q. F., & Lin, Z. K. (2020). The consistency of attitude and purchase intention in peer response conflicts in online reviews. Science Research Management, 41(11), 173–181.
[26]. Shi, W. H., Zhang, Q., & Cai, J. L. (2018). Research on the impact of contradictory online reviews on consumer attitudes and purchase intentions. Management Review, 30(7), 77–88.
[27]. Cao, Y., Li, Q. S., & Wan, G. Y. (2020). Research on the impact of online reviews on consumer snack purchase decisions. Management Review, 32(03), 157–166.
[28]. Wang, D. H., Yao, T., & Yao, F. (2015). To buy or not to buy: Research on ecological product purchase intentions from the perspective of contradictory attitudes. Nankai Business Review, 18(02), 136–146.
[29]. Ma, Y. L., & Hu, Z. M. (2013). Research on factors influencing and mechanisms of contradictory online reviews. Yunnan Social Sciences, (5), 78–81, 95.
[30]. Yue, X. (2022). Research on the impact of review information on consumers' contradictory attitudes from the perspective of Hovland's attitude change theory. Journal of Management Engineering, 36(04), 36–49.
[31]. Yue, X., & Wan, C. R. (2021). Research on consumer contradictory attitudes under the combined influence of personal, product, and situational factors. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Social Sciences Edition), 23(04), 19–27.
[32]. Cheng, B., & Gao, S. G. (2020). Research on the impact of the contradiction between initial and follow-up reviews on consumer contradictory attitudes. E-Commerce, (06), 43–44.
[33]. Ma, Y. L. (2014). The impact of conflicting online reviews on consumer attitudes. Economic Issues, (03), 37–40.
[34]. Xu, H. N. (2022). Research on factors influencing mobile game consumer loyalty and spending based on grounded theory [Master’s thesis, Beijing Foreign Studies University].
[35]. Gao, H. X., Sun, S. F., & Zhang, M. (2016). The impact of online word of mouth on consumer brand-switching behavior from a contradictory attitude perspective. Productivity Research, (10), 134–138.
[36]. Mo, X. Y. (2021). Research on methods for measuring contradictory attitudes based on eye-tracking experiments [Master’s thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications].
[37]. Maio, G., Esses, V., & Bell, D. (2000). Examining conflict between components of attitudes: Ambivalence and inconsistency are distinct constructs. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue canadienne des sciences du comportement, 32, 71–83.
[38]. Priester, J., & Petty, R. (1996). The gradual threshold model of ambivalence: Relating the positive and negative bases of attitudes to subjective ambivalence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 71, 431–449.
[39]. Tudoran, A., Olsen, S., & Dopico, D. (2012). Satisfaction strength and intention to purchase a new product. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 11.
[40]. Jiang, H., Liang, J., Wang, H., et al. (2015). The interplay of emotions, elaboration, and ambivalence on attitude–behavior consistency. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 15.
[41]. Lian, Y. Z., Li, X. X., & Shen, H. (2022). The mediating mechanism of consumer perceived authenticity on the impact of contradictory attitudes in marketing: Heterogeneity in analog and index marketing contexts. Journal of Central University of Finance & Economics, (12), 111–122.
[42]. Chen, J. Q., Li, G. S., & Lu, L. (2021). Souvenirs: To buy or not to buy? A study of consumer purchase intentions based on contradictory attitude theory. Tourism Science, 35(04), 108–127.
[43]. Xue, T. (2021). Research on purchase intentions of virtual goods based on the Technology Acceptance Model. China Business Review, No.843(20), 43–45.
[44]. Qu, Q. S. (2021). Research on factors influencing the willingness to quit mobile online games based on the SOR perspective. Knowledge Management Forum, 6(01), 56–65.
[45]. Zhang, B. S., Zhang, Q. P., & Zhao, C. G. (2021). Research on the impact of live streaming features on consumer purchase intentions in e-commerce: The mediating role of consumer perception. China Circulation Economy, 35(06), 52–61.
[46]. Zhang, Q. Y., & Sun, X. X. (2018). Research on the impact of consumer confusion on green brand purchase intentions: The mediating role of contradictory attitudes. Consumption Economics, 34(03), 80–87.
[47]. Chen, G. Q. (2020). Research on factors influencing the intention to purchase electric vehicles based on the Technology Acceptance Model [Master’s thesis, Yunnan University of Finance & Economics].
[48]. A. B. R. (1960). Consumer behavior as risk-taking. Chicago IL, 384–398.
[49]. Xia, X. Q., & Du, Z. L. (2014). Research on factors influencing consumer intentions to purchase internet financial products. Finance & Economics, (20), 55–201.
[50]. Shi, F., Meng, C., & Li, X. F., et al. (2017). Research on factors influencing online group-buying consumers' purchase intentions based on the SOR model. Business Economics Research, No.735(20), 53–55.
[51]. Lee, Y., 장세윤, & 양희순, et al. (2010). The difference of TAM according to purchase intention of customized golf gloves. Journal of the Korean Society of Clothing and Textiles, 34(7), 1100–1110.
[52]. Cao, S. L., & Xu, X. Y. (2020). Research on the monetization mechanism and players’ motivations in the mobile game "Onmyoji". Journalist, (07), 27–37.
[53]. Jonas, K., Diehl, M., & Brömer, P. (1997). Effects of attitudinal ambivalence on information processing and attitude-intention consistency. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 33(2), 190–210.
[54]. Jacoby, J., & Kaplan, L. B. (1972). The components of perceived risk [Monograph].
[55]. Wang, Y. (2021). Research on the impact of consumers' perceptions of online cultural products on consumption intentions [Master’s thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology].









