1. Introduction
The Janus particle emulsifier integrates the amphiphilic characteristics of molecular surfactants with the Pickering effect exhibited by homogeneous solid particles. This combination effectively stabilizes emulsification systems and offers novel means for manipulating, functionalizing, and delivering functional substances to interfaces. The utilization of Janus particle emulsifiers as a technique, with the application of soft material interface engineering, presents promising prospects for the integration of materials science with many disciplines. The optimization of Janus particles involves careful consideration of their composition, size, and microstructure. Various preparation techniques can yield a wide range of structures for Janus materials. These structures include asymmetric spherical and one-dimensional fibrous shapes, two-dimensional disc and sheet shapes, three-dimensional snowman and dumbbell shapes, as well as asymmetric hollow spherical shapes within and outside the shell [1]. The presence of a gap between Janus nanoparticles positioned at the interface of oil and water acts as a conduit for the movement of materials in a two-phase system. This unique characteristic, coupled with the smaller size, increased number of layers, and finer structure of Janus nanoparticles, is expected to exert a substantial influence on interfacial catalysis. Janus materials have demonstrated promising potential in several applications such as emulsification, encapsulation, catalysis, drug delivery, battery separators, and the fabrication of superstructure materials [2-4]. This study employs the research methodologies of literature review and literature analysis to investigate the assembly of Janus nanoparticles at the Pickering emulsion interface. It aims to examine the characteristics of Janus particles and their potential applications across several domains, with the intention of offering valuable insights for this particular topic of study.
2. Introduction of Janus Particle and Pickering Emulsion
2.1. Janus Particle
The etymology of the term 'Janus' can be traced back to the ancient Roman deity known as Janus. Janus is a unique example of an asymmetric composite functional material that manifests on particles possessing distinct chemical or polar properties. Janus materials exhibit a distinct spatial zoning, wherein they consist of two components possessing contrasting features such as hydrophilic/hydrophobic, polar/nonpolar, positive/negative charges, among others [3-4]. Janus nanoparticles possess the ability to incorporate diverse components with contrasting properties, owing to their heterogeneous structure. Consequently, they can exhibit the distinct characteristics of both materials concurrently. As an illustration, it is possible for Janus particles to possess a composition wherein fifty percent of their surface is composed of hydrophilic groups, while the remaining fifty percent is composed of hydrophobic groups. Additionally, these particles may exhibit a dual-colored surface, with the option of either fluorescence or magnetism. These particles possess distinct characteristics that are associated with their asymmetrical structure or functionalization [1, 4]. The Janus particle emulsifier is a notable example that integrates the advantageous characteristics of solid particles and the amphiphilic capabilities of molecular surfactants. This combination enables the Janus particle emulsifier to fulfill a distinctive function in interface engineering and various other domains [2].
2.2. Pickering emission
A "Pickering emulsion" is a emulsion stabilized by solid particles. Ramsden discovered that colloidal particles might stabilize emulsions without surfactants in the early 20th century. After a thorough research, Pickering named the emulsion system the "Pickering emulsion" due to its solid particle stability [5]. The consensus is that Pickering emulsion stabilizes by adsorbing solid particles at the oil-water interface under particular wettability conditions. These particles reorganize due to contact forces, forming a three-dimensional barrier that prevents liquid droplets from draining and rupturing. Single-layer and multi-layer films with solid particles stabilize emulsion [5]. Pickering emulsifiers stabilize emulsion. Traditional emulsions utilize emulsifiers to stabilize water or oil droplets in a continuous oil or water phase because these components are incompatible. Compared with the traditional emulsion stabilized by surfactant, Pickering emulsion has unique advantages: 1) environmentally friendly, less toxic than organic surfactant; 2) Cost saving can reduce the amount of expensive emulsifier: 3) emulsion has good stability [4]. Therefore, Pickering emulsion has broad application prospects in cosmetics, biological food, medicine, agriculture, petroleum and other fields.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest among scholars in utilizing the distinctive properties of Pickering emulsion to fabricate particles with diverse architectures by employing Pickering emulsion drops as templates. This method involves the selection of various solid particles as stabilizers for Pickering emulsions, with the incorporation of functional monomers into either the internal or continuous phase of the emulsion. Upon the initiation of polymerization, it becomes possible to combine solid particles possessing unique characteristics with functional polymers. This process allows for the preparation of organic-inorganic composites that exhibit distinct properties and structures, hence catering to the specific requirements of practical applications [4, 5].
2.3. Preparation of Janus particles by Pickering emulsion polymerization
The complexity of Janus material structure determines the particularity of its preparation method. A series of Janus material preparation methods have been developed around key issues such as component composition, size and morphology control, and localized functionalization modification, such as interface selective protection method, phase separation, microfluidic control, self-assembly, etc. [2, 3, 6], as shown in Figure 1. The interface protection approach exhibits a high degree of universality, as it is both straightforward and efficient in correctly managing the Janus structure. However, it should be noted that the yield of this method is significantly lower. The diversity in composition and morphology in Janus materials synthesized under microfluidic control is well-documented. However, it is worth noting that achieving precise control over their size at extremely small scales remains a challenge. While self-assembly is a viable method for fabricating nanoscale Janus materials and offers the ability to manipulate intricate and sophisticated structures, its compositional range is constrained. The phase separation approach offers convenient regulation and essential assurances for the industrial-scale manufacturing of Janus particles; yet, its precision is rather limited. Materials derived from various preparation methods exhibit a wide range of structures, including asymmetrical spherical, one-dimensional fibrous, two-dimensional disc and sheet-shaped, three-dimensional snowman and dumbbell-shaped, as well as asymmetrical hollow spherical structures both inside and outside the shell [2].
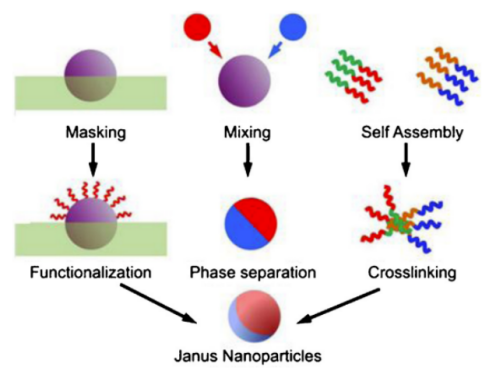
Figure 1. Some commonly used methods for preparing Janus particles [6].
The technique of topological selective surface modification, specifically the selective protection method, involves the utilization of the emulsion polymerization method. This method entails the use of a Pickering emulsion template to create diverse functional materials. The stable adsorption of solid particles on the oil/water interface is leveraged to selectively modify the exposed side of the material, which is immobilized on a plane. This precise modification process enables the accurate preparation of Janus particles, wherein each side of the particles possesses distinct properties [3]. The Pickering emulsion polymerization technique is widely employed as a synthetic method for the creation of Janus nanomaterials. This approach has several benefits in terms of size regulation, surface customization, and large-scale manufacturing. Additionally, it enables a wider range of localized modification reactions due to the disparity between the two mediums [5-7]. The preparation principle is shown in Figure 1. Inorganic particles form a monolayer at the interface between liquid phases 1 and 2 as Pickering emulsifiers. Approximately half of the inorganic particles immobilize in liquid phase 2. The liquid phase 1 component is chemically modified. Liquid phase 1 is the aqueous phase, while liquid phase 2 is the oil phase, which may contain paraffin or polymers. To obtain Janus particles, the oil phase component is dissolved and separated by a solvent. In another method, Janus composite particles can be made by polymerizing Janus particles. Based on liquid phase 2 and oil phase monomer, Pickering emulsion polymerization may generate Janus nanomaterials utilizing paraffin or polymer interfacial modification [3, 6-7].
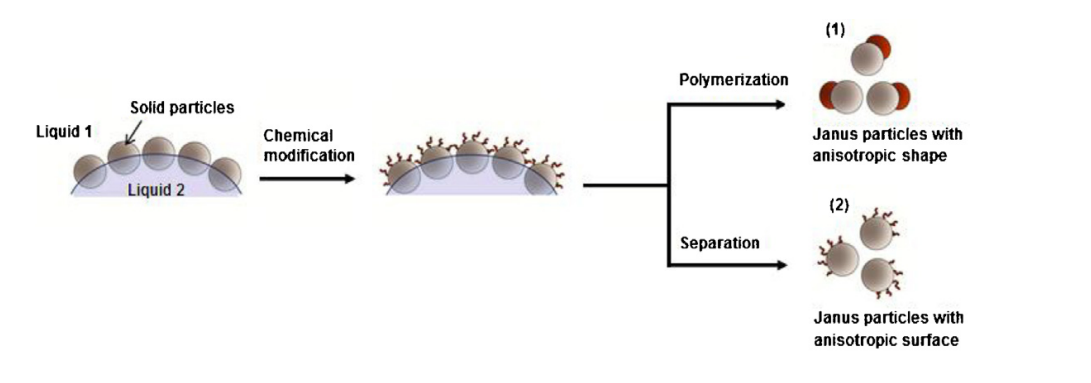
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the Janus nanoparticles prepared by Picking emission polymerization [6].
The paraffin interface modification method is based on the different states of paraffin at different temperatures. Firstly, the paraffin is made into a molten state, and the paraffin is dispersed through the emulsification of nanoparticles. Then, the temperature is changed to solidify the paraffin. This is beneficial for fixing and modifying the nanoparticles on the surface of the paraffin, mainly by changing the solvent to modify the particles adsorbed on the paraffin surface, resulting in Janus nanomaterials [3,6]. An O/W emulsion is produced by combining \( {SiO_{2}} \) dispersed in molten paraffin with water using high-speed emulsification. Once the system through a slow cooling process, the solid paraffin particles that are incorporated with \( {SiO_{2}} \) become disseminated within a methanol solution containing a modifier for the purpose of modification. Subsequently, the paraffin dissolves, resulting in the formation of Janus \( {SiO_{2}} \) particles. In the context of employing a paraffin water system, it is seen that solely inorganic nanoparticles undergo monolayer dispersion on the paraffin surface. This arrangement guarantees that half of the inorganic particles are shielded by the paraffin, while the remaining half are exposed to the solvent for subsequent modification. The achievement of monolayer dispersion is greatly influenced by the size of inorganic nanoparticles in this particular method. Nevertheless, the presence of inorganic nanoparticles often leads to self-aggregation and the formation of bigger aggregates, which can be attributed to their high surface free energy. Consequently, these aggregates exhibit enhanced stability. Rutong Song, a researcher from Southwest Petroleum University, conducted a study in which Janus \( {SiO_{2}} \) particles were synthesized through the utilization of a paraffin water interface [8]. When the diameter of \( {SiO_{2}} \) particles exceeds 100 nm, they exhibit the ability to build a homogeneous monolayer on the solid paraffin substrate. In the context of the paraffin water system, the presence of nanoparticles of insufficient size tends to result in the formation of aggregates, impeding their dispersion in a monolayer. Consequently, the preparation of Janus particles using this approach becomes challenging, particularly when smaller particles are involved [3, 6]. This particular approach possesses distinct advantages in effectively immobilizing particles in suitable places and preventing rotational movement of particles at the interface. The immobilization of particles also offers significant advantages in terms of particle separation and purification.
A polymer emulsion with a coating is created using inorganic particles as stabilizers to change the polymer interface. This embeds inorganic particles on polymers. After that, atom transfer radical polymerization modifies inorganic particles at the liquid/liquid interface. Finally, a solvent dissolves the polymer to create Janus particles. Polymer interface protection is better than paraffin interface protection for tiny Janus particles [3, 9]. The Pickering emulsion method for polymer interface modification uses immobilized modified silica particles as stabilizers. Monomers on opposite sides of silica nanoparticles can be bonded to Janus particles in one step. The stability of the preparation process of Janus particles is enhanced due to the amphiphilic and thermodynamic stability of the modified silica particles. The field of study known as Polymer Materials Science and Engineering focuses on the scientific and engineering principles related to polymers. The \( {SiO_{2}} \) vinyl acetate composite particles were generated by Thomas et al. by the process of Pickering emulsion polymerization [9]. As shown in Figure 4, the ATRP initiator was grafted onto \( {SiO_{2}} \) of polymer latex particles, which were removed from the polymer latex particles with acetone. Then, N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (PDMAEMA) with dual temperature and pH responsiveness was grafted onto the ATRP initiator to form polymer/ \( {SiO_{2}} \) Janus particles with dual responsive half crown, resulting in 30 nm Janus \( {SiO_{2}} \) particles [3, 9].
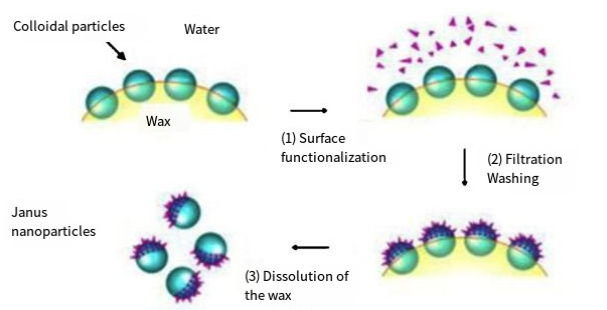
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the Janus nanoparticles by advertisement on the interface of water and water [6].
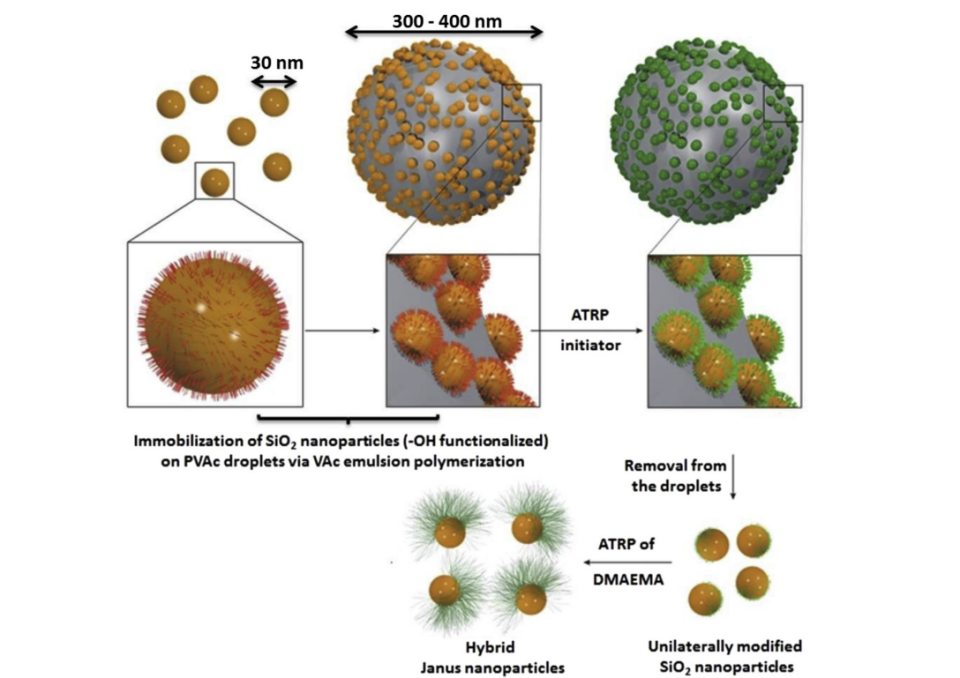
Figure 4. Synthesis of the \( {SiO_{2}} \) /PDMAEMA hybrid Janus nanoparticles by polymer interface modification [3, 9].
3. Prospects for the Preparation and Assembly of Janus Nanoparticles
The Janus particle emulsifier integrates the amphiphilic characteristics of molecular surfactants with the Pickering effect exhibited by homogeneous solid particles. This combination effectively stabilizes emulsification systems and offers novel means for manipulating interfaces, functionalizing them, and facilitating the delivery of functional substances to these interfaces. In recent times, there has been significant progress in the manufacturing of functional Janus colloids on a broad scale. This development has created opportunities for their utilization in various practical domains, including the effective treatment of petroleum effluent in the oil extraction and refining sectors. In the future, the integration of flexible polymer single chains with functional nanoparticles is anticipated to yield a novel and significant Janus structure, known as Janus nanoparticles. The authors propose the provision of a novel platform that can facilitate advancements in various fields such as material creation, energy generation, environmental remediation, and even biological diagnostics and therapeutics [2, 4].
Currently, the assembly of nanoparticles is primarily constrained to Pickering emulsions or basic interfacial assembly. However, there is a dearth of study on the assembly of particles on densely populated interfaces or inside three-dimensional systems. In recent years, the field of nanotechnology has witnessed significant advancements, leading to the successful synthesis of several nanoparticle variants, including Janus particles, nanorods, and nanowires. The particles have the ability to assemble and create multi-level ordered structures at the interface due to the interaction forces present, including van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, and capillary forces. These structures hold promise for applications in the development of optical, acoustic, electrical, and magnetic materials. Nevertheless, additional enhancements are required in the realm of nanoparticle assembly research. The precise manipulation of multi-level assembly dynamics in nanoparticles emerges as a key challenge in the fabrication of high-quality multi-level assemblies [2-3].
4. Conclusion
Janus particles have garnered significant attention in recent times. This paper provides a summary of the preparation methods of Janus particles in Pickering emulsion and the characteristics of their products, focusing on their high efficiency in stabilizing emulsion. Additionally, it analyzes the applications and prospects of Janus particles in the field of interface engineering, specifically in regulating emulsification behavior, constructing complex structure materials, and catalyzing interfaces. Nevertheless, this article exhibits certain limitations, including inadequate exploration of the distinct characteristics of particles generated through the selection of diverse raw materials during the preparation of Janus particles. Additionally, there is a lack of discussion regarding certain methodologies employed in the preparation of Janus particles. In future investigations, there will be a deliberate focus on the selection of experimental materials that possess distinct properties, with the aim of enhancing the understanding and application of nanoparticle assemblies. This will involve a comprehensive analysis and synthesis of the unique characteristics of these materials, thereby contributing to the advancement of research in this field. Currently, the assembly of nanoparticles is predominantly constrained to Pickering emulsions or basic interfacial assembly methods. However, there is a dearth of study on the assembly of particles on densely populated interfaces or within three-dimensional systems. In recent years, the field of nanotechnology has witnessed significant advancements, leading to the successful synthesis of many types and architectures of nanoparticles. The assembly of particles at the interface is facilitated by various interaction forces, including van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, and capillary forces. This phenomenon leads to the formation of multi-level ordered structures at the interface, which holds significant potential for the development of optical, acoustic, electrical, and magnetic materials.
References
[1]. Zhou Peng, et al. Preparation and Structural Regulation of Janus nanomaterials. Journal of Chemistry of China University, 2015, 36(7): 1431-1436.
[2]. Sun D Y, Ye Y L, Liang F X, & Yang Z Z. Research progress of Janus granular emulsifiers. Acta Chemologica Sinica, 2021, 72(12): 6203-6215.
[3]. Gao Dangge, et al. Research progress on controllable preparation of Janus nanomaterials. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering 1, 2019.
[4]. Su, Haiyang, et al. "Janus particles: design, preparation, andbiomedical applications." Materials today bio 4 (2019):100033.
[5]. Gao Dang Ge, Duan Xiying, Lv Bin, & Ma Jianzhong. (2015). Progress on stabilizing Pickering emulsion with nano-SiO_2. Printing and dyeing, (4), 50-54.
[6]. LESOIN, L., et al. "Colloids and Surfaces A: Physico-Chemical and Engineering Aspects." (2011): 1.
[7]. Han Xiao. Preparation of silica Janus flake material and its application in polymers. MS Thesis Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[8]. Song R T.Synthesis of Janus partides and study of their fluid properties[D].Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2014.
[9]. Ruhland, T. M., McKenzie, H. S., Skelhon, T. S., Bon, S. A., Walther, A., & Müller, A.H.(2015). Nanoscale hybrid silica/polymer Janus particles with a double-responsive hemicorona. Polymer, 79, 299-308.
Cite this article
Ding,Y. (2024). Preparation and properties of Janus nanoparticles at pickering emulsion interface. Applied and Computational Engineering,56,167-173.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhou Peng, et al. Preparation and Structural Regulation of Janus nanomaterials. Journal of Chemistry of China University, 2015, 36(7): 1431-1436.
[2]. Sun D Y, Ye Y L, Liang F X, & Yang Z Z. Research progress of Janus granular emulsifiers. Acta Chemologica Sinica, 2021, 72(12): 6203-6215.
[3]. Gao Dangge, et al. Research progress on controllable preparation of Janus nanomaterials. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering 1, 2019.
[4]. Su, Haiyang, et al. "Janus particles: design, preparation, andbiomedical applications." Materials today bio 4 (2019):100033.
[5]. Gao Dang Ge, Duan Xiying, Lv Bin, & Ma Jianzhong. (2015). Progress on stabilizing Pickering emulsion with nano-SiO_2. Printing and dyeing, (4), 50-54.
[6]. LESOIN, L., et al. "Colloids and Surfaces A: Physico-Chemical and Engineering Aspects." (2011): 1.
[7]. Han Xiao. Preparation of silica Janus flake material and its application in polymers. MS Thesis Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[8]. Song R T.Synthesis of Janus partides and study of their fluid properties[D].Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2014.
[9]. Ruhland, T. M., McKenzie, H. S., Skelhon, T. S., Bon, S. A., Walther, A., & Müller, A.H.(2015). Nanoscale hybrid silica/polymer Janus particles with a double-responsive hemicorona. Polymer, 79, 299-308.









