1 Industrial Digitization
In terms of the connotation and characteristics of digital industry, wish good (2021) points out industry digital refers to the traditional industry with digital technology, build data acquisition, transmission, storage, processing and feedback of complete closed-loop system, aims to eliminate different data barriers between levels and industry, promote the supply side to achieve quality and efficiency of double promotion, creating new industries, new forms and new business model, and continue to meet the demand side to improve the new requirements of the experience, is a kind of activities to promote the digital transformation. Zhao Peng [2] pointed out that the digital transformation of industry marks that China's economy and society have entered a new stage of high-quality development. At the same time, it is also an important opportunity to promote the inheritance and development of folk culture creativity. In Figure 1, Li Yonghong [3] pointed out that the driving mode of industrial digital integration, which refers to the application of information technology in traditional industries, so as to promote the efficiency of traditional industries and promote their transformation to digitalization and automation. Subsequently, the company is reconstructed based on the network environment, and with the help of information technology, rich data assets are generated, and the platform ecosystem is built, so as to expand the space for survival and development in the new era.
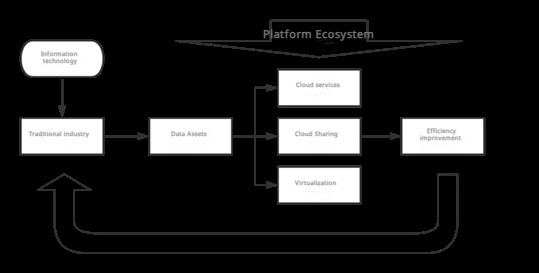
Figure 1. Digitalization of the industry
In terms of industrial digital development strategy, Guo Jin [4] pointed out that the development process of industrial digital transformation has a long time and has a high complexity. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the actual situation of the enterprise, the evolution law of the industry, the development stage of the industry and the progress trend of digital technology, in order to build a diversified target system. Yang Zhuofan [5] pointed out that the mode of industrial digital transformation in China mainly includes two categories: one is the reverse promotion mode driven by social motivation, and the other is the value-added service mode led by innovation motivation. On this basis, he proposed to optimize the "supply chain" system, broaden the layout of the "industrial chain", and extend the scope of the "value chain", so as to further promote the deepening process of industrial digital transformation. Du Xinran [6] pointed out that industrial digitalization is faced with many challenges, such as unclear market logic, unclear scale effect, and unclear order of development. The promotion of industrial digitalization in the future should follow a set of scientific and reasonable strategic logic, and promote the high-quality development of "demand-driven", "free guidance" and "key breakthrough" industrial digitalization mode. Zhu Taihui et al. [7] proposed to clarify the strategic focus of the future development of industrial digitalization from the aspects of strengthening the dual drive of industrial digital development, cultivating leading enterprises, enabling the digital transformation of small and medium-sized enterprises and promoting the digitalization of government governance.
In terms of the development value of industrial digitalization, Manyika et al. [8] pointed out that the wide application of core digital technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence and Internet of Things effectively broke the barriers between industries, gradually blurred the boundaries between industries, promoted the deep integration of industries, and strongly promoted the transformation and upgrading of basic industries. Wang Hongli et al. [9] pointed out that the industrial digital transformation is committed to integrating traditional production processes with cutting-edge technologies such as big data analysis, cloud computing technology, new artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things, as well as modern production services. Industrial digital transformation aims to build a flat industrial pattern, achieve efficient production process, provide high-quality service experience, create huge value, and shape a new industry environment. This series of changes will strongly promote the coordination, growth, transformation and upgrading of the industry. Cao Yuanjun [10] pointed out that the digital transformation of the industry has become an emerging force driving global economic growth. Developed countries generally regard digitalization as the strategic direction of the priority development of various industries, and actively promote the industry to digital transformation. In China, the deep integration of the new generation of information technology and various industries has given birth to digital productivity, and has become a key force to promote the growth of the China-style modern economic system.
In the practice of the digital industry research, LuHong [11] pointed out that the rural industry in the process of digital transformation challenges, put forward to fully use digital elements can assign rural development as the core strategy, through the implementation of digital reconstruction of agricultural industry chain, farmers live digital remodeling and rural development, is committed to building common prosperity, harmonious beautiful digital country. Wang Xiantao [12] used the fixed effect model to analyze the effect of industrial digitalization on industrial green total factor productivity and its action mechanism. The research results show that industrial digitalization plays a significant role in promoting the growth of industrial green total factor productivity. Yang Xueting et al. [13] pointed out that industrial digitalization constitutes the core channel for the deep integration of the digital economy and the real economy. From the three dimensions of basic support system, application scenario practice and policy support environment, Constructed an index system to evaluate the level of industrial digitalization, And according to the objective sequential analysis method to assign the weight of the index; In a linear aggregation approach, The level of industrial digitalization is quantified; With the help of kernel density estimation techniques, Clear the distribution and dynamic characteristics of the industrial digital level; Measure its global and local spatial autocorrelation by using the Moran index (Moran's I), With the help of Lisa diagram, the distribution of local spatial autocorrelation is intuitively shown; at the same time, Using the (spatial) Markov chain method, The transfer probability of the industry digitization level is analyzed.
2 The Logistics Industry and the Modern Agricultural Industry Have Integrated Development
Cui Chunxiao [14] and others, based on the theory of symbiotic relationship, advocate that the endogenous resources of modern agriculture and logistics industry should be incorporated into a symbiotic system for comprehensive integration.
In terms of the integrated development needs of logistics industry and modern agriculture, Zhao Mei [16] pointed out that the development of modern agricultural products e-commerce promotes the new reform in the mode of agricultural economic growth, and puts forward more stringent requirements for the development of agricultural logistics. Tomy P et al. [15] pointed out that agricultural products (FAPs) need to be specially treated to ensure the quality of their products, especially during the social and economic crisis. In developing countries, it has become imperative to develop and implement a robust supply chain logistics governance strategy to regulate the behavior of various supply chain actors involved in the logistics distribution system.
In terms of the value of the integrated development of logistics industry and modern agriculture, Chong Li [17] pointed out that the continuous progress of modern agriculture cannot be separated from the double improvement of the quality and output of agricultural products, while the modern logistics industry can help timely put agricultural products into the market and fully realize its value with its rapid, accurate and efficient circulation services. At the same time, the modern logistics industry also needs to rely on the high-quality agricultural products and resources provided by modern agriculture to further expand the scope of business and expand the development space. Zhang Xiaolin [18] stressed that the promotion of rural logistics will strongly promote and accelerate the pace of rural industrial integration, urban-rural integration and the construction of rural social organization.
In the current situation of the integration of logistics industry and modern agriculture, Wang Z [20] proposed a research system focusing on agricultural products logistics based on the path algorithm built by the logical Petri network. The system uses the path algorithm and analyzes the operation results through the simulation experiment. Mu Xiaoyang et al. [21], based on the relevant data of agriculture and logistics industry in Xinjiang from 2007 to 2018, etc., conducted an in-depth exploration on the coupling and coordinated development relationship of agriculture and logistics industry in Xinjiang by using the coupling and coordination model and spatial data analysis method. Liang Shuai and Jia Cunlu [22] also used the coupling coordination degree model and the entropy method to conduct an empirical analysis. The study shows that the coupling and coordinated development of agriculture and logistics industry in Shandong province is relatively ideal, and the coupling and coordination level shows a trend of gradual improvement with time. Currently, it has reached a state of high coordination, but there is still some room for optimization. Yang Liying [23], et al., constructed a coupling coordination evaluation model between agriculture and logistics industry. Rojas M D et al. [25] pointed out that in order to improve the production efficiency of agricultural products supply chain, adapt to the emerging technology trends, and effectively respond to various disturbances, the multimodal transport logistics system in agricultural development should be optimized.
In the logistics industry and the influencing factors of the development of modern agricultural integration, Yigang J [19] in the study adopts the method of explaining the structure equation, deeply analyzes the agricultural industry cluster and agricultural logistics industry sustainable symbiotic development relationship of many factors, and on this basis, build the agricultural enterprise cluster and agricultural logistics industry symbiotic development systematic drive model. The analysis results show that the macro policy orientation is the core driving force to promote the symbiotic development of agricultural enterprise cluster and agricultural logistics industry, and the symbiotic development effect is the final result of this process. Yin Guangcai [24] and others pointed out that the key factors affecting the integrated development of agriculture and logistics industry include policy environment, economic conditions, technical levels and human resources. The researchers emphasize that government support, market mechanism and information mechanism construction play an important role in promoting the integrated development of agriculture and logistics industry.
3 The Influence of Industrial Digitization on the Development of Logistics Industry
In terms of the current level of digitalization of China's logistics industry, Guzhen [26] pointed out that the application of digital technology in the logistics industry continues to deepen, which significantly improves the operation efficiency of the logistics industry. However, from the overall level, the integration of the digital industry and the logistics industry is still in the initial stage. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to explore how to promote the integration and development of digital industry and logistics industry at a higher level. Liu Yang [27] pointed out that the development of China's logistics industry started relatively late, and it has entered a stage of rapid development since the reform and opening up. At present, China's logistics industry has been relatively mature, however, with the growing logistics demand, the existing logistics level has been difficult to meet the market demand. By integrating modern intelligent information technology, intelligent logistics gives the logistics system the ability of thinking and learning, so that the information flow can be faster than the physical flow, so as to improve the work efficiency of the logistics industry. In order to lead the logistics industry to achieve a new upgrade, we should pay attention to the development trend of the industry, and build an intelligent development model, so as to effectively promote the upgrading of the logistics industry.
In terms of the value of the logistics industry digitalization, Barreto et al. pointed out that the rise of the industrial Internet of Things promotes the logistics supply chain to achieve a higher degree of intelligence, transparency and efficiency, while the application of big data technology further improves the visibility of the supply chain. Harris et al. believe that information technology plays a positive role in promoting the synergistic operation between multiple modes of transport and helps to promote the integration process of the global freight ecosystem. Liu Jingzhi [30] stressed that with the continuous progress and integrated application of digital technologies such as cloud computing, big data and artificial intelligence, logistics enterprises are facing unprecedented opportunities for development. The application of digital technology not only provides logistics enterprises with the ability to monitor and track the whole process of logistics, but also significantly improves the efficiency of logistics transportation and effectively reduces the logistics cost. Tao linli [31] found that digital technology has effectively promoted the high-quality development of logistics industry by promoting technological innovation and optimizing the efficiency of factor allocation.
In terms of the digitalization strategy of the logistics industry, Pan Hong [32] pointed out that realizing the digitalization strategy and management mode upgrade of the regional logistics enterprises in Hangzhou Bay Economic Zone is the key problem to be solved by the current logistics enterprises in this region. Therefore, it is necessary to clarify the specific objectives of the construction of digital management of logistics enterprises, build a public logistics information platform covering the whole region, and start to develop a digital logistics information system based on the industrial chain. Zou Junyi [33] emphasized the construction of intelligent logistics platform, strengthening the scientificity of logistics planning and layout, and accelerating the development process of international logistics, which are all important directions for the development of the current logistics industry. Qiu Xiwen [34] pointed out that in the process of transformation, the logistics industry is facing a complex trade-off relationship between cost input and marginal income. In this trade-off process, the impact of the intelligent transformation of the logistics industry on its industrial performance will appear as a key node, that is, when the marginal benefit exceeds the cost input. Further exploring the phenomenon of this key node will help to enhance the understanding of the interaction mechanism of various elements in the process of the intelligent transformation of the logistics industry.
In terms of practical research on the digitalization of the logistics industry, Yin Lvjiang [35] constructed the DEA-BCC model and DEA-Malmquist index model based on the panel data of the 11 provinces covered by the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2013 to 2022, to conduct static analysis and dynamic trend empirical analysis of the logistics efficiency of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. On this basis, the Tobit model is used to explore the specific impact of digital technology on the logistics efficiency of the Yangtze River Economic Belt from the two dimensions of digital technology infrastructure and digital technology application. Liao Mingyan [36] adopted the panel entropy weight method, coupling coordination model, Dagum Gini coefficient and other research methods to explore the regional differences and dynamic evolution trend of logistics industry and Kernel density estimation model. The research shows that the digital integration level of logistics industry and industrial industry in 30 provinces and cities shows the distribution pattern of "western-central-eastern" promoted step by step. At the same time, the regional differences of the digital integration level of the logistics industry show a trend of expanding year by year. Xinyu X et al. [37] used the coupling and coordination degree model to accurately measure the integration degree of China's logistics industry and digital economy. The results show that the integration level of logistics industry and digital economy shows significant regional characteristics of "the east is higher than the west". However, this regional difference is gradually narrowing over time.
4 The Influence of Industrial Digitization on the Development of Modern Agriculture
Ningtong [38] pointed out that agricultural industry digitalization refers to the comprehensive and in-depth supply-side reform of agricultural production through the comprehensive use of the Internet, automation and big data, so as to achieve the goal of accurate management and even intelligent decision-making.
In terms of the value of industrial digitization to agricultural development, SUCHARITHA G [39] points out that modern technology helps farmers access immediate data and expertise, effectively cutting labor costs and ensuring the accuracy of crop growth. Through automated farming methods, the profit level of 0.405 hectares of agricultural land is equivalent to that of 2.833 hectares of traditional agricultural land. KAMIENSKI C [40] pointed out that the Internet of Things, as a preferred solution for the improvement of intelligent management level, plays a pivotal role in precision irrigation in the agricultural field. With the implementation of freshwater intelligent management, crop yield can be greatly increased and production costs can be reduced, and at the same time, it also has a positive impact on promoting environmentally sustainable development. Zhang Chuanbiao [41] pointed out that under the macro guidance of the rural revitalization strategy, digital construction has become the key focus of promoting the development of agricultural modernization, and plays a significant role in promoting the dual improvement of intelligence and quality of agricultural development. Cheng Ding et al. [42] pointed out that rural digitalization has a significant positive effect on China's total factor productivity in agriculture, and this effect shows a decreasing trend in the grain production and marketing balance areas, main grain producing areas and main grain marketing areas. The process of rural digitization has promoted the improvement of agricultural technology efficiency.
In the study on the mechanism of the impact of industrial digitalization on agricultural development, Addison M et al. [43] adopted probit and bit estimator to make an in-depth analysis of the driving factors and intensity of digital technology adoption in the agricultural field, and used the inverse probability weighting and regression adjustment estimator technology to effectively alleviate the endogenous problems. The results showed a significant correlation between AD and the improvement and final livelihood outcomes of small farmers in rural Ghana. Sterie M C [44] analyzed the impact of the emergence and development of the digital process on the agricultural sector. Pu Xujin et al. [45] adopted the entropy method to quantify the high-quality development level of green and agricultural rural digitalization, and comprehensively applied fixed-effect model, intermediary effect model, threshold effect model and other methods to carry out in-depth and detailed empirical analysis. Lin Yumei [46] using the entropy method and SBM _ GML index of digital agriculture and agriculture green total factor productivity index for accurate measurement, and use the fixed effect model, mediation effect model and threshold effect model, empirical system analyzes the agricultural digital transformation of agricultural green growth effect and its specific effect path. According to the analytical framework of symbiosis theory, Wu Bin et al. [47] constructed the symbiotic system model of agricultural industry digitalization, and selected Lintao County of Gansu Province as an empirical case to make an in-depth analysis of the symbiotic unit, symbiotic interface, symbiotic mode and symbiotic environment of agricultural industry digitalization. The research shows that Lintao County has successfully constructed a continuous digital symbiosis system of agricultural industry in the county. Zou Chi [48] adopts the dynamic panel model and the space panel model and other means to deeply explore the action mechanism of the impact of digitalization on agricultural modernization.
In terms of the digital development strategy of agricultural industry, He Jingbo et al. [49] pointed out that Chongqing needs to further strengthen the overall integration, development and utilization of agricultural data resources in the digitalization of agricultural industry; constantly improve the support and management policies related to agricultural digitalization; promote the construction of the digital demonstration and test base of mountain agriculture; and formulate and implement scientific, reasonable and feasible digital dividend distribution solutions. Jian-li Yang [50] from the digital strategic height, focus on the new development concept, grasp the new stage of development and build a new pattern of development, put forward to strengthen the top-level design, build large agricultural database, strengthening agricultural science and technology innovation, promote agricultural new infrastructure construction, foster new agricultural practitioners, and improve the policy evaluation mechanism, etc. Sun Zhumei [51] pointed out that to accelerate the digital transformation and upgrading of the whole process, the government needs to speed up the planning guidance, platform building and policy support, strengthen 5G, remote sensing satellite, cold chain storage agricultural digital infrastructure construction, actively promote digital agricultural technology innovation, explore new mode of project continuous operations, enhance the value of data elements driving ability, and to improve farmers' information literacy.
In the provinces of agricultural industry digital development present situation, Guang Yu [52] pointed out that the digital transformation of Jilin province agricultural industry, facing digital infrastructure is not perfect, the applicability of agricultural information technology to improve, digital professional personnel lack of resources, as well as the agricultural industry digital transformation system is not perfect. It is proposed to improve digital infrastructure, strengthen the popularization and application of agricultural information technology, and actively cultivate digital professionals. Fourth, to constantly improve the system and mechanism of digital transformation of agricultural industry. Li Ling et al. [53] summarized the typical model of digital development of agricultural industry in Hebei Province and constructed a two-way fixed effect model, and deeply explored the factors affecting the digital development of agricultural industry in Hebei Province from a quantitative perspective. The research results show that the development of agricultural industry digitalization can effectively improve the income level of farmers, enhance the economic benefits of agricultural business entities, and play a positive role in promoting the overall development of agriculture.
5 The Influence of Industrial Digitization on the Integrated Development of Logistics Industry and Modern Agriculture
In the research, Yang Junge et al. [54] pointed out that the integrated development level of the national logistics industry and modern agriculture is relatively low, and there are differences in the eastern, central and western regions; the development level of technology integration is the lowest, and the market integration development level is the highest. Digital economy significantly promotes the integrated development of logistics industry and modern agriculture, and directly promotes the integration of technology and products and business. The heterogeneity analysis found that the digital economy had a significant promotion effect on the eastern and central regions, western regions and non-major grain producing areas, and more significantly on the western regions and non-major grain producing areas. Accordingly, accelerate logistics and agricultural digitization; encourage technological innovation, reduce transaction costs and expand market demand; improve marketization and improve industrial policies; accelerate the balanced development of digital economy and enhance the integrated development level of logistics industry and modern agriculture.
6 Literature Review
Through the review of domestic and foreign literature, the research on "industrial digitization" has achieved good results, and foreign scholars have first clarified its connotation. Although domestic research started late, scholars also put forward many guiding industrial digitalization strategies combined with localized practical research, which provides theoretical guidance for the transformation and upgrading of industrial digitalization in China. In the relevant research of "integrated development of logistics industry and modern agricultural industry", domestic and foreign scholars mainly focus on the effect and performance research of logistics industry and modern agricultural industry under the background of industrial integration. Domestic and foreign scholars have fully proved that the combination of logistics industry and modern agriculture has profound practical value through research. However, the research on the influence mechanism of the integrated development of logistics industry and modern industry is still insufficient. Only some of the factors affecting policy, economy, technology and talent on the integration of logistics industry and modern agricultural industry, but there are still narrow perspectives in the current research.
In the research on the influence of industrial digitalization on "logistics industry development", "modern agriculture development" and "logistics industry and modern agriculture", domestic and foreign scholars mainly focus on the first two. In the research of a single industry, domestic and foreign scholars mainly discuss the value of digitalization in the development of a single industry, the digital development strategy of a single industry, the influence mechanism of digitalization on a single industry and the practice status. Compared with the latter, the research of the former two has achieved good results. However, the research on the "impact of industrial digitalization on the development of the integrated development of logistics industry and modern agriculture" is still insufficient. Although some scholars focus on "the impact of the integrated development of industrial digital logistics industry and manufacturing industry", almost no scholars focus on this perspective. Therefore, in the follow-up research, it is hoped that the majority of scholars can focus more on the digital transformation and upgrading after the integration of the logistics industry and the modern agricultural industry, in order to provide practical guidance and reference for the logistics industry and agriculture after the industrial integration.
References
[1]. Zhu, H., & Wang, C. (2021). Industrial digital transformation under the new dual-cycle development strategy: Theory and countermeasures. Finance & Trade Economics, 42(3), 14–27.
[2]. Zhao, P. (2024). The intrinsic mechanism and realization path of industrial digitization driving the creativity and inheritance of folk culture. Journal of Shandong Normal University (Social Sciences Edition, 69(4), 119–130.
[3]. Li, Y., & Huang, R. (2019). Research on the model of digital industrialization and industrial digitization in China. Science and Technology Management Research, 39(16), 129–134.
[4]. Guo, J. (2022). Ideas and countermeasures for promoting industrial digital transformation in Shanghai. Science Development, (8), 11–21.
[5]. Yang, Z. (2020). Patterns, shortcomings, and countermeasures of industrial digital transformation in China. China Circulation Economy, 34(7), 60–67.
[6]. Du, X. (2022). Strategic logic and practical measures for industrial digital development. Theoretical Horizon, (7), 56–60.
[7]. Zhu, T., & Gong, J. (2022). Connotation and path of industrial digital development. Tsinghua Financial Review, (2), 93–96.
[8]. Manyika, J., Chui, M., & Roxburgh, R. (2011). Big data: The next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity. McKinsey Global Institute.
[9]. Wang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Practical significance of industrial digital transformation. Industrial Innovation Research, (5), 9–11.
[10]. Cao, Y. (2024). Connotation, model, and path of cultivating critical abilities of vocational students under industrial digital transformation: A case of agricultural mechanization. Anhui Agricultural Science, 52(14), 279–282.
[11]. Lu, H. (2024). Motivation, dilemmas, and responses to rural industrial digital transformation. Agricultural Economy, (10), 58–60.
[12]. Wang, X. (2023). The impact of industrial digitization on industrial green total factor productivity. Lease and Sale Intelligence, (5), 48–50.
[13]. Yang, X., & Zhang, D. (2023). Measuring and spatial characteristics of China's industrial digitalization level. Journal of Liaoning University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition, 51(3), 27–40.
[14]. Cui, C., & Wu, C. (2021). Collaborative decision-making research on agricultural production and modern logistics from the perspective of symbiosis theory. Agricultural Economy, (12), 141–142.
[15]. Tomy, P., Benny, T. K. K., et al. (2023). Fresh agricultural product logistics network governance: Insights from small-holder farms in a developing country. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 26(12), 1761–1784.
[16]. Zhao, M. (2020). The role and development measures of modern agricultural logistics in agricultural economic growth. Rural Practical Technology, (5), 18–19.
[17]. Li, C. (2023). Promoting coordinated development between modern agriculture and modern logistics. China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 44(10), 134+146.
[18]. Zhang, X. (2019). Research on the development path of rural logistics under the rural revitalization strategy. Contemporary Economic Management, (4), 46–51.
[19]. Yigang, J., Guanxin, Y., Jing, X., et al. (2021). Driving strategy and analysis of sustainable and symbiosis development relationship between agricultural industrial clusters and agricultural logistics industry. Sustainability, 13(24), 13800.
[20]. Wang, Z., Wang, L., & Xu, L. (2024). Application of routing algorithm based on logical Petri nets in the structural design of agricultural products logistics system. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 9(1).
[21]. Mu, X., Wang, L., & Huang, Q. (2020). Spatiotemporal evolution of coordinated development between agriculture and logistics in Xinjiang. Journal of Shihezi University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition, 34(5), 51–61.
[22]. Liang, S., & Jia, C. (2022). Research on the coupling and coordinated development of agriculture and logistics in Shandong Province. Guangdong Sericulture, 56(11), 70–73.
[23]. Yang, L., Zhou, Z., & Lin, L. (2023). Research on the coupling and coordinated development of agriculture and logistics in Guangxi. Contemporary Rural Finance and Economics, (7), 19–23.
[24]. Yin, G., & Hai, X. (2024). Research on the coupling and coordinated development of agriculture and logistics. Logistics Science and Technology, 47(2), 76–79.
[25]. Rojas, M. D., & Montoya-Torres, R. J. (2024). Multimodal logistics systems for agricultural development: A systematic review identifying the Latin American case. IISE Annual Conference Proceedings, 1–7.
[26]. Gu, Z. (2022). Research on the integrated development of digital industries and logistics industries. China Business Review, (23), 101–103. https://doi.org/10.19699/j.cnki.issn2096-0298.2022.23.101
[27]. Liu, Y. (2021). Discussion on the intelligent upgrading of the logistics industry driven by digitalization. China Market, (15), 170–172. https://doi.org/10.13939/j.cnki.zgsc.2021.15.170
[28]. Barreto, L., Amaral, A., & Pereira, T. (2017). Industry 4.0 implications in logistics: An overview. Procedia Manufacturing, 13, 1245–1252.
[29]. Harris, I., Wang, Y., & Wang, H. (2015). ICT in multimodal transport and technological trends: Unleashing potential for the future. International Journal of Production Economics, 159, 88–103.
[30]. Liu, J., & Liu, M. (2024). Discussion on the development of logistics enterprises empowered by digital technology. Shanghai Enterprises, (9), 47–49.
[31]. Tao, L. (2024). Research on provincial logistics industry efficiency under the background of the digital economy. Logistics Science and Technology, 47(19), 110–115.
[32]. Pan, H. (2012). Research on the digital management of regional logistics enterprises: A case study of the Hangzhou Bay Economic Zone in Zhejiang Province. Logistics Technology, 31(13), 380–382.
[33]. Zou, J. (2024). Research on the impact of the digital economy on the high-quality development of the logistics industry. China Business Review, 33(19), 106–109. https://doi.org/10.19699/j.cnki.issn2096-0298.2024.19.106
[34]. Qiu, X. (2024). Factors influencing the intelligent development of the logistics industry and policy recommendations. Hebei Enterprises, (11), 53–55. https://doi.org/10.19885/j.cnki.hbqy.2024.11.032
[35]. Yin, L., & Zeng, L. (2024). The impact of digital technology on the logistics efficiency of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Logistics Technology, 43(7), 149–160.
[36]. Liao, M., & Ling, Z. (2024). Regional differences and dynamic evolution of the integration level between China's logistics industry and industrial digitalization. Journal of Beijing Institute of Graphic Communication, 32(1), 30–38. https://doi.org/10.19461/j.cnki.1004-8626.2024.01.010
[37]. Xinyu, X., & Jian, W. (2023). Study on the impact of industrial digitization on carbon emissions: Evidence from China’s logistics industry. Environmental Research Communications, 5(10).
[38]. Ning, T. (2019). Thoughts on the digitalization of the agricultural industry in Yunnan Province. Rural Science and Technology, (14), 121–122.
[39]. Sucharitha, G., & Sai, M. M. (2021). Developments in agriculture technology using the Internet of Things. Internet of Things and Its Applications, 11(26), 341–360.
[40]. Kamienski, C., Soininen, J. P., Taumberger, M., et al. (2019). Smart water management platform: IoT-based precision irrigation for agriculture. Sensors, 19(2), 276.
[41]. Zhang, C. (2022). Exploration of agricultural industrial digitalization and digital industrialization. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 42(36), 26–27.
[42]. Cheng, D., & Huang, S. (2024). Can rural digitalization improve agricultural total factor productivity? Agricultural Economics and Management, (2), 38–51.
[43]. Addison, M., Bonuedi, I., Arhin, A. A., et al. (2024). Exploring the impact of agricultural digitalization on smallholder farmers' livelihoods in Ghana. Heliyon, 10(6), e27541.
[44]. Sterie, M. C., Petre, I. L., Stoica, D. G., et al. (2024). Assessing the impact of digitization on progress in agriculture: A bibliometric analysis. Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence, 18(1), 1724–1733.
[45]. Pu, X., Ma, K., & Wang, Y. (2024). Analysis of the impact of rural digitalization on promoting agricultural green and high-quality development. China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 45(6), 83–95.
[46]. Lin, Y., & Li, C. (2024). The impact of agricultural digital transformation on green agricultural growth. China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 45(4), 28–41.
[47]. Wu, B., & Xu, X. (2022). Agricultural industrial digital transformation: Symbiotic system and practical challenges—Based on a study of Lintao County, Gansu Province. Learning and Exploration, (2), 127–135.
[48]. Zou, C. (2022). Research on the impact of digitalization on agricultural modernization (Master's thesis). Guangxi Normal University.
[49]. He, J., Li, Q., & Pu, C. (2022). Current situation, problems, and countermeasures for the development of agricultural industrial digital transformation in Chongqing. Southern Agriculture, 16(7), 236–241.
[50]. Yang, J., Zheng, W., & Xing, J., et al. (2021). Empowering high-quality agricultural development with digital technology. Shanghai Economic Research, (7), 81–90+104.
[51]. Sun, Z., Liu, T., & Sun, D., et al. (2021). Analysis of the difficulties and countermeasures of agricultural industrial digital transformation: Based on a survey of 143 new agricultural business entities in Zaozhuang City. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 42(3), 122–128.
[52]. Yu, G., & Huo, Y. (2022). Research on the digital transformation of agricultural industries in Jilin Province. Rural Economy and Technology, 33(7), 71–73.
[53]. Li, L., & Liu, X. (2023). Mechanism, model, and countermeasures of agricultural industrial digital development in Hebei Province. Journal of Langfang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 23(1), 45–50.
[54]. Yang, J., & Wang, Q. (2024). The impact of the digital economy on the integration of the logistics industry and modern agriculture. China Circulation Economy, 38(8), 17–32. https://doi.org/10.14089/j.cnki.cn11-3664/f.2024.08.002
Cite this article
Wang,E. (2025). A Review of Research Literature on the Impact of Industrial Digitization on the Integrated Development of Logistics and Modern Agriculture. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,16,52-58.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhu, H., & Wang, C. (2021). Industrial digital transformation under the new dual-cycle development strategy: Theory and countermeasures. Finance & Trade Economics, 42(3), 14–27.
[2]. Zhao, P. (2024). The intrinsic mechanism and realization path of industrial digitization driving the creativity and inheritance of folk culture. Journal of Shandong Normal University (Social Sciences Edition, 69(4), 119–130.
[3]. Li, Y., & Huang, R. (2019). Research on the model of digital industrialization and industrial digitization in China. Science and Technology Management Research, 39(16), 129–134.
[4]. Guo, J. (2022). Ideas and countermeasures for promoting industrial digital transformation in Shanghai. Science Development, (8), 11–21.
[5]. Yang, Z. (2020). Patterns, shortcomings, and countermeasures of industrial digital transformation in China. China Circulation Economy, 34(7), 60–67.
[6]. Du, X. (2022). Strategic logic and practical measures for industrial digital development. Theoretical Horizon, (7), 56–60.
[7]. Zhu, T., & Gong, J. (2022). Connotation and path of industrial digital development. Tsinghua Financial Review, (2), 93–96.
[8]. Manyika, J., Chui, M., & Roxburgh, R. (2011). Big data: The next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity. McKinsey Global Institute.
[9]. Wang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Practical significance of industrial digital transformation. Industrial Innovation Research, (5), 9–11.
[10]. Cao, Y. (2024). Connotation, model, and path of cultivating critical abilities of vocational students under industrial digital transformation: A case of agricultural mechanization. Anhui Agricultural Science, 52(14), 279–282.
[11]. Lu, H. (2024). Motivation, dilemmas, and responses to rural industrial digital transformation. Agricultural Economy, (10), 58–60.
[12]. Wang, X. (2023). The impact of industrial digitization on industrial green total factor productivity. Lease and Sale Intelligence, (5), 48–50.
[13]. Yang, X., & Zhang, D. (2023). Measuring and spatial characteristics of China's industrial digitalization level. Journal of Liaoning University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition, 51(3), 27–40.
[14]. Cui, C., & Wu, C. (2021). Collaborative decision-making research on agricultural production and modern logistics from the perspective of symbiosis theory. Agricultural Economy, (12), 141–142.
[15]. Tomy, P., Benny, T. K. K., et al. (2023). Fresh agricultural product logistics network governance: Insights from small-holder farms in a developing country. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 26(12), 1761–1784.
[16]. Zhao, M. (2020). The role and development measures of modern agricultural logistics in agricultural economic growth. Rural Practical Technology, (5), 18–19.
[17]. Li, C. (2023). Promoting coordinated development between modern agriculture and modern logistics. China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 44(10), 134+146.
[18]. Zhang, X. (2019). Research on the development path of rural logistics under the rural revitalization strategy. Contemporary Economic Management, (4), 46–51.
[19]. Yigang, J., Guanxin, Y., Jing, X., et al. (2021). Driving strategy and analysis of sustainable and symbiosis development relationship between agricultural industrial clusters and agricultural logistics industry. Sustainability, 13(24), 13800.
[20]. Wang, Z., Wang, L., & Xu, L. (2024). Application of routing algorithm based on logical Petri nets in the structural design of agricultural products logistics system. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 9(1).
[21]. Mu, X., Wang, L., & Huang, Q. (2020). Spatiotemporal evolution of coordinated development between agriculture and logistics in Xinjiang. Journal of Shihezi University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition, 34(5), 51–61.
[22]. Liang, S., & Jia, C. (2022). Research on the coupling and coordinated development of agriculture and logistics in Shandong Province. Guangdong Sericulture, 56(11), 70–73.
[23]. Yang, L., Zhou, Z., & Lin, L. (2023). Research on the coupling and coordinated development of agriculture and logistics in Guangxi. Contemporary Rural Finance and Economics, (7), 19–23.
[24]. Yin, G., & Hai, X. (2024). Research on the coupling and coordinated development of agriculture and logistics. Logistics Science and Technology, 47(2), 76–79.
[25]. Rojas, M. D., & Montoya-Torres, R. J. (2024). Multimodal logistics systems for agricultural development: A systematic review identifying the Latin American case. IISE Annual Conference Proceedings, 1–7.
[26]. Gu, Z. (2022). Research on the integrated development of digital industries and logistics industries. China Business Review, (23), 101–103. https://doi.org/10.19699/j.cnki.issn2096-0298.2022.23.101
[27]. Liu, Y. (2021). Discussion on the intelligent upgrading of the logistics industry driven by digitalization. China Market, (15), 170–172. https://doi.org/10.13939/j.cnki.zgsc.2021.15.170
[28]. Barreto, L., Amaral, A., & Pereira, T. (2017). Industry 4.0 implications in logistics: An overview. Procedia Manufacturing, 13, 1245–1252.
[29]. Harris, I., Wang, Y., & Wang, H. (2015). ICT in multimodal transport and technological trends: Unleashing potential for the future. International Journal of Production Economics, 159, 88–103.
[30]. Liu, J., & Liu, M. (2024). Discussion on the development of logistics enterprises empowered by digital technology. Shanghai Enterprises, (9), 47–49.
[31]. Tao, L. (2024). Research on provincial logistics industry efficiency under the background of the digital economy. Logistics Science and Technology, 47(19), 110–115.
[32]. Pan, H. (2012). Research on the digital management of regional logistics enterprises: A case study of the Hangzhou Bay Economic Zone in Zhejiang Province. Logistics Technology, 31(13), 380–382.
[33]. Zou, J. (2024). Research on the impact of the digital economy on the high-quality development of the logistics industry. China Business Review, 33(19), 106–109. https://doi.org/10.19699/j.cnki.issn2096-0298.2024.19.106
[34]. Qiu, X. (2024). Factors influencing the intelligent development of the logistics industry and policy recommendations. Hebei Enterprises, (11), 53–55. https://doi.org/10.19885/j.cnki.hbqy.2024.11.032
[35]. Yin, L., & Zeng, L. (2024). The impact of digital technology on the logistics efficiency of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Logistics Technology, 43(7), 149–160.
[36]. Liao, M., & Ling, Z. (2024). Regional differences and dynamic evolution of the integration level between China's logistics industry and industrial digitalization. Journal of Beijing Institute of Graphic Communication, 32(1), 30–38. https://doi.org/10.19461/j.cnki.1004-8626.2024.01.010
[37]. Xinyu, X., & Jian, W. (2023). Study on the impact of industrial digitization on carbon emissions: Evidence from China’s logistics industry. Environmental Research Communications, 5(10).
[38]. Ning, T. (2019). Thoughts on the digitalization of the agricultural industry in Yunnan Province. Rural Science and Technology, (14), 121–122.
[39]. Sucharitha, G., & Sai, M. M. (2021). Developments in agriculture technology using the Internet of Things. Internet of Things and Its Applications, 11(26), 341–360.
[40]. Kamienski, C., Soininen, J. P., Taumberger, M., et al. (2019). Smart water management platform: IoT-based precision irrigation for agriculture. Sensors, 19(2), 276.
[41]. Zhang, C. (2022). Exploration of agricultural industrial digitalization and digital industrialization. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 42(36), 26–27.
[42]. Cheng, D., & Huang, S. (2024). Can rural digitalization improve agricultural total factor productivity? Agricultural Economics and Management, (2), 38–51.
[43]. Addison, M., Bonuedi, I., Arhin, A. A., et al. (2024). Exploring the impact of agricultural digitalization on smallholder farmers' livelihoods in Ghana. Heliyon, 10(6), e27541.
[44]. Sterie, M. C., Petre, I. L., Stoica, D. G., et al. (2024). Assessing the impact of digitization on progress in agriculture: A bibliometric analysis. Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence, 18(1), 1724–1733.
[45]. Pu, X., Ma, K., & Wang, Y. (2024). Analysis of the impact of rural digitalization on promoting agricultural green and high-quality development. China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 45(6), 83–95.
[46]. Lin, Y., & Li, C. (2024). The impact of agricultural digital transformation on green agricultural growth. China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 45(4), 28–41.
[47]. Wu, B., & Xu, X. (2022). Agricultural industrial digital transformation: Symbiotic system and practical challenges—Based on a study of Lintao County, Gansu Province. Learning and Exploration, (2), 127–135.
[48]. Zou, C. (2022). Research on the impact of digitalization on agricultural modernization (Master's thesis). Guangxi Normal University.
[49]. He, J., Li, Q., & Pu, C. (2022). Current situation, problems, and countermeasures for the development of agricultural industrial digital transformation in Chongqing. Southern Agriculture, 16(7), 236–241.
[50]. Yang, J., Zheng, W., & Xing, J., et al. (2021). Empowering high-quality agricultural development with digital technology. Shanghai Economic Research, (7), 81–90+104.
[51]. Sun, Z., Liu, T., & Sun, D., et al. (2021). Analysis of the difficulties and countermeasures of agricultural industrial digital transformation: Based on a survey of 143 new agricultural business entities in Zaozhuang City. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 42(3), 122–128.
[52]. Yu, G., & Huo, Y. (2022). Research on the digital transformation of agricultural industries in Jilin Province. Rural Economy and Technology, 33(7), 71–73.
[53]. Li, L., & Liu, X. (2023). Mechanism, model, and countermeasures of agricultural industrial digital development in Hebei Province. Journal of Langfang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 23(1), 45–50.
[54]. Yang, J., & Wang, Q. (2024). The impact of the digital economy on the integration of the logistics industry and modern agriculture. China Circulation Economy, 38(8), 17–32. https://doi.org/10.14089/j.cnki.cn11-3664/f.2024.08.002









