

Volume 171
Published on June 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Functional Materials and Civil Engineering
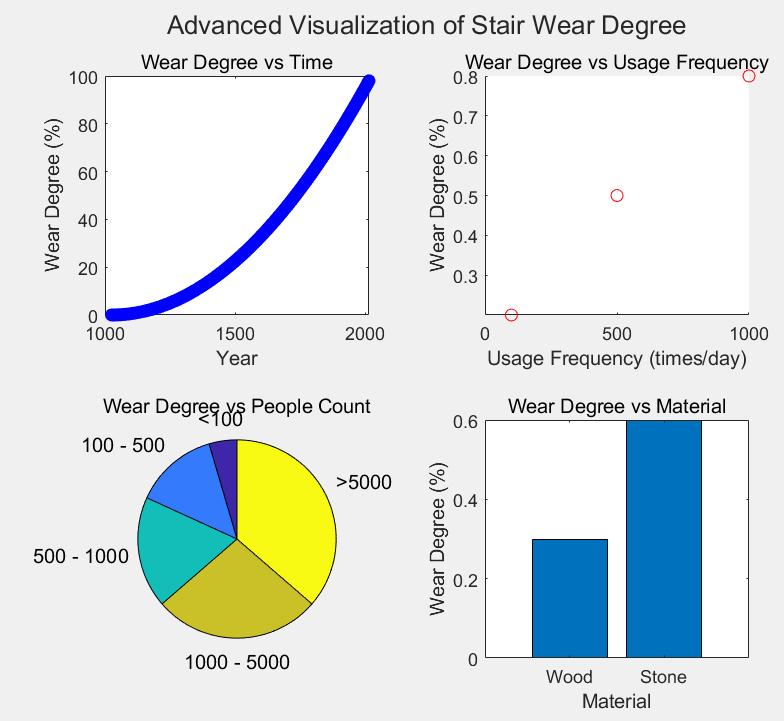
This paper focuses on the research of ancient building staircases, developing multiple models for wear analysis and traffic flow prediction. Firstly, relevant data on wear and traffic flow are collected, including material properties, surface conditions, and the number of staircase users. Model I is based on material mechanics and surface wear theory, constructing W = f (F, D, M) to examine the degree of wear; Model II combines LWR traffic flow and queuing theory, constructing Q = g(ρ, v, lq, tq) to analyze traffic flow; Model III is a PSO model that improves the first two, using the mean square error between predicted and actual data as the fitness function. The results show that the staircase wear model has good explanatory power, the traffic flow model has a high accuracy rate during peak and off-peak hours, and the mean square error of the combined model after PSO optimization is reduced by 30%, with improved fitting performance, providing an important reference for the maintenance, protection, and usage planning of ancient building staircases.

 View pdf
View pdf


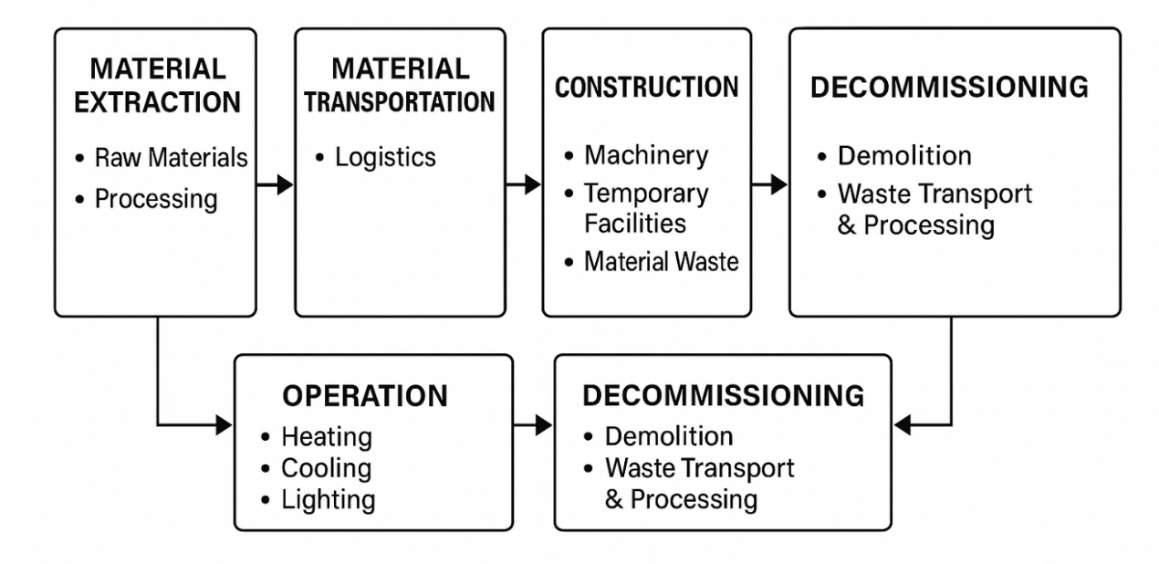
To enable systematic quantification and effective control of carbon emissions in the construction industry, this paper proposes a life cycle-based carbon emission model. Grounded in LCA principles, the model spans four stages: material production, construction, operation, and demolition. It integrates phased accounting with unified aggregation to ensure a closed-loop calculation process. Parameters are derived from the “Building Carbon Emission Calculation Standard” and the China Life Cycle Database (CLCD). Empirical validation on public buildings in Shanghai demonstrates the model’s stability and its ability to identify high-emission stages and optimization opportunities. The model proves applicable to carbon verification, green building evaluation, and full-process carbon management, showing strong practical value and scalability.

 View pdf
View pdf


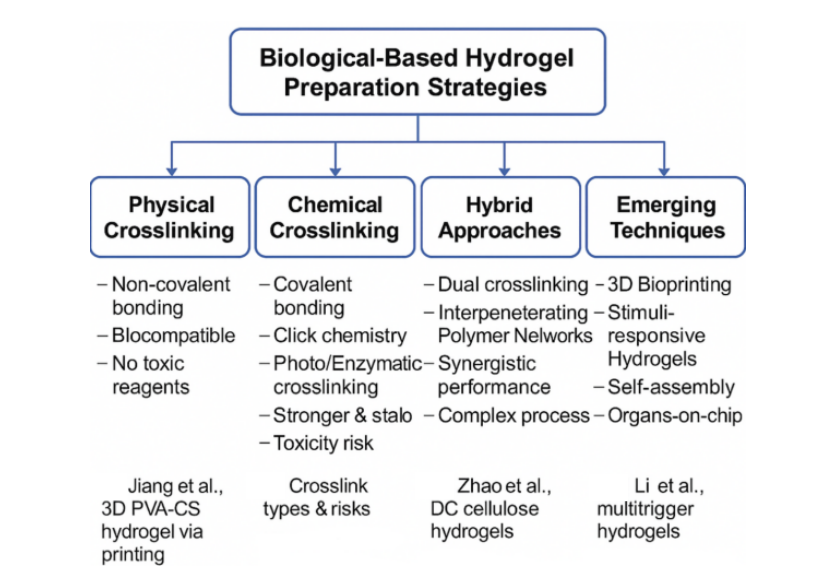
Bio-based hydrogels, derived from natural materials such as chitosan, alginate, gelatin, and collagen, have garnered significant attention for their outstanding biocompatibility and ability to mimic natural tissues. This review examines commonly used preparation methods, including physical, chemical and hybrid cross-linking, along with their primary components, such as polysaccharides and proteins. Owing to their flexibility and responsiveness, these hydrogels are widely used in areas such as soft robotics, cancer therapy and biosensing. However, despite promising advancements, significant challenges persist, particularly regarding their limited strength and stability. Future research should aim to enhance the performance and reliability of these materials to support their integration into complex medical and engineering systems.

 View pdf
View pdf




