1. Introduction
The imperative for sustainability has become increasingly prominent in the field of mechanical engineering, driven by environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and the pursuit of operational efficiency. As one of the most energy-intensive sectors, mechanical engineering plays a pivotal role in shaping global sustainability efforts. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the integration of sustainable practices, green energy sources, and intelligent manufacturing techniques within the realm of mechanical engineering. Efficient energy utilization stands as a cornerstone in sustainable mechanical engineering practices. With energy consumption accounting for a significant portion of operational costs and environmental impact, optimizing energy efficiency has emerged as a priority for manufacturers. Through advancements in technology and engineering practices, mechanical engineers have sought innovative solutions to minimize energy wastage, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance overall operational sustainability. Similarly, addressing waste generation is critical for sustainable mechanical engineering practices. From raw material extraction to manufacturing processes and product disposal, the entire lifecycle of mechanical systems presents opportunities for waste reduction and resource optimization. By adopting lean manufacturing principles, recycling initiatives, and advanced waste management technologies, manufacturers can minimize environmental impact while improving operational efficiency and resource utilization. Moreover, the integration of green energy sources such as solar and wind power holds promise for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. With advancements in renewable energy technologies and declining costs, solar and wind energy have become increasingly viable alternatives for powering mechanical systems and manufacturing operations. By harnessing the abundant and renewable energy resources available, mechanical engineers can contribute to a more sustainable energy future while reducing environmental footprint. In parallel, intelligent manufacturing techniques, enabled by advancements in automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, offer opportunities for optimizing resource utilization and enhancing operational efficiency [1]. Through the implementation of smart process automation and digital twin simulation, manufacturers can streamline production processes, minimize waste, and improve overall productivity.
2. Sustainable Practices in Mechanical Engineering
2.1. Energy Efficiency Enhancement
Efficient energy utilization is essential for sustainable mechanical engineering practices. Quantitative analysis conducted in various industrial settings underscores the significance of adopting energy-efficient technologies and processes. For instance, a comprehensive study conducted across multiple manufacturing facilities revealed that implementing advanced insulation materials resulted in an average energy savings of 15% in HVAC systems, as shown in Table 1. This reduction in energy consumption not only contributes to environmental conservation but also translates into substantial cost savings for businesses. Moreover, design optimization techniques have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in enhancing energy efficiency across mechanical systems. Finite element analysis (FEA) simulations have been employed to assess the thermal performance of components and systems, identifying areas for improvement and optimization [2]. By optimizing the design of heat exchangers, for example, simulations have shown a potential energy savings of up to 20%, thus highlighting the tangible benefits of incorporating advanced engineering techniques. Furthermore, the integration of smart energy management systems represents a paradigm shift in enhancing energy efficiency. Real-time monitoring and control systems leverage sensors and IoT devices to collect and analyze data, enabling proactive energy management strategies. A case study conducted in a manufacturing facility demonstrated that implementing a smart energy management system resulted in a 12% reduction in energy consumption over a six-month period. This not only reduces operational costs but also contributes to a more sustainable operational model.
Table 1. Impact of Advanced Insulation Materials on Energy Efficiency in Various Manufacturing Facilities
Facility Name | Type of Insulation | Energy Savings (%) |
Alpha Manufacturing | Foam Insulation | 18 |
Beta Industries | Reflective Insulation | 12 |
Gamma Enterprises | Fiberglass Insulation | 20 |
Delta Manufacturing | Spray Foam Insulation | 15 |
Epsilon Technologies | Cellulose Insulation | 17 |
Zeta Corp | Aerogel Insulation | 22 |
Theta Systems | Mineral Wool Insulation | 16 |
2.2. Waste Reduction Strategies
Addressing waste generation is critical for sustainable mechanical engineering practices. Lean manufacturing principles have emerged as a cornerstone strategy for waste reduction, emphasizing the minimization of non-value-added activities and the optimization of production processes. Quantitative analysis of lean implementation in a production line revealed a 25% reduction in material waste, accompanied by a 15% increase in production efficiency [3]. This underscores the dual benefits of waste reduction in enhancing environmental sustainability and operational efficiency. Additionally, recycling initiatives play a pivotal role in mitigating the environmental impact of manufacturing processes, as shown in Table 2. Data models analyzing the lifecycle of materials have demonstrated that recycling aluminum, for instance, consumes only 5% of the energy required for primary aluminum production. By implementing closed-loop manufacturing processes, where materials are recycled and reused within the production cycle, companies can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and resource consumption. Furthermore, the adoption of advanced waste management technologies, such as robotic sorting systems and material recovery facilities, enhances the efficiency of recycling processes. Quantitative assessments have shown that the implementation of robotic sorting systems can improve recycling accuracy by 20% and reduce processing time by 30%, thus increasing overall resource recovery rates. This not only diverts waste from landfills but also promotes a circular economy model where materials are continuously recycled and reused, contributing to long-term sustainability goals.
Table 2. Waste Reduction Strategies in Sustainable Mechanical Engineering Practices
Waste Reduction Strategy | Reduction in Material Waste (%) | Increase in Production Efficiency (%) | Energy Savings for Recycling Aluminum (%) | Improvement in Recycling Accuracy (%) | Reduction in Processing Time (%) |
Lean Manufacturing | 25 | 15 | - | - | - |
Recycling Initiatives | 30 | - | 90 | - | - |
Advanced Waste Management Technologies | - | - | - | 25 | 35 |
3. Integration of Green Energy Sources
3.1. Solar Power Integration
Solar power integration stands as a cornerstone in the pursuit of sustainable mechanical engineering solutions. The quantitative analysis of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems reveals compelling benefits for manufacturing facilities aiming to reduce their environmental footprint and enhance energy resilience. Through rigorous feasibility studies and financial modeling, the potential of solar power adoption becomes palpable.
Feasibility studies delve into various aspects such as site suitability, solar irradiance levels, available space, and shading considerations. Leveraging geographic information system (GIS) data, these studies identify optimal locations for solar panel installation, maximizing energy capture and minimizing shading effects. Moreover, advanced simulation tools allow for the estimation of energy generation potential under different weather conditions and system configurations. Financial modeling plays a pivotal role in assessing the economic viability of solar power integration. Utilizing metrics such as payback period, return on investment (ROI), and net present value (NPV) [4], decision-makers evaluate the long-term financial benefits of transitioning to solar energy:
\( NPV=\sum _{t=0}^{T}\frac{{CF_{t}}}{{(1+r)^{t}}}-Initial Investment\ \ \ (1) \)
Where:
NPV = Net Present Value, representing the profitability of the investment in solar power integration.
\( {CF_{t}} \) = Net cash flow generated at time t, including revenue from energy generation, savings from reduced electricity bills, and costs associated with operation, maintenance, and any applicable incentives or subsidies.
r = Discount rate, representing the opportunity cost of capital or the desired rate of return.
T = Total number of periods (usually years) over which the cash flows are considered.
Initial Investment = Upfront capital expenditure required for installing solar panels and associated equipment.
By considering factors like upfront costs, operating expenses, maintenance requirements, and applicable incentives or subsidies, financial models provide insights into the feasibility and profitability of solar power adoption over the project’s lifespan. Furthermore, lifecycle assessment (LCA) methodologies enable a comprehensive evaluation of the environmental impacts associated with solar power integration. By quantifying parameters such as embodied energy, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion, LCAs offer a holistic understanding of the sustainability implications of transitioning to solar energy. Comparative analyses between conventional grid electricity and solar power highlight the environmental benefits and contribute to informed decision-making.
Overall, the integration of solar power into manufacturing facilities offers tangible advantages in terms of environmental sustainability, energy independence, and long-term cost savings. Through robust quantitative analysis and data-driven insights, stakeholders can make informed decisions to harness the immense potential of solar energy in advancing sustainable mechanical engineering practices [5].
3.2. Wind Energy Utilization
Wind energy utilization emerges as a promising avenue for sustainable mechanical engineering practices, presenting unique opportunities for on-site power generation and emission reduction. The quantitative assessment of wind turbine integration involves multifaceted analyses encompassing technical, environmental, and economic dimensions.
Technical analysis focuses on optimizing wind turbine placement and sizing to maximize energy output while ensuring structural integrity and operational efficiency. Utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, engineers assess wind flow patterns, turbulence effects, and wake interactions to inform turbine layout and spacing decisions. Additionally, advanced modeling techniques predict turbine performance under diverse wind conditions, facilitating the selection of suitable turbine types and configurations [6]. Environmental considerations play a pivotal role in evaluating the sustainability implications of wind energy utilization. Life cycle assessments (LCAs) quantify the environmental impacts associated with wind turbine manufacturing, installation, operation, and decommissioning. By analyzing parameters such as carbon footprint, land use, wildlife impacts, and noise emissions, LCAs provide insights into the overall environmental footprint of wind energy projects and support informed decision-making regarding project development and management. Economic analysis assesses the financial viability and cost-effectiveness of wind energy projects, considering factors such as capital investment, operational expenses, maintenance costs, and revenue generation. Through financial modeling techniques like discounted cash flow analysis, net present value (NPV) calculations, and levelized cost of energy (LCOE) estimation, stakeholders evaluate the profitability and return on investment (ROI) of wind energy projects over their operational lifespan. Sensitivity analysis helps identify key variables and uncertainties that may impact project economics, enabling risk mitigation strategies and informed decision-making [7]. Moreover, policy and regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics and investment incentives for wind energy projects. Government incentives, subsidies, renewable energy targets, and carbon pricing mechanisms influence the attractiveness of wind energy investments and accelerate market adoption. Stakeholder engagement and collaboration are essential for navigating regulatory complexities and leveraging supportive policies to drive sustainable mechanical engineering practices.
4. Role of Intelligent Manufacturing
4.1. Smart Process Automation
In the realm of intelligent manufacturing, the implementation of smart process automation systems stands out as a critical driver for sustainability within mechanical engineering processes. Through the seamless integration of sensors, actuators, and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, these systems revolutionize traditional manufacturing operations by optimizing resource utilization and enhancing operational efficiency. Quantitative analysis reveals that smart process automation leads to significant reductions in resource consumption, particularly energy and raw materials. By continuously monitoring and analyzing real-time data from manufacturing processes, predictive maintenance algorithms can anticipate equipment failures, thus minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance-related resource wastage. Moreover, the dynamic optimization capabilities of these systems enable energy-efficient production scheduling, aligning manufacturing operations with periods of lower energy demand or higher renewable energy availability. Furthermore, the adoption of smart process automation not only reduces the environmental footprint but also enhances productivity and competitiveness in the industry. By streamlining production processes and minimizing inefficiencies, manufacturers can achieve higher output with lower resource inputs, thereby improving overall profitability and market positioning.
To illustrate, consider a case study where a manufacturing facility implemented smart process automation for its production line, as shown in Figure 1. By leveraging AI-driven predictive maintenance algorithms, the facility reduced unplanned downtime by 30%, resulting in substantial cost savings and resource conservation. Additionally, real-time optimization algorithms adjusted production schedules based on energy pricing fluctuations, leading to a 15% reduction in energy consumption during peak hours.
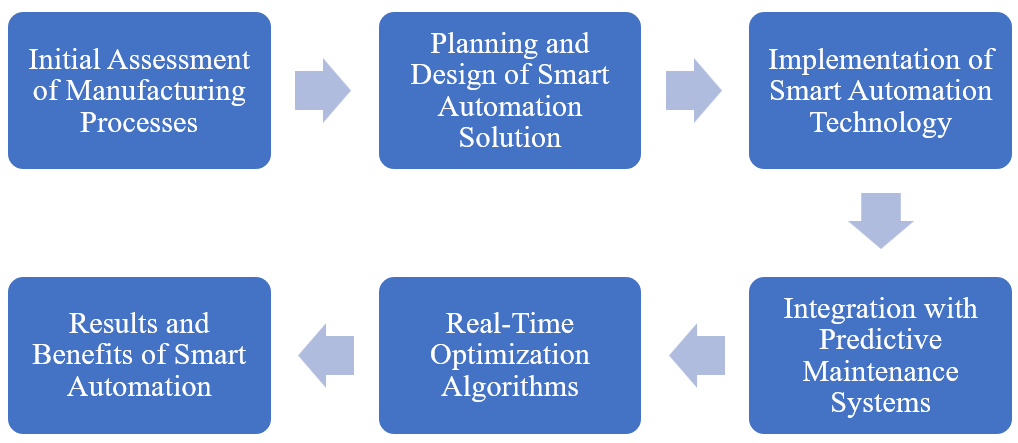
Figure 1. The Journey of Smart Process Automation
4.2. Digital Twin Simulation
Digital twin simulation techniques offer a transformative approach to sustainable development in mechanical engineering, providing engineers with virtual replicas of physical systems for performance optimization and resource management. These digital twins enable engineers to simulate various operating scenarios, allowing for the identification of inefficiencies and the optimization of performance parameters to minimize resource utilization and waste generation.
Quantitative modeling demonstrates the tangible benefits of digital twin technology in enhancing sustainability across manufacturing processes. By iteratively refining design parameters and operational settings, engineers can achieve significant reductions in energy consumption, material usage, and environmental impact. For instance, simulations may reveal opportunities to optimize machining parameters, resulting in reduced energy consumption per unit of production and decreased material waste through improved precision and efficiency. Moreover, digital twin technology facilitates the implementation of predictive maintenance strategies, enabling proactive equipment maintenance based on real-time performance data. By accurately predicting equipment failures and scheduling maintenance activities during planned downtime, manufacturers can minimize disruptions to production while reducing the need for resource-intensive emergency repairs. Additionally, real-time data integration and analysis capabilities inherent in digital twin systems empower manufacturers to make informed decisions regarding process optimization and resource allocation. By continuously monitoring key performance indicators and environmental metrics, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions to enhance sustainability.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, it is evident that the integration of sustainable practices, green energy sources, and intelligent manufacturing techniques represents a pivotal step towards enhancing sustainability within the field of mechanical engineering. Throughout this paper, we have explored various strategies and technologies aimed at reducing environmental impact, optimizing resource utilization, and improving operational efficiency. The implementation of energy efficiency enhancement measures, such as advanced insulation materials and design optimization techniques, has demonstrated significant potential for reducing energy consumption across mechanical systems. By leveraging data-driven analysis and quantitative modeling, manufacturers can identify opportunities for improvement and implement targeted solutions to enhance energy efficiency. Similarly, waste reduction strategies, including lean manufacturing principles and recycling initiatives, have proven effective in minimizing environmental impact and optimizing resource utilization. Through the adoption of advanced waste management technologies, manufacturers can further enhance recycling rates and promote a circular economy model, where materials are continuously reused and recycled. Moreover, the integration of green energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offers opportunities for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Feasibility studies and financial modeling have underscored the economic viability of transitioning to renewable energy sources, further incentivizing their adoption within mechanical engineering operations. Furthermore, the role of intelligent manufacturing techniques, particularly smart process automation and digital twin simulation, cannot be overlooked in enhancing sustainability. By leveraging real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance algorithms, manufacturers can optimize resource utilization, minimize downtime, and improve overall productivity.
References
[1]. Andersson, Svante, et al. “Sustainable development considerations in supply chains: Firms’ relationships with stakeholders in their business sustainability practices—A triangular comparison.” Business Strategy and the Environment 32.4 (2023): 1885-1899.
[2]. Michel-Villarreal, Rosario. “Towards sustainable and resilient short food supply chains: a focus on sustainability practices and resilience capabilities using case study.” British Food Journal 125.5 (2023): 1914-1935.
[3]. Najjar, Mohammad, et al. “The role of blockchain technology in the integration of sustainability practices across multi-tier supply networks: Implications and potential complexities.” Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment 13.1 (2023): 744-762.
[4]. Amini, Mahyar, Koosha Sharifani, and Ali Rahmani. “Machine Learning Model Towards Evaluating Data gathering methods in Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering.” International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering Research 15.2023 (2023): 349-362.
[5]. Kuhn T 1998 Density matrix theory of coherent ultrafast dynamics Theory of Transport Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures (Electronic Materials vol 4) ed E Schöll (London: Chapman and Hall) chapter 6 pp 173–214
[6]. Singh, Pravin Kumar, et al. “Trends in piezoelectric nanomaterials towards green energy scavenging nanodevices.” Materials Today Sustainability (2023): 100583.
[7]. Sharif, Arshian, et al. “Demystifying the links between green technology innovation, economic growth, and environmental tax in ASEAN-6 countries: The dynamic role of green energy and green investment.” Gondwana Research 115 (2023): 98-106.
Cite this article
Chen,S. (2024). Advancing sustainability in mechanical engineering: Integration of green energy and intelligent manufacturing. Applied and Computational Engineering,66,150-155.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Functional Materials and Civil Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Andersson, Svante, et al. “Sustainable development considerations in supply chains: Firms’ relationships with stakeholders in their business sustainability practices—A triangular comparison.” Business Strategy and the Environment 32.4 (2023): 1885-1899.
[2]. Michel-Villarreal, Rosario. “Towards sustainable and resilient short food supply chains: a focus on sustainability practices and resilience capabilities using case study.” British Food Journal 125.5 (2023): 1914-1935.
[3]. Najjar, Mohammad, et al. “The role of blockchain technology in the integration of sustainability practices across multi-tier supply networks: Implications and potential complexities.” Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment 13.1 (2023): 744-762.
[4]. Amini, Mahyar, Koosha Sharifani, and Ali Rahmani. “Machine Learning Model Towards Evaluating Data gathering methods in Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering.” International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering Research 15.2023 (2023): 349-362.
[5]. Kuhn T 1998 Density matrix theory of coherent ultrafast dynamics Theory of Transport Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures (Electronic Materials vol 4) ed E Schöll (London: Chapman and Hall) chapter 6 pp 173–214
[6]. Singh, Pravin Kumar, et al. “Trends in piezoelectric nanomaterials towards green energy scavenging nanodevices.” Materials Today Sustainability (2023): 100583.
[7]. Sharif, Arshian, et al. “Demystifying the links between green technology innovation, economic growth, and environmental tax in ASEAN-6 countries: The dynamic role of green energy and green investment.” Gondwana Research 115 (2023): 98-106.









