1. Introduction
The origins of iot monitoring and control technology can be traced back to the 1980s, when remote monitoring and control systems began to appear in the field of industrial automation. With the development of computer and communication technology, people began to try to connect sensors and actuators with the network to achieve remote monitoring and control. [1] In 1999, an MIT study first proposed the concept of the "Internet of Things," meaning that objects can be connected and communicated with each other through a network, enabling information sharing and intelligent control. Since then, Internet of Things monitoring and control technology has gradually become a research hotspot in industry, agriculture, health and other fields.[2] In recent years, with the continuous maturity of Internet of Things technology and driven by relevant national policies, a large number of innovative applications in the Internet of Things industry have been rapidly developed. From the explosive growth of consumer smart homes and smart items to the continuous innovation of enterprise in intelligent manufacturing, intelligent transportation, public safety and medical fields, the market size of the entire Internet of Things is expanding rapidly. However, the ensuing problem is that more and more Internet of Things information security incidents are frequent.
2. Related work
2.1. Application of edge computing in iot monitoring and control
Edge computing (also known as Edge computing) is a distributed computing architecture that moves the processing of applications, data, and services from the central node of the network to the logical edge nodes of the network. The "edge" is defined as any compute and network resource along the path between [3] the data source and the cloud data center. The basic principle of edge computing is that the computation should occur in close proximity to the data source for processing. In many cases, edge computing is more efficient than cloud computing for some computing services. By moving critical data processing functions to the edge of the network or near the source of the data, edge computing can help connected devices maintain the same level of efficiency even when the network connection is poor.
2.2. Application Research and Practical Cases
In the dynamic landscape of IoT monitoring and control, the convergence of machine learning techniques has emerged as a catalyst for transformative innovation. Here, we explore the dual facets of application research and practical cases, showcasing the symbiotic relationship between machine learning and intelligent IoT systems:
(1) Data Analysis and Predictive Maintenance
Machine learning algorithms empower IoT systems to extract actionable insights from vast datasets, enabling advanced data analysis. Key techniques include:
\( \sum i=1k\sum x∈{S_{i}}\\\\x-ui\\\\\frac{2}{2} \) (1)
Anomaly Detection: p(x)<ϵ
Research demonstrates the efficacy of these algorithms in identifying patterns and anomalies, optimizing system performance, and facilitating predictive maintenance strategies.
(2) Energy Optimization and Fault Detection:
Machine learning enhances energy optimization efforts by analyzing consumption patterns and dynamically adjusting resource allocation in IoT-enabled systems. Key formulas include:
\( \check{y} \) =f(x) (2)
(3) Resource Allocation:
\( \sum \frac{n}{i=1}{ω_{i}}{x_{i}} \) (3)
Real-time fault detection and diagnosis benefit from machine learning algorithms, ensuring system reliability and uptime through prompt remedial actions.
3. Application research and practical cases
3.1. Data Analysis and Predictive Maintenance
Machine learning can make real-time predictions. Through the Internet of Things and clustering algorithms, we can monitor and optimize production processes to ensure the safety of workers in dangerous areas. For example, consider the production process of a chemical plant. Data collected using iot sensors, such as temperature, pressure, and chemical concentrations, can be fed into a clustering algorithm for analysis. [4] By clustering historical and current data, potential production risks can be predicted and timely measures can be taken to avoid accidents. The combination of iot and clustering algorithms helps to achieve effective risk management. Clustering algorithms can use past data to predict a risk and automatically react to that risk.
3.2. Introduction to Experimental Framework: IoT and Clustering Algorithms
To validate the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms in IoT environments, experimental frameworks are essential. In this section, we introduce the experimental setup focusing on IoT and clustering algorithms. Machine learning relies on data, which spans various types, including numerical, visual, or textual data such as sensor data, images, or textual records. This section outlines the data collection and preparation process for training machine learning models in our experimental setup.
3.3. Energy Optimization and Fault Detection
In the Internet of Things (IoT) environment, real-time fault detection and diagnosis is a key component to ensuring system reliability and continuous operation. [5] This data includes equipment status, sensor readings, environmental conditions, and more. Machine learning algorithms are applied to this data to identify abnormal patterns and potential signals of failure. Troubleshooting typically involves the following key steps: 1) Feature extraction and selection: Fault related features are extracted from the monitored data. 2) Pattern recognition and classification: Machine learning algorithms are used to analyze and classify the extracted features to identify different types of failure modes. [6] 3) Fault location and reasoning: Based on the identified fault mode, infer the possible fault location and cause. 4) Corrective actions and feedback: Take appropriate corrective actions based on the diagnosis result, such as repairing the device, replacing parts, or adjusting the system configuration. In summary, by harnessing the power of connected devices, advanced analytics, and machine learning, businesses can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in today's dynamic market landscape.
4. Experiment methodology and results
4.1. IoTEnsemble: Machine learning-based iot attack detection
Based on the clustering results, it can profile the traffic pattern of each device behavior separately, thus effectively reducing the dependence on the generalization of a single model.[7] In the experimental phase, the researchers examined a 57.1 gigabyte iot traffic dataset spanning nine months and a rich malicious traffic dataset. The results show that IoTEnsemble can detect multiple botnet malware and cyberattacks more effectively than existing solutions in today's intelligent and functional iot environments. Compared to other methods, IoTEnsemble demonstrated higher accuracy and recall rates in this case, as well as better F1 values. As a result, IoTEnsemble has shown significant advantages in detecting malicious behavior based on common protocols, providing a reliable solution for countering cybersecurity threats.
4.2. Traffic activities implement clustering
The ultimate goal of the activity clustering method proposed in this paper is to aggregate the traffic used for the same activity so that each sub-model in the integrated model learns the traffic model of a single activity. The algorithm needs to meet three design goals: 1) [8] good interpretability, which can be understood by network administrators; 2) as little prior knowledge as possible, such as the number of protocols or activities used by the device; 3) Appropriate clustering granularity to ensure the correctness of clustering while using as few clusters as possible.
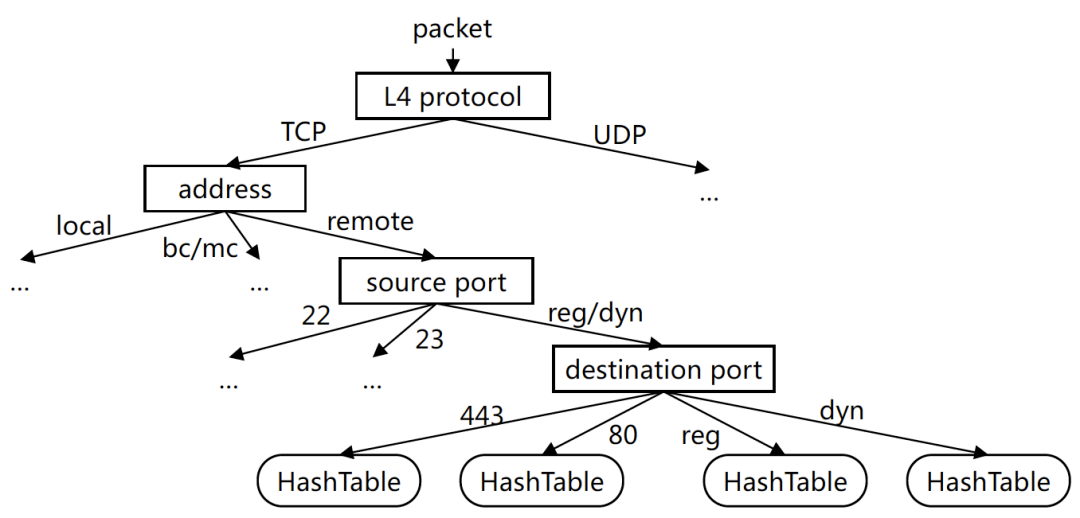
Figure 1. Activity clustering based on tree structure; bc/mc
An Internet of Things behavior clustering method based on tree structure is proposed (as shown in Figure 1). First, a packet from the bidirectional stream quintuple f=(device-IP, dst-domain/IP, src-port, dst-port, protocol) is initially clustered using four-level rules:
• L4 protocol: TCP or UDP;
• Address: dst-domain/IP is a resolved domain name, remote IP address, local IP address, or broadcast/multicast address;
• src-port: a system port number or a registered port or dynamic port number range;
• dst-port: indicates a system port number, registered port number range or dynamic port number range.
Since the iot device is generally on the client side, the source port number is often not helpful for clustering (unless it is a system port such as 22, 23 for SSH, Telnet), but the destination port in the registered port number range can still represent some common iot services, such as SSDP (1900), STUN (3478), etc. At the end of the tree structure, each leaf node contains a hash table, whose key value IS a bidirectional stream quintuple f, whose value is an incremental statistical structure IS=(Nin, Nout, Tin, Tout, S), where [9]N represents the number of packets, Trepresents the sum of packet arrival intervals, in and out represent the direction, and so on. S represents the set of package sizes. No matter how many packets a stream has, this structure can be maintained at a constant level of storage complexity.
4.3. Model construction
IoTEnsemble has two detection stages:
1. Rule matching: Using active key values can quickly filter out highly abnormal traffic, such as connections with unknown domain names and unknown protocols;
2. Integrated model: Learn traffic patterns for each activity and detect abnormal traffic by identifying deviations from normal patterns.
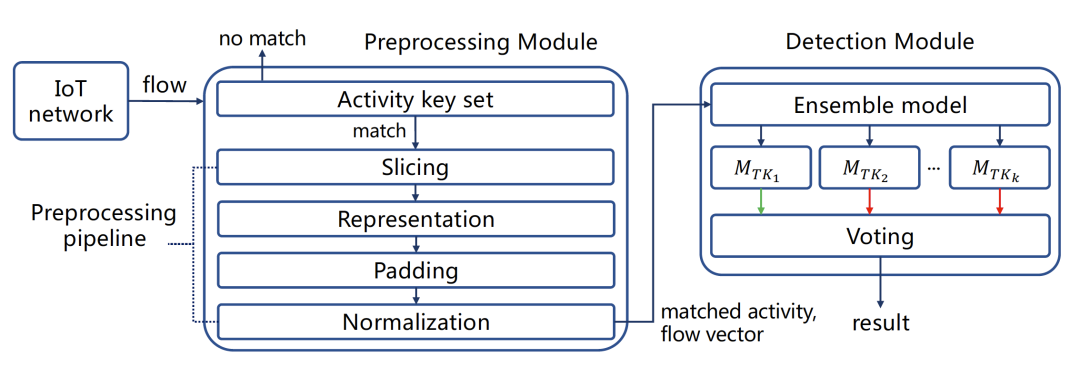
Figure 2. IoTEnsemble overall architecture
Figure 2 shows the overall structure of IoTEnsemble. The pre-processing module first receives iot traffic and uses a quintuple to match the set of active key values obtained through the clustering tree. Since the clustering tree algorithm results in an abstract plan (such as domain names containing wildcards, "reg/dyn" port number ranges, etc.), the matching is a fuzzy matching process, which reduces the possibility of false positives. [10] The pipeline includes four steps: segmentation, characterization, filling and normalization, and finally a sequence feature vector is constructed using the IP packet length and arrival time interval of the first r packets of a quintuple.
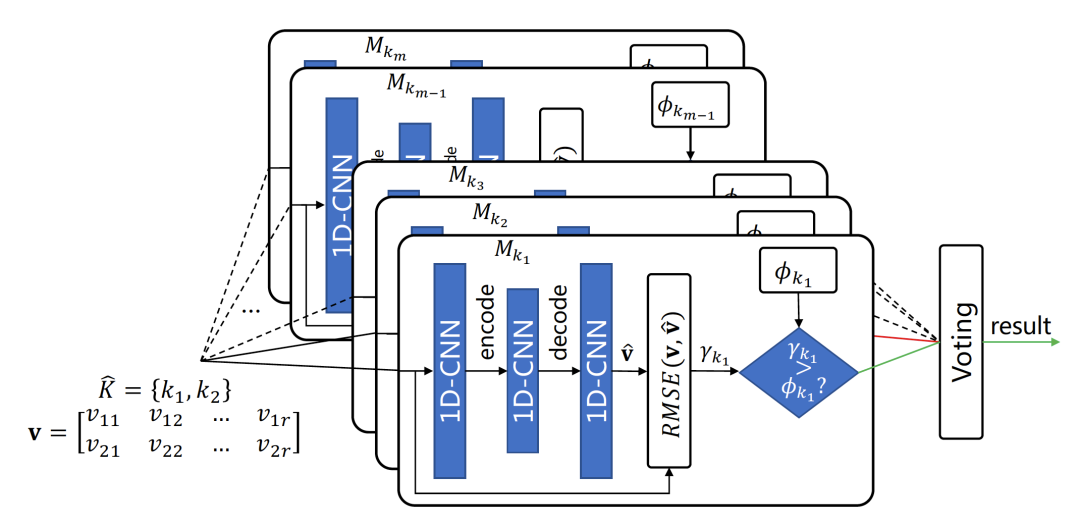
Figure 3. Detection module based on ensemble learning
The detection module consists of multiple unsupervised learning submodels, each learning traffic patterns independently (Figure 3). Benefits include no need for malicious traffic during training and the ability to detect zero-day attacks. Submodels employ 1D convolutional neural network autoencoders to learn data representation implicitly. During detection, higher reconstruction errors indicate non-conforming data, triggering detection.
4.4. Verification result
Six existing NADS were used as baselines to compare the abnormal traffic detection capabilities of the IoTEnsemble framework, including Kitsune, the SOTA solution published in NDSS. IoTEnsemble achieves better detection effect than other schemes for most attack categories. In contrast, Kitsune's performance on some of the more complex devices, such as cameras and audio, became significantly worse, while IoTEnsemble's detection ability was barely affected.
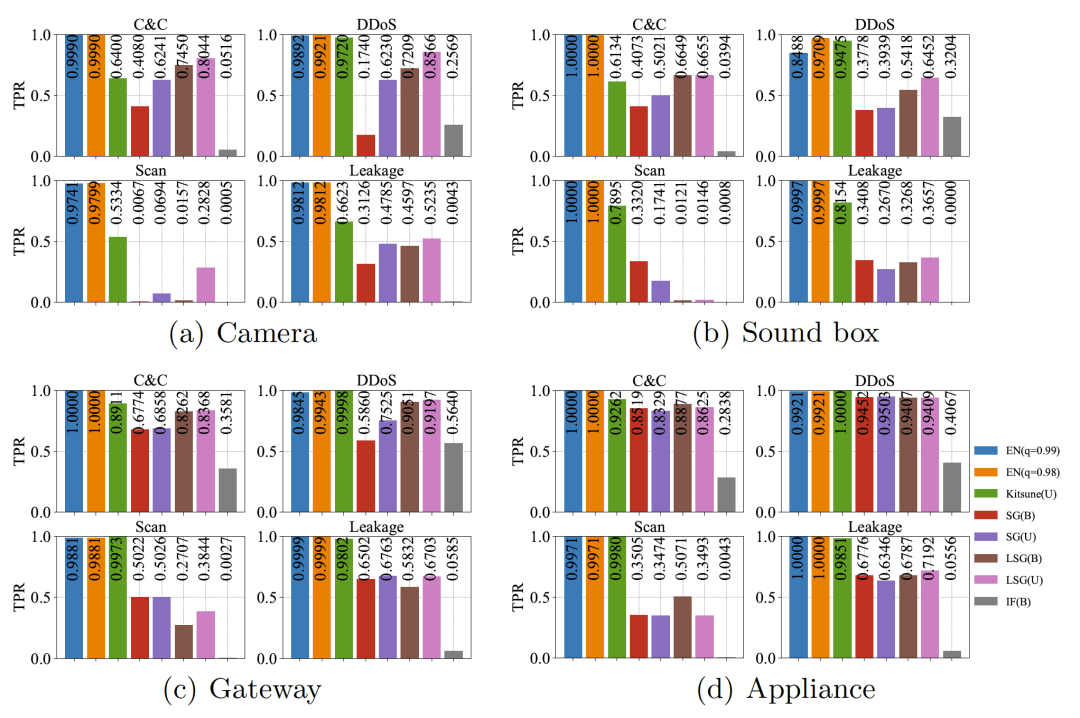
Figure 4. Comparison of IoTEnsemble and five baseline NADS
It can be seen from the results in FIG.4 that in machine learn-based iot fault detection, malware can evolve to use common protocols such as [11] HTTP to disguise its C&C channel. The experimental results show that IoTEnsemble achieves leading detection against multiple attacks regardless of the amount of activity in the iot network. This may be attributed to IoTEnsemble's integrated model and active clustering algorithm, which are able to more effectively capture the characteristics and patterns of different attack behaviors, thus improving the accuracy and comprehensiveness of detection.
5. Conclusion
To sum up, this experiment adopts advanced machine learning algorithm and network security technology, designs an anomaly detection system based on IoTEnsemble framework, and verifies it in a real IoT environment. The experimental results show that IoTEnsemble has significant performance advantages in detecting a variety of network attacks and malicious activities, showing higher detection accuracy and robustness compared to existing schemes. This achievement is not only of great significance for improving the level of IoT network security, but also provides useful reference and reference for the research and practice in related fields. From the point of view that iot and cloud computing continue to generate large amounts of data, this paper discusses the application of edge computing as a distributed computing architecture, and the role of machine learning in data analysis and fault detection. By combining iot with edge computing, latency can be reduced, efficiency improved, and security enhanced, thereby driving the development of intelligent systems.
References
[1]. Juan Emilio Zurita Macias,and Sergio Trilles. "Machine learning-based prediction model for battery levels in IoT devices using meteorological variables." Internet of Things 25. (2024):
[2]. Lucia Arnau Muñoz, et al. "Anomaly detection system for data quality assurance in IoT infrastructures based on machine learning." Internet of Things 25. (2024):
[3]. Zheng, Jiajian, et al. "The Random Forest Model for Analyzing and Forecasting the US Stock Market in the Context of Smart Finance." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.17194 (2024).
[4]. Yang, Le, et al. "AI-Driven Anonymization: Protecting Personal Data Privacy While Leveraging Machine Learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.17191 (2024).
[5]. Cheng, Qishuo, et al. "Optimizing Portfolio Management and Risk Assessment in Digital Assets Using Deep Learning for Predictive Analysis." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15994 (2024).
[6]. “The Application of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnostics: A New Frontier”. Academic Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 8, no. 2, Dec. 2023, pp. 57-61, https://doi.org/10.54097/ajst.v8i2.14945.
[7]. Zouhair LAKHYAR,and Ghizlane BAOUSSY. "Advances in the IoT and Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review of Current Approaches and Implications for Patient-Centered Healthcare Management." Journal of Research in Science and Engineering 6. 1 (2024):
[8]. Garcés-Jiménez Alberto, et al. "Industrial Internet of Things embedded devices fault detection and classification. A case study." Internet of Things 25. (2024):
[9]. Su, Jing, et al. "Large Language Models for Forecasting and Anomaly Detection: A Systematic Literature Review." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.10350 (2024).
[10]. Wang, Yong, et al. "Construction and application of artificial intelligence crowdsourcing map based on multi-track GPS data." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15796 (2024).
[11]. Padhi Shridhar, et al. "IoT Based Condition Monitoring for Railway Track Fault Detection in Smart Cities." IETE Journal of Research 69.9 (2023):
Cite this article
Li,H.;Wang,X.;Feng,Y.;Qi,Y.;Tian,J. (2024). Driving intelligent IoT monitoring and control through cloud computing and machine learning. Applied and Computational Engineering,64,75-80.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Juan Emilio Zurita Macias,and Sergio Trilles. "Machine learning-based prediction model for battery levels in IoT devices using meteorological variables." Internet of Things 25. (2024):
[2]. Lucia Arnau Muñoz, et al. "Anomaly detection system for data quality assurance in IoT infrastructures based on machine learning." Internet of Things 25. (2024):
[3]. Zheng, Jiajian, et al. "The Random Forest Model for Analyzing and Forecasting the US Stock Market in the Context of Smart Finance." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.17194 (2024).
[4]. Yang, Le, et al. "AI-Driven Anonymization: Protecting Personal Data Privacy While Leveraging Machine Learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.17191 (2024).
[5]. Cheng, Qishuo, et al. "Optimizing Portfolio Management and Risk Assessment in Digital Assets Using Deep Learning for Predictive Analysis." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15994 (2024).
[6]. “The Application of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnostics: A New Frontier”. Academic Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 8, no. 2, Dec. 2023, pp. 57-61, https://doi.org/10.54097/ajst.v8i2.14945.
[7]. Zouhair LAKHYAR,and Ghizlane BAOUSSY. "Advances in the IoT and Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review of Current Approaches and Implications for Patient-Centered Healthcare Management." Journal of Research in Science and Engineering 6. 1 (2024):
[8]. Garcés-Jiménez Alberto, et al. "Industrial Internet of Things embedded devices fault detection and classification. A case study." Internet of Things 25. (2024):
[9]. Su, Jing, et al. "Large Language Models for Forecasting and Anomaly Detection: A Systematic Literature Review." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.10350 (2024).
[10]. Wang, Yong, et al. "Construction and application of artificial intelligence crowdsourcing map based on multi-track GPS data." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15796 (2024).
[11]. Padhi Shridhar, et al. "IoT Based Condition Monitoring for Railway Track Fault Detection in Smart Cities." IETE Journal of Research 69.9 (2023):









