terahertz communication, 6 g, photon terahertz source, advanced terahertz devices, ten-ray model.
1.Introduction
In the past few decades, the world has developed very rapidly, and the demand for wireless connection is also increasing. From the previous 1 g to the current 5 g communication, not only the connection between people has become closer, but more and more intelligent devices have also realized the Internet, including industrial equipment, automobiles, sensors, home devices and so on. The Sixth Generation (6 g) system is a new wireless communications mode, which is expected to be realized between 2027 and 2030. Compared with 5 g systems,6g communication needs wider coverage, longer transmission distance, larger system capacity, faster data rate, shorter time delay, higher security and less communication energy consumption. Terahertz communication is a wireless communication technology based on terahertz frequency band, and the terahertz frequency band ranges from 100 GHZ to 10thz GHZ. The terahertz band is between microwave and infrared light, and has many unique features. [1]
The main characteristics of THz communication include the following aspects.
1.1.Wide bandwidth: Terahertz band has a wide range of spectrum resources, which can provide a data transmission rate as high as several hundred Gbps, far exceeding the traditional wireless communication technology.
1.2.Low energy consumption: The electromagnetic wave used in terahertz communication requires low energy, and has little impact on the human body and the environment, which can also save energy.[2]
1.3.Strong penetration: terahertz waves can penetrate many non-metallic materials, such as paper, plastic, cloth, etc. But the penetration of metals and water and other materials is poor. This makes terahertz communication have advantages in some special environments, such as medical imaging and security detection.
1.4.High security: Terahertz waves are easily disturbed during transmission, and it is difficult to be eavesdropped and disturbed. This makes THz communications have potential in fields with high security requirements, such as military communications, security monitoring and so on.
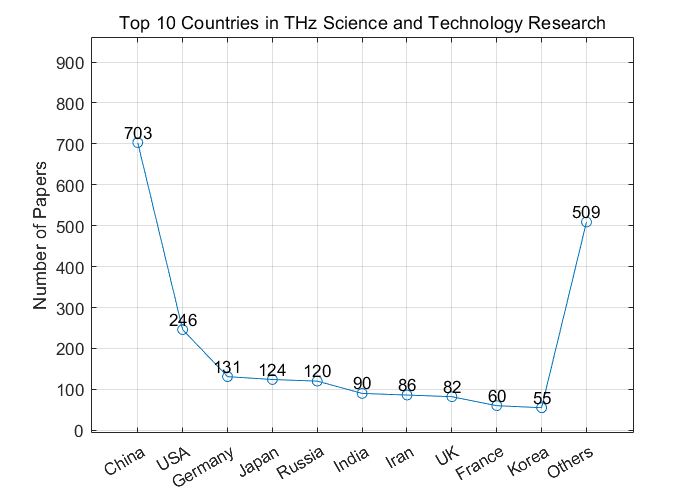
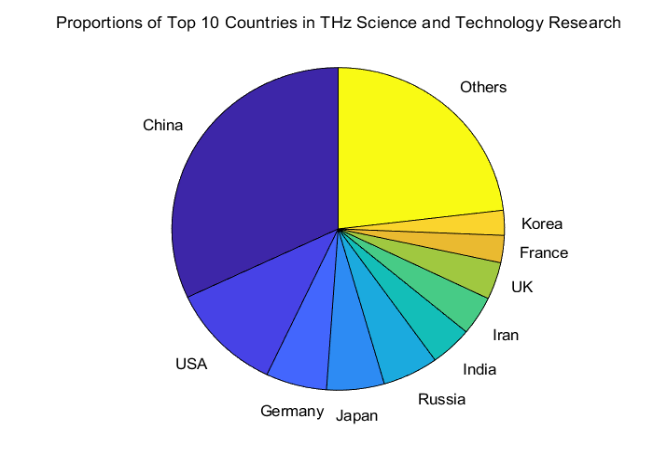
At present, terahertz communication has received widespread attention and research enthusiasm in the communication technology research community, which is reflected in the increase in the number of web of science related articles in recent years. The following two charts show the TOP10 countries in the field of Terahertz science and technology publications.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 1. the line chart of TOP10 countries in the field of Terahertz science and technology publications. |
Figure 2. the pie chart TOP10 countries in the field of Terahertz science and technology publications. |
2.Research background
In the 1970s, the terahertz term was first used to describe the range of spectral frequencies covered by interferometers, diode detectors, etc. Before the mid-1980s, infrared and microwave on both sides of the terahertz band were well understood and relevant technologies were mature, but people's understanding of the terahertz band was still very limited. In addition, because terahertz waves coincide with the millimeter wave band in long wave and the infrared band in short wave, It is the transition region from macroscopic classical theory to microscopic quantum theory, from electronics to photonics, so it is called the "terahertz gap" in the electromagnetic spectrum, and the boundary was not clearly defined at the time. The terahertz band ensures a wide range of throughput, which can be extended to several THz theoretically, thus generating a capacity of one trillion bits per second (Tbps). At present, active research groups around the world are cooperating to study new designs, materials and manufacturing methods to provide their own strength for the development of THz.[3]
Table 1 lists examples of groups and projects that carry out terahertz communication research all over the world. This research found that many laboratories around the world are carrying out terahertz research. Besides, various funding agencies have been supporting terahertz projects.
|
(a)Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Terahertz Communications Group |
USA |
This group is working to develop high-speed communications systems in the terahertz band for faster data transfer speeds and higher bandwidth. |
|
(b)University of Cambridge Terahertz Communications Project |
UK |
This project aims to exploit the high bandwidth characteristics of the terahertz band to develop new terahertz devices and systems for wireless communication and data transmission. |
|
(c)Terahertz Communication Group, Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Research, Germany |
Germany |
This group is committed to the research and application of terahertz communication technology, including terahertz antenna design, signal processing and communication system integration. |
|
(d)Terahertz Communication Laboratory, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore |
Singapore |
The laboratory focuses on the research and development of terahertz communication technology, including terahertz antenna design, modulation and demodulation technology and communication system performance evaluation. |
|
(e)National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Terahertz Communication Project |
USA |
This project aims to develop standards and test methods for terahertz communication to promote the commercialization and application of terahertz communication technologies. |
|
(f)European Terahertz Communications Project (TERAPOD) |
Europe |
This project, funded by the European Commission, aims to develop new devices and systems for high-speed terahertz communications to meet the needs of future wireless communications. |
3.purpose and significance of the research
Around 2020, the data transmission rate of wireless communication systems will be close to 100gbit /s, but due to the increase in People's Daily life needs, the requirements for data transmission rates are gradually increasing. How to accelerate the data transmission rate of wireless communication by applying different techniques and measures in the original wireless high-speed communication technology is an important research direction in the field of wireless communication. It is envisaged that links of terabits per second will be produced in the near future. However, implementing this idea is very difficult. Traditional wireless communication systems (below 5 GH) and even recently researched millimeter-wave communication solutions (30-300 GHz) can not achieve such high data rates. [4] Therefore, we need to constantly explore and discover new solutions in order to further improve the transmission rates. In this case, the terahertz (THz) band (0.1-10 THz) has become the key wireless technology to meet this demand. Terahertz ultra-high-speed wireless network is a new type of wireless network, which is different from the traditional wireless network. It works in the terahertz frequency band and can support several data transmission rates of 10 Gbps or even 1 Tbps. Terahertz frequency band is wide, and most of them have not been allocated to use, can carry a large amount of data, and has a wide range of application prospects. In addition, the use of terahertz frequency band for communication can effectively alleviate the increasingly tight spectrum resources and the capacity of the current wireless system.[5]
4.application areas of terahertz communication
Terahertz communication in life, military, communication and other aspects have broad application prospects, the following list a few terahertz communication can be applied in the field
4.1.Communications in outer space
Terahertz communication is a new wireless communication technology, which uses terahertz electromagnetic waves to transmit data. Terahertz communication has the advantages of large bandwidth, low energy consumption, strong anti-interference and strong penetration ability in outer space communication. Terahertz electromagnetic waves provides a large bandwidth, which means that more data can be transmitted in outer space communication, thus meeting the demand of high-speed data transmission.[6] Terahertz communication uses low electromagnetic wave energy, and the energy required to transmit data is less than that of other communication technologies, so terahertz communication can effectively save energy. In the environment of outer space, there are various interference sources, such as cosmic rays and interstellar dust, which will affect the quality of communication signals. Terahertz communication can better resist these interferences, providing a more stable and reliable communication connection. Moreover, terahertz electromagnetic wave have strong penetration ability, which can penetrate some common obstacles, such as clouds, dust and so on. In outer space, there may be some obstacles, such as asteroids and dust clouds. Terahertz communication can better penetrate these obstacles and achieve a more stable communication connection.[7]
4.2.Military communications
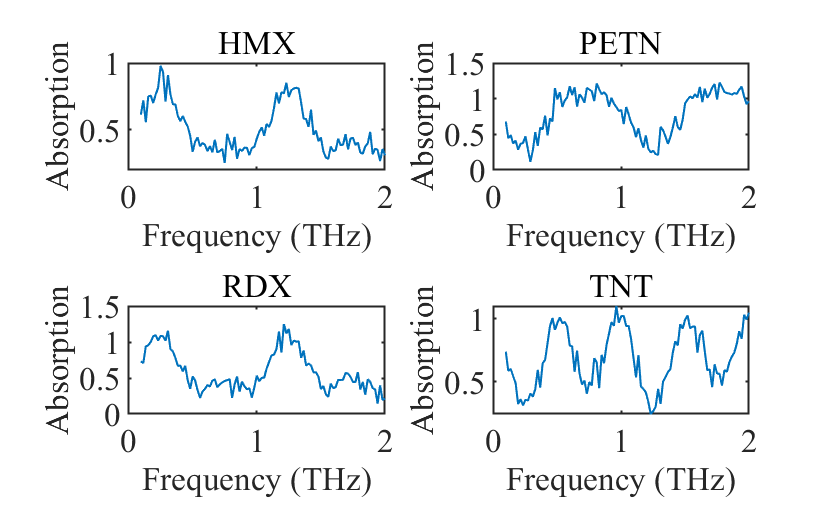
Terahertz communication has a very high application value, which is highly valued by governments and research institutions, including national defense security and military fields are the first, terahertz communication can be used in terahertz radar and other military fields, because the terahertz wavelength is very short, so it can detect more tiny targets and obtain more accurate positioning, second, terahertz frequency band has a rich frequency band, and the terahertz frequency band is very important. It can emit a large number of pulses and detect the enemy's stealth technology, and it has a good pass rate for absorbing materials, can ignore coatings, and has strong anti-stealth capabilities. Compared with microwave radar, it has high resolution, strong anti-jamming ability and strong anti-stealth ability. Compared with infrared radar and LiDAR, it has lower attenuation in suspended particulates and in dust, smoke and battlefield pollution conditions, so terahertz radar has a stronger ability to penetrate dust and smoke than infrared and lidar, and can achieve all-weather work.[8]. The figure 3 is the absorption spectra of the four types of explosives detected are presented below.
|
|
|
Figure 3. the absorption spectra of the four types of explosives detected |
As shown in the figure, different types of explosives will produce strong absorption at specific frequencies, and different explosives have different absorption spectra and dispersions, and explosives can be identified according to this information .
5.Technical challenges of terahertz communication
The first problem is the cost. Terahertz communication is ultra-fast in the time domain, and it must be based on ultra-fast laser with shorter pulse. This laser light source is very expensive in price, and it needs a stimulating medium. First, it is the crystal, usually single crystal, and the production cost is very high. Then it is the semiconductor material of the antenna. This is a technical monopoly, and many technology companies can not develop it themselves. Only for purchase.
The second problem is technology. The development and maturity of science and technology will be more and more perfect as time goes on. Terahertz technology is less than 30 years now. Because of the lack of accumulated experience, many technical bottlenecks have not been broken, and there are many limitations and loss factors. The effective area of the terahertz antenna is proportional to the square of the carrier signal, resulting in large transmission losses. In addition, theoretical and experimental data show that atmospheric water vapor has a strong absorption effect on terahertz pulse. In the time domain, there will be a rapidly oscillating signal after the main pulse, and in the frequency domain, there will be a sharp absorption line at some frequencies on the spectrum. In view of the limited output power of terahertz transceiver, high gain directional antenna is needed for communication distances beyond several meters.
Finally,its own problem is that Terahertz radiation is a special low energy photon. The terahertz band is located between laser and microwave, which has some characteristics of both, such as wave-particle duality, but is more special than both.[9]
6.Generation and detection of terahertz waves
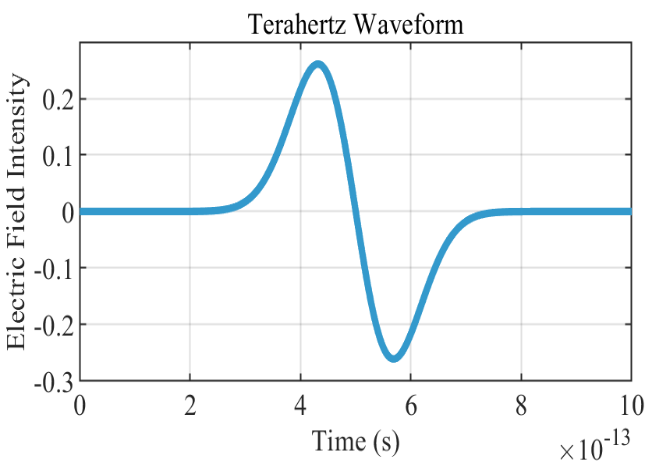
There are many ways to generate terahertz waves, and the most common ones are light excitation and electron excitation. Optical excitation refers to the generation of terahertz waves by using a laser source. First of all, a strong laser beam is focused on a nonlinear optical crystal or gas, so that the frequency of the light is doubled or mix. Then, by choosing appropriate optical crystal or gas material, the frequency of the light can be converted to the terahertz band. This method can generate high-power terahertz waves, but it needs more complicated equipment and technology. Electron excitation is the generation of terahertz waves by using electron beams. First, a high-energy electron beam is accelerated to high speeds and passed through a metal or semiconductor thin film. When the electron beam interacts with the thin film, terahertz waves will be produced. This method can generate high-frequency terahertz waves, but it needs high-energy electron beam and complicated accelerator equipment. There are also various methods for detecting and receive terahertz waves. [10] Among them, terahertz wave detector is the most common one. Terahertz wave detectors are usually based on the photoelectric or thermal effect. Photoelectric effect detectors converts photons into electrons by using the energy of terahertz waves, and then detects terahertz waves by the movement of the electrons. Thermal effect detectors converts photons into heat energy by using the energy of terahertz waves, and then detect terahertz waves by measuring the change of heat energy. Besides detectors, terahertz wave antennas can also be used to receive terahertz waves. Terahertz wave antennas are usually made of metal or semiconductor materials that convert terahertz waves into electric signals. [11] These electric signals can be processed by amplifiers and filters, and then transmitted to the receiver by cable or wireless for further analysis and processing. The graph below is a terahertz wave image that I generated using matlab. The following figures show the terahertz waveform diagram and electric field diagram simulated by matlab
|
|
|
|
Figure 4. the terahertz electric field diagram |
Figure 5. the terahertz waveform diagram |
The images show the terahertz wave waveform. The X-axis represents time (from 0 to 1 picosecond) and the Y-axis represents frequency (from 0 to 10 THz). The color bar indicates the intensity of the waveform. From this image, the frequency and time characteristics of terahertz waves can be observed.
7.Transmission characteristics of terahertz waves
First of all, terahertz electromagnetic waves have a high penetration ability. Compared with visible light, terahertz electromagnetic waves have lower transmission losses in the atmosphere and can penetrate many non-metallic materials, such as paper, plastics, fabrics, etc. This makes the terahertz band have a wide range of applications in the fields of non-destructive testing, safety inspection and medical imaging.
Secondly, electromagnetic waves in the terahertz band has high resolution. The terahertz band has a wavelength range from millimeter to micron, which is shorter than the RF and microwave bands, so it has higher resolution. This makes the terahertz band very important for high-resolution imaging and spectral analysis.
In addition, electromagnetic waves in the terahertz band will be weakly interfered in the transmission process. Due to the low frequency of the terahertz frequency band, electromagnetic waves in the terahertz frequency band are less interfered than radio and microwave frequency bands. This makes the THz communication system have high anti-interference performance, which is suitable for communication in complex environment.
However, the transmission distance is relatively short in the terahertz band. The transmission distance of terahertz electromagnetic wave is limited because of its large transmission loss in the atmosphere. Therefore, it is necessary to use relay stations or increase the number of antennas to extend the transmission distance in terahertz communication systems.[12]
8.Part of a terahertz communication system
The terahertz communication system mainly includes photon terahertz source, chip development, advanced terahertz devices and so on , which can be used as the core component of the future 6 g mobile communication system, integrated into the existing optical wireless communication architecture, and realize high-speed broadband access.
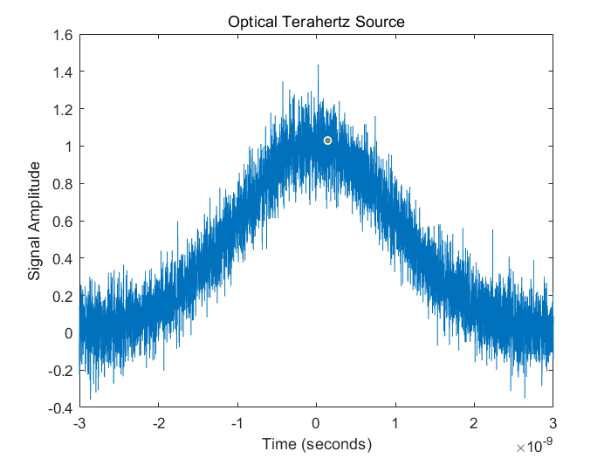
A photon THz source is a light source that can generate THz frequencies. Photon terahertz sources are usually based on optical nonlinear effects, generating terahertz radiation through the interaction of a laser beam with a nonlinear material. The working principle of photon terahertz source is based on photoelectric effect and optical nonlinear effect. [13] First, a strong light pulse is generated through the laser and is divided into two beams of light, one known as the "pump light" and the other known as the "probe light." Pumping light through a nonlinear crystal produces pairs of high-frequency photons that have an energy difference equal to the energy of a terahertz wave. The detected light then interacts with the resulting photon pairs, converting the photon pairs into terahertz waves through the photoelectric effect.
|
|
|
|
Figure 6. the optical terahertz source waveform |
Figure 7. the optical terahertz source spectrogram |
Terahertz communication-related chips can be divided into two categories, one is the RF chip, and the other is the baseband chip, the development of baseband chip is the development of integrated circuit chips with baseband processing functions in the word communication system. Terahertz technology-related chips usually use mature processes, and in the ISSCC paper this year, basically use 28nm and previous processes (most use 65nm processes), and for RF chips, mainly use III-V semiconductor HEMT and HBT transistors. And silicon based materials such as CMOS and SiGe, discuss how to achieve high output power and long-distance communication in the terahertz frequency band, the discussion of baseband chip is mainly about how to achieve high-speed signal modulation, and baseband chip can control the RF circuit.
Advanced terahertz devices include terahertz laser, terahertz detector, terahertz antenna and so on. Researchers around the world through unremitting efforts to improve the shortcomings of various devices, and enhance their characteristics, such as high penetration, high safety, high orientation, recently developed by the Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne, a nanodevice can generate high-power terahertz waves, the device can generate high-power signals in picoseconds, thus generating high-power terahertz waves. The device consists of two metal plates close together, with a distance as low as 20 nanometers between them. When a voltage is applied, electrons rush to one of the plates, where they form a nanoplasma. As soon as the voltage reaches a certain threshold, the electrons are shot at the second plate almost immediately.[14] This rapid movement, achieved with such a fast switch, creates a high-intensity pulse that can generate high-frequency waves, and the new nanodevice, which is ten times faster, can generate both high-energy and high-frequency pulses
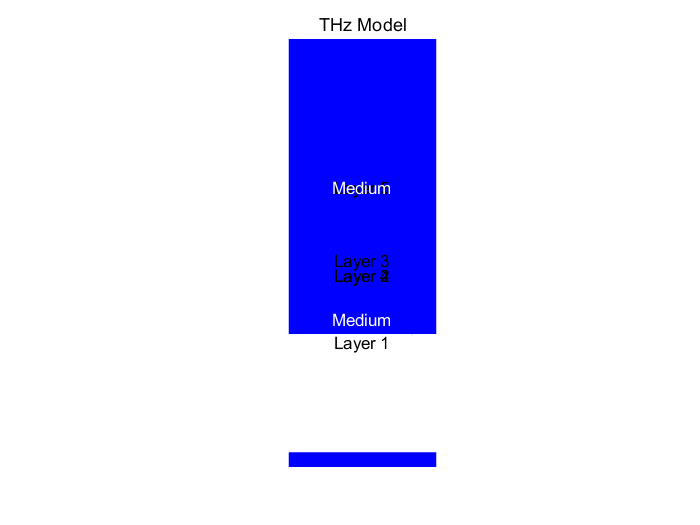
9.Terahertz channel modeling
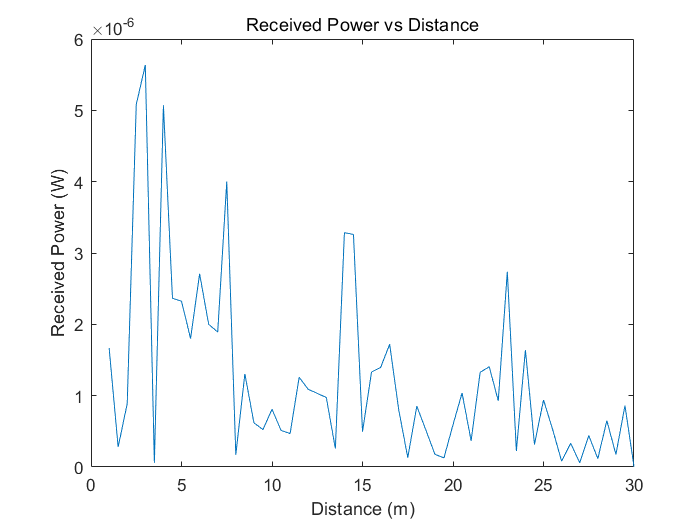
The following is my terahertz channel model modeling with matlab, and I use the ten-ray model to model. First, we define some known parameters, including frequency f, transmit antenna gain Gt, receive antenna gain Gr, light speed c, transmit power Pt and reflection coefficient F_S. Where, f is 2.4 GHz, Gt and Gr are both 1, c is 3e8 m/s, Pt is 1 W, and F_S is 0.7. Then, we calculate the wavelength lamda, which is obtained by c/f. Next, we build a three-dimensional coordinate system with the transmitting point Tx as the origin. We create an empty array P_L to store the received power. Then, we use a loop that starts at a distance d of 1 and increases by 0.5 each time until it ends at 30. For each distance value, we calculate the received power of different reflection paths. First, we calculate the received power p0 for the direct path. Calculate the distance R0 from the transmitting point Tx to the receiving point Rx, and then use the formula
sqrt(GtGr)lamda/(4pi)(exp(1i2pi*R0/lamda)/R0)
Calculate the received power. Next, we calculate the received power of other reflection paths, including ground reflection, wall reflection, and multiple reflection paths. The received power calculation method of each reflection path is similar to that of the direct path, only the corresponding reflection coefficient F_S is increased. Finally, we sum the received power of all paths and take the square of the absolute value to get the total received power. Store the value in the P_L array. After the loop is over, we use the plot function to plot the relationship between distance and received power. The x axis represents distance d and the y axis represents the received power P_L. The model is used to calculate the relationship between the received power and the distance under certain parameters. The power loss of direct and multiple reflection paths is considered in the model, and the total received power is obtained by calculating the power contribution of each path. By drawing the curve of the relationship between the distance and the received power, the signal attenuation at different distances can be analyzed.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 8. the curve of the relationship between the distance and the received power |
Figure 9. the terahertz model |
The knowledge used includes the path loss model: Path loss is the attenuation of signal power due to the increase in the distance the signal travels during propagation. The common path loss models include free space propagation model and secondary attenuation model.
Free Space Path Loss (FSPL) :
FSPL = 20log10(d) + 20log10(f) + 20log10(4π/c),
where d is the propagation distance, f is the signal frequency, and c is the speed of light.
Two-Ray Ground Reflection Model:
PL = 10log10((d^2 * Gt * Gr)/(Ht * Hr)^2)
where PL is the path loss, d is the propagation distance, Gt and Gr are the gain of the transmitting and receiving antennas, and Ht and Hr are the height of the transmitting and receiving antennas.
Received signal power: The received signal power is the power of the received signal, which can be calculated according to the path loss model and the transmitted power. Multipath propagation: Multipath propagation refers to the reflection and diffraction phenomenon of the signal in the process of propagation. Multipath propagation causes the signal to have multiple different arrival times and phases at the receiving end, resulting in multipath interference and fading. Commonly used multipath propagation models include Rayleigh fading model and Rice fading model. Rayleigh Fading Model: The Rayleigh fading model applies to wireless channels with no direct path, where the signal only experiences the influence of multiple scattering paths.
The Probability Density Function (PDF) of the Rayleigh fading model is as follows:
F (x) = exp (x/sigma ^ 2) * (x ^ 2 / (2 sigma ^ 2))
and x is the received signal amplitude, sigma is the standard deviation of Rayleigh fading.
Rician Fading Model: The Rician fading model is applicable to wireless channels with direct paths and multiple scattering paths, where both the direct path and the scattering path affect the signal.
The Probability Density Function (PDF) of the Rice fading model is as follows:
f(x) = (x/(σ^2 + K)) * exp(-(x^2 + K)/(2σ^2)) * I0(xK / σ^2)
where x is the amplitude of the received signal, σ is the standard deviation of Rayleigh fading, K is the Rice factor (representing the power difference between the direct path and the scattering path), I0 is a modified Bessel function of order zero.
10.Conclusion
The application of THz wireless communication is expected to bring about a historic breakthrough in science and technology. The terahertz frequency band (0.1-10 THz) provides a large number of applications, which can meet communication needs and market needs outside the 5 g networks. Terahertz communication is a new communication technology, which is expected to bring a historic breakthrough in science and technology. The terahertz frequency band (0.1-10 THz) provides a large number of applications, which can meet communication needs and market needs outside the 5 g networks. The background, composition and challenges of terahertz communication, and how to generate and detect terahertz waves are introduced. In addition, THz communication has broad application prospects and potential. The development and application of THz communication technologies can be promoted by exploring THz/optical hybrid wireless links, THz automotive applications, THz communication for enhancing the performance of data centers, THz communication for mobile networks and THz 3D beamforming technology. Meanwhile, the development trend of software-defined radio and software-defined network will also support the further development of terahertz wireless technology.
References
[1]. H. Elayan, O. Amin, B. Shihada, R. M. Shubair, and M.-S. Alouini, "Terahertz Band: The Last Piece of RF Spectrum Puzzle for Communication Systems," IEEE, Student Member, IEEE.
[2]. G. Wang, H. Gu, J. Li, Z. Yu, O. Li, Q. Liu, K. Zeng, J. He, Y. Chen, J. Lu, W. Tong, and D. Wessel, "Terahertz Sensing and Communication for Future Intelligent Internet Networks."
[3]. F. Sizov, "Brief history of THz and IR technologies."
[4]. J. M. Jornet and I. F. Akyildiz, "Channel modeling and capacity analysis for terahertz band communication," IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 394-407.
[5]. Y. Wang, H. Cheng, J. Zhang, and X. Zhang, "Terahertz wireless communications based on 300-GHz uni-traveling-carrier photodiodes," IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 588-597.
[6]. S. U. Hwu and K. B. deSilva, "Terahertz (THz) wireless systems for space applications."
[7]. M. Civas and O. B. Akan, "Terahertz Wireless Communications in Space."
[8]. Z. Liu and X. C. Zhang, "Terahertz wave for military and security applications," Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, vol. 49, no. 12, p. 123001.
[9]. J. M. Jornet and I. F. Akyildiz, "Graphene-based plasmonic terahertz communications for dense nano-networks," IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 907-917.
[10]. T. Nagatsuma, G. Ducournau, C. C. Renaud, and A. J. Seeds, "Advances in terahertz communications accelerated by photonics," Nature Photonics, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 371-379.
[11]. X. C. Zhang and X. Zhang, "Terahertz technology for defense and security applications," Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 126, no. 17, p. 170901.
[12]. S. Yang, L. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and J. Huang, "Terahertz communications: The opportunities and challenges of key technology development," Journal of Communications and Information Networks, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1-12.
[13]. S. M. R. Islam et al, "Terahertz Communication: The Path Towards 6G Wireless Networks."
[14]. M. Tonouchi et al, "High-Power Terahertz Wave Generation Using Nanodevices."
Cite this article
Yao,S.;Teng,J. (2024). Terahertz communication for 6G networks: Opportunities and challenges. Applied and Computational Engineering,46,232-241.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. H. Elayan, O. Amin, B. Shihada, R. M. Shubair, and M.-S. Alouini, "Terahertz Band: The Last Piece of RF Spectrum Puzzle for Communication Systems," IEEE, Student Member, IEEE.
[2]. G. Wang, H. Gu, J. Li, Z. Yu, O. Li, Q. Liu, K. Zeng, J. He, Y. Chen, J. Lu, W. Tong, and D. Wessel, "Terahertz Sensing and Communication for Future Intelligent Internet Networks."
[3]. F. Sizov, "Brief history of THz and IR technologies."
[4]. J. M. Jornet and I. F. Akyildiz, "Channel modeling and capacity analysis for terahertz band communication," IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 394-407.
[5]. Y. Wang, H. Cheng, J. Zhang, and X. Zhang, "Terahertz wireless communications based on 300-GHz uni-traveling-carrier photodiodes," IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 588-597.
[6]. S. U. Hwu and K. B. deSilva, "Terahertz (THz) wireless systems for space applications."
[7]. M. Civas and O. B. Akan, "Terahertz Wireless Communications in Space."
[8]. Z. Liu and X. C. Zhang, "Terahertz wave for military and security applications," Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, vol. 49, no. 12, p. 123001.
[9]. J. M. Jornet and I. F. Akyildiz, "Graphene-based plasmonic terahertz communications for dense nano-networks," IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 907-917.
[10]. T. Nagatsuma, G. Ducournau, C. C. Renaud, and A. J. Seeds, "Advances in terahertz communications accelerated by photonics," Nature Photonics, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 371-379.
[11]. X. C. Zhang and X. Zhang, "Terahertz technology for defense and security applications," Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 126, no. 17, p. 170901.
[12]. S. Yang, L. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and J. Huang, "Terahertz communications: The opportunities and challenges of key technology development," Journal of Communications and Information Networks, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1-12.
[13]. S. M. R. Islam et al, "Terahertz Communication: The Path Towards 6G Wireless Networks."
[14]. M. Tonouchi et al, "High-Power Terahertz Wave Generation Using Nanodevices."