1. Introduction
Nowadays, the vast majority of TDC is implemented by fully digital circuits, usually including counters and delay units. Initially, it was mostly implemented on Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs). The current research is mostly based on Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) to implement TDC, which has higher performance, higher flexibility, and shorter development time. Scholars Zhao Xuepeng, Su Shujing, and Gao Peng designed TDC based on FPGA, which combined direct counting with Time Amplitude Conversion (TAC) method for time interval measurement under external driving, achieving precise measurement of large time ranges [1]. Scholars Mhiri, M., Saad, S., Hammadi, A. B., and Besbes, K. used a ring oscillator with gate control and a frequency divider for time conversion and measurement to realize a novel TDC design that can be applied to a wide range of RF applications [2]. This paper summarizes the current research and application areas of TDCs. The first is the development of the three generations of TDCs and their research history, in chronological order, to express the ever-increasing architecture and resolution, as well as the changes in the factors affecting the performance of each generation of TDCs. The second part is the basic principles of TDC and its applications, which can be categorized into the precise measurement of time and as phase and frequency discriminators in an all-digital phase-locked loop. Then, the significance of TDC time resolution enhancement to the application field is analyzed from these two aspects. Studying the development and application status of TDC technology can provide application and enhancement ideas for many related fields. It can provide a reference for some fields that need precise time measurement.
2. History of development
The first generation TDC began in the 1980s. TDC began to be applied in the field of high-energy particles, using complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology, but the measurement of time intervals was first processed using analog circuits. Analog circuits were susceptible to the influence of power supply voltage, so analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) was also required to digitize analog values. The accuracy is affected by the resolution of the timer performing the measurement [3].
The structure of the second-generation TDC uses all digital circuits and does not involve the problem of analog circuits, and the intervals of time can be directly converted into digital codes. It is divided into counter-based TDC and delay line-based TDC, the accuracy of which depends on the frequency of the clock and the accuracy of which depends on the delay time of a single delay cell on the delay line. There are not many TDCs based on delay lines alone, and in order not to be limited by the limited number of delay cells, the length of the time interval that can be measured can be extended by connecting the delay cells into a ring.
The third generation of TDCs, also based on all-digital circuits, uses a variety of ways to reduce the delay of individual gates in many applications, thus improving the time resolution and making the gate delays independent of the manufacturing process of the integrated circuits. For example, by using an impulse response based TDC structure and a three-stage conversion scheme, higher accuracy and faster conversion of the TDC can be achieved by introducing clock edge control circuits and accelerated conversion circuits [4].
Nowadays, the development of integrated circuit CMOS fabrication processes continues to carry out nanoscale research and development, while the need for accuracy in time-dependent measurements is increasing with the development of physical experiments and other application scenarios. In this case, the resolution of the TDC needs to be continuously improved, and larger ranges are also required.
3. Applications and rationale
3.1. Rationale
A TDC typically consists of an input stage circuit, a time-amplitude converter circuit, an analog selector, a coarse counting module, a register bank, and an ADC. TDCs can also be used in conjunction with counters, capture modules in microcontrollers, and other devices (As shown in Figure 1).
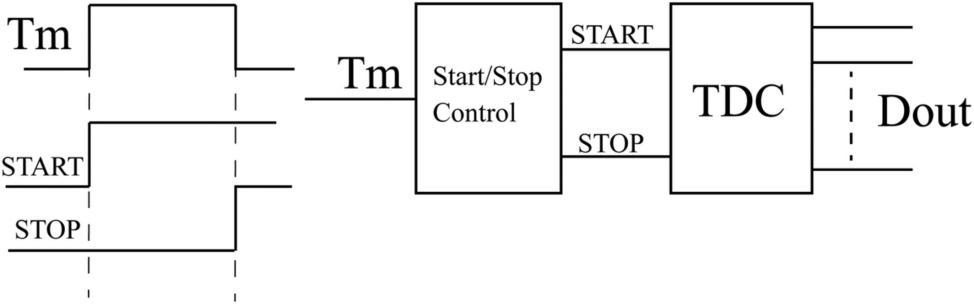
Figure 1. Principle diagram of time-to-digital converter [5]
TDC, as a working structure closely related to time signals, accurately measures the time interval between two events and quantifies it into a digital code, which is widely used in many application scenarios for precise time measurement. More TDC architectures that extend on the basic principles.
3.2. Application
3.2.1. Accurate time measurement. Measuring time pulses and calculating lengths from measured times are common needs in many scientific and practical applications. The main application area of TDC is the accurate measurement of time. Nowadays there are four main methods to measure time, which are Time Expanded Counting (TEC), TAC, Time Vernier and Tap Delay Line. They are all based on the time-to-digital conversion module to measure the length of time, and after the time-domain information, further measurements of other physical quantities are also possible [3].
The pixel detector is one of the most advanced position-sensitive detectors available and has a wide range of applications in areas such as internal diameter trace detection systems for gas pedal physics experiments and X-ray imaging. There is a great role in readout electronics, and many experiments in readout electronics are based basically on TDC to realize measurements [6].
The TDC can measure the arrival time of the rising edge of a scintillation pulse as the time information of the scintillation pulse at a lower threshold. The time resolution of the TDC directly affects the accuracy of the time information extraction of the readout circuitry, and thus the signal-to-noise ratio of the system. As a time reference, it can be used in analog-to-digital conversion circuits to process time-domain signals. Based on this, the scholars Chenhao Liu and Ge Jin realized the time measurement by combining the time interpolation technique to measure the multiple "stop" signals corresponding to a start pulse in a single time [7].
3.2.2. Characterize phase or frequency in ADPLLs. In addition to processing time-domain signals, an important application of the TDC in electronic circuits is as a phase discriminator between the reference clock and the feedback output of a numerically controlled oscillator in an all digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL). Figure2 shows an ADPLL architecture with the components of the structure being a digital phase detector (PD), a time-to-digital converter (TDC), a digital proportional-integral controller (PIC), a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO), a digital PIC and a DCO. This is a nonlinear negative feedback control system that synchronizes the output with the input in frequency and phase. Based on this purpose, TDC and and the adder can play a role in measuring frequency and phase. The TDC quantizes the error signal and combines it with the sign bit to output the corresponding error code, which gets fed back to the digital phasor, which will make a phase comparison with the reference signal. At the same time, the output signal of the DCO also serves as the output signal of the whole ADPLL circuit. The control code of the DCO is continuously corrected according to the phase error, completing the adjustment of the output signal frequency, realizing the output signal and the reference signal frequency to reach the same.
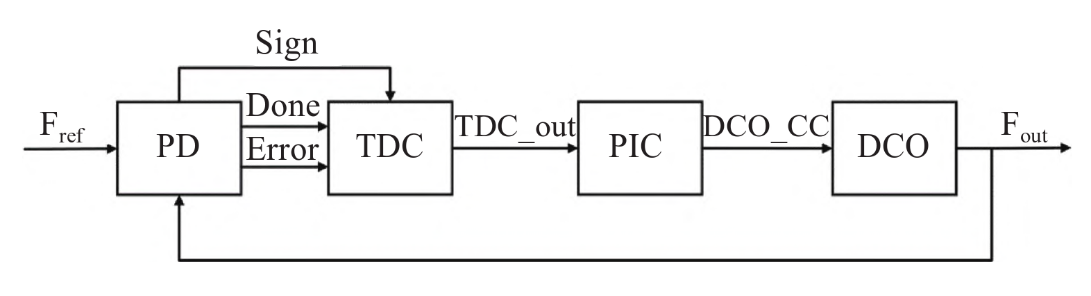
Figure 2. Structure diagram of one kind of all-digital phase-locked loop [8]
A TDC based on the CMOS process is introduced [9-10]. Chen et al. propose this monitoring scheme that can be used to monitor the clock cycle variation of phase-locked loops. The clock cycle variation is an important health status indicator of phase-locked loops, and this detection scheme can be used with the TDC to monitor the health status of PLLs.
4. Discussion
Currently, TDC is very well researched and new breakthroughs in accuracy are constantly being made. There are new applications in many architectures, and there are great research advances in the fields of electronics, physics, and information, which can specifically help the development of aerospace, readout electronics, hardware security, distance measurement, and many other fields. Nowadays, simultaneous integrated phase-locked loop applications are becoming more and more widespread, such as smart sensors based on integrated phase-locked loops, which can be applied in the field of automation. Not only that, the gradual digitization of traditional analog systems and the further increase in the accuracy requirements of time domain conversion and time measurement all indicate that new architectures and high-precision research on TDCs are crucial for the future development of science and technology.
5. Conclusion
In this thesis, TDC is described from three aspects: development history, principles, and applications. However, with the rapid development of TDC research and the wide range of applications of TDC with cross-disciplines. With the ultimate goal of attaining time interval measurement, TDC develops a system based on signal discrimination. Additionally, TDC completes the function of multi pulse time interval measurement, which can accommodate a wider range of measurement requirements in experiments. The All Digital Phase Locked Loop (ADPLL) circuit construction allows for the identification of the phase and frequency information between the feedback output and reference clock. It also offers a wide range of potential applications in other sectors of high-precision time measurement and circuit signal processing. The selection of literature should be more comprehensive, and future research should continue to explore the transformation of TDC's practical applications and the enhancement of architectural performance.
Acknowledgment
First of all, I would like to thank my family and friends for encouraging and supporting me while I was writing this essay. Then I would like to thank my teachers and professors who guided me in perfecting the content; without their help, I would not have completed my paper.
References
[1]. Zhao Xuepeng, Su Shujing, Gao Yuan. 2022. Design of a high precision time interval measurement circuit [J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 43(03):273-280.
[2]. Mhiri, M., Saad, S., Hammadi, A. B., & Besbes, K. (2018, March). A 15b, Sub-10PS Resolution, Gateable Pseudo-Delay Ring Oscillator Time-to-Digital Converter for Wide Range RF Applications. In 2018 15th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD) (pp. 447-452). IEEE.
[3]. El-Hadbi, A., Elissati, O., & Fesquet, L. (2019, May). Time-to-digital converters: A literature review and new perspectives. In 2019 5th International Conference on Event-Based Control, Communication, and Signal Processing (EBCCSP) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
[4]. Wu, J., Jiang, Q., Song, K., Zheng, L., Sun, D., & Sun, W. (2016). Implementation of a high-precision and wide-range time-to-digital converter with three-level conversion scheme. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 64(2), 181-185.
[5]. Mattada, M. P., & Guhilot, H. (2021). Time-to-digital converters — A comprehensive review. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 49(3), 778-800.
[6]. Lang Zijian, Gao Chaosong, Qin Jiajun et al. 2022. Design and simulation of high precision TDC ASIC prototype for pixel detector [J]. Nuclear Physics Review, 39(02):206-214.
[7]. Liu Chenhao, Jin Ge. 2022. A large range time measuring system study of picosecond multi-pulse time interval [J]. Application of Electronic Technology, 48(10):108-112.
[8]. WANG W, ZHANG T H, LIU B Z, et al. 2023. ADPLL circuit design with fast lock time [J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 40(4):95-100.
[9]. Tancock, S., Rarity, J., & Dahnoun, N. (2021, June). Developments in Time-to-Digital Converters during 2020. In 2021 7th International Conference on Event-Based Control, Communication, and Signal Processing (EBCCSP) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
[10]. Chen, W. H., Hsu, C. C., & Huang, S. Y. (2020, November). Rapid PLL monitoring by a novel min-MAX time-to-digital converter. In 2020 IEEE International Test Conference (ITC) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
Cite this article
Huang,H. (2024). Current status and applications of time-to-digital converters. Applied and Computational Engineering,53,79-83.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhao Xuepeng, Su Shujing, Gao Yuan. 2022. Design of a high precision time interval measurement circuit [J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 43(03):273-280.
[2]. Mhiri, M., Saad, S., Hammadi, A. B., & Besbes, K. (2018, March). A 15b, Sub-10PS Resolution, Gateable Pseudo-Delay Ring Oscillator Time-to-Digital Converter for Wide Range RF Applications. In 2018 15th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD) (pp. 447-452). IEEE.
[3]. El-Hadbi, A., Elissati, O., & Fesquet, L. (2019, May). Time-to-digital converters: A literature review and new perspectives. In 2019 5th International Conference on Event-Based Control, Communication, and Signal Processing (EBCCSP) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
[4]. Wu, J., Jiang, Q., Song, K., Zheng, L., Sun, D., & Sun, W. (2016). Implementation of a high-precision and wide-range time-to-digital converter with three-level conversion scheme. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 64(2), 181-185.
[5]. Mattada, M. P., & Guhilot, H. (2021). Time-to-digital converters — A comprehensive review. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 49(3), 778-800.
[6]. Lang Zijian, Gao Chaosong, Qin Jiajun et al. 2022. Design and simulation of high precision TDC ASIC prototype for pixel detector [J]. Nuclear Physics Review, 39(02):206-214.
[7]. Liu Chenhao, Jin Ge. 2022. A large range time measuring system study of picosecond multi-pulse time interval [J]. Application of Electronic Technology, 48(10):108-112.
[8]. WANG W, ZHANG T H, LIU B Z, et al. 2023. ADPLL circuit design with fast lock time [J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 40(4):95-100.
[9]. Tancock, S., Rarity, J., & Dahnoun, N. (2021, June). Developments in Time-to-Digital Converters during 2020. In 2021 7th International Conference on Event-Based Control, Communication, and Signal Processing (EBCCSP) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
[10]. Chen, W. H., Hsu, C. C., & Huang, S. Y. (2020, November). Rapid PLL monitoring by a novel min-MAX time-to-digital converter. In 2020 IEEE International Test Conference (ITC) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.









