1 Introduction
In the 21st century, biotechnology has been developing rapidly. DNA was first recognised in the search for genes. [21] Scientists were searching for inherited characteristics and later discovered that DNA sequence was the determinant to traits carried by organisms. By manipulating the “code of life”, we have discovered novel applications in genetic engineering. It is gradually becoming a more prevalent part of our daily lives, and greater public awareness is needed.
Transgenic technology uses modern biotechnology to integrate beneficial genes into an organism's genome, enhancing or adding new traits. [20] In earlier days, scientists genetically modified simpler microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses due to the relative structural simplicity of their genetic material. One of the breakthroughs in transgenic technology was brought on by a method called CRISPR. CRISPR stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. It is a component of bacterial immune systems that can cut DNA, and has been repurposed as a gene editing tool. CRISPR was discovered by Ishino et al. in 1987. (Ishino et al., 1987) By utilising CRISPR, researchers insert new DNA fragments via gene tapping. The knocking in of a new genetic sequence creates possibilities from treating diseases to cultivating drought-resistant crops. The successful insertion of genetic sequence at a precise location, can be used for gene therapy and could potentially correct genetic mutations that cause human diseases. This is undoubtedly a fast and efficient approach compared to gene recombination which has a low frequency and high uncertainty. Yet, the regulations and policies have slowed down the development due to ethical concerns and knowledge gap between scientists, public and policy makers. The emerging field also lacks experts, which further hurdle the development of relevant reagents and materials. (Roberts, 2023)
Genetically modified technology has extended to agriculture, aiming to address the food crisis. However, diverse stakeholders have raised concerns about the impact of GMOs on health and the environment. Many countries have approved the planting of genetically modified crops. For example, in the United States, new genetically modified varieties are continuously approved for consumption and plantation. [3] The European community has also authorised the import of seven genetically modified crops. Globally, people also have positive views on transgenic technology to varying degrees. In a survey in North America, about 69% of respondents agreed and only 22% disagreed that biotechnology should be encouraged in crops. With regard to its application in food, 58% of American respondents who are farmers strongly support this application. Among American consumers, genetically modified crops meet many of their needs. This shows that investigated American farmers have positive views on genetically modified agricultural products. [3] However, C. Neil Stewart, a professor and Rat Cheff Chair of Excellence in Plant Molecular Genetics at University of Tennessee, believes that, contrary to biotechnology, traditional breeding and domestication can better change the plant genome. [3] However, although the acceptance of genetically modified products is on the rise, the acceptance is still relatively low. Other surveys have shown that Europeans' unwillingness towards genetically modified foods has decreased from 86% in 1999 and 66% in 2010 to 60% in 2019. [3]
Transgenic technology has both pros and cons. Some individuals exploit it for unlawful profit, bypassing regulations, and pursuing projects like 'customised babies'. When considering the use of this technology in animals, genetically modified species like mice serve as scientific research models, but this has sparked concerns regarding animal welfare. When viewed on a larger picture, genetically modified crops may have an impact on soil and water sources as a consequence of large scale plantations of high economical value crops. In short, we should approach genetically modified technology rationally and discuss it based on solid evidence. The argument should also factor in ethics and morality, as well as environmental impacts. Therefore, in this report, I will study the various applications of transgenic technology and discuss the advantages and disadvantages to humans, animals and the environment.
2 Research review
2.1 DNA and its importance
DNA is a double helix macromolecule, consisting of phosphate group, nitrogenous base, and deoxyribose sugar. There are four bases, namely adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In the double helix structure, the bases follow the principle of complementary pairing, namely A paired with T and C paired with G. Among them, when A and T pair, there are two hydrogen bonds, and when C and G pair, three hydrogen bonds are formed. Although there are only four bases, each organism has its own unique DNA sequence except in monozygotic twins.
During the transcription process, the DNA unwinds, and the RNA polymerase moves from the 3’ end to the 5' end to read the template. A messenger RNA is synthesised from 5’ end to the 3’end. Subsequently, messenger RNA travels to the cytoplasm. In the ribosome, the messenger RNA acts as a template for protein synthesis. The ribosomes read each codon, and add a complementary amino acid, forming a polypeptide chain, which could be further modified in the Golgi apparatus.
Why is DNA information important? This is because once genetic information goes wrong during transcription and translation, this may result in reduced function or non-functional proteins. Sickle type anaemia is an example. It is a genetic disorder characterised by curved sickle shaped red blood cells in patients. Such red blood cells are prone to rupture, leading to haemolytic anaemia and in severe cases, death. The reason is an amino acid error occurred on the peptide chain of the patient's haemoglobin molecule thus affecting the function of the protein. [9] The mutated haemoglobin therefore has lower elasticity and a shorter lifespan.
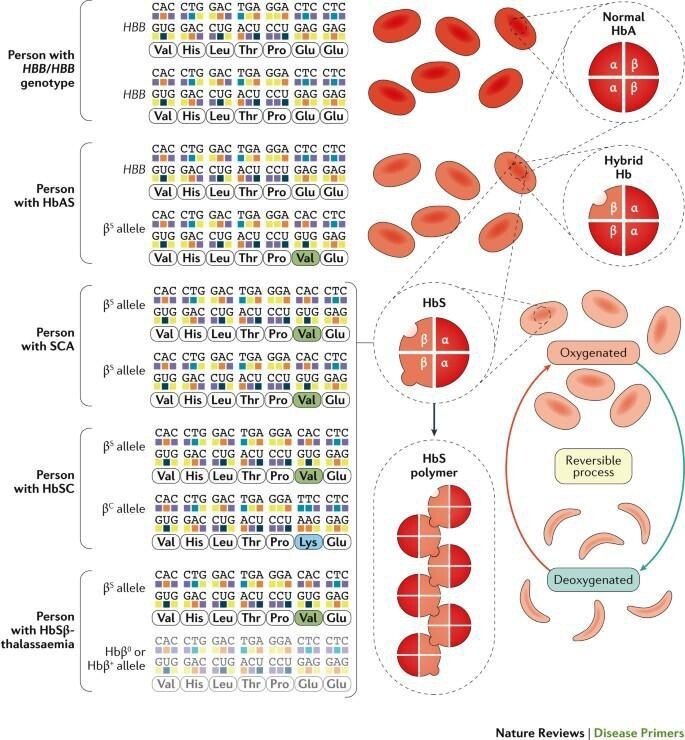
Figure 1. The genetic and protein structure comparison between sickle cell anaemia patient, carrier, and healthy individuals. [9]
2.2 DNA repair and CRISPR
During the growth and development of organisms, DNA mutations and damage cannot be avoided. DNA polymerase involved in DNA replication and repair can make mistakes, leading to potential adverse mutations in cells. However, cells are equipped with complex systems to compensate for these errors. DNA repair, cell cycle checkpoints and cell death pathways collectively reduce the harmful consequences of an error-coded DNA. First, various nucleic acid endonucleases identify the site of DNA damage. Upon identification, DNA damage response factors will assemble at the site and the damaged strand is removed by an exonuclease. DNA polymerase repairs and synthesises a new strand via mechanisms such as homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining. The repair ends with ligase sealing the newly synthesised strain to fill in the space removed by the exonuclease. While cells have its mechanism to check for errors in DNA replication and repair them, scientists have been utilising this mechanism as an approach in genetic modification.
2.3 History of genome editing
Over decades of research, this field has evolved into a captivating and pivotal domain, serving as the foundation for numerous medical and biological investigations. From deciphering the structure of DNA to the revolutionary CRISPR editing, the progress in genetic modification tools is astounding. It is enthralling to witness the scientific community's advancements in this realm.
Starting from the discovery of double helix in 1953, Arthur Kornberg isolated DNA polymerase from bacterial extracts in 1958 and successfully synthesised DNA in vitro for the first time within a year. (Arthur Kornberg, 2005) In the 1970s, recombinant DNA, which is essentially DNA produced by combining DNA elements from different organisms was invented. By introducing genetic material from one organism to another, this discovery established the principles of modern genetics and became the basis for many future experiments. The 1980s was a milestone on the timeline of genetic engineering, transforming many genetic experiments into real-world products and ideas, changing the landscape of the 1990s. In 1981, the first genetically modified animal was invented and in 1982, the first genetically engineered human drug, synthetic insulin, was developed. In 1986, the first human recombinant vaccine was approved. From 1990 to 2003, the Human Genome Project successfully mapped the human genome, identified over 20,000 genes, and recorded their genomic loci. In 1999, the first human chromosome sequencing was completed, marking the beginning of the history of human genetic engineering sequencing. In 2003, the ENCODE (Encyclopaedia of DNA Elements) project was launched with the aim of creating a complete list of functional elements in the human genome at the protein and RNA levels, including regulatory elements that control transcription, translation, and replication. (Synthego, 2019)
CRISPR was discovered in the 20th century, and in the 21st century, focus was drawn to map the human genome and formulate new regulations. After 2010, genetically modified technology mainly revolved around CRISPR. In 2012, Prof. Jennifer Doudna, Prof. Emmanuelle Charpentier, and their team elucidated the biochemical mechanism of CRISPR technology. Equally important, in 2013, Feng Zhang's work demonstrated the practicality of CRISPR beyond the bacterial world, in eukaryotic cells. [12] In 2018, Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics jointly launched a project targeting blood diseases. The experimental treatment of thalassemia has been approved to begin clinical trials. [12] In the summer of 2020, the results of CRISPR clinical trials slowly began to flow out. Victoria Gray was the first patient to receive treatment for sickle cell disease, and her promising results began to make headlines. Less than six months later, at the ASH meeting held in December 2020, data released showed that a total of 10 patients receiving CTX001 treatment made significant progress (Hematology.org, 2019). Seven of the patients are currently undergoing β Mediterranean anaemia treatment, and the other three patients are currently receiving treatment for sickle cell anaemia. All of these patients have significantly improved foetal haemoglobin levels in their blood, relieved pain, and no longer require blood transfusions. (Synthego, 2023a) In October 2020, Prof. Emmanuelle Charpentier and Prof. Jennifer Doudna won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their development of CRISPR. [19]
2.4 CRISPR and CRISPR engineering
Scientists have longed for an idea of transgenic technology, to edit and modify DNA sequence, via the mechanisms of DNA repair of cells. The search has been a long journey, as this technique should ideally be simple, fast yet accurate. The primitive transgenic technology is very complex, with a low success rate and high cost. Fast forward to 2012, scientists had discovered a new genome editing method derived from CRISPR-Cas-9, a long-standing system in bacteria that can protect them against invading viruses. (Synthego, 2023b) The system has two major components, a DNA cleavage protein such as Cas-9 and an RNA molecule called guiding RNA. They gather together to form a complex that can recognise and cleave specific parts of DNA. Its workflow is: firstly, Cas-9 must locate and combine with a common sequence in the genome called protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). Once PAM is bound, the guide RNA will unfold a portion of the double helix. RNA strands are designed to match and bind specific sequences of the DNA. Once the correct sequence is found, Cas-9 can then cleave DNA, causing double strand breaks to allow gene editing. (Nature Video, 2017) The cells would attempt to repair, and ideally add the sequence of desired. With CRISPR, scientists can customise their guiding RNA to cut DNA at almost every location of interest.
With this foundation built, scientists are also committed to developing CRISPR gene therapy and gene editing cell therapy for treating various monogenic diseases, including haematological diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, hereditary blindness, and immune diseases. CRISPR gene therapy is not limited to DNA editing for the treatment of genetic diseases and cancer, they are also being developed for the treatment of HIV and other infectious diseases, which may provide alternative therapies for diseases which are very hard to cure. With the development of better gene delivery virus vectors, CRISPR therapy has sparked great interest in medicine, marking a major breakthrough. In 2003, The first gene therapy, Gendicine, was available in China and can be used to treat cancer. This has prompted a new exploration of gene therapy. Soon, scientists discovered an enzyme in 2005, which was found to be able to treat AIDS in 2014.This has lowered a lot of opposing voices, as people start seeing the utilisation of genetic engineering in revolutionising medical advancement for the benefits of patients. (Roberts, 2021) In 2021, The US Food and Drug Administration has agreed to begin testing CRISPR gene editing as a treatment for HIV. The first human antiretroviral one-time gene therapy for HIV infected people will be carried out. [14]
3 Discussion/ Development
Since the emergence of transgenic technology, it has been developing in praise and doubt. Some people think that this technology is worth continuous development because its achievements are very exciting. Today, there are many practical examples which mark the success in this area. For instance, changing the nutrition profile of livestock products, so that people with lactose intolerance can enjoy dairy products. However, if you view this issue from another perspective, it is argued that transgenic technology may infringe animal rights. In addition, the mass production of crops and livestock will change the landscape of the local environment, bringing negative impacts to the environment.
3.1 Application of transgenic technology in scientific research
In medical research, scientists harvest this technology to create excellent animal models for the study of experimental physiology and pathology therapeutics. For example, with the rapid spread of COVID-19 in the world, the research community urgently needs animal models to verify treatment and vaccine for the disease, as well as to understand the infection pathway and pathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In order to find suitable models, many laboratory and domestic animal species have been challenged by SARS-CoV-2. Traditional non-transgenic animal models have many limitations in scientific research. Its pathogenesis cannot accurately simulate the course of human disease and is not applicable to the study. Consequently, we need to modify their genes to make them a more accurate representation. Therefore, if laboratory mice are as susceptible to SARS CoV-2 as humans, it will be easier to use mice to study COVID-19. One way to make mice susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 is to genetically modify them to express hACE2 gene. These genetically engineered mouse models would have an increased susceptibility to SARS CoV-2 and function as a better animal model for related studies. The natural intolerance of mice to SARS-CoV-2 infection, together with various available genetic tools and molecular switches, provides a unique opportunity to make this species more useful for COVID-19 research. [6]
The mouse model is also suitable for other human diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Given the prevalence and adverse sequelae of the disease, the development of animal models has been a focus of research. Non-transgenic animal models are not as effective, and the animals being tested cannot realistically simulate the situation in which humans suffer from this disease. Therefore, transgenictechnology has shown great potential. Misfolded APP is thought to be the cause of Alzheimer’s. Thus, the goal is to use transgenic mouse models that mimic a series of Alzheimer's disease-related pathologies to reduce or remove misfolded APP. Although no model can fully replicate human diseases, these models have made significant contributions to the understanding of the pathophysiology of diseases, especially the β- Amyloid protein mouse model as the protein plaques are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. They are also widely used for preclinical testing of potential treatment methods and play a crucial role in the development of immunotherapy for Alzheimer's disease. Undoubtedly, these models will continue to play a central role in preclinical testing and will be used as tools to gain a deeper understanding of Alzheimer's disease. [2]
In the 1990s, another possible medical use of transgenic animals exploited was developing organs suitable for transplantation. As pigs and humans have some common physiological characteristics, it has become the focus of most studies. However, pig tissue is immunologically incompatible with human: pig xenotransplantation will cause a rapid, complement-based hyperacute rejection, which will destroy the transplanted tissue. Several transgenic methods have been developed to overcome this rejection, including the production of transgenic pigs expressing human decay accelerating factor. [1] However, the ability of transgenic technology to develop animal models is also very limited and is restricted by many factors such as the age of patients and the development of diseases. At the present technical level, it is a challenge yet to be solved. [4]
When viewing the utilisation of genome engineering in animals for medical-related studies from other perspectives, the limitations are very clear. For example, conducting transgenic experiments on animals requires a large number of animals as samples and it is time-consuming. This makes the cost higher as space and care is required. Moreover, using a large number of animals as animal models can lead to animal abuse and have a certain negative impact on the survival and development of animals. In addition, although genetically modified technology can allow animals to simulate the human body environment, there are still differences compared to the real human body. Therefore, although there have been successful cases in animal model testing, certain drugs that have been successfully tested on animals cannot be used arbitrarily for humans. With this, it is important to consider the likelihood of translation when using genetically modified animals as experimental models.
3.2 Application of transgenic technology in crops
Transgenic technology can be applied in crops to improve nutritional value in plants and improve yield rate. Genetic modification in plants may change the way plants grow or make them resistant to specific diseases. In some places, people who lack food rich in vitamin A, such as animal liver, may suffer from vitamin A deficiency. One of the symptoms of these patients is night blindness. Vitamin A micronutrient deficiency affects 250 million people around the world. Lack of vitamin A will lead to blindness and low immune level. Approximately 250000 – 500000 children who lack vitamin A become blind each year (West and Darnton Hill, 2001). For adults, the impact is also severe, especially for pregnant and lactating women. Nearly 600000 women die in childbirth each year, many of them due to complications that can be reduced by better supplementation of vitamin A. [23]
A solution suggested by the scientific community is to increase vitamin A consumption by modifying staple foods to have higher vitamin A precursors or content, such as the ‘golden rice’. ‘Golden rice’ is a crop genetically modified to increase β-carotene content, a precursor of vitamin A. During the culture process, it was observed that the total carotenoids increased by 23 times or up to 37 micrograms per gram compared to the non-GMO rice. By increasing the precursor of vitamin A in major food sources, this would effectively solve the problem of vitamin A deficiency in many people around the world, especially in developing countries where most people suffer from this form of malnutrition.
Besides improving nutritional value, transgenic technology can help in reducing the cost of crops plantation. For example, maize can be genetically modified to improve its resistance to pests. Wild type maize is extremely susceptible to the infestation of the European maize borer, a pest that is very detrimental to maize cultivation. Many farmers are deeply troubled by it. When maize is genetically modified, it can resist pests by extracting the insecticidal protein Cry1Ab from Bacillus thuringiensis. Another example inserting an ACP thioesterase gene from the California Umbrella genus, thereby achieving high lauric acid levels in rapeseed plants. After entering the human body, lauric acid will combine with glycerol to form an antiviral substance, lauric acid glyceride. The structure of glyceryl laurate is similar to that of the outer membrane of microorganisms, which can be destroyed and killed. Through its antibacterial, antiviral effects, it can potentially achieve the goal of preventing influenza and other infectious diseases. Therefore, transgenic technology is equally applicable to crops and plants.
Unfortunately, in some circumstances, the outcome is not as expected. For example, the "golden rice" mentioned above helps to increase the content of vitamin A in rice, but its price remains high. This is not a good thing for some poor African, Southeast Asian, and Latin American countries as such genetically modified crops were expected to be affordable, so people can consume and thus reduce the prevalence of night blindness from the root of the problem. So far, the price of genetically modified crops remains a significant issue. At the same time, there are not many examples of genetically modified crops like "golden rice" that can make crops healthier and more nutritious, and the development of such crops is relatively low. Furthermore, genetically modified crops can have an impact on the local environment (such as soil, microorganisms, etc.) when planted, such as genetically modified weeds, which flourish and create damage to local ecological environment. [13]
Equally important, genetically modified plants may disrupt ecological balance. As an example, a GMO plant may be developed to resist pests. However, as a primary consumer, the pest would lose their food source and thus reduce drastically. This will cause the secondary consumer to lose the food source unless they have multiple sources of food and can quickly adapt to change their diet.
This will provide a safe ground for the flourishing and reproduction of the producer plant but will heavily influence the upper levels in the food chain, as the primary consumer may be wiped out from the populations.
3.3 Application of transgenic technology in animals
Animals are an important part of our daily lives. Therefore, it is crucial to discuss the applications of transgenic technology in animals. Transgenic technology may improve the production characteristics of livestock. For example, myostatin, known to inhibit lean muscle growth, can be targeted to produce high muscle cattle. In addition, after nearly 20 years of modification of the mouse genome, there are a large number of candidate genes which can alter growth traits of livestock. Among them, the introduction of growth hormone genes significantly improved the growth rate and terminal body size of animals. [1] Secondly, genetically modified animals can also reduce their environmental impact. Improving efficiency and productivity through genetically modified organisms can reduce the use of limited land and water resources, while protecting soil and underground water. A good example is the genetically engineered pig (Enviro Pig TM) (Golovan et al., 2001). Non-transgenic pigs cannot fully utilize phosphorus in their food. If dietary supplements are used, production costs will increase. At the same time, incomplete utilisation of feed by pigs can lead to an increase in phosphorus content in waste, leading to pollution issues such as eutrophication. Golovan et al (2001) reported the production of transgenic pigs expressing salivary phytase, an enzyme that allows pigs to digest phosphorus in food. In addition to reducing phosphorus production by up to 75%, salivary phytase also provides basic complete digestion of dietary phytate phosphorus. Using phytase transgenic pigs in commercial pork production can reduce environmental phosphorus pollution caused by animal husbandry. (Phillips, 2008)
On the other hand, the application of new technology may lead to unwanted issues. We can analyse this from a different perspective. At a technical level, transgenic technology can cause trait deregulation, leading to poor performance of gene products. When we view for long-term impact, transgenic produce may lose advantages genetic information which may affect the performance of produce. Removing traits or enhancing current traits could mean that the livestock is now more prone to future diseases and infections. This may affect the performance of produce although the impact is unmeasurable. From the consumer side, it is important that the transgenic animals are safe to consume and have other advantages such as higher nutritional and economical value to encourage them to switch their choices. Another alternative is lab grown meat which tastes almost the same as real meat. It is cultivated from cells, which means people can eat meat without having to slaughter animals, and it can be a solution to feeding the world's growing population. However, this has also raised concerns among many people, who doubt the safety and reliability of this meat, as it goes against nature, for its fast production rate and yield. While lab grown meat consumes less space and is more environmentally friendly, many are against the idea of eating meat from the lab. Lab grown meat is currently regulated by the US Department of Agriculture and the US Food and Drug Administration, as it is still in the early stages of development and cultivation. [22]
In summary, the potential applications of biotechnology in animals are endless. The development of useful biotechnological tools on animals continues. So, there is a need to develop, discuss, and implement procedures and policies that assess the risks, food safety, efficacy, and consumer benefits of the products produced via these technologies. This in turn allows transgenic technologies to be of greater and better use. [21]
3.4 Application of transgenic technology in virus and bacteria
Bacteria and viruses, unseen by the naked eye, have been utilised in this area as well. The simpler structure of these organisms makes it a convenient target for genetic modification. In China, before the emergence of genetically modified technology, large areas of cotton cultivation were always affected by pests and diseases, leading to a significant decrease in cotton production. It is now known that bacteria such as Bacillus thuringiensis and Beauveria bassiana can resist insects. If its genes are transferred to cotton, it can protect it from pests and diseases, and increase the yield of cotton significantly. Compared to conventional methods of spraying pesticides, this method can protect the environment, while reducing contamination from pesticides, improving cotton quality. The expression of Bt gene, a pest resistant gene in cotton plants to prevent some major pests, has been widely accepted by farmers in three major producing countries, in China, India, and the United States. Nevertheless, this may also reduce the number of cottons eating insects such as cotton bollworms, thereby affecting the birds that feed on these insects and potentially affecting ecological balance. Virus expression vectors based on plant viruses have also greatly enhanced the therapeutic production of plant manufacturing. It is reported that plant virus expression vectors are used to produce therapeutic agents for some diseases, and some virus derived antigens produced in plants show appropriate antigenicity and immunogenicity. From this, although viruses can cause illness in people, it can also be applied to treat diseases.
The most famous application of genetically modified technology in bacteria is the production of insulin using Escherichia coli. The main function of insulin is to reduce blood sugar level, and diabetes patients need this hormone to regulate their blood sugar level. As a treatment, patients need to inject insulin to bring down their high blood sugar. However, there are more and more patients diagnosed with diabetes, and the demand for insulin is growing. If we rely solely on artificial insulin supply, the production will be much lower than the demand. Researchers now transfer insulin-producing genes into E. coli. Due to the rapid reproduction of E. coli, a large amount of insulin can be produced in a relatively short period of time, thereby supplying market demand. [7]
Recent studies have shown that bacteriophages play an important role in gene transfer. Target gene or DNA is first inserted into a phage, and then a large amount of DNA is replicated using the strong reproductive ability of the phage. Finally, the target gene is transferred into the target cell to complete gene transfer. [15] An increasing number of studies have confirmed the effectiveness and safety of using bacteriophages as carriers for the systematic delivery of therapeutic genes and drugs in cancer treatment. Compared with non-viral gene transfer methods, the transmission and expression efficiency of engineered bacteriophages and eukaryotic viruses in cancer cells is much higher. By using phage as a vector, developed drugs can effectively localise targeted cancer cells. At present, various phage shells have been successfully utilised in the treatment of liver cancer cells and cervical cancer cells. They have tremendous plasticity and a high safety profile. Many experiments have shown the enormous potential of these viruses in cancer gene therapy. Future experiments are exciting to look into development of new vectors or recombination of prokaryotic viruses with existing vectors. [15]
In the past few years, CRISPR has been widely used for diagnostic applications, as it can leverage the powerful functions of Cas-9 and other Cas nucleases. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the field of CRISPR diagnosis was still in its early stages. Two years after the outbreak of the epidemic, research in this field has experienced rapid growth. With multiple Cas nucleases, there is a potential of CRISPR diagnosis for almost every virus regardless of the type of genetic materials it carries. [8]. For bacterial pathogens, CRISPR is also applicable. At present, it can diagnose bacterial diseases including Salmonella enteritidis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. [17]
However, there are still other aspects which hinders the research on genetically modified bacteria and viruses. Firstly, some people believe that genetically modified bacteria and viruses are very dangerous. If these organisms fall into the hands of criminals, all humanity will be in a very dangerous situation. The second issue is preservation and handling. If not properly preserved, bacterial and viral leakage can be a devastating disaster to humans, animals, and the environment. So, we need to pay attention to the safety aspects of research and ensure that genetically modified organisms bring more benefits to people.
4 Conclusion
Overall, genetically modified technology is influencing our lives in a positive way. Taking CRISPR technology as an example, it fundamentally changes the significance of genome editing, improving the speed and breadth of science, and we have already felt the impact of CRISPR on drug discovery, diagnosis, and gene drive.
The advantages of genetically modified technology are evident. Firstly, it has an important impact in scientific research, and its results are very promising. At present, genetically modified technology can be used to control vector-borne diseases by releasing improved mosquitoes, reducing the infection rate of some diseases transmitted through mosquitoes. [5] In addition, many researchers are constantly searching for new methods to apply this technology to solve real-world problems, including epigenome editing, cell and gene therapies, infectious disease research, and the protection of endangered species.
However, although its advantages outweigh its disadvantages, the best technology requires regulations and compliance, and cannot be developed freely without restrictions. Citizens should be educated to have more awareness of genetically modified technology, as this is the key to increasing its acceptance. At the same time, better policies and regulatory regulations should be formulated to streamline and regulate the application of genetic engineering, to prevent the abuse of genetically modified technology. We also need to exercise ethical control. In future development, we cannot go against natural laws. For example, genetic engineering babies by Chinese scientists. (Normile, 2019) There is also standardisation in experimental operations to minimise the loss of advantageous genes or features. I hope that genetically modified organisms can make steady progress in the long development ahead, especially in medical research, and make greater contributions to human exploration and research of new things.
References
[1]. Clark, J. and Whitelaw, B. (2003). A future for transgenic livestock. Nature Reviews Genetics, 4(10), pp.825–833. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1183.
[2]. Elder, G.A., Gama Sosa, M.A. and De Gasperi, R. (2010). Transgenic Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine: A Journal of Translational and Personalized Medicine, 77(1), pp.69–81. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/msj.20159.
[3]. Ewa, W.-G., Agata, T., Milica, P., Anna, B., Dennis, E., Nick, V., Godelieve, G., Selim, C., Naghmeh, A. and Tomasz, T. (2022). Public perception of plant gene technologies worldwide in the light of food security. GM Crops & Food, 13(1), pp.218–241. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/21645698.2022.2111946.
[4]. Fan, C., Wu, Y., Rui, X., Yang, Y., Ling, C., Liu, S., Liu, S. and Wang, Y. (2022). Animal models for COVID-19: advances, gaps and perspectives. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, [online] 7, p.220. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01087-8.
[5]. Flores, H.A. and O’Neill, S.L. (2018). Controlling vector-borne diseases by releasing modified mosquitoes. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(8), pp.508–518. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579- 018-0025-0.
[6]. Gurumurthy, C.B., Quadros, R.M., Richardson, G.P., Poluektova, L.Y., Mansour, S.L. and Ohtsuka, M. (2020). Genetically modified mouse models to help fight COVID-19. Nature Protocols, [online] 15(12), pp.3777–3787. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-00403-2.
[7]. Hwang, H.-G., Kim, K.-J., Lee, S.-H., Kim, C.-K., Min, C.-K., Yun, J.-M., Lee, S.U. and Son, Y.-J. (2016). Recombinant Glargine Insulin Production Process Using Escherichia coli. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26(10), pp.1781–1789. doi:https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1602.02053.
[8]. Kaminski, M.M., Abudayyeh, O.O., Gootenberg, J.S., Zhang, F. and Collins, J.J. (2021). CRISPR- based diagnostics. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 5(7), pp.643–656. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00760-7.
[9]. Kato, G.J., Piel, F.B., Reid, C.D., Gaston, M.H., Ohene-Frempong, K., Krishnamurti, L., Smith, W.R., Panepinto, J.A., Weatherall, D.J., Costa, F.F. and Vichinsky, E.P. (2018). Sickle cell disease. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, [online] 4(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.10.
[10]. Kornberg, A. (n.d.). The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959. [online] NobelPrize.org. Available at: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/1959/kornberg/facts/ [Accessed 8 Sep. 2023].
[11]. Mah, A. and Roberts, R. (2022). Synthego | Full Stack Genome Engineering. [online] www.synthego.com. Available at: https://www.synthego.com/blog/genome-editing-techniques#7..
[12]. Offord, C. (2018). US Companies Launch CRISPR Clinical Trial. [online] The Scientist Magazine®. Available at: https://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/us-companies-launch-crispr- clinical-trial-64746.
[13]. Paine, J.A., Shipton, C.A., Chaggar, S., Howells, R.M., Kennedy, M.J., Vernon, G., Wright, S.Y., Hinchliffe, E., Adams, J.L., Silverstone, A.L. and Drake, R. (2005). Improving the nutritional value of Golden Rice through increased pro-vitamin A content. Nature Biotechnology, [online] 23(4), pp.482–487. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1082.
[14]. Parkins, K. (2021). FDA approves first trial investigating CRISPR gene editing as HIV cure. [online] www.clinicaltrialsarena.com. Available at: https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/crispr-gene-editing-hiv-cure/.
[15]. Petrov, G., Dymova, M. and Richter, V. (2022). Bacteriophage-Mediated Cancer Gene Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, [online] 23(22), p.14245. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214245.
[16]. Phillips, T. (2014). Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) | Learn Science at Scitable. [online] Nature.com. Available at: https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/genetically-modified- organisms-gmos-transgenic-crops-and-732.
[17]. Roberts, R. (2022). Synthego | Full Stack Genome Engineering. [online] www.synthego.com. Available at: https://www.synthego.com/blog/crispr-infectious-disease. [Accessed 11 Dec. 2023].
[18]. Synthego (2023). CRISPR: Gene editing and beyond. [online] www.youtube.com. Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4YKFw2KZA5o [Accessed 28 Aug. 2023].
[19]. The Nobel Prize Organization (2020). The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2020. [online] NobelPrize.org. Available at: http://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemistry/2020/161307-press-release-swedish/.
[20]. USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. (2022). China: Agriculture GMOs Safety Assessment Administrative Measures Finalized. [online] Available at: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/china- agriculture-gmos-safety-assessment-administrative-measures-finalized [Accessed 28 Aug. 2023].
[21]. Wheeler, M.B. (2013). Transgenic Animals in Agriculture | Learn Science at Scitable. [online] www.nature.com. Available at: https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/transgenic-animals-in-agriculture-105646080/#:~:text=The%20production%20of%20transgenic%20livestock..
[22]. Wiener-Bronner, D. (2023). Meat without slaughter: Here’s everything you need to know about lab-grown meat | CNN Business. [online] CNN. Available at: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/06/23/business/lab-grown-meat-explainer/index.html [Accessed 23 Sep. 2023].
[23]. Zimmermann, R. and Qaim, M. (2004). Potential health benefits of Golden Rice: a Philippine case study. Food Policy, [online] 29(2), pp.147–168. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2004.03.001.
Cite this article
Yang,S. (2024). To what extent is transgenic technology beneficial to human beings?. Journal of Food Science, Nutrition and Health,2,23-30.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Food Science, Nutrition and Health
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Clark, J. and Whitelaw, B. (2003). A future for transgenic livestock. Nature Reviews Genetics, 4(10), pp.825–833. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1183.
[2]. Elder, G.A., Gama Sosa, M.A. and De Gasperi, R. (2010). Transgenic Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine: A Journal of Translational and Personalized Medicine, 77(1), pp.69–81. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/msj.20159.
[3]. Ewa, W.-G., Agata, T., Milica, P., Anna, B., Dennis, E., Nick, V., Godelieve, G., Selim, C., Naghmeh, A. and Tomasz, T. (2022). Public perception of plant gene technologies worldwide in the light of food security. GM Crops & Food, 13(1), pp.218–241. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/21645698.2022.2111946.
[4]. Fan, C., Wu, Y., Rui, X., Yang, Y., Ling, C., Liu, S., Liu, S. and Wang, Y. (2022). Animal models for COVID-19: advances, gaps and perspectives. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, [online] 7, p.220. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01087-8.
[5]. Flores, H.A. and O’Neill, S.L. (2018). Controlling vector-borne diseases by releasing modified mosquitoes. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(8), pp.508–518. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579- 018-0025-0.
[6]. Gurumurthy, C.B., Quadros, R.M., Richardson, G.P., Poluektova, L.Y., Mansour, S.L. and Ohtsuka, M. (2020). Genetically modified mouse models to help fight COVID-19. Nature Protocols, [online] 15(12), pp.3777–3787. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-00403-2.
[7]. Hwang, H.-G., Kim, K.-J., Lee, S.-H., Kim, C.-K., Min, C.-K., Yun, J.-M., Lee, S.U. and Son, Y.-J. (2016). Recombinant Glargine Insulin Production Process Using Escherichia coli. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26(10), pp.1781–1789. doi:https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1602.02053.
[8]. Kaminski, M.M., Abudayyeh, O.O., Gootenberg, J.S., Zhang, F. and Collins, J.J. (2021). CRISPR- based diagnostics. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 5(7), pp.643–656. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00760-7.
[9]. Kato, G.J., Piel, F.B., Reid, C.D., Gaston, M.H., Ohene-Frempong, K., Krishnamurti, L., Smith, W.R., Panepinto, J.A., Weatherall, D.J., Costa, F.F. and Vichinsky, E.P. (2018). Sickle cell disease. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, [online] 4(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.10.
[10]. Kornberg, A. (n.d.). The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959. [online] NobelPrize.org. Available at: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/1959/kornberg/facts/ [Accessed 8 Sep. 2023].
[11]. Mah, A. and Roberts, R. (2022). Synthego | Full Stack Genome Engineering. [online] www.synthego.com. Available at: https://www.synthego.com/blog/genome-editing-techniques#7..
[12]. Offord, C. (2018). US Companies Launch CRISPR Clinical Trial. [online] The Scientist Magazine®. Available at: https://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/us-companies-launch-crispr- clinical-trial-64746.
[13]. Paine, J.A., Shipton, C.A., Chaggar, S., Howells, R.M., Kennedy, M.J., Vernon, G., Wright, S.Y., Hinchliffe, E., Adams, J.L., Silverstone, A.L. and Drake, R. (2005). Improving the nutritional value of Golden Rice through increased pro-vitamin A content. Nature Biotechnology, [online] 23(4), pp.482–487. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1082.
[14]. Parkins, K. (2021). FDA approves first trial investigating CRISPR gene editing as HIV cure. [online] www.clinicaltrialsarena.com. Available at: https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/crispr-gene-editing-hiv-cure/.
[15]. Petrov, G., Dymova, M. and Richter, V. (2022). Bacteriophage-Mediated Cancer Gene Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, [online] 23(22), p.14245. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214245.
[16]. Phillips, T. (2014). Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) | Learn Science at Scitable. [online] Nature.com. Available at: https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/genetically-modified- organisms-gmos-transgenic-crops-and-732.
[17]. Roberts, R. (2022). Synthego | Full Stack Genome Engineering. [online] www.synthego.com. Available at: https://www.synthego.com/blog/crispr-infectious-disease. [Accessed 11 Dec. 2023].
[18]. Synthego (2023). CRISPR: Gene editing and beyond. [online] www.youtube.com. Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4YKFw2KZA5o [Accessed 28 Aug. 2023].
[19]. The Nobel Prize Organization (2020). The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2020. [online] NobelPrize.org. Available at: http://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemistry/2020/161307-press-release-swedish/.
[20]. USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. (2022). China: Agriculture GMOs Safety Assessment Administrative Measures Finalized. [online] Available at: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/china- agriculture-gmos-safety-assessment-administrative-measures-finalized [Accessed 28 Aug. 2023].
[21]. Wheeler, M.B. (2013). Transgenic Animals in Agriculture | Learn Science at Scitable. [online] www.nature.com. Available at: https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/transgenic-animals-in-agriculture-105646080/#:~:text=The%20production%20of%20transgenic%20livestock..
[22]. Wiener-Bronner, D. (2023). Meat without slaughter: Here’s everything you need to know about lab-grown meat | CNN Business. [online] CNN. Available at: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/06/23/business/lab-grown-meat-explainer/index.html [Accessed 23 Sep. 2023].
[23]. Zimmermann, R. and Qaim, M. (2004). Potential health benefits of Golden Rice: a Philippine case study. Food Policy, [online] 29(2), pp.147–168. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2004.03.001.









