1. Introduction
Nowadays, people are often aware of the importance of a healthy diet through various media in their lives. As a traditional light dish, Cantonese soup attracts people’s attention and has been a suitable option to choose wisely [1]. In Chinese culinary practices, chicken soup, a commonly consumed type of Cantonese soup, is often considered a comfort food and is traditionally believed to have medicinal properties.
It typically contains chicken, which is a source of protein, and various vegetables, providing essential vitamins and minerals. The broth, often rich in electrolytes like sodium and potassium, can be hydrating, which might influence overall nutrient intake and absorption [2]. Earlier studies demonstrated that patients with colds experienced greater relief from nasal congestion and runny nose when treated with chicken soup compared to hot or cold water [3]. This benefit is possibly attributed to the soup's ability to inhibit the migration of neutrophils, thereby reducing inflammation. Chicken soup may contain a number of substances with beneficial medicinal activity including an anti-inflammatory mechanism that could ease the symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections [3]. With growing evidence in more recent years, chicken soup has gained recognition for its potential to boost metabolism and combat viral infections [4].
Nonetheless, whether daily consumption of Cantonese chicken soup can result in improved self-reported energy levels and nutrient intakes is still unexplored. Though there is diverse and abundant research about various kinds of Chinese soup, there are different perspectives provided to get an approach. Therefore, we seek to assess the impact of daily consumption of Chinese chicken soup on energy and nutrient intakes over a two-week period among high school students. We hypothesized that daily consumption of Chinese chicken soup will result in higher self-reported energy levels and improved nutrient intakes among high school students. This paper would deepen the insight of chicken soup from a nutritional perspective.
2. Methods
2.1. Study design
The study was a randomized, double blinded study with 3 weeks intervention periods (Fig.1). It was conducted from February 26, 2024 to March 18, 2024. Participants were randomly divided into two groups: the intervention group, which was instructed to consume chicken soup every noon, and the control group, which continued with their regular diets without including chicken soup.
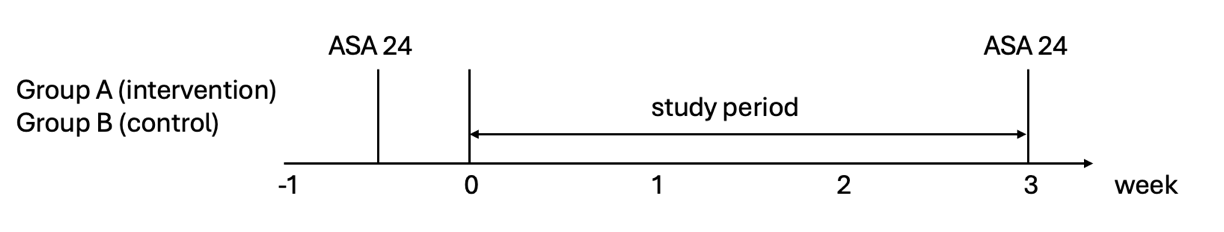
Figure 1. Study flow of this three-week randomized controlled trial
2.2. Subjects
Eighteen participants including 6 girls and 10 boys from the same high school with an average age of 16 years old. More than half of the participants have a regular sleep schedule and healthy exercise habits, and they were recruited from YK Pao high school. Each subject gave written content after being informed about the study. All students completed the study.
2.3. Chinese chicken soup preparation
2.3.1 Ingredients:
(1) 3 Whole chickens
(2) goji berries, ginger, and other healthful ingredients
(3) salt
2.3.2 The soup was prepared according to a family recipe:
(1) The prepared chickens were put in an electric pressure cooker.
(2) Add water into it.
(3) The cooker's power was set at 65 kPa (114°C) for 20 min and then at 55 kPa (112°C) for 50 minutes.
(4) Removed the upper floating materials by filtering them through a cheesecloth.
Each participant had the same recipe so that the homogeneity of the recipe could minimize the experimental error caused by different proportions of ingredients, thus, ensuring consistency.
2.4. Dietary assessment
Two ASA 24 questionnaires were done to collect information about the diet in terms of energy levels and nutrient intakes. ASA 24 (The Automated Self-Administered 24-hour) is an online dietary assessment tool designed to collect detailed information about an individual's dietary intake over a 24-hour period [5]. Moreover, it allowed participants to enter information about the foods and beverages they consume, including portion sizes, preparation methods, and brand names. The first ASA 24 was sent to subjects when at the end of week 0, the second ASA 24 was sent to subjects at the end of week 3.
2.5. Energy and macronutrient intakes
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, protein, and fat, have a unique set of properties that influence health in the form of energy. Energy intake refers to the amount of energy or calories consumed through food. It is measured in units of kilocalories (kcal) or kilojoules (kJ). We used ASA 24 to guide subjects through a series of questions to recall their food and beverage intake. ASA24 provides an accurate assessment of energy and nutrient intake in a 24-h period [6]. The participants were asked to provide specific information about the types, amounts, and preparation methods of the items consumed. Moreover, they were asked about portion sizes of food consumed. It’s a valid tool to provide accurate nutrient and energy intake through the calculation ofparticipants’ intakes through their selections of food. Once they completed the recall, they were able to review the entered information for accuracy and completeness. After submitting the recall, ASA 24 generated reports summarizing energy and macronutrient intake. In this analysis, we applied the mean percentage contributions to total energy intake (% TEI) of each macronutrient.
2.6. Statistical analyses
Descriptive variables were used to summarize participant characteristics including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), baseline intakes of total energy, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviations (SD). Categorical variables are presented as percentages ± SD. Independent samples t-tests were used to compare continuous variables between the intervention group and the control group. Chi square tests were used to compare categorical variables between the intervention group and the control group. Paired t-tests were performed to compare pre- and post-ASA24 responses in total energy and macronutrient intakes. All analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel. All p-values were set at a 2-sided α level of 0.05.
3. Results
As shown in Table 1, it has summarized the baseline characteristics of 16 high school students. Firstly, the number of male and female participants is relatively equal 55.6% of them are boys and 44.4% are girls. The mean value of BMI is 20.3, representing a normal level of body weight among them. Moreover, there is a greater proportion of students who are active, but there is no statistically significant difference between the two groups. The data related to the level of macronutrients and energy intakes is collected from four perspectives: the mean value of total energy is 1961 kcal, there’s no significant difference between the intervention group and the control group, and the result is the same goes with carbohydrates, protein, and fats.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of sixteen high school students in the intervention and the control group (n=16)1
All | Control (n=8) | Intervention (n=8) | p-value | |
Age, mean ± SD | 15.6 ± 1.04 | 15.6 ± 1.32 | 15.4 ± 0.73 | 0.67 |
Sex, % | 0.99 | |||
Females | 44.4 | 44.6 | 44.6 | |
Males | 55.6 | 55.6 | 55.6 | |
BMI, mean ± SD | 20.3 ± 1.95 | 20.6 ± 1.60 | 20.1 ± 2.33 | 0.61 |
Physical activity status, % | 0.81 | |||
Active | 55.6 | 55.6 | 55.6 | |
Inactive | 44.4 | 44.4 | 44.4 | |
Total energy intake, mean ± SD | 1961 ± 248.8 | 2040.7 ± 208.1 | 1881.9 ± 272.0 | 0.19 |
Carbohydrates, mean ± SD | 35.6 ± 8.61 | 37.8 ± 7.68 | 33.3 ± 9.35 | 0.29 |
Protein, mean ± SD | 30.4 ± 10.9 | 27.4 ± 8.61 | 33.1 ± 12.8 | 0.32 |
Fats, mean ± SD | 27.0 ± 7.14 | 27.4 ± 4.33 | 26.6 ± 9.44 | 0.80 |
1Independent samples t-tests were used to compare continuous variables between the intervention group and the control group. Chi square tests were used to compare categorical variables between the intervention group and the control group.
In Table 2, it shows the mean difference in total energy and macronutrients between the two groups. In the control group, the level of energy, carbohydrates, and fats has all increased to some extent, but the level of protein has decreased. On the other hand, the intervention group has an overall hoist in the value of macronutrients except for energy has decreased. The difference in carbohydrates within the intervention group is statistically significant (p-value = 0.025), and the rest differences are not found to be significant (p>0.05).
Table 2. Differences in intakes of total energy and macronutrients between the intervention group and the control group after the three-week intervention (n=16)
Mean difference | ||
Control (n=8) | Intervention (n=8) | |
Total energy intake, mean ± SD | 6.14 ± 213 | -88.4 ± 164 |
Carbohydrates (%TEI)2, mean ± SD | 1.0 ± 6.61 | 2.67 ± 2.92* |
Protein (%TEI)2, mean ± SD | -1.22 ± 9.20 | 2.56 ± 8.63 |
Fat (%TEI)2, mean ± SD | 6.22 ± 9.74 | 0.778 ± 7.22 |
1Paired t-tests were performed to compare pre- and post-ASA24 responses in total energy and macronutrient intakes.
2 %TEI: percentage contributions to total energy intake.
*p<0.05
4. Discussion
Most of the scientific literature and studies surrounding chicken soup focus on its potential benefits for relieving symptoms of common colds and its anti-inflammatory properties, rather than measuring energy levels. There has not been a widely recognized or specific scientific study directly linking daily chicken soup consumption to increased energy levels and macronutrient intakes. To date, our study is the first randomized controlled trial that explored such effects. In this study, we found no significant difference in total energy intake, %TEI from both protein and fat after the three-week intervention although %TEI from carbohydrates significantly increased. Therefore, this study does not provide evidence that chicken soup improves energy levels and macronutrient intakes.
The belief in chicken soup's ability to boost energy levels may stem more from anecdotal evidence and traditional practices rather than strictly controlled scientific studies. Chicken soup is often considered a comfort food, rich in nutrients from its ingredients like chicken, vegetables, and broth, which can contribute to overall well-being and possibly a subjective feeling of increased energy or vitality, especially during illness.
However, its ingredients, including protein from chicken and vitamins and minerals from vegetables, do contribute to a balanced diet, which is key to maintaining energy levels. Broth-based soups can also help with hydration, which is crucial for energy. The observed significant increase in the % of TEI from carbohydrates following the three-week intervention presents an intriguing phenomenon. One proposed explanation is that regular consumption of chicken soup may sway participants' dietary preferences, nudging them towards foods higher in carbohydrates, whether as part of the study meals or in their general diet. This inclination could stem from altered taste preferences or a pursuit of more diverse textures and flavors found in carbohydrate-rich foods. Additionally, the perception of chicken soup as a healthy choice could lead participants to feel entitled to indulge in less healthy options elsewhere in their diet, including an increased intake of carbohydrate-rich foods.
Our study has several strengths. Firstly, the baseline characteristics showed no significant differences among the participants between the control and the intervention group, which helps to avoid confounding factors and make the result more accurate. Secondly, we recognize that although there is a basic recipe for chicken soup, countless variations exist, with some being equally effective and others less so. In this study, we used the recipe that relies on traditional, proven methods and ingredients which are thought to deliver the most reliable results. Thirdly, participant engagement was exemplary, with a 100% adherence rate as all participants remained actively involved and did not withdraw at any point during the study's three-week duration.
However, some limitations should be noted for this study as well. First of all, the sample size of our study is very small A smaller sample size decreases the statistical power of a study, which is the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis. This means there's a higher risk of not detecting a true effect when it actually exists, potentially leading to false negatives. Findings from our study with a such a small sample size may not be generalizable to the broader population. This limitation is especially critical if the sample is not representative of the population at large, leading to biased results. Moreover, the duration of the experiment is relatively short that 3-weeks might not be able to detect obvious effects and differences.
5. Discussion
To sum up, the consumption of chicken soup does not seem to improve total energy intake, except it significantly increased % total energy intake from carbohydrates in the three-week of the intervention. Future studies can be improved by increasing the sample size by including a larger and more diverse group of participants would enhance the generalizability of the findings to a broader population.
References
[1]. Carreiro, A. L., Dhillon, J., Gordon, S., Higgins, K. A., Jacobs, A. G., McArthur, B. M., Redan, B. W., Rivera, R. L., Schmidt, L. R., & Mattes, R. D. (2016). The macronutrients, appetite, and energy intake. Annual Review of Nutrition, 36, 73-103. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071715-050713
[2]. Lin, P. M. C., Ren, L., & Chen, C. (2017). Customers’ perception of the authenticity of a Cantonese restaurant. Journal of China Tourism Research, 13(2), 211-230. https://doi.org/10.1080/19388160.2017.1301763
[3]. Morell, S. F., & Daniel, K. T. (2014). Nourishing broth: An old-fashioned remedy for the modern world. Hachette UK.
[4]. Barrett, B. (2023). Acute respiratory infection colds and flu. In D. Rakel (Ed.), Integrative Medicine (5th ed., chap. 19). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
[5]. Rennard, B. O., Ertl, R. F., Gossman, G. L., Robbins, R. A., & Rennard, S. I. (2000). Chicken soup inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro. Chest, 118(4), 1150-1157. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.118.4.1150
[6]. Subar, A. F., Kirkpatrick, S. I., Mittl, B., Zimmerman, T. P., Thompson, F. E., Bingley, C., Willis, G., Islam, N. G., Baranowski, T., McNutt, S., Potischman, N., & Krebs-Smith, S. M. (2012). The automated self-administered 24-hour dietary recall (ASA24): A resource for researchers, clinicians, and educators from the National Cancer Institute. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 112(8), 1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2012.04.016
Cite this article
Hu,J. (2024). Effects of daily consumption of Chinese chicken soup on energy and macronutrients intake. Journal of Food Science, Nutrition and Health,2,1-4.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Food Science, Nutrition and Health
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Carreiro, A. L., Dhillon, J., Gordon, S., Higgins, K. A., Jacobs, A. G., McArthur, B. M., Redan, B. W., Rivera, R. L., Schmidt, L. R., & Mattes, R. D. (2016). The macronutrients, appetite, and energy intake. Annual Review of Nutrition, 36, 73-103. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071715-050713
[2]. Lin, P. M. C., Ren, L., & Chen, C. (2017). Customers’ perception of the authenticity of a Cantonese restaurant. Journal of China Tourism Research, 13(2), 211-230. https://doi.org/10.1080/19388160.2017.1301763
[3]. Morell, S. F., & Daniel, K. T. (2014). Nourishing broth: An old-fashioned remedy for the modern world. Hachette UK.
[4]. Barrett, B. (2023). Acute respiratory infection colds and flu. In D. Rakel (Ed.), Integrative Medicine (5th ed., chap. 19). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
[5]. Rennard, B. O., Ertl, R. F., Gossman, G. L., Robbins, R. A., & Rennard, S. I. (2000). Chicken soup inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro. Chest, 118(4), 1150-1157. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.118.4.1150
[6]. Subar, A. F., Kirkpatrick, S. I., Mittl, B., Zimmerman, T. P., Thompson, F. E., Bingley, C., Willis, G., Islam, N. G., Baranowski, T., McNutt, S., Potischman, N., & Krebs-Smith, S. M. (2012). The automated self-administered 24-hour dietary recall (ASA24): A resource for researchers, clinicians, and educators from the National Cancer Institute. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 112(8), 1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2012.04.016









