1. Introduction
The field of intelligent transportation is a dynamic field. In the past decade, with the continuous development of intelligent transportation technology, the number of urban vehicles has shown a geometric increase, and intelligent transportation system has ushered in the era of real-time road condition information acquisition. Highways have entered the era of "one net", all thanks to the emergence of emerging technologies, such as autonomous driving, vehicle-road collaboration, unattended, artificial intelligence, 5G, cloud networking and blockchain.[1] In the future, intelligent transportation is expected to develop into an intelligent "ecosystem", and the entire transportation system will have the ability to react and make autonomous judgments similar to humans.
One of the hot topics in the current industry discussion is "cloud edge collaboration", although this concept has not yet formed a clear definition and consensus in the industry, but it can be likened to the transportation system to achieve "knee-jerk" reaction and autonomous judgment basis. With the expansion of the cloud platform boundary, a large number of devices accessing the network will generate a large amount of data at the network edge. [2] The construction of edge computing platform can better coordinate data processing and application deployment, and realize the autonomy of edge weak network in the case of sensitive delay and limited bandwidth.
Improve transportation economy: [3] Edge computing can reduce system cost and improve economy. For example, in the urban rail transit system, by installing detection and control equipment for each screen door, it has edge computing capability, and can independently control its own opening and closing, thereby improving the economy of the system.
Increase passenger value-added services: Edge computing can bring more value-added services to passengers and enhance the passenger experience. For example, the smart bus networking solution provided by Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. for bus Online enables unified scheduling of multimedia terminals by deploying on-board intelligent mobile gateways to provide passengers with a better ride experience
2. Related work
2.1. Intelligent Traffic Flow Management
The intelligent traffic management system should be the interdisciplinary research object of the integration of information, physical and social domains. As a transportation system based on Cyber-Physical-Social Systems (CPSS) [4], between the social domain and the information domain, the social domain is perceived by the information domain through various means, and the information domain provides various information services for the operation of the social domain. Between the information domain and the physical domain, the information domain realizes the overall perception and regulation and optimization of the physical domain through various technical means, and the change of the physical domain can also bring the corresponding impact on the information domain. Between the physical domain and the social domain, the physical domain is the basis for the realization of various activities in the social domain of the traffic system, the demand of the social domain is the driving force of the corresponding operation of the physical domain, and the operation mode of the social domain will affect the development and change of the physical domain.
In order to realize important applications such as intelligent traffic management, autonomous driving and vehicle-road collaboration, intelligent transportation system needs the support and assistance of a large amount of data, especially in the traffic peak period, the collection, processing and analysis of a large number of real-time data will produce a huge amount of data transmission. The huge amount of data information requires more computing power on the edge side for analysis, calculation and processing. From the perspective of the chip platform, the large computing power chip needs to meet the following three characteristics, one is to have high computing power, while having an excellent energy consumption ratio; [5]In September 2022, NVIDIA launched the chip NVIDIA Drive Thor, which can achieve the highest 2000TOPSAI computing power and 2000TFLOPS floating point computing power, constantly refresh the single-chip computing power ceiling, and provide more possibilities for autonomous driving manufacturers to develop more diverse application scenarios.
2.2. Edge computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources, such as iot devices or local edge servers. Edge computing, whose applications are initiated at the edge, produces faster network service responses that meet the industry's basic needs in real-time business, application intelligence, security, and privacy protection. Edge computing is between physical entities and industrial connections, or at the top of physical entities. The biggest difference between edge computing and cloud computing is that cloud computing provides services in the cloud, while edge computing services provide services near the data collection, and the location shifts from the cloud to the edge node or edge server. [6] It can be said that edge computing is an extension of cloud computing, and it is cloud computing that sinks some businesses to the edge layer.
The infrastructure diagram for edge computing is as follows:
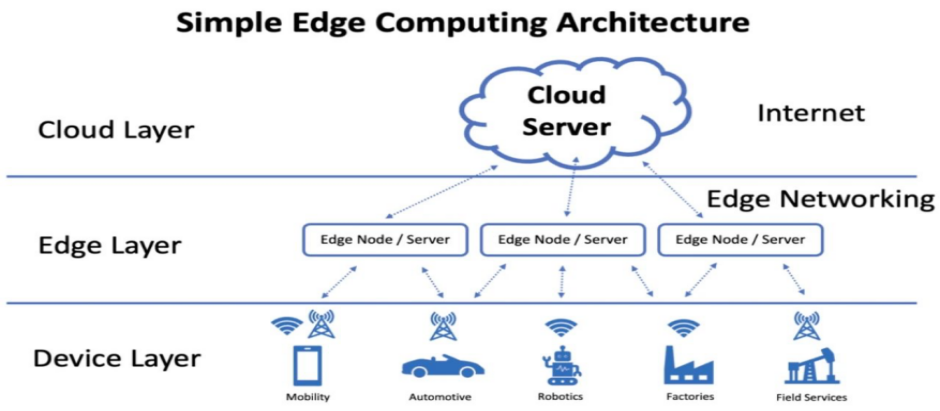
Figure 1. Infrastructure for edge computing
Edge computing occurs at the edge layer, between the cloud layer and the device layer, and the obvious benefits are that it is closer to the user, so latency is lower, real-time responsiveness is improved, the impact of network instability or insufficient bandwidth is reduced, business continuity and availability is improved, and data security is enhanced.
Forbes cites wearable [7] ECG monitoring devices that can monitor the wearer's heart rate in real time. Generally speaking, this data is normal for most users, right? If the data is sent to the cloud center for analysis every time, and then returned to the user to tell the user that everything is normal, it will be a time-consuming and bandwidth consuming action, which is a waste of cloud resources. So how can we improve it? If we can analyze the collected data directly on the wearable device, the data will not need to go around the cloud center, and if there is an abnormal heart rate, it can be fed back to the user faster. This reduces costs while improving efficiency and user experience.
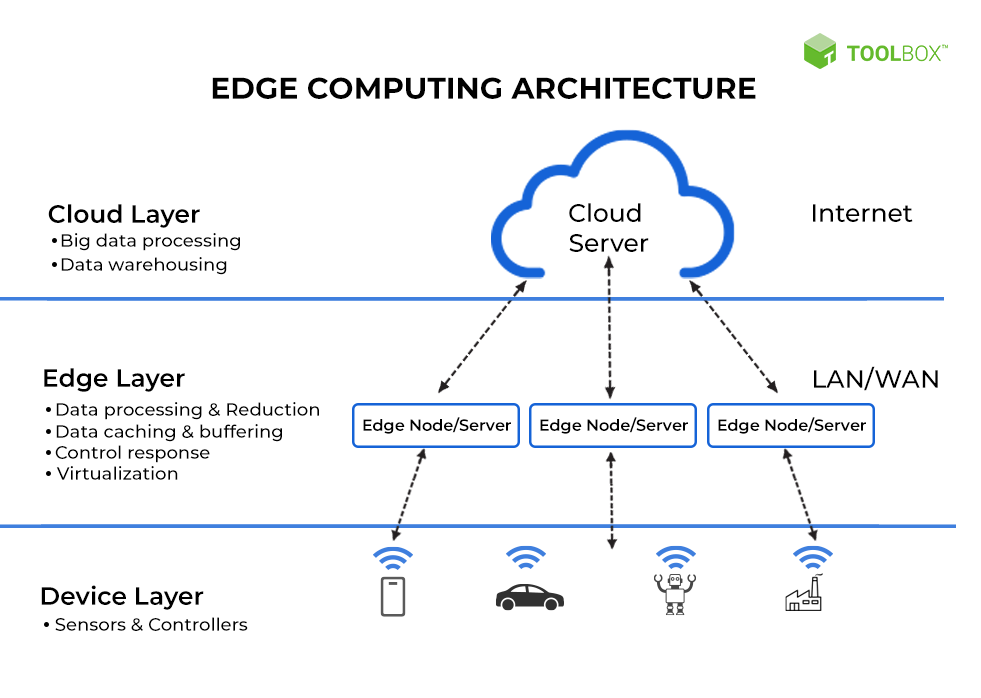
Figure 2. Practical application framework of edge computing
As can be seen from the above figure, the edge layer is mainly used to process, filter, cache, and virtualize the data collected at the device layer. If necessary, the processed data is sent to the cloud for more advanced and complex processing and storage.
2.3. Edge computing drives intelligent traffic flow
Edge computing plays a crucial role in enabling important applications such as intelligent traffic management, autonomous driving, and vehicle-road collaboration in the intelligent transportation system. These applications heavily rely on the support and assistance of vast amounts of data, particularly during peak traffic periods. [8] The collection, processing, and analysis of real-time data generate a significant volume of data transmission. This influx of data necessitates increased computing power at the edge for analysis, calculation, and processing.
Intelligent transportation and intelligent network applications demand diverse computing tasks with varying attributes to be handled at the edge. Edge computing, as the "nerve end" of the intelligent transportation system, offers unique advantages. It enhances traffic safety by empowering vehicles with computing capabilities to respond promptly to safety threats, even in network-deprived scenarios. Edge computing reduces network delays and improves data security and privacy by processing data near the source, mitigating reliance on cloud-based processing.For example, onboard intelligent mobile gateways deployed in buses facilitate precision marketing and ensure smooth operation even in areas with poor network signals, thereby enriching the passenger's ride experience.
3. Application of Edge Computing in Intelligent Transportation
According to a McKinsey consulting study, transportation accounts for the highest proportion of industry applications of edge computing. [9] With the increase of the amount of urban traffic data, the real-time demand of users for massive traffic information will also increase. If all the data is sent back to the cloud computing center, there will be problems such as waste of bandwidth resources and delay, but if the data is analyzed and processed in real time on the edge server, users can be instructed according to the real-time conditions of the road surface and available resources.
3.1. Vehicle-road collaborative application
The most typical application scenario, such as smart car, cannot make a judgment after data transmission to the cloud, but need to let a large number of real-time data, which is the value of edge computing. Then it is better to let the vehicle itself also have a certain amount of computing power to deal with this problem. At the same time, we can also envision a scenario in which a sudden natural disaster, signal interference, or technical failure causes autonomous cars and trains in an area to fall into a no-network state. Then they can only rely on "knee-jerk" reactions from the computing power conferred on them by edge computing to ensure their safety.
In addition, intelligent transportation is developing from single scene traffic management to integrated scene traffic services. [10]V2X scenarios can help intelligent driving to be safer, more efficient, more economical and more convenient, such as speed limit warning, bad weather warning, parallel traffic warning, intersection scheduling, etc., and V2X key technologies include perception, high-definition mapping and positioning. High computing requirements, high mobility, high reliability and real-time have brought major technical challenges, and edge computing will have more technological breakthroughs in the field of vehicle-road collaboration.
3.2. Intelligent transportation realization path
1. Data collection
The edge computing server collaborative service system is installed on the roadside edge computing server and is mainly used to collect the original data of various sensors, including the data acquisition of radar, video and bayonet devices. Support equipment communication protocols of major mainstream manufacturers, support industry-related data communication protocols.
2. Data analysis and processing
Real-time analysis and processing data to achieve multi-data fusion, target tracking and traffic volume acquisition, remote control, multi-platform linkage, protocol output, traffic operation state warning and abnormal event detection, etc., can achieve thunder data fusion thunder data fusion, cross-regional data fusion, radar array data fusion [11]. And can establish a complete data optimization mechanism through AI deep learning function to maintain the reliability and stability of the system and data.
3. Manage device configuration
It provides the cooperative control function of radar, surveillance camera, capture camera, micro weather station and other road measurement equipment and facilities associated with the current edge computing. Ensure the uniqueness, continuity and consistency of vehicle identity information in the continuous detection area, realize the full positioning, tracking, monitoring, track mapping, behavior analysis of the vehicle, etc., when detecting abnormal events, it can directly drive the road remote control camera to rotate to the event orientation, and scale the video screen to the appropriate official observation size, according to the predetermined event level.
4. Side data exchange center
Supports the edge computing data exchange function, and can directly send data information to other application systems and communication devices on the edge computing, and has the edge off-line autonomy. [12] This function can play an important role in real-time perception and early warning in vehicle-road cooperation. In vehicle-road collaboration, edge computing can be used for real-time perception and early warning of vehicles and road facilities. For example, in the process of vehicle driving, edge computing can sense and analyze the vehicle in real time, and identify the driving state of the vehicle. At the same time, the data of road facilities (such as cameras, radar sensors, etc.) can be calculated at the edge to realize real-time perception and early warning of road conditions.
3.3. Challenges, Solutions, and Future Outlook
In the integration of edge computing within intelligent transportation systems, various challenges must be navigated. These obstacles span technical complexities to broader concerns surrounding data security and system interoperability. Nevertheless, with innovative solutions and ongoing advancements, the future outlook for edge computing in intelligent transportation appears promising.Despite these challenges, edge computing offers significant potential to transform intelligent transportation systems. Here are some solutions and future trends shaping the outlook for edge computing in this domain:
Standardization and Integration: Initiatives to standardize protocols and promote interoperability among systems will facilitate seamless integration of edge computing solutions, fostering smoother communication and collaboration across the transportation ecosystem.
Advanced Security Measures: Innovations in edge computing security, such as encryption techniques and secure authentication mechanisms, are enhancing data security and privacy protections. These advancements will instill greater confidence in using edge computing for sensitive transportation applications.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into edge computing systems will enable more sophisticated data analysis and decision-making capabilities. Real-time processing of sensor data combined with AI-driven insights will optimize traffic management and enhance road safety.
Edge Computing Hardware and Software Advancements: Ongoing advancements in edge computing hardware and software, including low-power processors, specialized accelerators, and optimized algorithms, will enhance computing capabilities at the edge. These advancements will unlock new possibilities for intelligent transportation systems.
Research and Innovation: Continued research and innovation in edge computing will drive further advancements in intelligent transportation. Areas of focus may include edge-native applications, edge-to-cloud orchestration, and edge-based AI models tailored for transportation-specific use cases.
By addressing these challenges and leveraging emerging trends, edge computing is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of intelligent transportation, ushering in an era of safer, more efficient, and interconnected mobility solutions.
4. Conclusion
The key application value of edge computing collaborative services in intelligent transportation is self-evident. Through the application of real-time perception and warning, real-time decision and control, information security and privacy protection, and the provision of personalized traffic services and experiences, edge computing collaborative services can greatly improve the efficiency and reliability of intelligent transportation. However, to fully understand the advantages of edge computing in smart transportation, we need to consider its current status compared to related technologies such as cloud computing. Cloud computing provides powerful computing power and storage resources, and is suitable for large-scale data processing and analysis, as well as application scenarios requiring long-term storage and high-performance computing. However, in the field of intelligent transportation, especially for applications requiring real-time response and low latency, cloud computing has certain limitations. Because data transmission and processing need to be transmitted to the cloud server through the network, it may lead to high latency, which is not ideal in some scenarios with high real-time requirements.
In conclusion, the advantages of edge computing in smart transportation are obvious. By realizing functions such as real-time response, low latency, information security and privacy protection, edge computing collaborative services provide important support for the efficient operation of intelligent transportation systems. With the advancement and development of technology, we can expect to see more innovative edge computing technology applied in intelligent transportation, further promoting the development of intelligent transportation systems.
Authorship
Baoming Wang and Haotian Zheng: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing- Original.
Kun Qian: Visualization, Investigation.
Xiaoan Zhan: Supervision.
Junliang Wang: Software, Validation.
References
[1]. Cao, K., Liu, Y., Meng, G., & Sun, Q. (2020). An overview on edge computing research. IEEE access, 8, 85714-85728.
[2]. Khan, W. Z., Ahmed, E., Hakak, S., Yaqoob, I., & Ahmed, A. (2019). Edge computing: A survey. Future Generation Computer Systems, 97, 219-235.
[3]. Srivastava, S., Huang, C., Fan, W., & Yao, Z. (2023). Instance Needs More Care: Rewriting Prompts for Instances Yields Better Zero-Shot Performance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.02107.
[4]. Choudhury, M., Li, G., Li, J., Zhao, K., Dong, M., & Harfoush, K. (2021, September). Power Efficiency in Communication Networks with Power-Proportional Devices. In 2021 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
[5]. Hassan, N., Yau, K. L. A., & Wu, C. (2019). Edge computing in 5G: A review. IEEE Access, 7, 127276-127289.
[6]. Bandyopadhyay, A., Huang, C., Fan, W., Miller, A., & Gilbertson-White, S. (2023). Mental toll on working women during the COVID-19 pandemic: An exploratory study using Reddit data. PloS one, 18(1), e0280049.
[7]. Rosner, B., Tamimi, R. M., Kraft, P., Gao, C., Mu, Y., Scott, C., ... & Colditz, G. A. (2021). Simplified breast risk tool integrating questionnaire risk factors, mammographic density, and polygenic risk score: development and validation. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 30(4), 600-607.
[8]. Sun, Y., Cui, Y., Hu, J., & Jia, W. (2018). Relation classification using coarse and fine-grained networks with SDP supervised key words selection. In Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management: 11th International Conference, KSEM 2018, Changchun, China, August 17–19, 2018, Proceedings, Part I 11 (pp. 514-522). Springer International Publishing.
[9]. Ball, T., Cook, B., Levin, V., & Rajamani, S. K. (2004). SLAM and Static Driver Verifier: Technology transfer of formal methods inside Microsoft. In Integrated Formal Methods: 4th International Conference, IFM 2004, Cnaterbury, UK, April 4-7, 2004. Proceedings 4 (pp. 1-20). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
[10]. Alam, Muhammad, Joaquim Ferreira, and José Fonseca. "Introduction to intelligent transportation systems." Intelligent transportation systems: Dependable vehicular communications for improved road safety (2016): 1-17.
[11]. "Research on promotion of lower limb movement function recovery after stroke by using lower limb rehabilitation robot in combination with constant velocity muscle strength training." 2021 7th international symposium on mechatronics and industrial informatics (ISMII). IEEE, 2021.
[12]. Dimitrakopoulos, George, and Panagiotis Demestichas. "Intelligent transportation systems." IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine 5.1 (2010): 77-84.
Cite this article
Wang,B.;Zheng,H.;Qian,K.;Zhan,X.;Wang,J. (2024). Edge computing and AI-driven intelligent traffic monitoring and optimization. Applied and Computational Engineering,77,225-230.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Cao, K., Liu, Y., Meng, G., & Sun, Q. (2020). An overview on edge computing research. IEEE access, 8, 85714-85728.
[2]. Khan, W. Z., Ahmed, E., Hakak, S., Yaqoob, I., & Ahmed, A. (2019). Edge computing: A survey. Future Generation Computer Systems, 97, 219-235.
[3]. Srivastava, S., Huang, C., Fan, W., & Yao, Z. (2023). Instance Needs More Care: Rewriting Prompts for Instances Yields Better Zero-Shot Performance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.02107.
[4]. Choudhury, M., Li, G., Li, J., Zhao, K., Dong, M., & Harfoush, K. (2021, September). Power Efficiency in Communication Networks with Power-Proportional Devices. In 2021 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
[5]. Hassan, N., Yau, K. L. A., & Wu, C. (2019). Edge computing in 5G: A review. IEEE Access, 7, 127276-127289.
[6]. Bandyopadhyay, A., Huang, C., Fan, W., Miller, A., & Gilbertson-White, S. (2023). Mental toll on working women during the COVID-19 pandemic: An exploratory study using Reddit data. PloS one, 18(1), e0280049.
[7]. Rosner, B., Tamimi, R. M., Kraft, P., Gao, C., Mu, Y., Scott, C., ... & Colditz, G. A. (2021). Simplified breast risk tool integrating questionnaire risk factors, mammographic density, and polygenic risk score: development and validation. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 30(4), 600-607.
[8]. Sun, Y., Cui, Y., Hu, J., & Jia, W. (2018). Relation classification using coarse and fine-grained networks with SDP supervised key words selection. In Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management: 11th International Conference, KSEM 2018, Changchun, China, August 17–19, 2018, Proceedings, Part I 11 (pp. 514-522). Springer International Publishing.
[9]. Ball, T., Cook, B., Levin, V., & Rajamani, S. K. (2004). SLAM and Static Driver Verifier: Technology transfer of formal methods inside Microsoft. In Integrated Formal Methods: 4th International Conference, IFM 2004, Cnaterbury, UK, April 4-7, 2004. Proceedings 4 (pp. 1-20). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
[10]. Alam, Muhammad, Joaquim Ferreira, and José Fonseca. "Introduction to intelligent transportation systems." Intelligent transportation systems: Dependable vehicular communications for improved road safety (2016): 1-17.
[11]. "Research on promotion of lower limb movement function recovery after stroke by using lower limb rehabilitation robot in combination with constant velocity muscle strength training." 2021 7th international symposium on mechatronics and industrial informatics (ISMII). IEEE, 2021.
[12]. Dimitrakopoulos, George, and Panagiotis Demestichas. "Intelligent transportation systems." IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine 5.1 (2010): 77-84.









