1. Introduction
The pervasive issue of fouling, marked by the unwanted collection of contaminants, has multifaceted repercussions on human daily life, industrial transport and marine ecological environment. The oceans, which envelop about 70% of the Earth and underpin nearly 90% of global freight logistics, face significant economic setbacks due to fouling This is compounded by the ocean’s myriad of electrolytes and microorganisms that heighten metal degradation. Beyond the oceans, fouling hampers utilities like power lines, trigger pipeline congestion, and endangers subsea structures, although anti-fouling measures have been in place for centuries, many are ecologically unsound. Superhydrophobicity, a cornerstone for fouling deterrence, is a key research area, with the aim of melding environmental consciousness with operational efficiency. Through evolution, nature has developed highly functional and efficient approaches in adaptation to the environment with marvelous capabilities of superhydrophobicity, superoleophobicity, superamphiphobicity etc. Self-cleaning properties of lotus leaves (Fig.1a), drag-resistance of shark skin (Fig.1b) are both plethora of intricate adaptive behaviors of living organisms have been explored.
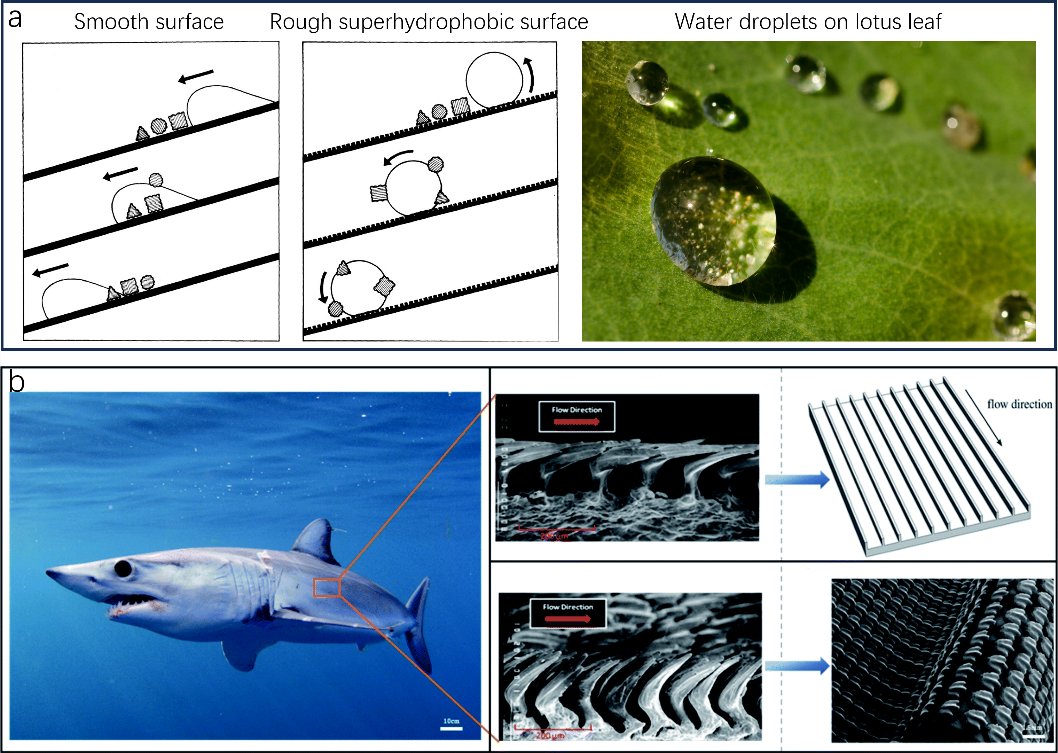
Figure 1. Superhydrophobic hierarchical surface structures of lotus leaf and shark skin. (a) A cartoon demonstrating the self-cleaning effect on a lotus leaf. (b) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the sharkskin.
These magnificent characteristics of plants and animals are basically achieved by their hierarchical micro, nano-structures made up of low surface energy chemicals. As a result, inspired by these delicate, brilliant features people learnt from nature, many researchers are now focusing on finding ways to construct biomimetic anti-fouling surfaces and boosting their applications in the fields of marine industries, medicine, etc. This review delves into the physical structures of two bio-inspired surfaces: the lotus leaf and shark skin, emphasizing their fouling resistance and applications. Section two elaborates on two theoretical models for superhydrophobicity: the Wenzel and Cassie Baxter states. Section three explores the self-cleaning properties of the lotus leaf. Section four details both the anti-bacterial applications of devices inspired by the lotus leaf, which can remove bacteria through three distinct methods, and self-cleaning applications based on the lotus effect. Sections five and six provide insights into the theoretical model of shark skin for drag reduction and its practical applications on aircraft and turbine blades. The review concludes with an overview of the limitations and potential of these bio-inspired surfaces.
2. Superhydrophobic surfaces
The properties of a surface are predominantly influenced by its chemical composition and the microstructure of its outermost physical layer. A surface is deemed superhydrophobic when its water contact angle exceeds 150 degrees, making it highly water-repellent. However, certain materials, like carbon fiber woven fabrics, exhibit hydrophobic traits even with contact angles less than 150 degrees. This is attributed to their unique chemical bonds; the surface of carbon fiber consists of non-polar carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds. These non-polar bonds resist forming attachments with water, rendering the carbon fiber surface hydrophobic. This is a notable exception, and we’ll delve into the fundamental theories of superhydrophobicity next.
The magnitude of the contact angle is determined by the adhesion force, the adhesion force will be formed by the different properties of the solid surface, the different properties of the liquid and the interaction between the solid and the liquid. A stronger adhesive force results in a larger contact area and a reduced angle, while a weaker force leads to the opposite. Roughness can amplify the solid’s surface area, thereby geometrically augmenting hydrophobicity, as described by the Wenzel model. On the other hand, air can remain trapped below the drop, which also leads to a superhydrophobic behavior, because the drop sits partially on air (Cassie model). This understanding has inspired the design of artificial superhydrophobic surfaces by emulating natural biological structures. An illustrative diagram is provided below for clarity
\( cos{θ^{*}}=-1+φs(1+cosθ)\ \ \ (1) \)
\( cos{θ^{*}}=rcosθ\ \ \ (2) \)
where \( {θ^{*}} \) is the apparent contact angle on a rough (hydrophobic) substrate, \( θ \) is the Young’s contact angle (determined on a flat surface of the same nature) , \( r \) is defined as the ratio of the actual over the apparent surface area of the substrate.
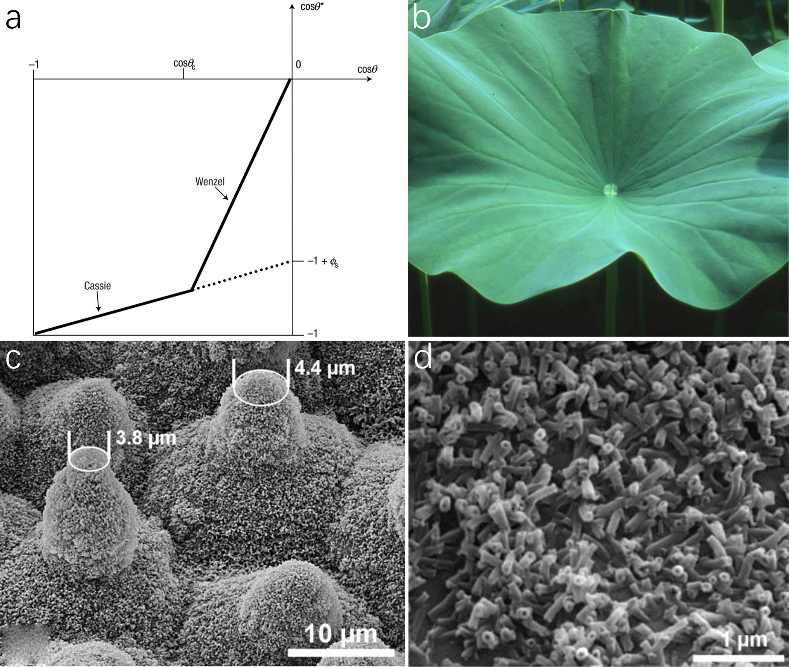
Figure 2. Superhydrophobic hierarchical micro-nano scale surface strucures of lotus leaf. (a) Two models of superhydrophobic. (b) Image of lotus leaf high water repellency on the upper side. (c) SEM of hierarchical structures with papillae and wax tubules clusters. (d) SEM image of epicuticular wax crystals.
As shown in Fig. 2a, when \( θ \) is greater than \( {θ_{c}} \) (the threshold value), the air is trapped between the water droplet layer and the solid surface, so it shows the Cassie state, it depends on Equation (1). when \( 90° \lt θ \lt {θ_{c}} \) , the surface shows wetted condition and it belong to Wenzel model on Equation (2).
3. Self-cleaning properties of lotus leaf
Natural superhydrophobic species have gained great interest in many daily applications such as anti-fouling, anti-corrosion, anti-microorganism, anti-adhesion, etc. Superhydrophobic lotus leaf with water contact angle /sliding angle being \( \gt 160° \) / \( \lt 10° \) shows excellent self-cleaning properties referred to as lotus effect. Various contaminants including bacteria, algae, pathogenic microorganisms, dust, etc. could be carried away along the way where water droplets on lotus leaf are rolling off. Superhydrophobicity is defined by contact angle \( \gt 150° \) and sliding angle \( \lt 10° \) which is similar to that of lotus leaf. Therefore, replicating lotus leaf geometric structures and chemical composition is one way of implementing superhydrophobicity. Drawing inspiration from the lotus effect, numerous superhydrophobic surfaces mimicking the lotus leaf have been developed for diverse applications, including solar panels, window panes, paper, textiles, and more. This section delves into the superhydrophobic nature and water contact angle hysteresis of the lotus leaf.
3.1. Superhydrophobicity of lotus leaf
Lotus leaf (Nelumbo nucifera) (Fig. 2b) being an icon for remarkable water repellency and self-cleaning is the result of their hierarchical surface geometry including micro-scale convex epidermal cell papillae and nano-sized hair-like wax tubules as well as the hydrophobicity of wax materials. Lotus leaf surface is covered with epidermis cells forming papillae shapes with varying heights and spacing distances. As shown in Fig. 2c, the shape of papillae is ogive rather than cylindrical with its apex radius to be 4 \( μm \) smaller than that from the bottom. The surfaces of papillae are covered with clusters of high-density, hair-like nano-scale wax crystals (Fig. 2d). It has been reported that the small radius of papillae apex are protective of most of the hydrophobic wax materials on papillae due to only the minimum damage area on papillae tips leaving the rest of the papillae intact when facing destruction such as mechanical abrasion.
Furthermore, the hierarchy of lotus leaf surface with micro-scale papillae and nano-sized wax tubules is crucial in maintaining superhydrophobicity. Cheng et al. have demonstrated the importance of nano-scale hair-like wax crystalloids in the effect of water repellency by means of measuring contact angles of lotus leaf’s surfaces with and without wax tubules by thermal annealing. Compared to the intact lotus leaf, the annealed sample without nano-scale wax tubules showed an apparent decrease in water contact angle. The significance of roughness on hydrophobicity can be implied from Wenzel theory in which the apparent contact angle is defined by the following equation:
\( cos{θ_{w}}=rcosθ \) ,
where \( θ \) refers to contact angle on smooth homogeneous surfaces, r refers to the ratio of the rough surface area to the projected flat surface area which is always greater than one. According to the Wenzel equation, a hydrophobic surface becomes more hydrophobic with an increase in r under roughening situation while a hydrophilic surface becomes more hydrophilic with roughness. Therefore, the presence of nano-scale epicuticular wax tubules to increase the roughness of lotus leaf surface is responsible for the large contact angle in superhydrophobic lotus leaf surfaces. Yamamoto et al. illustrated the importance of nanostructures on lotus leaf by dipping in ethanol to remove wax tubules. The results showed that water contact angle dropped dramatically from 162 \( ° \) to 122 \( ° \) which is in consistent with the Wenzel theory. Therefore, multi-scale hierarchy is proved to be a significant characteristic in achieving superhydrophobicity.
3.2. Water contact angle hysteresis of lotus leaf
The lotus leaf’s self-cleaning mechanism is driven not just by its pronounced superhydrophobicity and high contact angle but also by its low water hysteresis. This hysteresis is characterized by the slight variance between the advancing and receding contact angles. Owing to this low hysteresis, water droplets on the lotus leaf can effortlessly roll off, collecting and removing contaminants like dust, microorganisms, and bacteria in their path (refer to Fig. 1a). Moreover, the leaf’s significant contact angle ensures that no water remnants are left behind, preserving a clean and untouched surface.
Low hysteresis in lotus leaf can be explained by varying heights of papillae, the presence of highly-dense, nano-scale wax tubules, and small spacing distances between wax tubules allowing water droplets to form Cassie-Baxter state. The varying heights of ogive-like papillae provide a reduced adhesion between water and papillae allowing air cushions to form in the interface of solid and liquid. The water droplets on lotus leaf only sit on the tips of papillae with minimum contact area which makes droplets to roll off effortlessly when the surface tilted even only a few degrees. The presence of nano-sized wax tubules and their spacing distances also shows great impact on low hysteresis. Cheng et al. have demonstrated the importance of nano-scale hair-like wax crystalloids on the rolling behavior of droplets. The annealed sample without nano-scale wax tubules remained pinned on the surface even when the substrate was tilted vertically whereas the intact lotus sample showed excellent sliding off behavior at slightest incline. The disappearance of nano hair-like wax crystalloids made water droplets on lotus leaf transit from Cassie-Baxter state into Wenzel state where all drops completely infiltrate into the nanostructures without any air fraction. Therefore, two level roughness of lotus leaf surfaces, in particular nano-scale wax tubules, is significant in designing self-cleaning surfaces with low water contact angle hysteresis. However, sticky water droplets on intact lotus leaf can also form through water condensation or long-time underwater immersion where nanostructures of lotus leaf cannot prevent water from penetrating which shows limitation of two-level roughness on self-cleaning properties.
4. Nanoparticles-modified lotus-leaf-like anti-fouling surfaces
The lotus leaf’s self-cleaning capability stems from its unique two-level hierarchical surface structure, which effectively shields the leaf from contaminants like dust, algae, microorganisms, and bacteria. To replicate the self-cleaning attributes of the lotus leaf, researchers have explored various fabrication techniques, including soft lithography, sol-gel methods, templation, etching, self-assembly, and electrospinning. However, most of the methods either require specialized, costly instrumentations or cannot be easily scaled up for large-area coatings. Surfaces modified with nanoparticles can not only precisely mimic the two-level hierarchical surface structure of lotus leaf, but also show flexibility in fabrication. Surfaces with different contact angles can be controlled by altering the diameters and aggregate sizes of nanoparticles. Furthermore, given that nanoparticles are typically affixed to substrates using methods like layer-by-layer, chemical vapor, or electrochemical deposition, creating expansive surfaces with basic equipment becomes feasible.
While many nanoparticles have been used in producing self-cleaning biomimetic surfaces including antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO), TiO2, Al2O3, SiO2 nanoparticles etc., silica-based nanoparticles are the most commonly used recipe in self-cleaning superhydrophobicity due to their limited residual hydroxyl groups after treated with hydrophobic agents. Ma et al. developed decorated electrospun fibers with fine silica nanoparticles using layer-by-layer deposition which reached a contact angle of 168 \( ° \) and an almost zero sliding angle. Hoefnagels et al. reported superhydrophobic cotton textiles that transferred the initial hydrophilic cotton into superhydrophobic cotton textiles by covalently bonding modified silica nanoparticles onto hydrophilic cotton serving as lotus-leaf-like nanostructures. Due to the promising self-cleaning properties of nanoparticle-modified cotton materials, superhydrophobic cotton fabrics can be used in many aspects including outdoor sports shoes, waterproof raincoats, stain-resistant overcoats, etc.
Designing superhydrophobic surfaces with extraordinary stability, durability, and flexibility which shows a promising future for many self-cleaning applications is limited by their hierarchical roughness. Therefore, developing highly durable surfaces has been attracting great interest in producing self-cleaning designs. Xu et al. have developed a robust lotus-leaf-like hierarchical structure using inorganic SiNCO nanoparticles. Due to the stable inorganic SiNCO nanoparticles grafted on the ceramic substrate, the material revealed satisfactory stability under high temperature, stirring abrasion, and aqueous solutions of several acids and alkalis.
Transparent self-cleaning designs are desirable for uses in solar cell panel, car window shields, paper, and so on. However, surface roughness, an indispensable condition in fulfilling superhydrophobicity, is inversely dependent on light transmittance. With increasing hierarchical surface roughness, more light is scattered resulting in surface opaque. Few transparent superhydrophobic surfaces with nanoparticles is reported. Wong et al. recently reported an ultra-durable, transparent self-cleaning surface with fluoro-functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles. The surfaces succeeded in achieving a contact angle of 161 \( ° \) , a sliding angle of 10 \( ° \) which meet the requirements of superhydrophobicity and 85% visible light transmittance. Besides, the superhydrophobic surfaces could be coated on different substrates including paper towels, bricks, wood, and aluminum with excellent chemical-, mechanical- and photostability showing a promising future for large-scale fabrication.
4.1. Nanoparticles-modified lotus-leaf-like surfaces for anti-bacterial applications
Bacterial cell adhesion and subsequent colonization, culminating in biofilm formation, present significant challenges. These can result in environmental issues, industrial equipment malfunction, and contamination of fuels, chemicals, and water. This impacts a range of applications, from microfluidics and biomedical devices to ships and food packaging. The exemplification of bacteria adhesion and propagation was first carried out by Zobell et al. demonstrating that bacteria prefer to colonize on solid surfaces. Biofilm is mainly formed following three steps: (1) bacteria attachment on solid surfaces via forces such as Van der Waals, electrostatic, and hydrodynamic force, etc. (2) colonization of bacteria in forms of extracellular polymeric substances producing mushroom-like biofilm. (3) detachment of some bacteria cells which will be settled in another surface area to form biofilm. Therefore, limiting bacteria attachment on surfaces is the most important in designing anti-bacterial surfaces. The 20th century saw the advent of antibiotics designed to eliminate or inhibit bacterial growth. However, their widespread accessibility and efficacy led to overuse, prompting bacteria to develop resistance. Nature offers inspiration: numerous plants and animals have evolved anti-bacterial mechanisms through anti-biofouling and bactericidal properties. Lotus leaf with their remarkable self-cleaning performance due to hierarchical micro-scale papillae covered with nano-sized wax crystalloids has been attract much attention to researchers for promising anti-fouling, bactericidal films. This section reviews nanoparticle-modified, lotus-leaf-inspired surfaces that employ physical and photocatalytic sterilization techniques.
4.1.1. Anti-biofouling of lotus-leaf-like surfaces. Bacteria adhesion leading to biofilm formation on surfaces can cause serious defects on the functionalities of superhydrophobic surfaces. Two main strategies for creating anti-bacterial surfaces are killing bacteria cells that are in contact with surfaces and programming hierarchical micro- and nano-structures that prohibit bacteria from contacting the surfaces. Producing anti-biofouling surfaces is crucial since the accumulation of dead bacteria cells can lead to the destruction of surface functions. Inspired by the self-cleaning properties of superhydrophobic lotus leaf which prohibit bacteria cell attachment, many researchers have designed anti-bacterial surfaces mimicking the hierarchical surface structures of lotus leaf exhibiting excellent anti-bacterial adhesion performances. Chu et al. developed an agricultural plastic film by combing carbon dots (CDs) and silica nanoparticles (SiO2) which were used to create micro/nano hierarchical structures with montmorillonite (MMT)/ organically modified montmorillonite (OMMT) to lower surface energy blending with low-density polyethylene (PE). The anti-bacterial performance of the resultant PE/FSi-SiO2/CDs@MMT and PE/FSi-SiO2/CDs@OMMT with two kinds of bacteria including Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). Large bacteria colonies were seen co-cultured on surfaces of base PE materials while there were almost no colonies observed on surfaces of PE/FSi-SiO2/CDs@MMT and PE/FSi-SiO2/CDs@OMMT. This reduction in bacteria adherence is a result of the multi-scale micro-/nanostructures that existed on the lotus-leaf-like surfaces where lots of air was trapped in the interface area between surfaces and liquid leading to a reduced contact area for bacteria. With the reduced contact area between bacteria and surfaces, it is hard for bacteria to attach to and penetrate into the targeted surfaces. As a result, the multi-scale micro-nano surface structures imparted by CDs and silica nanoparticles gave rise to excellent anti-fouling, anti-bacterial adhesion properties for a wide range of agricultural applications.
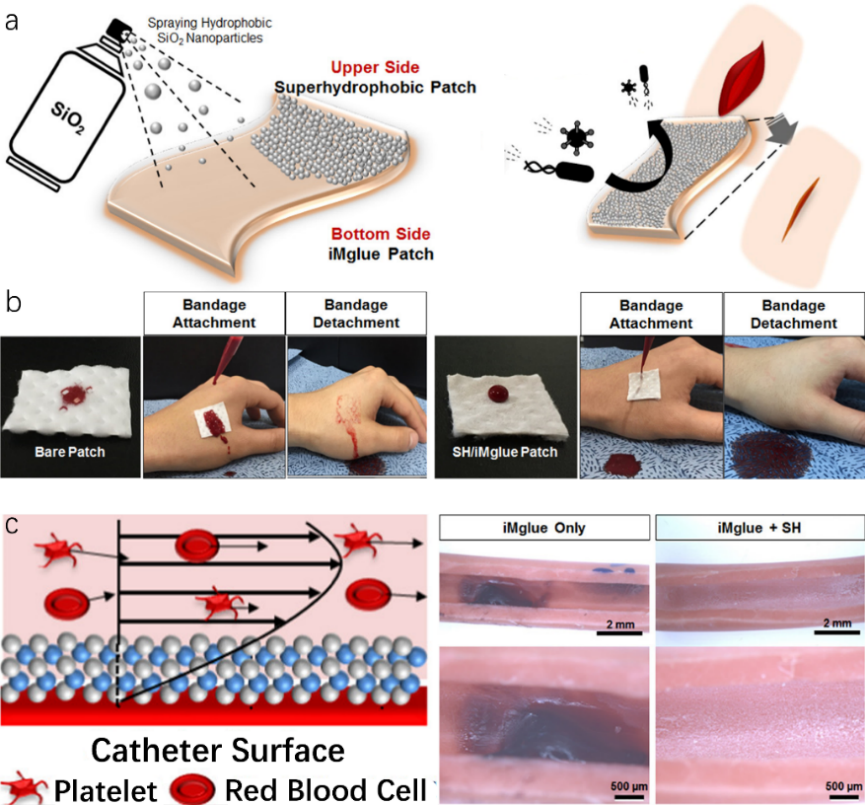
Figure 3. Lotus leaf-like superhydrophobic surface for anti-biofouling applications. (a) Schematic image of a superhydrophobic patch by spraying hydrophobic SiO2 nanoparticles on the iMglue-coated patch and its anti-biofouling mechanism. (b) Blood-proof effect of SiO2/iMglue patch. (c) Antithrombotic mechanism and performance of SiO2(TiO2/SiO2)2 thin coatings.
Other lotus-leaf-like anti-fouling surfaces for biomedical applications were carried out by Han et al.. An anti-biofouling patch, fabricated by simply spraying hydrophobic SiO2 nanoparticles on an iMglue-covered cotton surface, showed superior anti-biofouling quality due to the lotus effect (Fig. 3a). Minimum contact area between foulants like dust, bacteria, antigens, etc. and patch directly led to a reduction in cells adherence which could lead to undesirable biofilm formation. Fig. 3b compared blood-repellent performance on bare patch and SiO2/iMglue patch respectively. The bare patch without lotus leaf structures was fully contaminated with blood full of microorganisms which could cause further infection for wounds. On the contrary, SiO2/iMglue patch exhibited extraordinary blood repellency without any contamination on the skin beneath as a result of the micro-nano structure by SiO2 nanoparticles. Furthermore, a superhydrophobic SiO2(TiO2/SiO2)2 thin coating through layer-by-layer growth of SiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles was produced to exploit potential antithrombotic catheter application. As illustrated in Fig. 3c, superhydrophobic SiO2(TiO2/SiO2)2 thin coating allowed air pockets to be trapped in the interface between coating and liquid which allows platelets and red blood cells to flow at a faster shear rate near coating. On the contrary, bare iMglue coating displayed an apparent blood coagulation since no air pockets were formed due to the absence of any hierarchical structures leading to a comparative slower shear rate on the surface. As a result, the biomimetic anti-biofouling coating with biomedical multifunctionalities emphasized the importance of hierarchical surface structures in designing superhydrophobic surfaces with anti-biofouling properties which can be achieved by applying modified nanoparticles.
4.1.2. Physical sterilization of lotus-leaf-like surfaces. According to the lotus effect, lotus leaf surfaces repel most microorganisms especially bacteria due to their extraordinary anti-biofouling quality owing to the unique hierarchical micro-scale papillae covered with nanosized wax crystalloids. However, as time goes on, some of bacteria will be attached to the surfaces leading to biofilm formation. Therefore, developing bactericidal mechanisms on superhydrophobic functional surfaces is very important. Apart from the famous self-cleaning and anti-biofouling properties that the superhydrophobicity lotus leaf possesses, recently researchers have found that lotus leaf hierarchical structures make lotus leaf possible to display excellent bactericidal activity via a cell-rupturing mechanism. Fig. 4 compared images of bacteria on both the silicon surface and fresh lotus leaf surface after 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h incubation respectively. After 3 h incubation, no bacteria have appeared on fresh lotus leaf compared to that of silicon surface indicating excellent anti-biofouling performance. With increasing incubation time, more bacteria appeared on fresh lotus leaf but none of which were alive. Compared with the bacteria cells found on silicon surface, the dead cells on fresh lotus leaf were highly deformed and cellular components were engulfed by nanostructured wax tubules. It is reasonable to believe that bacterial inactivation is the result of mechanical cell rupture in which wax nanotubes of lotus leaf stretched bacteria membranes to crack leading to leakage of intracellular components.
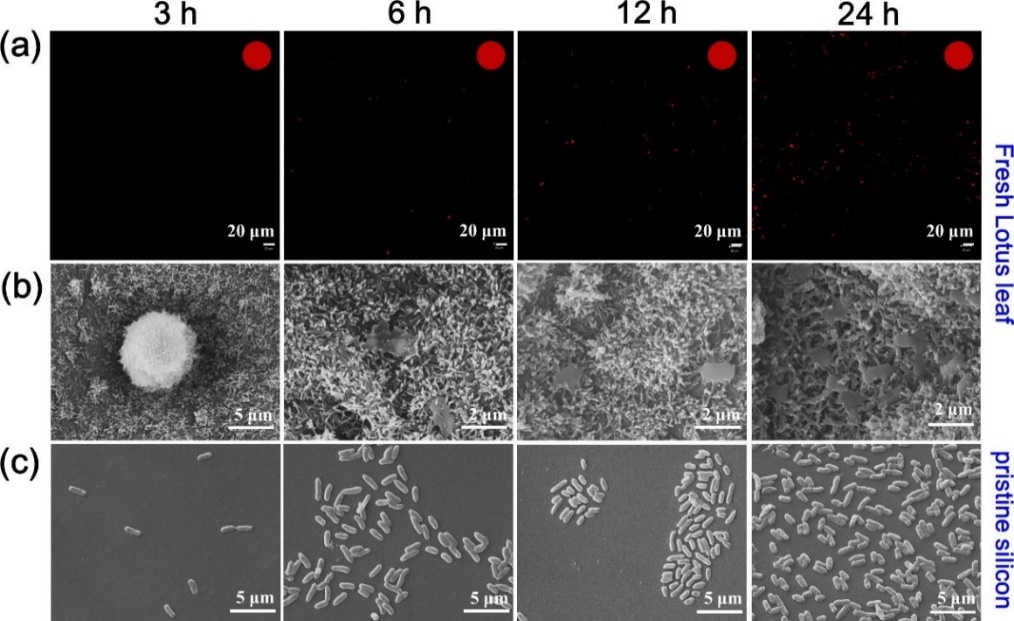
Figure 4. Representative SEM and Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) images of bacteria on the pristine silicon and fresh lotus leaf surfaces after 3 h, 6 h, 12 h and 24 h incubation. (a) CLSM images of E. coli cells on lotus leaves and insets in the top right corner present the percentages of live bacteria (green) and dead bacteria (red). (b) SEM images of E. coli cells modalism on fresh lotus leaf. (c) SEM images of E. coli cells on the pristine silicon surfaces.
4.1.3. Photocatalytic sterilization of lotus-leaf-like surfaces. Pure physical bacteria sterilization usually takes a long time with low efficiency and intensity. Therefore, other sterilization strategies such as photocatalytic sterilization are investigated to overcome those difficulties. Photocatalytic sterilization is a highly effective, low-cost strategy to eliminate biological pollution with the following steps: (1) photocatalyst materials generate photo-generated holes (h+) and photo-generated electrons (e-) when stimulated by certain light. (2) h+ and e- react with oxygen and water to produce various reactive oxygen (ROS) species such as superoxide anion radical (•O2−), hydrogen peroxide(H2O2), singlet oxygen (1O2), and hydroxyl radical (•OH). (3) ROS have strong oxidizing properties to kill bacteria by destroying their cell walls, cell membranes, DNA, lipids, proteins, etc. Wan et al. reported a lotus-leaf-like cotton fabric loading with TiO2 nanoparticles which could sterilize 100% Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli within 30 min under UV irradiation. The TiO2 nanoparticles serving dual functions not only fully mimicked lotus leaf hierarchical surface structures transiting intrinsic hydrophilic cotton into hydrophobic fabric, but also functioned as photocatalysts for photocatalytic sterilization. Although TiO2 nanoparticles are the most common in the photocatalyst system, ultraviolet light is indispensable in functioning TiO2 photocatalyst nanoparticles which can cause limitations in many applications. On the contrary, ZnO nanoparticles as photocatalysts require only visible light to trigger which can be widely applied to fields that require non-toxicity, biocompatibility, etc. Hu et al. have developed a laser-treated organic polysilazane (OPZ) coating with uniformly dispersed ZnO nanoparticles showing an anti-bacterial rate of 93.89% (Fig. 5a). The addition of ZnO nanoparticles increased the superhydrophobicity of OPZ coating with contact angle/sliding angle to 164.1 \( ° \) /1.5 \( ° \) via increasing surface roughness. The resulting OPZ-ZnO coating was able to prevent most of the bacteria from penetrating into the micro-protrusions and kill the adhesive bacteria by means of photocatalytic sterilization.
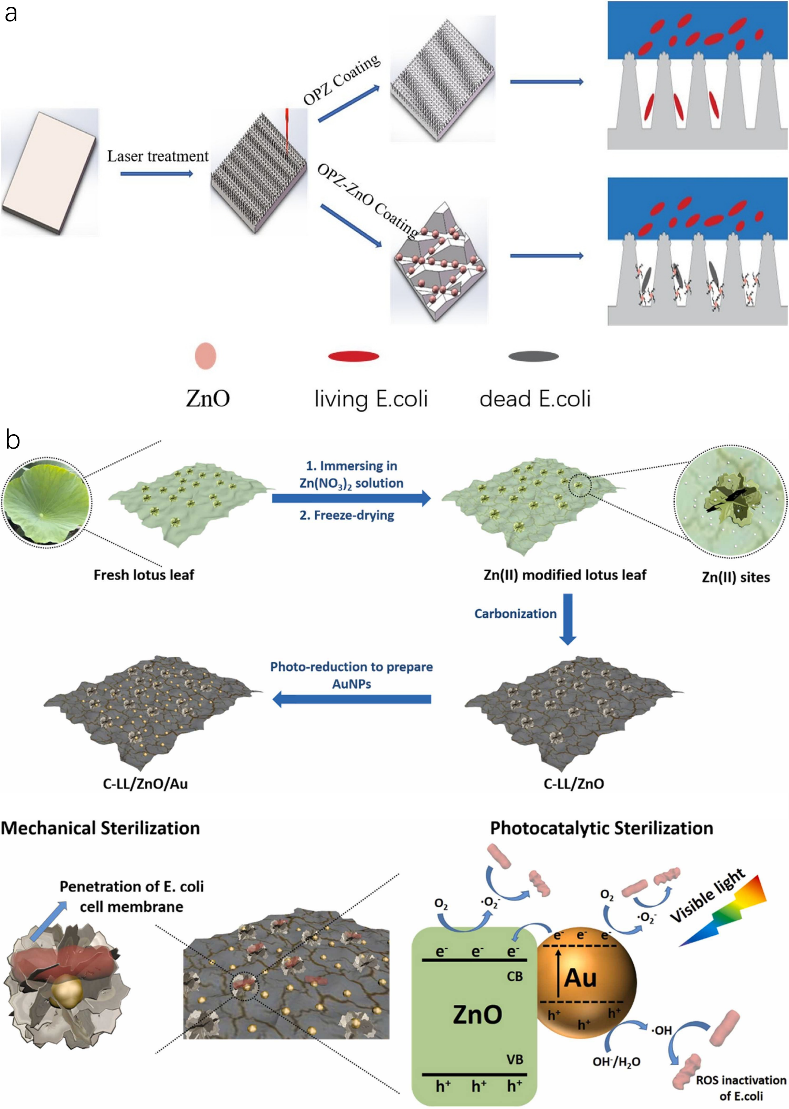
Figure 5. Lotus leaf-like nanoparticles-modified coatings for anti-bacterial applications. (a) Scheme of anti-bacterial performance of OPZ coatings with/without ZnO nanoparticles. (b) Schematic illustration for the preparation of C-LL/ZnO/Au as well as the synergistic mechanical sterilization and photocatalytic sterilization mechanism under visible light irradiation.
Due to the limited physical mechanical sterilization time and efficiency via cell rupture by lotus leaf hierarchical surface structures, developing synergistic anti-bacterial performance through both physical sterilization and photocatalytic sterilization is significant. Xu et al. for the first time developed a synergistic physical and photocatalytic sterilization method using carbonized lotus leaf/ZnO/Au for improving anti-bacterial performance. As shown in Fig. 5b, fresh lotus leaf was treated with Zn(NO3)2 solution to decorate Zn(II) on lotus leaf which was further freeze-dried and calcined under N2 gas to form C-LL/ZnO. With the aid of photoreduction, gold nanoparticles were added to construct C-LL/ZnO/Au with preserved hierarchical surface structures of the lotus leaf. The C-LL/ZnO/Au exhibited remarkable synergistic bactericidal performance against E. coli that all the bacteria cells were inactivated within half an hour under visible light due to the introduction of gold nanoparticles which largely enhanced both physical and photocatalytic sterilization enforcement. The introduction of Au nanoparticles increased the surface roughness of the product and the sharpness of papillae which directly led to bacteria cell wall damage leading to a reduced number of bacteria alive. Subsequently, Au nanoparticles generated e- and h+ under visible light via localized surface plasmon resonance effect. Some e- reacted with oxygen to produce •O2− while as the rest were transferred to the conduction band of ZnO to further generate •O2− due to a lower Fermi level of Au compared to ZnO. Meanwhile, the h+ of Au nanoparticles reacted with OH-/H2O to form •OH. All the ROS created by Au nanoparticles and ZnO were capable of destroying the integrity of bacteria by destroying their membranes and biomacromolecules which led to total death of bacteria cells. The resultant physical sterilization rate of C-LL/ZnO/Au was reported to be 79.5% in 30 min which was 4.7 times of the antibacterial rate of the natural lotus leaf. The photocatalytic sterilization rate alone of C-LL/ZnO/Au was 93.8%. In comparison, under synergistic sterilization of physical and photocatalytic, the anti-bacterial rate of C-LL/ZnO/Au achieved 100% within 30 mins.
4.2. Nanoparticles-modified lotus-leaf-like surfaces for self-cleaning performance
Self-cleaning capabilities are crucial in preventing performance deterioration caused by dust and various liquids. Such features have broad applications, spanning functional clothing, surgical attire, military uniforms, spacesuits, and protective building coatings, among others. Drawing inspiration from the lotus leaf’s superhydrophobicity—attributed to its hierarchical surface structures of micro-scale papillae cells adorned with randomly dispersed epicuticular wax crystalloids—researchers have crafted nanoparticle-modified, biomimetic lotus leaf surfaces. These innovative surfaces showcase exceptional liquid repellency and self-cleaning efficacy against particulates like dust. The morphology of these nanoparticles closely emulates the structures and functionalities of the lotus leaf’s wax crystalloid tubules, resulting in biomimetic surfaces that exhibit high liquid contact angles for various fluids, as illustrated in Fig. 6a-c. Zhao et al. demonstrated a superhydrophobic fibrous membrane with SiO2 nanoparticles where droplets of honey, milk, juice, coffee, and black ink maintained their spherical shapes instead of immersing into the membrane (Fig. 6a). Lotus leaf-inspired applications usually reveal poor durability and stability due to their complex preparation process and high costs which strongly restrict large-scale applications in many daily and industrial products. Siddiqui et al. fabricated a transparent superhydrophobic surface that showed extraordinary stability towards corrosive liquids such as 1 M NaOH, 1 M NaCl, 1 M HCL, and hot water (Fig. 6b). Liu et al. developed a durable superhydrophobic conductive coating which displayed stable superhydrophobicity towards different liquids such as milk, cola, coffee, and various droplets with different pH values ranging from pH=1 to pH=14.
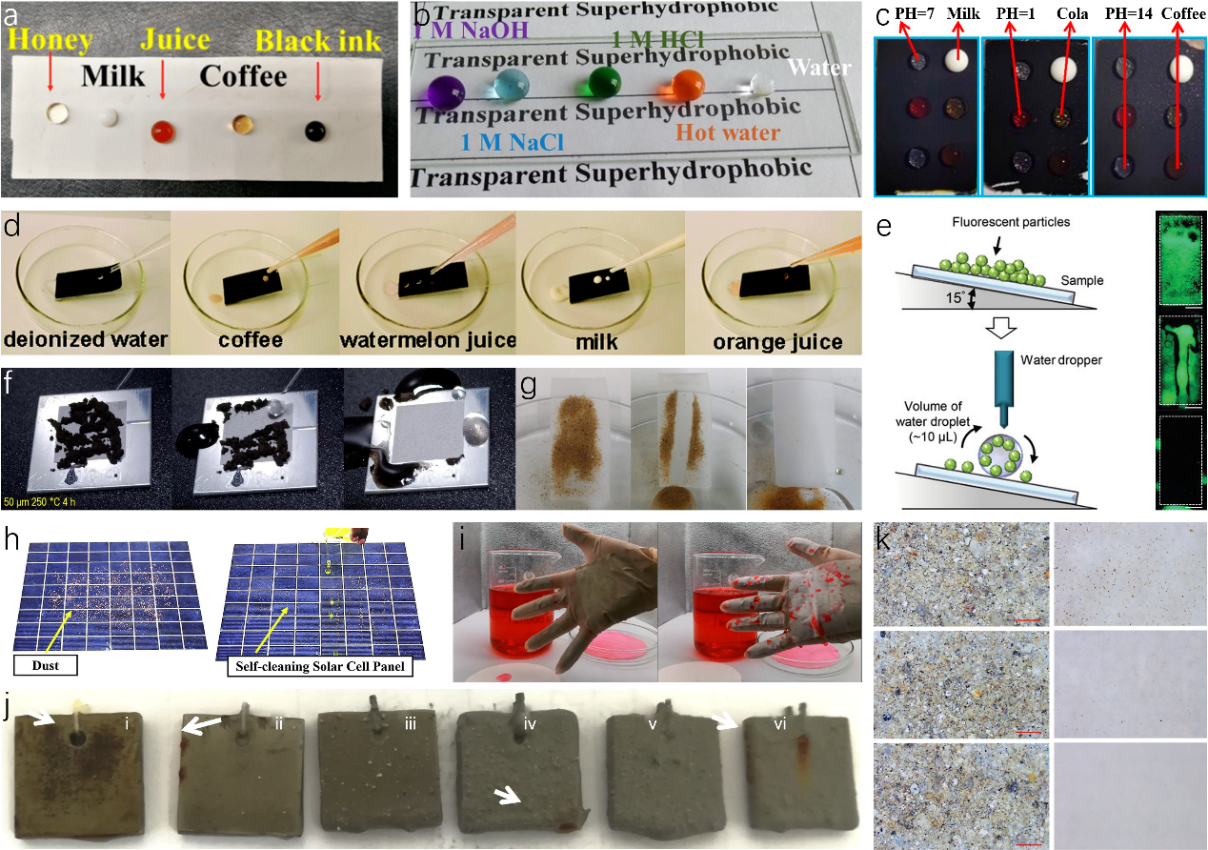

Figure 6. Self-cleaning performance of lotus leaf-like nanoparticles-modified superhydrophobic surfaces. (a) Image of five kinds of fluids on SBS/PDA/SiO2 fibrous membrane coating. (b) Various corrosive fluid droplets including (1 M NaCl, NaOH, HCl aqueous solution, and hot water) placed on the coated superhydrophobic glass surface. (c) The states of different droplets on the coating surface. (d) Photographs of various liquid repellency tests on a coated filter paper, including deionized water, coffee, watermelon juice, milk, and orange juice. (e) Schematic of self-cleaning test setup and performance. (f) Self-cleaning properties for graphene oxide powders of LAS1 heat-treated for 4 h at 250 °C. (g) Photographs of the self-cleaning process on the superhydrophobic surface. (h) Photographs of self-cleaning capacity of superhydrophobic solar cell panels. (i) Self-cleaning performance of uncovered and SBS/PDA/SiO2 modified gloves after immersion in red dye solution. (j) Image of coatings after immersing in water for 95 h (i) acrylic resin, (ii) 2 wt.% TiO2, (iii) 10 wt.% TiO2, (iv) 20 wt.% TiO2, (v) 30 wt.% TiO2 and (vi) 40 wt.% TiO2. (k) Dust removal performance by wind on the surfaces of bare glass, FHA hydrophobic coating, FHA/SiO2 superhydrophobic coating from top to bottom respectively.
Self-cleaning performance is attributed to the air pockets trapped in the solid/air interfaces of hierarchical micro- and nano-structures of lotus leaf forming Cassie-Baxter state which minimize the contact area between foulant and leaf surfaces allowing droplets to roll off effortlessly and to carry foulants along the way. Cao et al. illustrated a liquid-repellent surface that permeated six kinds of common liquids including deionized water, coffee, watermelon juice, milk, and orange juice to easily roll off without leaving any traces (Fig. 6d). Through dropping water droplets of tilted lotus leaf-like surfaces, particles such as fluorescent particles mimicking dust and PM2.5 particles, graphene oxide powders, and sands were removed (Fig. 6e-g). The outstanding self-cleaning capacity of lotus leaf-like designs can be widely applied in various fields such as solar cells, protective coatings, underwater infrastructures, furniture, marbles, etc. solar cells, converting solar energy into electricity, depend largely on light absorption which can be easily diminished by blocking solar panels surfaces with dust. An improved performance can be achieved by introducing self-cleaning capacity. As shown in Fig. 6h, the solar cell panel covered with superhydrophobic coating exhibited no performance degradation by removing all dust particles on the surface in one single attempt through water droplets. Protective clothing especially gloves that command extreme cleanness are widely used in daily, industrial, and research activities. Fig. 6i compared the water repellency between uncovered and superhydrophobic covered gloves. The superhydrophobic modified gloves were undyed without any droplets and retained its original state while the uncovered gloves were stained with red dye and turned pink with droplets stuck on the surface. Metal materials are commonly used in infrastructures and metal corrosion underwater is a common issue that could cause fortunes in maintenance services. Sun et al. developed TiO2/acrylic resin coatings that showed excellent anti-corrosion capacity on metal (Fig. 6j). After immersion in water for 95 h, no corrosion products were found on the surface with 30wt% TiO2 nanoparticles indicating an enhanced water resistance against corrosion under the addition of nanoparticles. Almost all of the self-cleaning ability of lotus leaf-like devices are accomplished by adding water droplets on the surfaces which would limit uses in some applications. Wang et al. fabricated superhydrophobic FHA/SiO2 coatings with obvious anti-soiling capacity only by wind (Fig. 6k). All volumes of dust including large and small particles on the surface FHA/SiO2 superhydrophobic coating were completely removed by breeze compared to the bare glass where fine and small dust particles were still adhered on the surface.
5. Drag Reduction Properties of Shark Skin Surface
In the world of biomimetics, sharks have consistently piqued interest. Their ability to achieve remarkable speeds in the water, despite their substantial size, is intriguing. It was once widely held that smoother surfaces with minimal roughness would face less resistance in fluid environments. However, a closer examination of shark skin tells a different story: it’s intricately covered with placoid scales set in a diamond-like arrangement. These scales, illustrated in Fig. 7a, are etched with grooves that align with the direction of the shark’s movement. Made of an enamel-like substance, the placoid scales are characterized by sleek spines and basal plates deeply embedded in the dermis. The presence of this riblet configuration on the scales refines the fluid boundary layer on the shark’s skin, curbing turbulence onset and effectively cutting down the drag as the shark propels through the ocean.
5.1. Scale Shape and Arrangement of Shark Skin
Sharks are adorned with tiny scales, known as denticles or placoid scales, that bear a striking resemblance to teeth. Each scale is composed of a pulp cavity enveloped by a tough enameloid layer and is anchored to the skin’s collagenous layer, referred to as the Stratum Laxum, as illustrated in Fig. 7b. The part of the shark’s body that interacts with water is shaped by the interlocking crowns of these scales. In certain species, these scale crowns are equipped with diminutive riblets or keels that align with the direction of the water flow. Interestingly, some scales have evolved the capability to bristle or elevate when the flow direction reverses. This adaptation is facilitated by modifications in the base’s length relative to the crown and specific alterations to the base shape in particular body areas. Normally, flow passes over the surface from left to right, but when flow reverses from right to left, scale bristling can occur. The length of scales is typically consistent within specific body regions of a species but can vary across regions and species. Similarly, the number of keels per scale remains consistent within a species and location. The length of the scales is usually 100 ~ 200 μm, and the width between the ribs is 50 ~ 100 μm. The compact and orderly arrangement of placoid scales, forming a tooth-like pattern with the tips pointing in the same direction, and the overlapping of adjacent scales at the edges, all contribute to the shark’s excellent drag reduction capabilities in water.
In 1936, a striking observation was made by British biologist Gray: the theoretical energy dolphins should expend during swift swimming was a staggering seven times more than their actual consumption. This revelation ignited interest in the biomimetics of drag reduction for large marine animals known for their speed. By the 1980s, the exploration of riblet structures for drag minimization was underway, and materials designed to reduce drag were being tested on aircraft. Recognizing its potential, NASA earmarked this as a pivotal aviation technology for the 21st century, integrating it into their research endeavors in 1983 and initiating flight tests by 1986. Lockheed Corporation ventured into designing surfaces punctuated with consistently spaced grooved microstructures. Their experiments yielded promising results, showcasing a friction drag reduction exceeding 10%. This breakthrough captured the attention of the global research community.
In modern engineering and science, drag reduction technology has always been of great interest and pursuit. With the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and environmental protection, drag reduction has become one of the key objectives in many industries. The application of drag reduction technology can significantly reduce the drag force on moving objects in fluid media, thereby improving efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and increasing the service life of equipment. Hirt et al. introduced a technique called micro-groove rolling for preparation. They applied this method to roll a 20 mm \( × \) 2.0 mm AlMg3 plate. However, their focus was primarily on the preparation method itself, without delving into the investigation of drag reduction performance. Denkena et al., on the other hand, proposed a grinding wheel groove structure preparation process known as multi-profile grinding. This approach offers advantages in terms of efficiency and process stability. Unfortunately, they did not explore the drag reduction aspects but just raised an approach to prepare biomimetic grooves of shark skin either.
5.2. The Effect of Denticle Pattern and Spacing on the Drag Reduction Function of Sharkskin
Sharks, with their adept swimming capabilities, have evolved a skin design that has long fascinated researchers and engineers: a unique covering of minuscule, tooth-like structures known as denticles. Given the variance in denticle sizes across different shark species, the influence of denticle patterns and spacing on the drag-reducing properties of sharkskin has become a focal point of research. The goal is to discern the optimal combination of denticle pattern and spacing to minimize drag during swimming. By delving into the nuances of sharkskin and probing how denticle patterns and spacings modulate drag reduction, scientists like Liwen et al. aspire to unearth insights that could redefine biomimicry and catalyze breakthroughs across sectors.
In their research, Liwen and colleagues zeroed in on the denticle configurations on sharkskin and the functional ramifications of varying patterns. They opted for a specific denticle shape, crafting three unique patterns using advanced multi-material additive manufacturing methods. These patterns were imprinted onto pliable panels, which were then fashioned into dual-layer membranes for testing (as depicted in Fig. 7c). The team undertook both static drag assessments and dynamic swimming trials to holistically comprehend the hydrodynamics linked to sharkskin denticle configurations. Through dynamic tests, they sought to discern if surface denticles bolster self-propelled swimming velocities and how denticle pattern alterations impact swimming efficacy. They specifically probed whether expanding denticle spacing and trimming the membrane’s surface area could enhance swimming prowess. Moreover, they juxtaposed the performance of linearly arranged denticles with a staggered layout. These denticle rearrangements led to membranes with varied denticle counts and overall surface areas. The initial hypothesis posited that the linearly-overlapped denticle arrangement would outperform others in self-propelled speeds, given its unique row alignment, setting it apart from the riblet surface. Concurrently, they theorized that the linearly-non-overlapped pattern, with its diminished surface area, might showcase superior swimming performance relative to other configurations.
However, the outcomes of the study did not align with these initial expectations. Surprisingly, the linearly-non-overlapped membrane demonstrated the slowest self-propelled swimming speeds, while the linearly-overlapped pattern was significantly slower than the staggered-overlapped pattern. The findings of the investigation highlight that only one of the three biomimetic membrane patterns exhibited clear superiority during dynamic swimming experiments. The staggered-overlapped pattern consistently achieved the highest self-propelled speeds across all tested heave conditions. Despite the fact that the total surface area of the denticles and membrane in the staggered-overlapped pattern was nearly three times that of the smooth control, the swimming speeds were, on average, approximately 20% faster. In conclusion, the staggered-overlapped pattern outperformed both the linear-overlapped pattern and the linear-nonoverlapped pattern, demonstrating significantly better swimming performance.
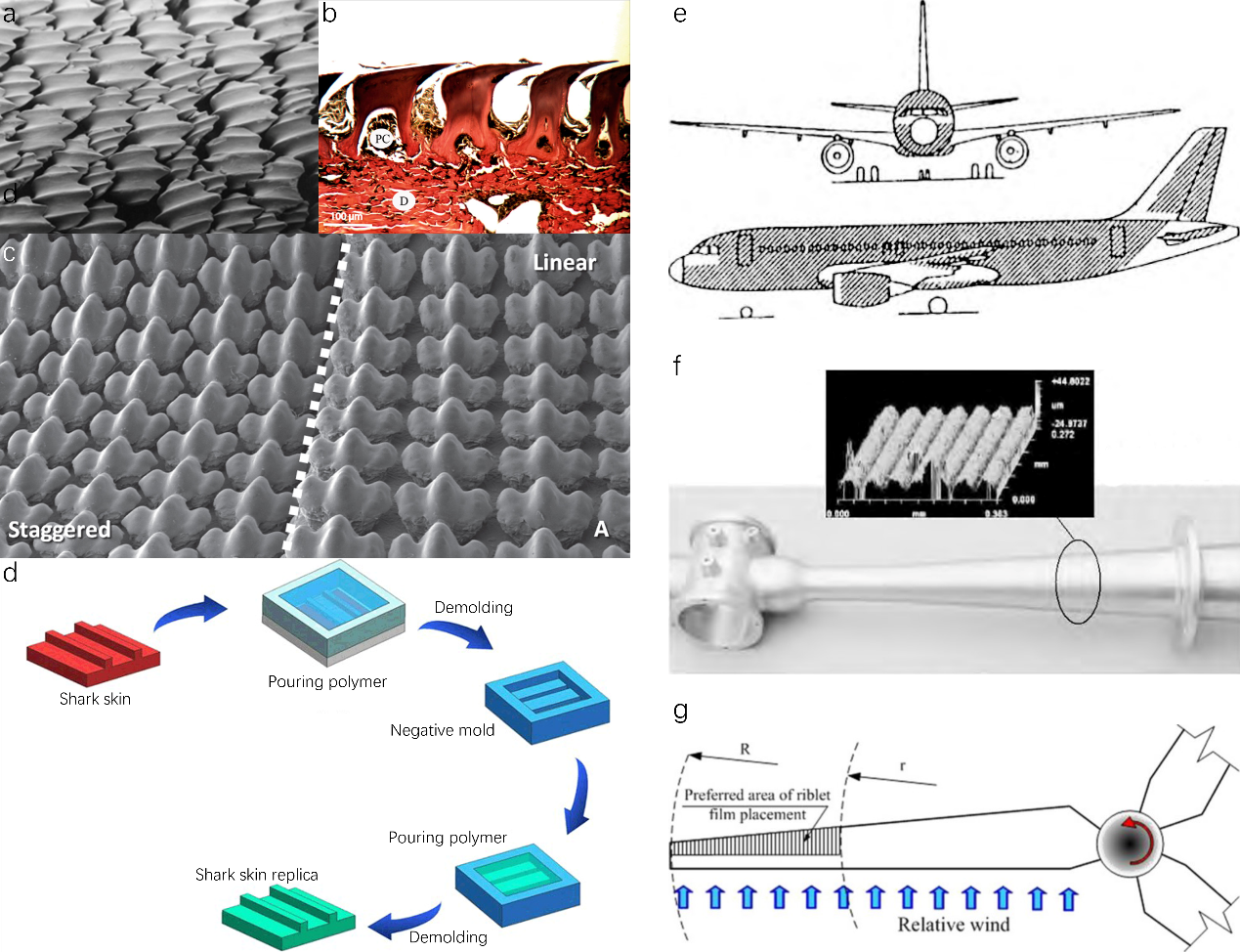
Figure 7. Original and artificial shark skin-inspired hierarchical micro-nano scale surface structures. (a) Placoid scales of shark skin. SEM image of staggered and linear alignment of the placoid scales. (b) Side view of placoid scales of a shortfin mako shark. The pulp cavity (PC) of the scale on the left is visible, and the scales are anchored to the skin’s dermis (D) by collagen fibers. (c) SEM image of staggered and linear alignment of the placoid scales. (d) The fundamental principle of bio-replicated forming method. (e) A320 skin covered with grooved film by 3M Corporation. (f) Precision cast intake manifold with micro-groove structure. (g) Wind tunnel testing of large-scale wind turbine blades and blade coating.
6. Application of the Drag Reduction Property of Sharkskin
The remarkable drag reduction property of sharkskin has garnered significant attention from various industries seeking innovative solutions to improve efficiency and performance. Inspired by the unique characteristics of sharkskin, scientists and engineers have been exploring its applications to overcome drag-related challenges in diverse fields. From aerospace to transportation, sports equipment to medical devices, the potential applications of Sharkskin’s drag reduction capabilities are vast and promising. The technique that they commonly use to replicate the surface riblet structure of sharkskin is the bio-replicated forming method, which basically uses a real biological surface as a template, and micro-replicates the surface microstructures (Fig. 7d). Various technical solutions are employed, including micro-molding, micro-embossing, vacuum casting replication, elastomeric stamping, and electrocasting. While these methods may have different technical details, they all adhere to the same fundamental principle bio-replicated forming method.
One significant factor leading to increased drag in riblet surfaces, inspired by sharkskin, is the expansion of the wetted surface area. Typically, in turbulent flow conditions, an enlarged surface area correlates with heightened fluid drag, given that shear stresses act over a broader region. Yet, with riblet surfaces, an interesting dynamic emerges: vortices form above the riblets, concentrating their interaction mainly at the tips. This confines high-velocity flow development primarily within the valleys. As a result, only the localized region around the riblet tips undergoes increased shear stresses. In contrast, the bulk of the riblet surface is subjected to reduced shear stresses, attributed to the low-velocity fluid flow nestled in the valleys. The strategic placement of vortices over the riblet tips effectively curtails cross-stream velocity fluctuations within the valleys, especially when compared to a flat plate.
Understanding the influence of the wetted surface area and the specific distribution of shear stresses on riblet surfaces is pivotal for leveraging the drag-reducing attributes of sharkskin across various domains. Two prominent applications of this technology include the integration of sharkskin riblet designs onto aircraft exteriors and turbine blades. These applications will be delved into in greater detail in the subsequent sections.
6.1. Application of Sharkskin Riblet Structure on the Aircraft Body Surface
The utilization of imitation sharkskin film on the aircraft body of Cathay Pacific’s Airbus A340 has emerged as a notable implementation in the aviation industry. This long-lasting film, inspired by the unique properties of Sharkskin, offers several advantages, including the potential to enhance the annual profitability of each aircraft by approximately 1 million US dollars, along with notable environmental benefits. Airbus has employed groove films, covering approximately 70% of the surface area of their A320 test aircraft (Fig. 7e), resulting in fuel savings ranging from 1% to 2%. Moreover, the application of a V-shaped micro-riblet film structure on the wings has demonstrated a drag reduction of approximately 6.6% under lower Reynolds number conditions compared to conventional smooth wings. These advancements highlight the significant potential for implementing sharkskin-inspired technologies to improve aircraft performance, fuel efficiency, and environmental sustainability in the aviation sector.
6.2. Application of Sharkskin Riblet Structure on the Turbine Blade
In a study conducted by Chamorro et al., a comprehensive investigation was carried out on a large wind turbine blade featuring a full size airfoil profile. The researchers implemented a groove film provided by 3M Corporation on the surface of the blade, as illustrated in Figure 7f-g. The outcomes of their study unveiled notable findings concerning the impact of these grooves on the aerodynamic performance of the blade. When the entire wing profile was covered with V-grooves, each exhibiting a height of 100 micrometers, a maximum damping effect of 6% was observed. Conversely, when the wing profile was partially covered with V-grooves, each with a height of 80 μm, a damping effect of 4% was achieved. In essence, these results indicate that the presence of grooves on the blade surface contributes to a reduction in drag, leading to a 5% decrease in overall damping. Consequently, this reduction in damping translates into an additional electrical energy production increase of 3.4%. The findings from Chamorro et al.’s study shed light on the potential of utilizing groove films to enhance the aerodynamic efficiency and power generation capabilities of wind turbine blades. Such advancements hold significant promise for the renewable energy sector, promoting improved performance and increased energy output in wind energy conversion systems.
7. Conclusion and outlook
This paper delves into the physical structures and principles underpinning superhydrophobic technology in bionics and its applications in self-cleaning. Topics covered include lotus-leaf-inspired anti-fouling surfaces, antibacterial applications, drag-reducing attributes of shark skin, and the superhydrophobic denticle patterns and spacing on skin surfaces. While significant strides have been made in these areas, challenges persist, such as the durability of anti-fouling hydrophobic materials, adaptability in extreme conditions, and production costs. The scientific community’s journey through superhydrophobic technology has been marked by deep and expansive research. Dettre and Johnson, in 1964, linked superhydrophobicity to rough hydrophobic surfaces. By 1977, they highlighted the self-cleaning capabilities of superhydrophobic nanostructured surfaces. Between 1986 and 1995, a plethora of innovative superhydrophobic materials emerged and found practical applications. Today, this technology’s imprint is ubiquitous, from aerospace fuselage materials to everyday waterproof sprays for clothing and footwear. Looking ahead, there’s potential to merge superhydrophobic structures with traits like high-temperature and oxidation resistance, expanding its reach across industries. The promise of superhydrophobic technology is immense, and continuous research endeavors aim to address current challenges, fostering mutual learning and driving benefits for humanity.
References
[1]. F. M. C. Fazey, P. G. Ryan, Environmental Pollution 2016, 210, 354.
[2]. C. E. Zobell, E. C. Allen, J Bacteriol 1935, 29, 239.
[3]. J. J. Stanković, I. Marjanović, J. Papathanasiou, S. Drezgić, J Mar Sci Eng 2021, 9, 74.
[4]. M. P. Schultz, J. A. Bendick, E. R. Holm, W. M. Hertel, Biofouling 2011, 27, 87.
[5]. P. Kim, T.-S. Wong, J. Alvarenga, M. J. Kreder, W. E. Adorno-Martinez, J. Aizenberg, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6569.
[6]. U. von Ammon, S. A. Wood, O. Laroche, A. Zaiko, L. Tait, S. Lavery, G. Inglis, X. Pochon, Mar Environ Res 2018, 133, 57.
[7]. S. M. Evans, T. Leksono, P. D. McKinnell, Mar Pollut Bull 1995, 30, 14.
[8]. T. Darmanin, F. Guittard, Materials Today 2015, 18, 273.
[9]. L. Li, V. Breedveld, D. W. Hess, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2013, 5, 5381.
[10]. W. Barthlott, C. Neinhuis, Planta 1997, 202, 1.
[11]. G. Tian, D. Fan, X. Feng, H. Zhou, RSC Adv 2021, 11, 3399.
[12]. D. W. Bechert, M. Bruse, W. Hage, Exp Fluids 2000, 28, 403.
[13]. R. Subbaiyan, A. Ganesan, V. Varadharajan, J Pure Appl Microbiol 2023, 17, 1374.
[14]. M. Yao, Z. Yan, X. Sun, B. Guo, C. Yu, Z. Zhao, X. Li, Z. Tan, H. Zhang, F. Yao, J. Li, Acta Biomater 2023, 166, 201.
[15]. S. Nishimoto, B. Bhushan, RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 671.
[16]. A. Lafuma, D. Quéré, Nat Mater 2003, 2, 457.
[17]. H. J. Ensikat, P. Ditsche-Kuru, C. Neinhuis, W. Barthlott, Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2011, 2, 152.
[18]. C. NEINHUIS, Ann Bot 1997, 79, 667.
[19]. P. Wagner, R. Fürstner, W. Barthlott, C. Neinhuis, J Exp Bot 2003, 54, 1295.
[20]. Z. Guo, W. Liu, Plant Science 2007, 172, 1103.
[21]. A. Marmur, Langmuir 2004, 20, 3517.
[22]. A. Otten, S. Herminghaus, Langmuir 2004, 20, 2405.
[23]. J. Zhang, X. Sheng, L. Jiang, Langmuir 2009, 25, 1371.
[24]. Y. T. Cheng, D. E. Rodak, C. A. Wong, C. A. Hayden, Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1359.
[25]. R. N. Wenzel, Ind Eng Chem 1936, 28, 988.
[26]. M. Yamamoto, N. Nishikawa, H. Mayama, Y. Nonomura, S. Yokojima, S. Nakamura, K. Uchida, Langmuir 2015, 31, 7355.
[27]. A. B. D. Cassie, S. Baxter, Transactions of the Faraday Society 1944, 40, 546.
[28]. Y.-T. Cheng, D. E. Rodak, A. Angelopoulos, T. Gacek, Appl Phys Lett 2005, 87, 1.
[29]. Y. Liu, C.-H. Choi, Colloid Polym Sci 2013, 291, 437.
[30]. X. Sheng, J. Zhang, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2011, 377, 374.
[31]. C. Sun, Z.-Z. Gu, H. Xu, Langmuir 2009, 25, 12439.
[32]. J. Feng, B. Huang, M. Zhong, J Colloid Interface Sci 2009, 336, 268.
[33]. J. Li, J. Zheng, J. Zhang, J. Feng, J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2016, 16, 5875.
[34]. H. Ogihara, J. Xie, T. Saji, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2013, 434, 35.
[35]. J. G. Wan, S. H. Li, C. Y. Ma, G. W. Guo, Q. W. Meng, Adv Mat Res 2013, 807–809, 2797.
[36]. M. Ma, M. Gupta, Z. Li, L. Zhai, K. K. Gleason, R. E. Cohen, M. F. Rubner, G. C. Rutledge, Advanced Materials 2007, 19, 255.
[37]. H. F. Hoefnagels, D. Wu, G. de With, W. Ming, Langmuir 2007, 23, 13158.
[38]. B. Leng, Z. Shao, G. de With, W. Ming, Langmuir 2009, 25, 2456.
[39]. Y. Zhao, Y. Tang, X. Wang, T. Lin, Appl Surf Sci 2010, 256, 6736.
[40]. M. Yu, G. Gu, W. D. Meng, F. L. Qing, Appl Surf Sci 2007, 253, 3669.
[41]. G. Y. Bae, B. G. Min, Y. G. Jeong, S. C. Lee, J. H. Jang, G. H. Koo, J Colloid Interface Sci 2009, 337, 170.
[42]. M. Xu, N. Lu, H. Xu, D. Qi, Y. Wang, S. Shi, L. Chi, Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1438.
[43]. F. Zhao, X. Wang, B. Ding, J. Lin, J. Hu, Y. Si, J. Yu, G. Sun, RSC Adv 2011, 1, 1482.
[44]. J. Feng, M. Zhong, W. Lin, J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2012, 12, 2679.
[45]. R. H. Wu, Adv Mat Res 2012, 450–451, 881.
[46]. L. Zhai, F. Ç. Cebeci, R. E. Cohen, M. F. Rubner, Nano Lett 2004, 4, 1349.
[47]. D. Ebert, B. Bhushan, J Colloid Interface Sci 2012, 368, 584.
[48]. J. Bravo, L. Zhai, Z. Wu, R. E. Cohen, M. F. Rubner, Langmuir 2007, 23, 7293.
[49]. H. Ogihara, J. Xie, J. Okagaki, T. Saji, Langmuir 2012, 28, 4605.
[50]. W. S. Y. Wong, Z. H. Stachurski, D. R. Nisbet, A. Tricoli, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 13615.
[51]. C. E. Zobell, E. C. Allen, J Bacteriol 1935, 29, 239.
[52]. J. W. Costerton, P. S. Stewart, E. P. Greenberg, Science (1979) 1999, 284, 1318.
[53]. J. Ma, Y. Sun, K. Gleichauf, J. Lou, Q. Li, Langmuir 2011, 27, 10035.
[54]. J. I. Lim, M. J. Kang, W.-K. Lee, Appl Surf Sci 2014, 320, 614.
[55]. M. I. Kayes, A. J. Galante, N. A. Stella, S. Haghanifar, R. M. Q. Shanks, P. W. Leu, React Funct Polym 2018, 128, 40.
[56]. X. Chu, P. Zhang, S. Shi, Y. Liu, W. Feng, N. Zhou, J. Li, J. Shen, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2023, 658, 130621.
[57]. K. Han, T. Y. Park, K. Yong, H. J. Cha, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019, 11, 9777.
[58]. R. Jiang, L. Hao, L. Song, L. Tian, Y. Fan, J. Zhao, C. Liu, W. Ming, L. Ren, Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 398, 125609.
[59]. J. Wan, H. Li, L. Xu, J. Yan, Y. Liao, X. Wang, Cellulose 2023, 30, 3953.
[60]. L. Hu, L. Zhang, D. Wang, X. Lin, Y. Chen, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2018, 555, 515.
[61]. M. Xu, X. Wang, B. Wang, Y. Tang, Z. Qin, S. Yin, Z. Liu, H. Sun, Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2022, 215, 112468.
[62]. J. Zhao, T. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Huang, Y. Tang, Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 516.
[63]. A. R. Siddiqui, Wen. Li, Fajun. Wang, Junfei. Ou, A. Amirfazli, Appl Surf Sci 2021, 542, 148534.
[64]. X. Liu, K. Chen, D. Zhang, Z. Guo, Coatings 2021, 11, 95.
[65]. W.-T. Cao, W. Feng, Y.-Y. Jiang, C. Ma, Z.-F. Zhou, M.-G. Ma, Y. Chen, F. Chen, Mater Horiz 2019, 6, 1057.
[66]. S. Oh, J. Cho, J. Lee, J. Han, S. Kim, Y. Nam, Advanced Science 2022, 9, 2202781.
[67]. S. Zhao, H. Du, Z. Ma, G. Xiao, J. Liu, Y. Jiang, S. Hu, H. Zhao, C. Wen, L. Ren, Mater Des 2022, 223, 111145.
[68]. S. Hayne, S. Margel, Mater Today Chem 2023, 30, 101497.
[69]. S. S. Latthe, R. S. Sutar, V. S. Kodag, A. K. Bhosale, A. M. Kumar, K. Kumar Sadasivuni, R. Xing, S. Liu, Prog Org Coat 2019, 128, 52.
[70]. C. Sun, J. Dai, H. Zhang, F. Zhang, N. Zhang, Prog Org Coat 2019, 128, 21.
[71]. J. Wang, K. Li, J. Zhang, J. Feng, Prog Org Coat 2023, 183, 107679.
[72]. 1983, 7, 251.
[73]. M. WALSH, L. WEINSTEIN, in 11th Fluid and PlasmaDynamics Conference, American Institute Of Aeronautics And Astronautics, Reston, Virigina, 1978.
[74]. M. WALSH, in 20th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, American Institute Of Aeronautics And Astronautics, Reston, Virigina, 1982.
[75]. M. J. Walsh, AIAA Journal 1983, 21, 485.
[76]. G. Hirt, M. Thome, CIRP Annals 2008, 57, 317.
[77]. B. S. Liu, W. Wu, Y. S. Zeng, Review on application and fabrication of shark skin bionic structure, Beijing Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology Research Institute, 2014, 04-0056-07.
[78]. B. Denkena, J. Köhler, B. Wang, CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 2010, 3, 14.
[79]. L. Wen, J. C. Weaver, P. J. M. Thornycroft, G. V Lauder, Bioinspir Biomim 2015, 10, 066010.
[80]. A. Lang, M. L. Habegger, P. Motta, in Encyclopedia of Nanotechnology, Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, 2015, pp. 1–8.
[81]. X. Pu, G. Li, Y. Liu, ChemBioEng Reviews 2016, 3, 26.
[82]. B. S. Liu, W. Wu, Y. S. Zeng, Review on application and fabrication of shark skin bionic structure, Beijing Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology Research Institute, 2014, 04-0056-07.
[83]. L. P. Chamorro, R. E. A. Arndt, F. Sotiropoulos, Renew Energy 2013, 50, 1095.
[84]. S.-J. Lee, S.-H. Lee, Exp Fluids 2001, 30, 153.
[85]. D. W. Bechert, M. Br, R. Meyer, Naturwissenschaften 2000, 87, 157.
[86]. Z. S. She, W. D. Su, Description of the hierarchical structure of turbulent pulsation, Proceedings of the 41st Yong Scientist Forum of China Association for Science and Technology, 2001, 7-03-008456-X.
[87]. S.-J. Lee, Y.-G. Jang, J Fluids Struct 2005, 20, 659.
Cite this article
Tang,Z.;Zhu,J.;Ni,Y. (2024). Lotus leaf and shark skin-inspired micro-, nano-, hierarchical superhydrophobic surfaces for anti-fouling applications. Applied and Computational Engineering,84,100-117.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. F. M. C. Fazey, P. G. Ryan, Environmental Pollution 2016, 210, 354.
[2]. C. E. Zobell, E. C. Allen, J Bacteriol 1935, 29, 239.
[3]. J. J. Stanković, I. Marjanović, J. Papathanasiou, S. Drezgić, J Mar Sci Eng 2021, 9, 74.
[4]. M. P. Schultz, J. A. Bendick, E. R. Holm, W. M. Hertel, Biofouling 2011, 27, 87.
[5]. P. Kim, T.-S. Wong, J. Alvarenga, M. J. Kreder, W. E. Adorno-Martinez, J. Aizenberg, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6569.
[6]. U. von Ammon, S. A. Wood, O. Laroche, A. Zaiko, L. Tait, S. Lavery, G. Inglis, X. Pochon, Mar Environ Res 2018, 133, 57.
[7]. S. M. Evans, T. Leksono, P. D. McKinnell, Mar Pollut Bull 1995, 30, 14.
[8]. T. Darmanin, F. Guittard, Materials Today 2015, 18, 273.
[9]. L. Li, V. Breedveld, D. W. Hess, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2013, 5, 5381.
[10]. W. Barthlott, C. Neinhuis, Planta 1997, 202, 1.
[11]. G. Tian, D. Fan, X. Feng, H. Zhou, RSC Adv 2021, 11, 3399.
[12]. D. W. Bechert, M. Bruse, W. Hage, Exp Fluids 2000, 28, 403.
[13]. R. Subbaiyan, A. Ganesan, V. Varadharajan, J Pure Appl Microbiol 2023, 17, 1374.
[14]. M. Yao, Z. Yan, X. Sun, B. Guo, C. Yu, Z. Zhao, X. Li, Z. Tan, H. Zhang, F. Yao, J. Li, Acta Biomater 2023, 166, 201.
[15]. S. Nishimoto, B. Bhushan, RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 671.
[16]. A. Lafuma, D. Quéré, Nat Mater 2003, 2, 457.
[17]. H. J. Ensikat, P. Ditsche-Kuru, C. Neinhuis, W. Barthlott, Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2011, 2, 152.
[18]. C. NEINHUIS, Ann Bot 1997, 79, 667.
[19]. P. Wagner, R. Fürstner, W. Barthlott, C. Neinhuis, J Exp Bot 2003, 54, 1295.
[20]. Z. Guo, W. Liu, Plant Science 2007, 172, 1103.
[21]. A. Marmur, Langmuir 2004, 20, 3517.
[22]. A. Otten, S. Herminghaus, Langmuir 2004, 20, 2405.
[23]. J. Zhang, X. Sheng, L. Jiang, Langmuir 2009, 25, 1371.
[24]. Y. T. Cheng, D. E. Rodak, C. A. Wong, C. A. Hayden, Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1359.
[25]. R. N. Wenzel, Ind Eng Chem 1936, 28, 988.
[26]. M. Yamamoto, N. Nishikawa, H. Mayama, Y. Nonomura, S. Yokojima, S. Nakamura, K. Uchida, Langmuir 2015, 31, 7355.
[27]. A. B. D. Cassie, S. Baxter, Transactions of the Faraday Society 1944, 40, 546.
[28]. Y.-T. Cheng, D. E. Rodak, A. Angelopoulos, T. Gacek, Appl Phys Lett 2005, 87, 1.
[29]. Y. Liu, C.-H. Choi, Colloid Polym Sci 2013, 291, 437.
[30]. X. Sheng, J. Zhang, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2011, 377, 374.
[31]. C. Sun, Z.-Z. Gu, H. Xu, Langmuir 2009, 25, 12439.
[32]. J. Feng, B. Huang, M. Zhong, J Colloid Interface Sci 2009, 336, 268.
[33]. J. Li, J. Zheng, J. Zhang, J. Feng, J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2016, 16, 5875.
[34]. H. Ogihara, J. Xie, T. Saji, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2013, 434, 35.
[35]. J. G. Wan, S. H. Li, C. Y. Ma, G. W. Guo, Q. W. Meng, Adv Mat Res 2013, 807–809, 2797.
[36]. M. Ma, M. Gupta, Z. Li, L. Zhai, K. K. Gleason, R. E. Cohen, M. F. Rubner, G. C. Rutledge, Advanced Materials 2007, 19, 255.
[37]. H. F. Hoefnagels, D. Wu, G. de With, W. Ming, Langmuir 2007, 23, 13158.
[38]. B. Leng, Z. Shao, G. de With, W. Ming, Langmuir 2009, 25, 2456.
[39]. Y. Zhao, Y. Tang, X. Wang, T. Lin, Appl Surf Sci 2010, 256, 6736.
[40]. M. Yu, G. Gu, W. D. Meng, F. L. Qing, Appl Surf Sci 2007, 253, 3669.
[41]. G. Y. Bae, B. G. Min, Y. G. Jeong, S. C. Lee, J. H. Jang, G. H. Koo, J Colloid Interface Sci 2009, 337, 170.
[42]. M. Xu, N. Lu, H. Xu, D. Qi, Y. Wang, S. Shi, L. Chi, Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1438.
[43]. F. Zhao, X. Wang, B. Ding, J. Lin, J. Hu, Y. Si, J. Yu, G. Sun, RSC Adv 2011, 1, 1482.
[44]. J. Feng, M. Zhong, W. Lin, J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2012, 12, 2679.
[45]. R. H. Wu, Adv Mat Res 2012, 450–451, 881.
[46]. L. Zhai, F. Ç. Cebeci, R. E. Cohen, M. F. Rubner, Nano Lett 2004, 4, 1349.
[47]. D. Ebert, B. Bhushan, J Colloid Interface Sci 2012, 368, 584.
[48]. J. Bravo, L. Zhai, Z. Wu, R. E. Cohen, M. F. Rubner, Langmuir 2007, 23, 7293.
[49]. H. Ogihara, J. Xie, J. Okagaki, T. Saji, Langmuir 2012, 28, 4605.
[50]. W. S. Y. Wong, Z. H. Stachurski, D. R. Nisbet, A. Tricoli, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 13615.
[51]. C. E. Zobell, E. C. Allen, J Bacteriol 1935, 29, 239.
[52]. J. W. Costerton, P. S. Stewart, E. P. Greenberg, Science (1979) 1999, 284, 1318.
[53]. J. Ma, Y. Sun, K. Gleichauf, J. Lou, Q. Li, Langmuir 2011, 27, 10035.
[54]. J. I. Lim, M. J. Kang, W.-K. Lee, Appl Surf Sci 2014, 320, 614.
[55]. M. I. Kayes, A. J. Galante, N. A. Stella, S. Haghanifar, R. M. Q. Shanks, P. W. Leu, React Funct Polym 2018, 128, 40.
[56]. X. Chu, P. Zhang, S. Shi, Y. Liu, W. Feng, N. Zhou, J. Li, J. Shen, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2023, 658, 130621.
[57]. K. Han, T. Y. Park, K. Yong, H. J. Cha, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019, 11, 9777.
[58]. R. Jiang, L. Hao, L. Song, L. Tian, Y. Fan, J. Zhao, C. Liu, W. Ming, L. Ren, Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 398, 125609.
[59]. J. Wan, H. Li, L. Xu, J. Yan, Y. Liao, X. Wang, Cellulose 2023, 30, 3953.
[60]. L. Hu, L. Zhang, D. Wang, X. Lin, Y. Chen, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2018, 555, 515.
[61]. M. Xu, X. Wang, B. Wang, Y. Tang, Z. Qin, S. Yin, Z. Liu, H. Sun, Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2022, 215, 112468.
[62]. J. Zhao, T. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Huang, Y. Tang, Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 516.
[63]. A. R. Siddiqui, Wen. Li, Fajun. Wang, Junfei. Ou, A. Amirfazli, Appl Surf Sci 2021, 542, 148534.
[64]. X. Liu, K. Chen, D. Zhang, Z. Guo, Coatings 2021, 11, 95.
[65]. W.-T. Cao, W. Feng, Y.-Y. Jiang, C. Ma, Z.-F. Zhou, M.-G. Ma, Y. Chen, F. Chen, Mater Horiz 2019, 6, 1057.
[66]. S. Oh, J. Cho, J. Lee, J. Han, S. Kim, Y. Nam, Advanced Science 2022, 9, 2202781.
[67]. S. Zhao, H. Du, Z. Ma, G. Xiao, J. Liu, Y. Jiang, S. Hu, H. Zhao, C. Wen, L. Ren, Mater Des 2022, 223, 111145.
[68]. S. Hayne, S. Margel, Mater Today Chem 2023, 30, 101497.
[69]. S. S. Latthe, R. S. Sutar, V. S. Kodag, A. K. Bhosale, A. M. Kumar, K. Kumar Sadasivuni, R. Xing, S. Liu, Prog Org Coat 2019, 128, 52.
[70]. C. Sun, J. Dai, H. Zhang, F. Zhang, N. Zhang, Prog Org Coat 2019, 128, 21.
[71]. J. Wang, K. Li, J. Zhang, J. Feng, Prog Org Coat 2023, 183, 107679.
[72]. 1983, 7, 251.
[73]. M. WALSH, L. WEINSTEIN, in 11th Fluid and PlasmaDynamics Conference, American Institute Of Aeronautics And Astronautics, Reston, Virigina, 1978.
[74]. M. WALSH, in 20th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, American Institute Of Aeronautics And Astronautics, Reston, Virigina, 1982.
[75]. M. J. Walsh, AIAA Journal 1983, 21, 485.
[76]. G. Hirt, M. Thome, CIRP Annals 2008, 57, 317.
[77]. B. S. Liu, W. Wu, Y. S. Zeng, Review on application and fabrication of shark skin bionic structure, Beijing Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology Research Institute, 2014, 04-0056-07.
[78]. B. Denkena, J. Köhler, B. Wang, CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 2010, 3, 14.
[79]. L. Wen, J. C. Weaver, P. J. M. Thornycroft, G. V Lauder, Bioinspir Biomim 2015, 10, 066010.
[80]. A. Lang, M. L. Habegger, P. Motta, in Encyclopedia of Nanotechnology, Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, 2015, pp. 1–8.
[81]. X. Pu, G. Li, Y. Liu, ChemBioEng Reviews 2016, 3, 26.
[82]. B. S. Liu, W. Wu, Y. S. Zeng, Review on application and fabrication of shark skin bionic structure, Beijing Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology Research Institute, 2014, 04-0056-07.
[83]. L. P. Chamorro, R. E. A. Arndt, F. Sotiropoulos, Renew Energy 2013, 50, 1095.
[84]. S.-J. Lee, S.-H. Lee, Exp Fluids 2001, 30, 153.
[85]. D. W. Bechert, M. Br, R. Meyer, Naturwissenschaften 2000, 87, 157.
[86]. Z. S. She, W. D. Su, Description of the hierarchical structure of turbulent pulsation, Proceedings of the 41st Yong Scientist Forum of China Association for Science and Technology, 2001, 7-03-008456-X.
[87]. S.-J. Lee, Y.-G. Jang, J Fluids Struct 2005, 20, 659.









