1. Introduction
Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction is the most common form of allergy, having symptoms including rash, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, sneezing, red eyes, and itchiness. More severe symptoms can result in asthma. Though the most common cause of mortality is anaphylaxis, most cases occur in medical treatments instead of in everyday circumstances. However, the significance of allergy treatments is not negligible. According to the British Society of Immunology, cases of allergy are increasing every year globally. As in China, studies shown allergic rhinitis was 17.6% in major cities (Zhang). Therefore, the paper will discuss the treatments for type 1 hypersensitivity reaction as a consequence of hay fever.
2. Mechanism of disease
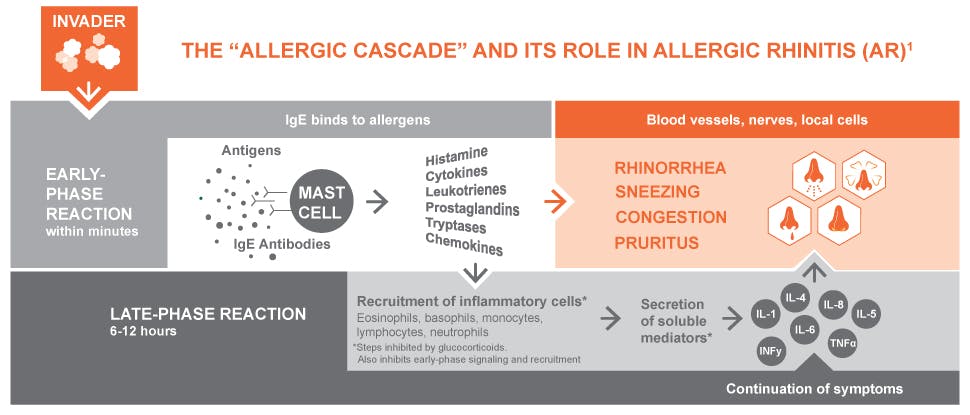
Figure 1. Process of an allergic response (“Allergic Rhinitis (AR) Causes & Mechanisms | Haleon HealthPartner”) [1].
2.1. Recognition of allergen
T-lymphocytes bear antigen-specific receptors on the cell membrane to be able to recognize any pathogens. When T-lymphocytes are activated, they produce cytokines. Cytokines will facilitate mast cell growth and activate leukocytes, which are white blood cells including basophils and eosinophils. White blood cells are responsible for attacking the pathogen.
T-lymphocytes also activate B-lymphocytes to produce Immunoglobin E (IgE) antibodies. With more cytokines present, more IgEs will be available [2]. IgE identifies specific antigens, in the case of hay fever are pollens.
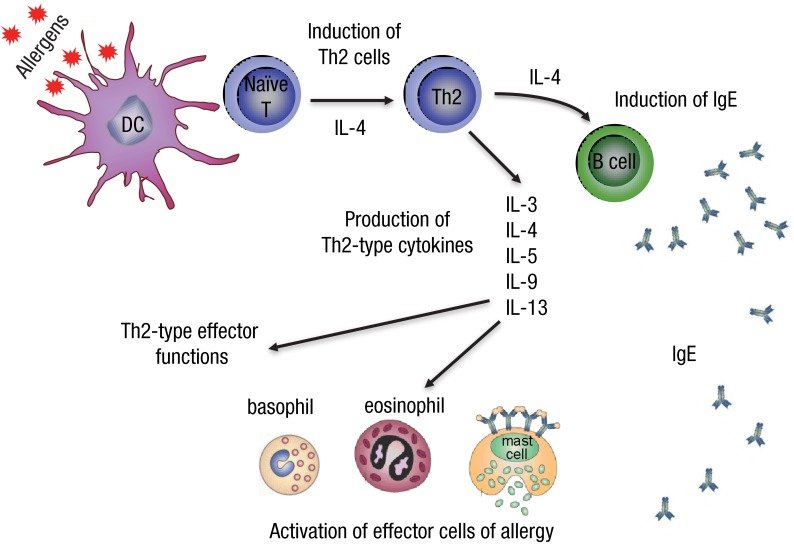
Figure 2. Cell behaviors when recognized allergens [3].
2.2. Cellular Response
There are FcεRI receptors as well as other receptors located on the cell membrane of mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. These receptors will cause cells to release chemical mediators that amplify allergy symptom.
Mast cells are inflammatory cells, whereas basophils are white blood cells. Nevertheless, they carry the same function. Mast cells and basophils both experience a process called degranulation triggered by the binding of IgE to the FcεRI receptors. During degranulation, chemical mediators, such as histamines and lipid mediators are released. However, basophils can also be activated by the cytokines that are produced by t-lymphocytes. The specific type of activation is dependent on the type of receptor that generates degranulation.
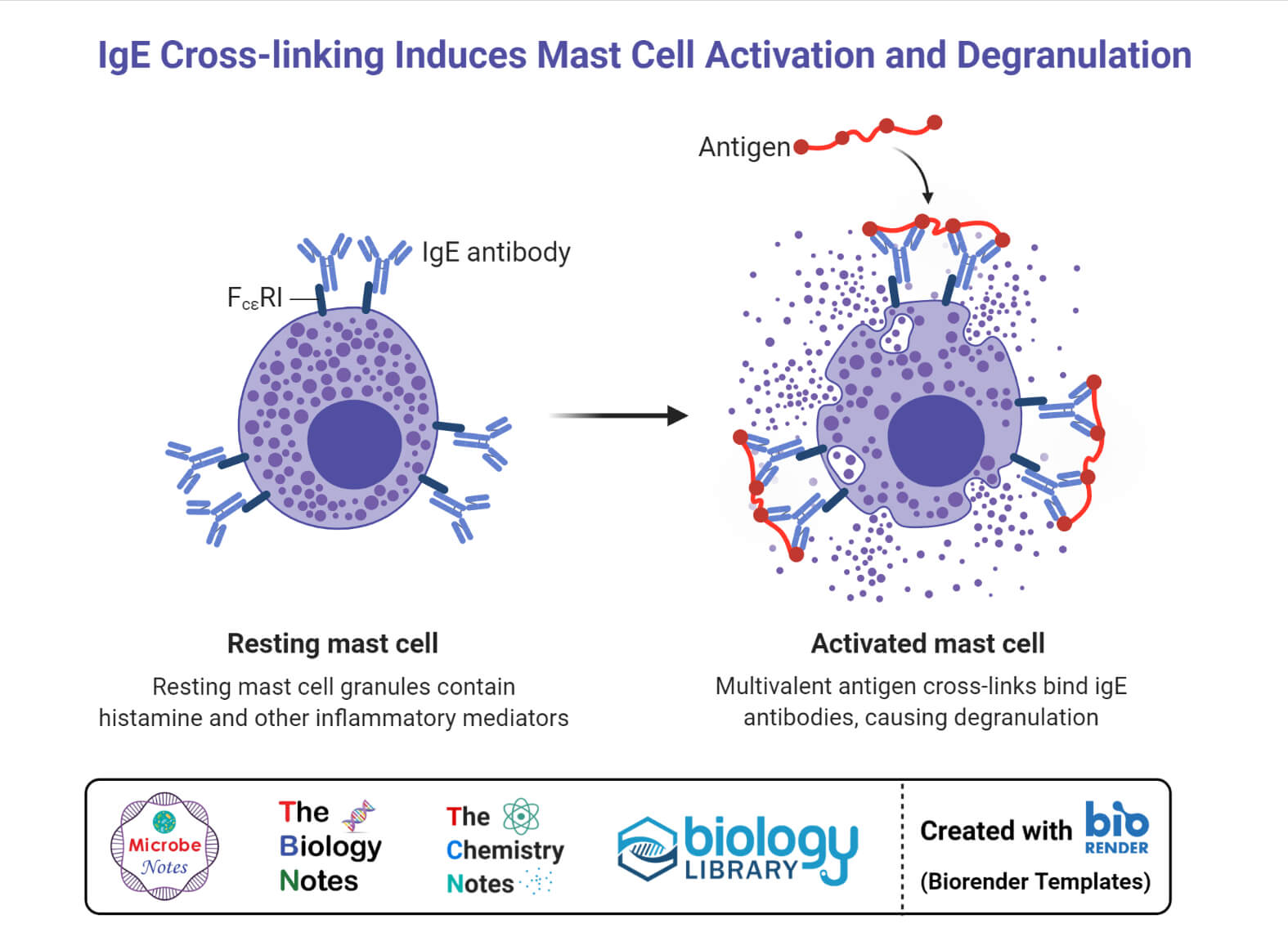
Figure 3. Mast cell or basophil degranulation [4].
Eosinophils have two functions. First, they release toxic proteins and free radicals when activated, which breaks down allergens but may also cause tissue damage. Second, activation by cytokines induces the synthesis of chemical mediators to generate the inflammatory response by activating epithelial cells and recruiting more eosinophils and basophils to an allergic response. (Epithelial cells are those that secret mucus) However, when they are not activated, their FcεRI receptors will not be available for binding.
Symptoms of immediate response happen more seriously in the site with more mast cell degranulation. Therefore, the amount of allergen, IgE, and the route of allergen introduced is what affects the state of allergy. In the case of hay fever, sneezing and an increased amount of mucus are the more common symptoms since pollens are inhaled by the patients. In more serious cases, allergens or IgE can activate cells in the blood through dissolution, and cause effects like rashes and red eyes.
2.3. Histamine causes immediate responses
Histamine is a type of chemical that binds to the H1 receptor located on smooth muscles, blood vessels, skin, nerves, and the brain. The receptors send signals to the corresponding organs to make the environment physically hostile to the pathogens. Receptors on the blood vessels dilate the vessel and increase blood flow beneath the skin, thereby causing red eyes and rashes. Moreover, they also increase the permeability of the blood vessel, resulting in a greater amount of tissue fluid diffusing out of the vessel, attributed to lacrimation and rhinorrhea. Receptors on the nerves stimulate the peripheral nervous system so that there are itches and sneezes.
H1 receptors on the smooth muscles impact the airway of the body by contracting and constricting the bronchial muscles, or by activating submucosal mast cells which secret more mucus to block the airway. These cause asthma, which is a more extreme case of type 1 hypersensitivity [5]. .
2.4. Late-phase reactions
Late-phase reactions happen even in mild cases, therefore it is necessary to still take drugs over a certain period of time.
Cytokines are continued to be released by cells, therefore, the reaction will continue. Mast cells consistently grow and release histamines (though the level decreases) and lipid mediators, causing smooth muscle contraction, increased vascular permeability, and mucus secretion. This is the reason why even without exposure to allergens, patients still have chronic diseases, for instance, asthma. It is when the airway experiences long-term inflammation, the condition in it becomes extremely sensitive. As vascular permeability remains high, asthmatics are more exposed to chemical irritants that can cause discomfort. With more mucus present in the airway, they are also more sensitive when there is a change in the status of mucus.
3. Loratadine
3.1. Chemical Structure
Loratadine is tricyclic structure, that derives from the first-generation antihistamine, Azatadine. IUPAC name is Ethyl 4-(8-chloro-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo[5,6]. cyclohepta[1,2-b]. pyridin-11-ylidene)-1-piperidinecarboxylate. It is also known as Claritin under the brand name.
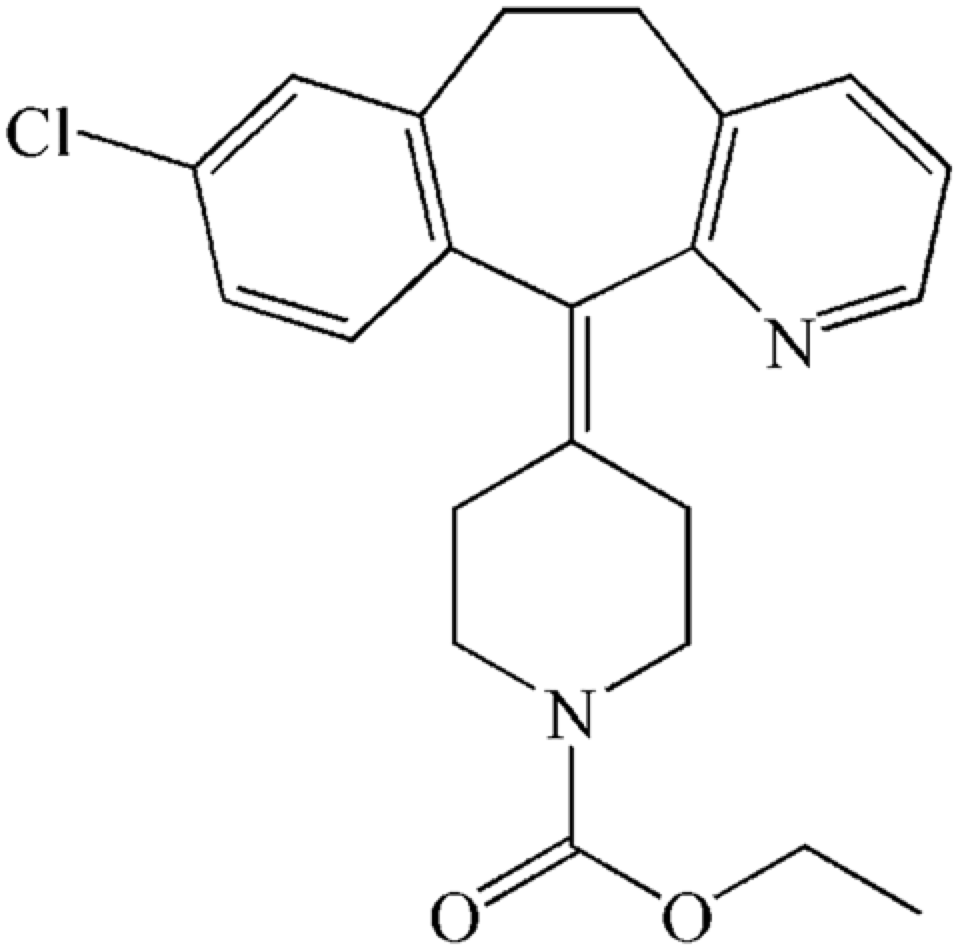
Figure 4. Chemical structure of Loratadine [6].
3.2. Preparation
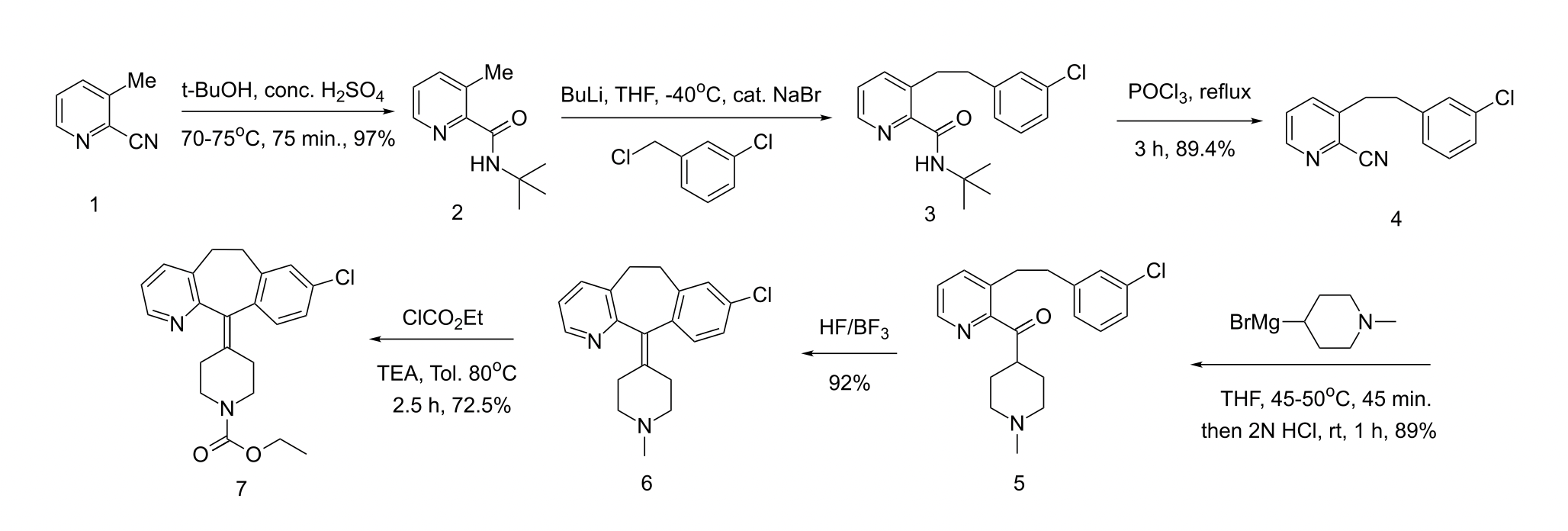
Figure 5. Loratadine Synthesis [6].
Loratadine is a derivative of Azatadine. The preparation of Loratadine initially uses 2-cyano-3-methyl-pyridine as presented in Compound 1. Compound 1 experiences alkylation, in the form of Ritter reaction. Ritter reaction utilizes H2SO4 as a proton donator, and t-BuOH as a nucleophile to attack the CN triple bond. In Step 1, t-BuOH is protonated by H2SO4 to form CH3 carbocation thus becomes an electrophile. Because the resonance intermediate is highly electrophilic, water then attacks the amine carbon to form an amide. Compound (a) and Compound (b) are tautomer, but the structure tend to be Compound (b). Eventually, the proton bonded to oxygen on the ketone detaches and forms the end result. The functional group in Figure 7 refers to the methyl pyridine in Figure 5 [7].
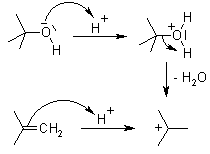
Figures 6. Step 1 of Ritter’s Reaction [7].
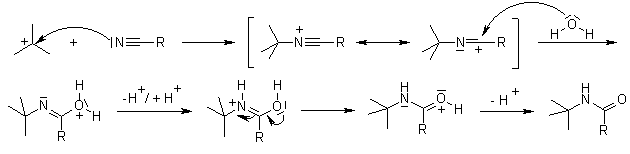
Figure 7. Step 2 of Ritter’s Reaction [7].
Alkylation of Compound 2 with m-chlorobenzyl (the nucleophilic agent) forms Compound 3. It is then dissolved in THF to react with POCl3. Figure 8 explains the reaction mechanism from Compound 3 to Compound 4, where POCl3 acts as an electrophile under SN2 reaction. Lone pairs of electrons from oxygen transfer to phosphorus to make a bond, breaking the double bond with the carbonyl. Therefore the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen form double bonds with carbon. The amide then loses 2 protons due to deprotonation and elimination, hence becoming nitrile [8].
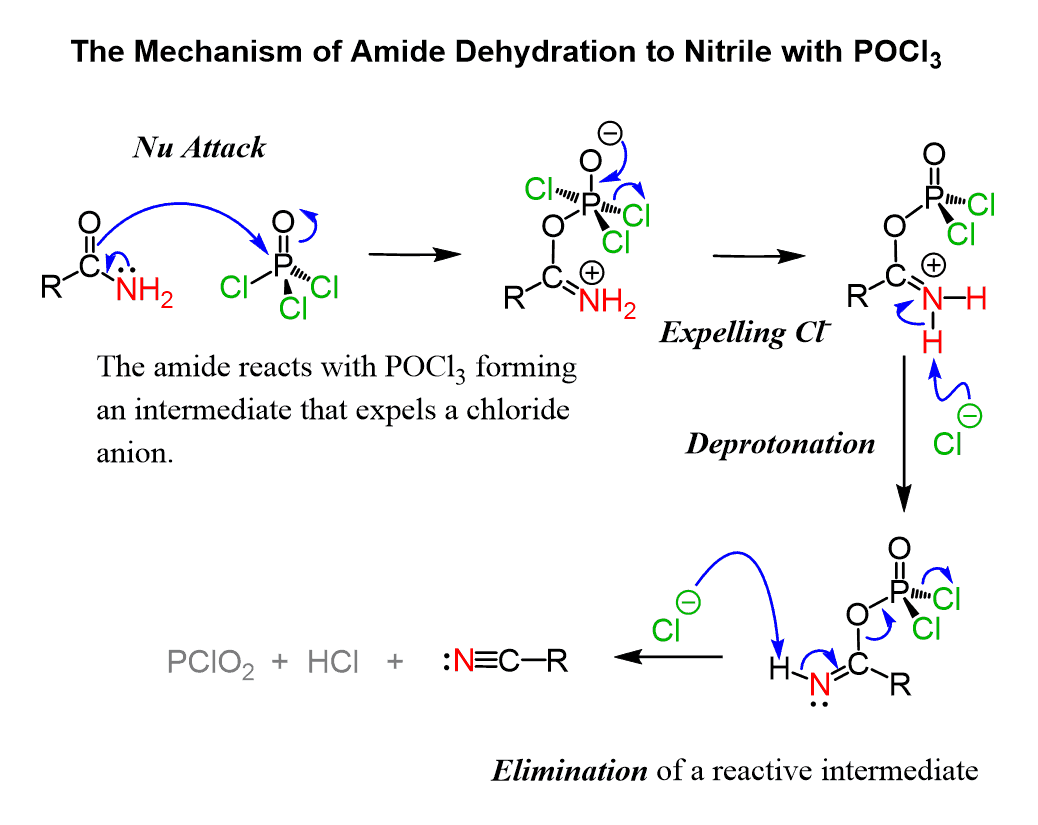
Figure 8. Amide Dehydration to Nitrile [8].
The reason to remove nitrile before substituting methyl group for chlorobenzyl is that CN has a lower pKa (9.1) [9]. than methane, which is not an acid. The protecting group tert-butyl that replaces the nitrile, allows the methyl group to be replaced by chlorobenzyl later.
From Compound 4 to Compound 5, a Grignard reagent is used to form ketone from nitrile and attach N-methylpiperidyl to the benzene ring. A Grignard reagent is a compound having a formula of RMgX, where X is a halogen and R is an alkyl group, in this case, N-methylpiperidyl [10]. The carbon labeled 2 and 3 in Figure 9 can be seen as N-methylpiperidyl. Figure 9 is a diagram of Grignard reaction with H3O, whereas loratadine synthesis utilizes HCl. Step 1, the addition of N-methylpiperidyl to nitrile carbon to form an imine. In steps 2 and 3, imine is protonated. In step 4, water is added to the compound, which results in deprotonation in step 6 as oxygen becomes a cation. Step 5 involves another proton transfer ascribed to amino nitrogen having a lone pair of electrons. In step 6, ammonia leaves as the unstable oxygen forms a double bond with carbonyl carbon. In step 7, the unstable oxygen-cation experiences another protonation and forms the end result. Eventually, N-methylpiperidyl binds to the main compound, forming Compound 5.
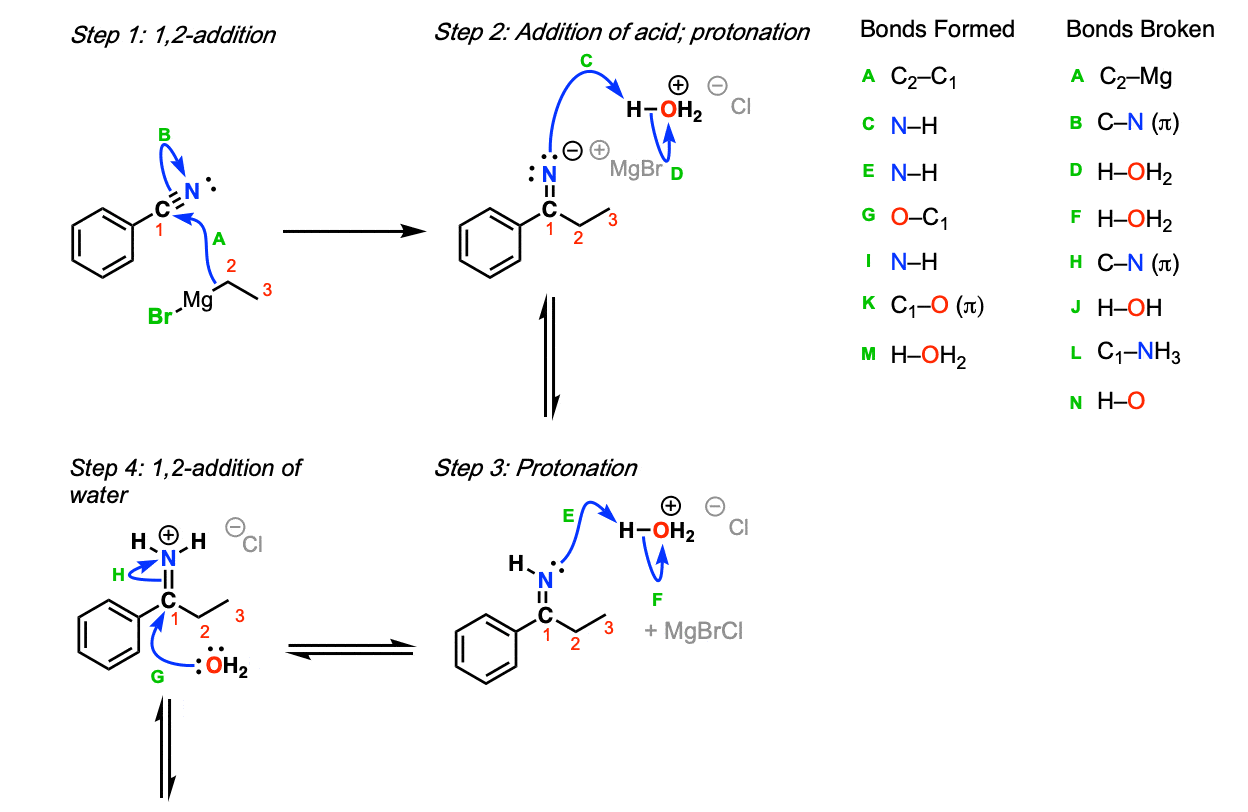
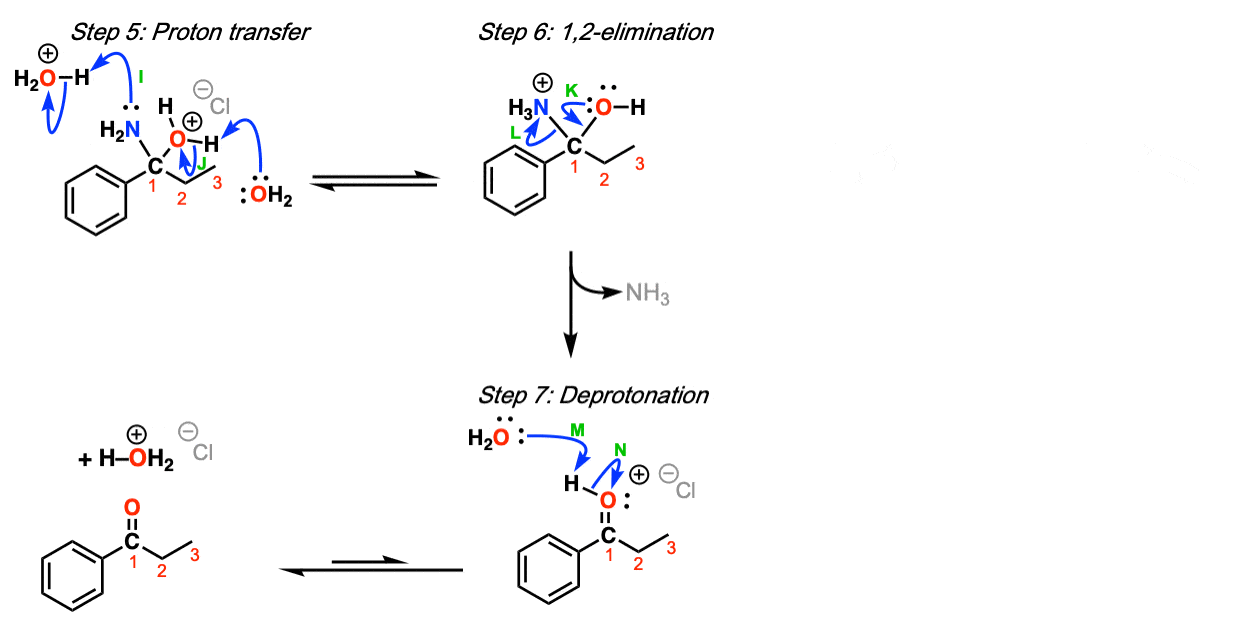
Figure 9. Addition of Grignard reagent to nitrile to give ketones [11].
Compound 5 undergoes an intramolecular reaction to form Compound 6, which is achieved by electrophilic aromatic substitution. This is when the π bond of the chlorobenzene ring acts as a nucleophile to attack the carbonyl. With the catalyst of hydrofluoric acid or borane, a substitution reaction is more likely to occur, on account of having a proton donator. In step (a), δ-carbon acts as a nucleophile to attack the ketone carbonyl. A proton is transferred to the oxygen anion, while γ-carbon charges positively. Double bonds are formed to stabilize the charge. Simultaneously, OH is protonated, thus the compound is dehydrated.
Figure 10. Intramolecular ring formation. From step (a) to step (d)
Loratadine replaces CH3 in Compound 6 with an additional structure CO2Et, making the structure more polar, which is less likely to cause side effects in the central nervous system compared to Azatadine. This mechanism will be explained later in this article [12].
3.3. Mechanism
Loratadine is the most common form of antihistamine. Rather than acting as a competitive antagonist of the histamine receptor, it acts as an inverse agonist of H1 receptors.
3.3.1. Inverse agonism. Usually, without the interference of histamine, the H1 receptor is at the equilibrium of inactive and active conformation (a) (b). This situation is known as constitutive receptor activity. Histamine is a type of agonist that binds to the active state of the receptor to increase its stability, thereby shifting the equilibrium conformation to the more active conformation as conformations tend to be stable (c). Antihistamine inhibits H1 receptors from shifting to the active conformation by binding to the inactive state to increase the stability of inactivity (d). Antihistamine performs inverse agonism, as it does not inhibit the binding of agonists with receptors, but alters the constitutive activity. Hence, as histamine binds with the H1 receptor, the state of activity is still at equilibrium. As a result, limits the effect of histamine on the H1 receptor [13].
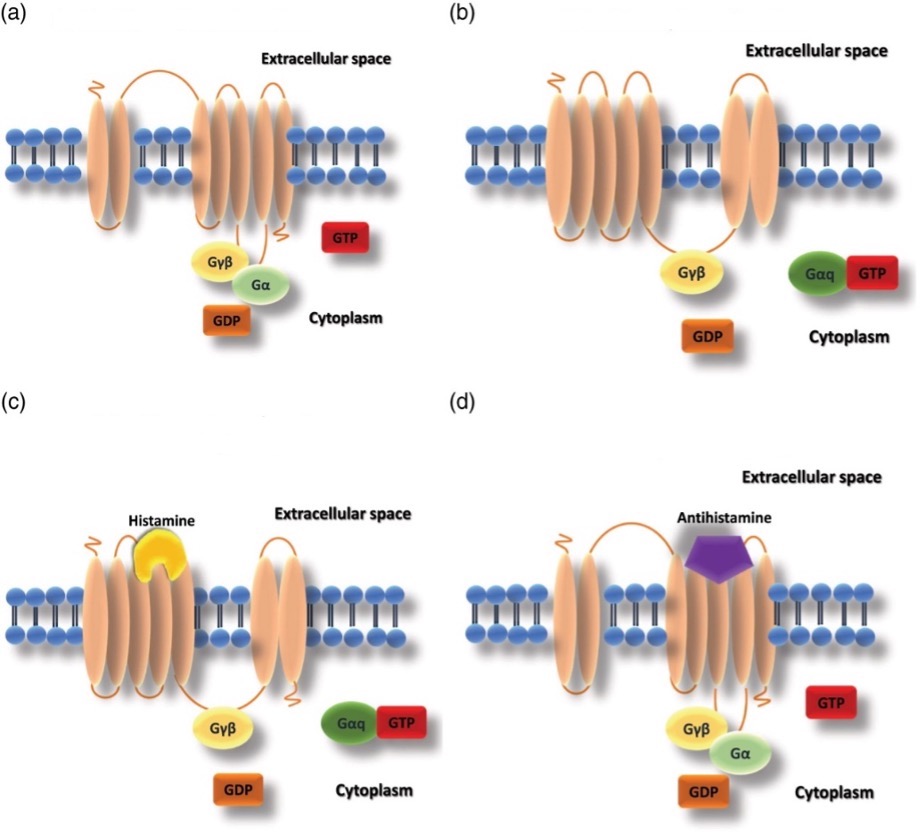
Figure 11. The state of histamine receptors with histamine or antihistamine. (a) Inactive H1 receptor conformation; (b) Active H1 receptor conformation; (c) Active H1 receptor conformation with histamine bond; (d) inverse agonism conformation. [13].
3.3.2. Antagonist. Antagonists compete with the agonists that bind to the receptors. Once bonded to the receptors, they prevent both the agonists and inverse agonists from binding to the receptor, thereby decreasing the activity of the receptor.
3.3.3. First and second-generation antihistamine. A common concern regarding antihistamine drugs is the presence of H1 receptors in the brain. First-generation antihistamines are lipophilic in their properties, so during the delivery of the drug, antihistamines could permeate the blood-brain barrier that is also made of lipids, and cause side effects such as drowsiness and sedation. This is the consequence of histamines also playing a significant role in brain function. Therefore, first-generation antihistamines were limited only to patients aged 2 years or above, and often as sedation side effects. Nevertheless, second-generation antihistamines, including loratadine, are less lipid soluble, hence they have less effect on brain function. Moreover, loratadine is a substrate for p-glycoprotein. P-glycoprotein is located on the blood-brain barrier, a protein that pumps foreign substances out of the cells. When antihistamines enter the brain, p-glycoprotein will pump it back into the bloodstream. This is how second-generation antihistamines avoid side effects [14].
3.4. Mode of delivery
After being taken orally, loratadine diffuses throughout the whole body and binds specifically to the H1 receptors on the surface of epithelial cells, endothelial cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, airway cells, and smooth muscle cells. Loratadine is rapidly absorbed and achieves peak concentration within 1 to 2 hours. (DrugBank) The standard dosage for loratadine is 5 to 10 mg per day [15].
3.5. Adverse Effect
Usually, there are no side effects of loratadine. Adverse effects of loratadine involve in allergic responses and should be treated immediately.
4. Sodium Cromoglycate
4.1. Chemical Structure
IUPAC name is 5,5′-(2-hydroxypropane-1,3-diyl)bis(oxy)bis(4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylic acid), also known as Cromolyn Sodium.
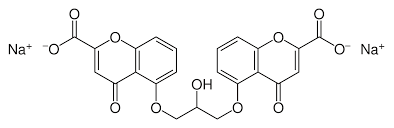
Figure 12. Chemical structure of sodium cromoglycate [16].
Sodium cromoglycate is a relatively new type of drug,
4.2. Preparation
4.2.1. Derivative from khellin. Sodium Cromoglycate was first synthesized in 1965 from the naturally occurring plant chromone, khellin, by Roger Altounyan (an asthmatic himself) and his colleagues from the Fisons Research Laboratories in the UK. Khellin is obtained from the seeds of Ammi visnaga, which were primarily used to treat intestinal colic. Yet, the seeds were never widely accepted as they often cause discomfort. During the experiment, Altounyan and his colleagues aimed to relax the smooth muscle that could possibly cause gastrointestinal upset by synthesizing substances from khellin, which led them to the discovery of sodium cromoglycate [17].
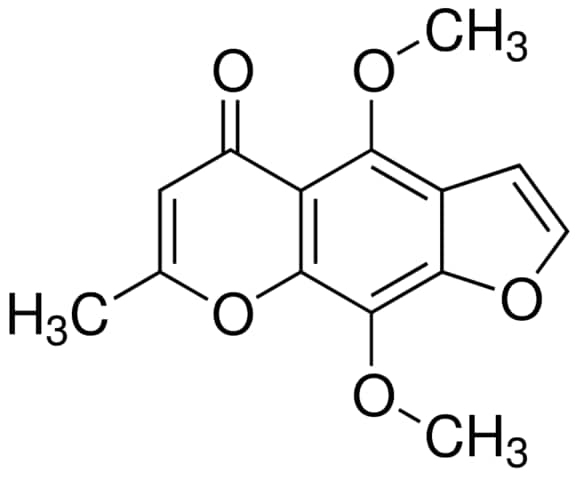
Figure 13. Chemical structure of khellin [17].
4.2.2. Chemical synthesis. Sodium cromoglycate can also be chemically synthesized.
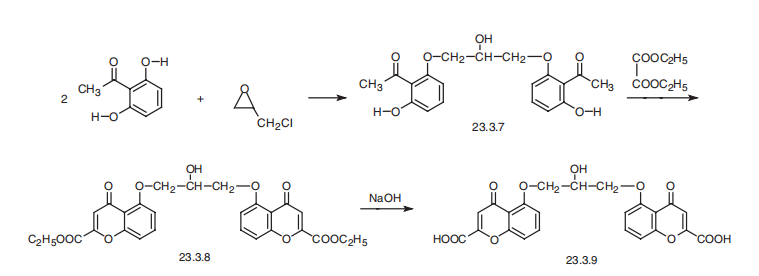
Figure 14. Sodium cromoglycate synthesis [18].
In the first step, 2,6-dihydroxyacetophenone reacts with epichlorohydrine to form compound 23.3.7. by an epoxide ring opening reaction. Due to the ring strain and the torsional strain of an eclipsed conformation of the substituents, the compound is highly reactive. The hydroxide on the 2,6-dihydroxyacetophenone acts as a nucleophile to attack epichlorohydrine, and breaks the bond. Chloride acts as the leaving group in this reaction. (Figure 14) As the methyl group labeled out in Figure 14 binds to the hydroxide, the other end of the carbon chain is attached to the other 2,6-dihydroxyacetophenone.
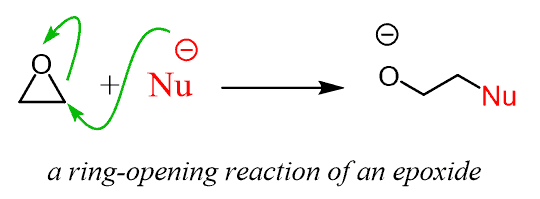
Figure 15. Epoxide Ring-Opening Reaction [19].
Formation of 23.3.8 involves a ring closure. During the first step, OH acts as a nucleophile to attack the carbon in the middle of the diethylester. The carbon then becomes partially negative so it breaks the bond of diethylester. In the third step, carbon acts as a nucleophile because it has a spare pair of electron, and attacks the carbon on the other side of the chain. Compound 23.3.8 is formed.
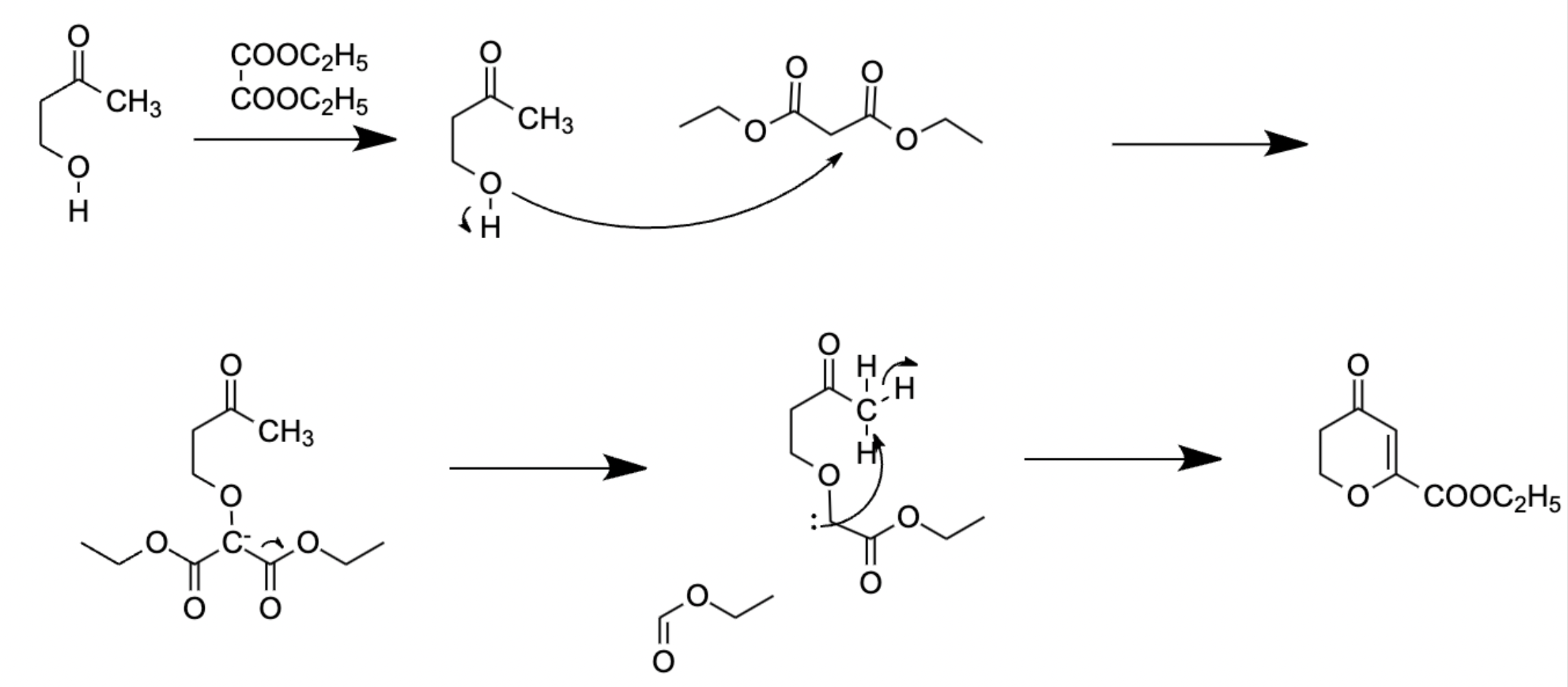
Figure 16. Ring closing reaction with diethylester.
The final step is hydrolysis with sodium hydroxide. It replaces ethoxide with hydroxide. The hydroxide from sodium NaOH acts as a nucleophile to attack the carbon center of the ester. It breaks the double bond and forms a tetrahedral intermediate. Then, as the double bond reforms, the ethoxide acts as the leaving group. So far, the hydroxide has replaced the ethoxide [20].
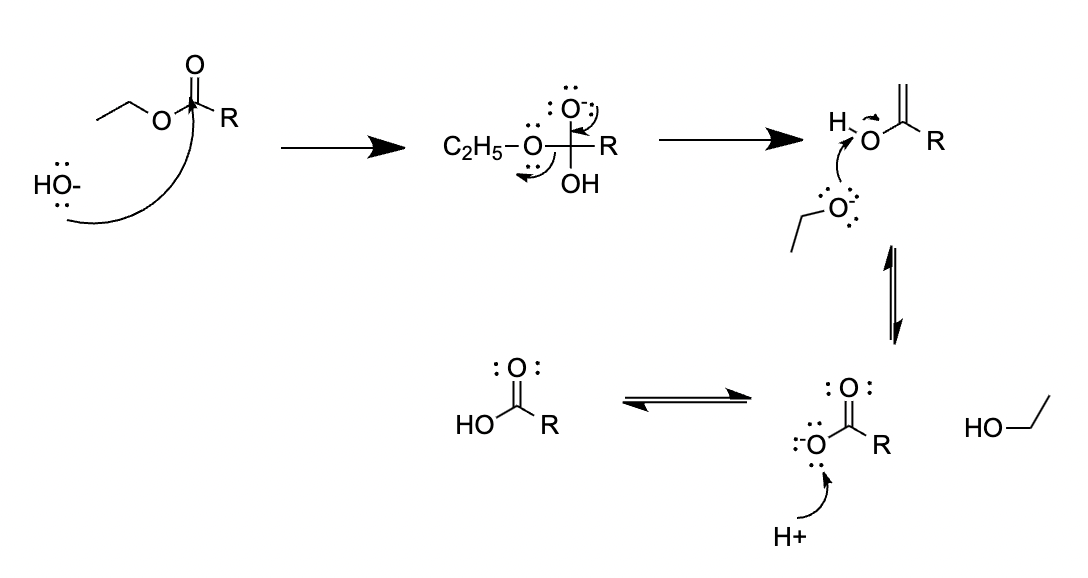
Figure 17. Hydrolysis of ethyl ester.
4.3. Mechanism
Sodium cromoglycate is a type of mast cell stabilizer. As mentioned above, mast cells and leukocytes release histamines. Experiments showed that sodium cromoglycate inhibits the release of histamines and other chemical mediators by mast cells, but not by leukocytes, suggesting that it is specifically bonded to mast cells. The precise mechanism at the cellular level is unclear, but there are hypotheses regarding the mechanism. The degranulation of mast cells depends highly on the intracellular elevation of calcium level. It also depends on the chloride channel, which generates hyperpolarization on the cell membrane. This chloride channel is what allows the influx of calcium. When the chloride channel is blocked by sodium cromoglycate, histamine release can be reduced but not inhibited. This means that degranulation does not happen, meaning that the mast cell is stabilized. Figure helps to explain this mechanism in a flow chart [21].
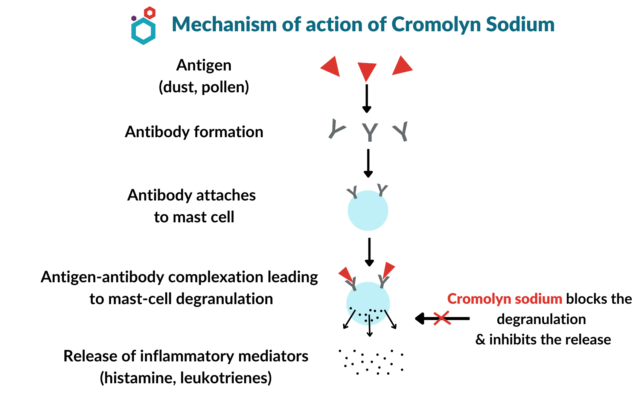
Figure 18. Mechanism of action of sodium cromoglycate (Aditi)
Other research has shown that sodium cromoglycate can suppress the activation of inflammatory cells, therefore reducing the release of mediators. There was also research that showed its inhibitory effect on B-lymphocytes, to reduce the level of IgE by inhibiting the switch recombination agents inside the B-lymphocytes [22].
4.4. Mode of delivery
In allergic responses like allergic rhinitis, is taken as nasal inhalation, 3 to 6 times a day. As for inflammatory responses around the eye, sodium cromoglycate can be used as eyedrops 4 to 6 times a day. Oral forms is used for mastocytosis, which is not an allergic response.
4.5. Adverse Effect
The eyedrops may cause transient burning of the eyes, such as dryness, irritation, itchiness, and rash. With nasal spray, it can cause nasal congestion, sneezing, itching, rhino conjunctivitis, and headaches. (Minutello and Gupta) These are mainly due to the stimuli that it might create on surrounding cells of the allergy site.
5. Conclusion
By analyzing the mechanism of type 1 hypersensitivity and the pharmacology of allergy treatments, it creates a foundation for future studies of every other medicine. As for further studies, this research paper inspires other medical treatments to type 1 hypersensitivity, based on the scientific explanation it provides with.
References
[1]. Allergic Rhinitis (AR) Causes & Mechanisms | Haleon HealthPartner. (n.d.). Www.haleonhealthpartner.com. https://www.haleonhealthpartner.com/en-us/respiratory-health/conditions/allergic-rhinitis-conditions-home/allergic-rhinitis/allergic-rhinitis-causes-mechanism/
[2]. Berger, A. (2000). Science commentary: Th1 and Th2 responses: what are they? BMJ, 321(7258), 424–424. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.321.7258.424
[3]. Fujita, H., Meyer, N., Akdis, M., & Akdis, C. A. (2012). Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance to Allergens. New Trends in Allergy and Atopic Eczema, 30–38. https://doi.org/10.1159/000331868
[4]. Sapkota, A. (2021, April 30). Mast Cells- Definition, Structure, Immunity, Types, Functions. Microbe Notes. https://microbenotes.com/mast-cells/
[5]. A, C., Travers, P., Walport, M., & Shlomchik, M. J. (2012). Effector mechanisms in allergic reactions. Nih.gov; Garland Science. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK27112/
[6]. Nuklear. (2015, November 28). Synthesis of Loratadine from 2-Cyano-3-Methyl Pyridine. Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Loratadine_synthesis.svg
[7]. Ritter Reaction. (n.d.). Www.organic-Chemistry.org. Retrieved July 27, 2023, from https://www.organic-chemistry.org/namedreactions/ritter-reaction.shtm
[8]. Vijayraj. (2020, February 27). Amide Dehydration Mechanism by SOCl2, POCl3, and P2O5. Chemistry Steps. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/amide-dehydration-mechanism-by-socl2-pocl3-and-p2o5/
[9]. pKa Chart. (n.d.). Retrieved July 27, 2023, from https://cactus.utahtech.edu/smblack/ chem2310/summary_pages/pKa_chart.pdf
[10]. Sigma Aldrich. (2021). Solvent Miscibility Table. Merck, 1(1). https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/ MX/en/technical-documents/technical-article/genomics/cloning-and-expression/blue-white-screening
[11]. Addition of Grignard reagents to nitriles to give ketones (after hydrolysis). (2023, January 22). Master Organic Chemistry. https://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/reaction-guide/addition-of-grignard-reagents-to-nitriles-to-give-ketones-after-hydrolysis/
[12]. Rich, R. R. (2009). Clinical immunology : principles and practice (pp. 1317–1329). Mosby/Elsevier. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780323044042100892 (Original work published 2008)
[13]. Mandola, A., Nozawa, A., & Eiwegger, T. (2019). Histamine, histamine receptors, and anti-histamines in the context of allergic responses. LymphoSign Journal, 6(2), 35–51. https://doi.org/10.14785/lymphosign-2018-0016
[14]. Introduction to Antihistamines. (2022, February 2). Www.youtube.com. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3zUKX1lOoug
[15]. Cardin, D. (n.d.). Loratadine dosage, forms, and strengths. Single Care. https://www.singlecare. com/prescription/loratadine/
[16]. File:Sodium cromoglycate.svg - Wikipedia. (2009, August 1). Commons.wikimedia.org. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sodium_cromoglycate.svg
[17]. Kuzemko, J. A. (1989). Twenty years of sodium cromoglycate treatment: a short review. Respiratory Medicine, 83, 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0954-6111(89)80245-8
[18]. Cromoglicic acid | 16110-51-3. (n.d.). ChemicalBook. Retrieved August 4, 2023, from https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB8855235.htm
[19]. Epoxides Ring-Opening Reactions. (2020, June 18). Chemistry Steps. https://www. chemistrysteps.com/ring-opening-reactions-of-epoxides/
[20]. Ester Hydrolysis with NaOH: Ester Hydrolysis, Ester Hydrolysis with NaOH and H2SO4, Mechanism of ester hydrolysis with NaOH and Synthesis of Ester. (n.d.). BYJUS. https://byjus.com/chemistry/ester-hydrolsysi-with-naoh/
[21]. Norris, A. A. (1996). Pharmacology of sodium cromoglycate. 26, 5–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/ j.1365-2222.1996.tb00661.x
[22]. Aditi. (2022, September 21). Cromolyn Sodium | Mechanism of action, Uses & Side effects. Macsen Labs. https://www.macsenlab.com/blog/cromolyn-sodium-overview/
Cite this article
Zhang,X. (2024). Loratadine and sodium cromoglycate – Two drugs under type 1 hypersensitivity reaction in response to hay fever. Applied and Computational Engineering,85,61-71.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Allergic Rhinitis (AR) Causes & Mechanisms | Haleon HealthPartner. (n.d.). Www.haleonhealthpartner.com. https://www.haleonhealthpartner.com/en-us/respiratory-health/conditions/allergic-rhinitis-conditions-home/allergic-rhinitis/allergic-rhinitis-causes-mechanism/
[2]. Berger, A. (2000). Science commentary: Th1 and Th2 responses: what are they? BMJ, 321(7258), 424–424. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.321.7258.424
[3]. Fujita, H., Meyer, N., Akdis, M., & Akdis, C. A. (2012). Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance to Allergens. New Trends in Allergy and Atopic Eczema, 30–38. https://doi.org/10.1159/000331868
[4]. Sapkota, A. (2021, April 30). Mast Cells- Definition, Structure, Immunity, Types, Functions. Microbe Notes. https://microbenotes.com/mast-cells/
[5]. A, C., Travers, P., Walport, M., & Shlomchik, M. J. (2012). Effector mechanisms in allergic reactions. Nih.gov; Garland Science. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK27112/
[6]. Nuklear. (2015, November 28). Synthesis of Loratadine from 2-Cyano-3-Methyl Pyridine. Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Loratadine_synthesis.svg
[7]. Ritter Reaction. (n.d.). Www.organic-Chemistry.org. Retrieved July 27, 2023, from https://www.organic-chemistry.org/namedreactions/ritter-reaction.shtm
[8]. Vijayraj. (2020, February 27). Amide Dehydration Mechanism by SOCl2, POCl3, and P2O5. Chemistry Steps. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/amide-dehydration-mechanism-by-socl2-pocl3-and-p2o5/
[9]. pKa Chart. (n.d.). Retrieved July 27, 2023, from https://cactus.utahtech.edu/smblack/ chem2310/summary_pages/pKa_chart.pdf
[10]. Sigma Aldrich. (2021). Solvent Miscibility Table. Merck, 1(1). https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/ MX/en/technical-documents/technical-article/genomics/cloning-and-expression/blue-white-screening
[11]. Addition of Grignard reagents to nitriles to give ketones (after hydrolysis). (2023, January 22). Master Organic Chemistry. https://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/reaction-guide/addition-of-grignard-reagents-to-nitriles-to-give-ketones-after-hydrolysis/
[12]. Rich, R. R. (2009). Clinical immunology : principles and practice (pp. 1317–1329). Mosby/Elsevier. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780323044042100892 (Original work published 2008)
[13]. Mandola, A., Nozawa, A., & Eiwegger, T. (2019). Histamine, histamine receptors, and anti-histamines in the context of allergic responses. LymphoSign Journal, 6(2), 35–51. https://doi.org/10.14785/lymphosign-2018-0016
[14]. Introduction to Antihistamines. (2022, February 2). Www.youtube.com. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3zUKX1lOoug
[15]. Cardin, D. (n.d.). Loratadine dosage, forms, and strengths. Single Care. https://www.singlecare. com/prescription/loratadine/
[16]. File:Sodium cromoglycate.svg - Wikipedia. (2009, August 1). Commons.wikimedia.org. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sodium_cromoglycate.svg
[17]. Kuzemko, J. A. (1989). Twenty years of sodium cromoglycate treatment: a short review. Respiratory Medicine, 83, 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0954-6111(89)80245-8
[18]. Cromoglicic acid | 16110-51-3. (n.d.). ChemicalBook. Retrieved August 4, 2023, from https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB8855235.htm
[19]. Epoxides Ring-Opening Reactions. (2020, June 18). Chemistry Steps. https://www. chemistrysteps.com/ring-opening-reactions-of-epoxides/
[20]. Ester Hydrolysis with NaOH: Ester Hydrolysis, Ester Hydrolysis with NaOH and H2SO4, Mechanism of ester hydrolysis with NaOH and Synthesis of Ester. (n.d.). BYJUS. https://byjus.com/chemistry/ester-hydrolsysi-with-naoh/
[21]. Norris, A. A. (1996). Pharmacology of sodium cromoglycate. 26, 5–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/ j.1365-2222.1996.tb00661.x
[22]. Aditi. (2022, September 21). Cromolyn Sodium | Mechanism of action, Uses & Side effects. Macsen Labs. https://www.macsenlab.com/blog/cromolyn-sodium-overview/









