

Volume 168
Published on June 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering
Bio-inspired surfaces are developed to combat the unwanted buildup of substances like sediment, scale, or biological organisms on equipment and surfaces across various industries. This discussion encompasses various types of fouling, categorized by Young's modulus into hard and soft, and delves into crucial factors such as surface energy and wettability, which are essential for material development. We have identified a range of anti-fouling techniques from nature, inspiring the creation of synthetic surfaces based on these models. Despite these innovations, challenges such as durability, cost, and effectiveness against a broad spectrum of fouling organisms remain. To address these issues comprehensively, a strategy that integrates both mechanical properties and chemical treatments is essential, enhancing the performance and longevity of these bio-inspired surfaces.

 View pdf
View pdf



As research into lovastatin derivatives continues to advance, exploring their structural diversity and potential therapeutic applications has become increasingly significant in pharmaceutical chemistry. This paper focuses on the total synthesis of aculeatiols A-C, derived from Aspergillus aculeatus, and provides a comprehensive account of the key strategies and steps employed throughout the synthesis process. Initially, a linearization analysis was conducted, identifying 35 potential structures, from which the most suitable linearized structure was selected for synthesis. The core reactions utilized in this study included Robinson annulation, olefin metathesis, and asymmetric synthesis, which were crucial for constructing the complex molecular framework and ensuring the accurate stereochemical features of the target compounds. Furthermore, applying the "chiral pool" concept facilitated the optimization of the synthetic pathway, enhancing the efficiency of the synthesis. This research not only offers effective methodologies for the synthesis of novel lovastatin derivatives but also contributes valuable insights into their structure-activity relationships. The findings underscore the importance of continued exploration in this area, as they promise to develop more effective cholesterol-lowering therapies and personalized medicine approaches, ultimately benefiting patient care and treatment outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf



The reliability and stability of electrical distribution networks are essential in modern power systems. In high-voltage electrical distribution networks such as 110kV, faults occurring on transmission towers can result in significant disruptions, leading to economic losses and safety hazards. So, accurate fault location is crucial for minimizing downtime and enabling rapid restoration for the power systems. This paper reviews the current wave fault location method and introduces a new method to increase accuracy in identifying faults that can be caused by ungrounding, small resistance grounding, and arc suppression coil grounding. The method makes use of a time system through a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), which has high precision and fast execution time. The time system based has a time accuracy of 10 nanoseconds. Moreover, it can maintain operational integrity for at least 17 seconds when the Global Positioning System (GPS) loses signal from satellites. The wave fault location method is also implemented through FPGA, and the results are analyzed and visualized using MATLAB, demonstrating the accuracy of the fault location in the distribution lines.

 View pdf
View pdf


The aerodynamic properties of the airfoil are of great significance in improving the aerodynamic properties of the small fixed-wing UAV. This study demonstrates a numerical evaluation of the planar aerodynamic properties of a typical NACA 0018 airfoil at Reynolds numbers varying between 3×105 and 5×105 as well as angles of attack between 0° and 20°. The computational fluid dynamics (CFD) flow simulation tool ANSYS Fluent, which is based on the limited volume approach, is used to perform the computation. Based on the continuity equation and Navier-Stokes control equation, the Spalart-Allmaras turbulence model is used for simulation. The research reveals the relationship between the pressure distribution, lift and drag ratio of the airfoil and the angle of attack at diverse Reynolds numbers and ultimately reaches the conclusion that NACA 0018’s best condition of aerodynamic properties is at the Reynolds number of 5×105 and under the angles of attack within 12°~14°. This analysis provides a basis for wing optimization design and can be widely used in aerospace and wind turbine design.

 View pdf
View pdf


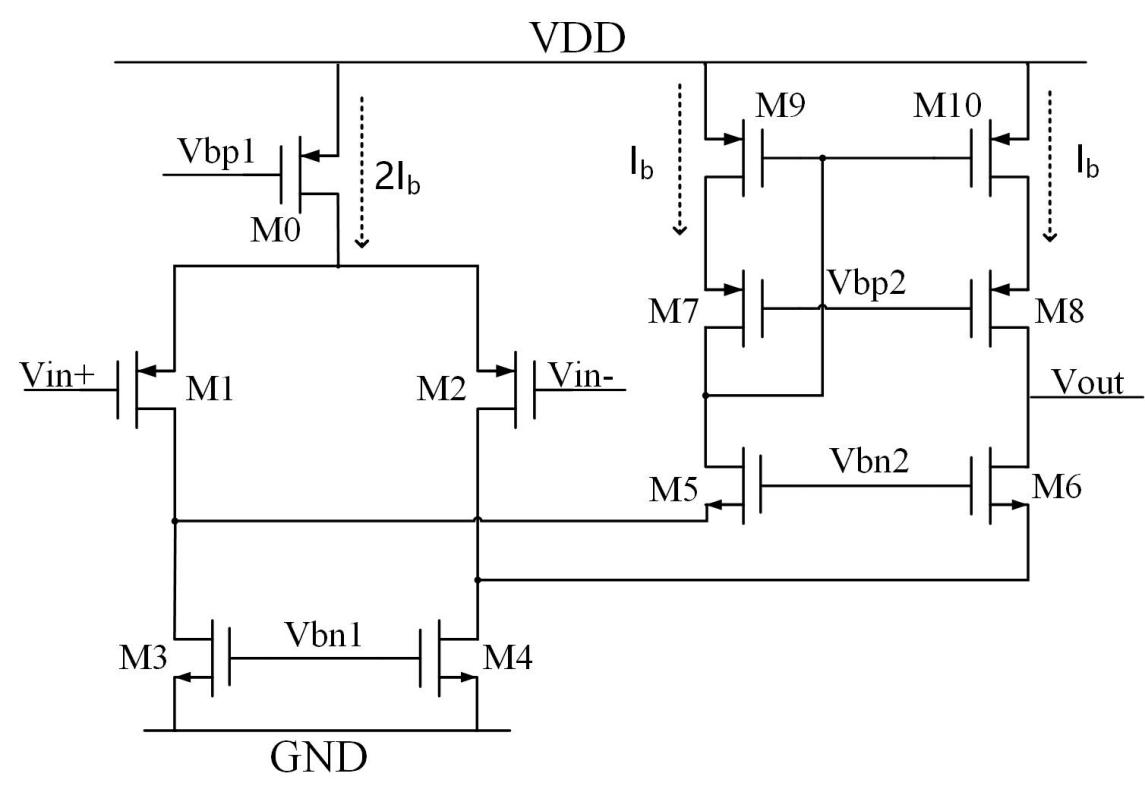
High efficiency operational transconductance amplifier is an important analog circuit designed to optimize the balance between power consumption and performance. This amplifier is suitable for mobile devices, sensor interfaces, and other low-power applications due to its high gain and low power consumption characteristics. This article provides a design for implementing a high-efficiency operational transconductance amplifier, which achieves higher gain and bandwidth on the basis of traditional common source and common gate. A recycling folded cascode amplifier with bias circuit was designed using Cadence 0.18 μm CMOS technology. The power consumption and load capacitance of the two circuits were the same and the various parameters of the two circuits were simulated and verified. Sacrificing some phase margin under small signal conditions increased the gain by 6dB, bandwidth by 1.89 times, and the speed of the operational amplifier was accelerated; The slew rate under high signal is 1.5 times faster than before, and the setup time is shorter. The CMRR and PSRR have both been improved.

 View pdf
View pdf



The increasing integration of electronic equipment in electric vehicles (EVs) compared to traditional vehicles significantly elevates the challenges posed by electromagnetic interference (EMI) to the functionality of printed-circuit boards (PCBs). This paper provides a comprehensive review of recent advancements in the field of PCB electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in EVs. By examining the principle of EMI generation and conduction, as well as EMI sources within EVs, the article identifies its specific impacts on PCB. Moreover, mitigative solutions are proposed, including the suppression of primary EMI sources, the implementation of shielding techniques, and EMC-oriented PCB design. In the end, this paper analyzes the feasibility of each solution, and provides recommendations for future research in this area.

 View pdf
View pdf


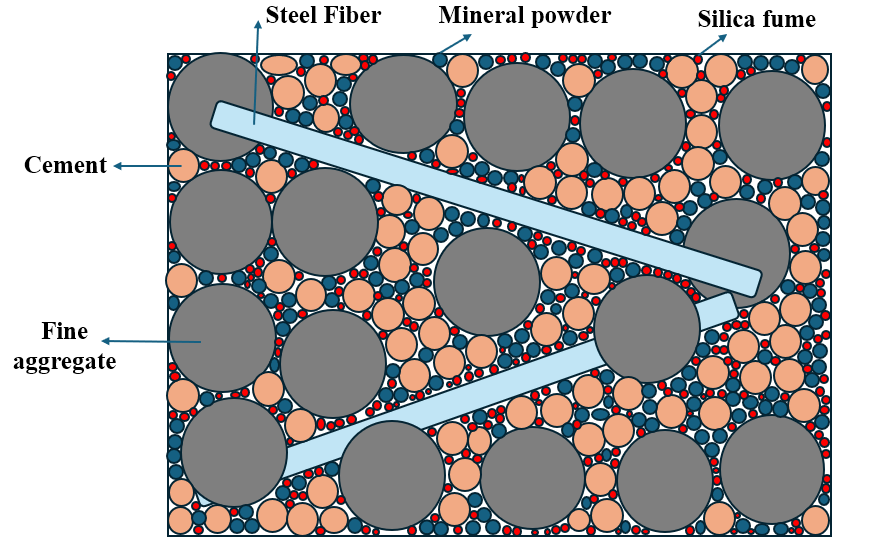
With the increasing traffic load, traditional concrete bridges gradually exhibit issues such as aging, cracking, and insufficient durability. Ultra-high Performance Concrete (UHPC), as a new type of cementitious composite material, has been widely applied in recent years in the construction of new bridges and the reinforcement and maintenance of aging bridges due to its excellent mechanical properties and durability. This paper first introduces the development of UHPC and its material characteristics. By studying relevant literatures and engineering cases, it provides an in-depth analysis of UHPC's specific applications in the reinforcement of bridge decks, main girders, and piers. The results show that UHPC can effectively prevent fatigue cracks in the bridge deck and girder and improve the structural bearing capacity due to its high strength and fatigue resistance. Additionally, the excellent impermeability of UHPC significantly improves the corrosion resistance of main girders and piers, thereby extending the service life of bridges. However, there are still some construction challenges in the practical application of UHPC. As construction technology advances and material costs decrease, UHPC is expected to have a broader application prospect in both bridge reinforcement and new construction projects.

 View pdf
View pdf


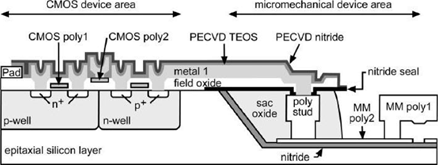
In Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) thermal flow sensors, CMOS integration plays a crucial role, especially in enhancing the performance of MEMS thermal flow sensors. This paper reviews the basic principle of CMOS-MEMS thermal flow sensor, introducing three prevalent types. The impact of CMOS integration on sensor performance is introduced, with their advantages highlighted: high integration, low cost, and low energy consumption. Their limitations are also addressed, including Limited material choice, inaccuracy due to heat loss, increased processing complexity and high cost, alongside proposed solutions to enhance their performance. The paper focuses on three basic application sectors of CMOS-MEMS thermal flow sensors. Finally, he potential for multi-module integration and extreme temperature resilience is discussed, indicating a promising trajectory for future advancements in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the growing urban population and water requirement, the need for decentralized wastewater treatment to complement centralized systems is imminent. This paper reviews six decentralized domestic wastewater treatment technologies and evaluates them with efficiency, cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and applicability. RAF-HRBC and GDMBR technologies are best suited for urban areas since their high efficiency and small footprint. In contrast, artificial wetlands are more suitable for rural environments due to the large amount of land they require. Despite the promise of these technologies, most of them are unable to meet drinking water standards, suggesting that they still need to be supplemented with other treatment methods to achieve potable water quality.

 View pdf
View pdf


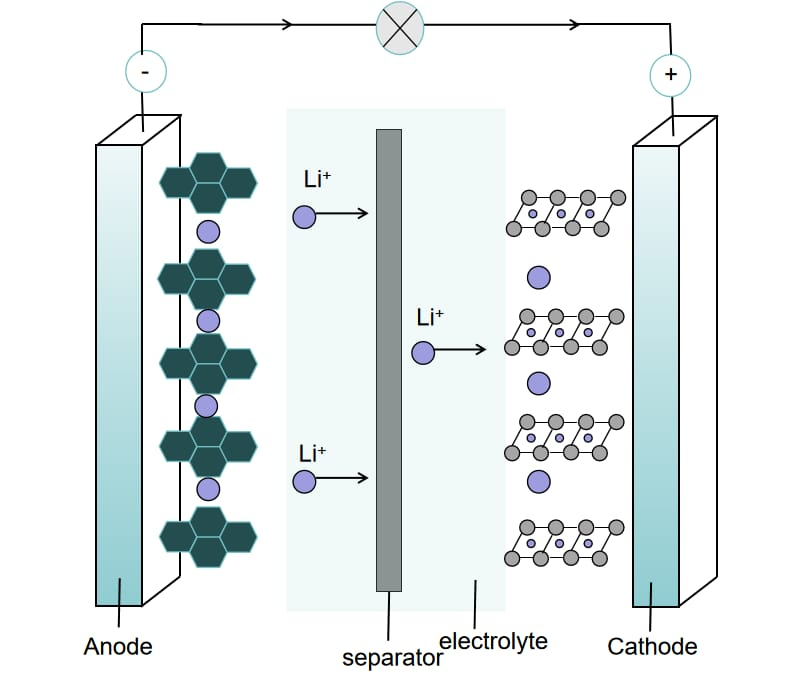
In survey of new generation of social and economic development, we can see new fears manifested in the energy crisis and global warming causing an even wide concern about this. Travelling in traditional fuel vehicles is exacerbated by the trend of introducing more tram lines, and the models of tram cars being manufactured gain diversity, among them the BEVs[1], HEVs[2], and FCEVs[3]. The lithium-ion battery, a major electromechanical device in these electric vehicles, is an important part for energy storage that accounts for most of the performance of the vehicle. The SEI membrane, the most vital constituent of a lithium-ion battery (LIB), determines the cycle life, capacity retention, and overall safety of the LIB. This review assesses the SEI's chemical structure, formation mechanisms, and growth processes, including their impact on the aging of lithium-ion batteries. Several factors were mentioned here, such as the type of electrolyte, electrodes, and the working environment, concerning the stability of an SEI membrane. This paper also summarizes the characterization technique, which besides other things include X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and cyclic voltammetry (CV), for explaining the SEI films. This project will be aimed at the mitigation of these SEI formation and battery aging beyond the current state of the art to be able to increase further.

 View pdf
View pdf




