1. Introduction
3D printing is a type of digital fabrication technology that manufactures physical objects from the addition of single or multiple types of materials, layer by layer. The object’s geometric representation is first modeled on computer software, and the 3D printer can convert the computer aided design (CAD) file into the physical object [1,2]. Nowadays, 3D printing technology is widely used in niche markets for products that need customization. Consumers will have more choices and control over the product’s design to fit their specifications. 3D printing technology is portable, and with that being said, manufacturing locations could be located nearer to customers, resulting in a decrease in overall transportation costs, and more energy being saved [2]. 3D printing is an environmentally friendly technology that is also very cost-effective [2,3]. The technology is also extremely capable of producing components with high geometric complexity, which makes components made from 3D-printed materials have a greater variety of structures [1-3]. Therefore, this paper focuses on concluding the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing technology, and discusses the future direction of developments.
2. Construction and Material from 3D printing technology
2.1. Advantages and disadvantages
There are many advantages to construction and materials from 3D printing. One advantage is that this technology is environmentally friendly and very sustainable due to its ability to reuse non-biodegradable materials such as plastic while still being effective and efficient. The technology also produces very little industrial waste and has the potential to reduce carbon emissions [2-4]. Another advantage is that 3D printing technology is very portable, which means manufacturing locations could be nearer to customers, which decreases overall transportation costs, and saves time and energy. This also enables 3D-prinitng technology to be able to work in all kinds of locations, which may be the answer to facility rebuilding during or after disasters [2]. Moreover, 3D printing technology provides automation for construction, which also means a decrease in labor costs and labor injuries [2]. Lastly, 3D printing technology can handle designs that are geometrically complex; this characteristic enables it to produce complex structures or shapes. More complex structure and shape mean that 3D printed materials can potentially reach higher performances, durability, and functionality [1,3,4].
Although this new technology has a lot of advantages; its disadvantages are also worth discussing. Firstly, the raw material needed to produce 3D printed material is usually more expensive than conventional materials [1]. Furthermore, because it provides automation; there will be less need for manufacturing labor, which will cause low skilled workers to lose their jobs [2]. Besides, 3D-printed materials and construction are still relatively new technologies, and there is still a lack of sufficient research and testing.
2.2. Applications
3D printing technology is a very applicable technology; it can be applied to almost any industry. This paper will conclude its applications in three aspects: medical, architectural, and automobile.
2.2.1. Medical industry. 3D printing technology can be used to produce replicas of skin tissues at low costs; the precision of the 3D printer enables it to produce the skin’s texture and structures. The technology can also be used to print out cartilage or bones to combat diseases as shown in Figure 1; the bone can be printed from materials such as titanium. Another usage of the technology in the medical industry is that it can be used to directly print out medicines; the technology is able to produce dosage forms with complex drug-release profiles [2].
In addition, 3D printing technology is able to print out cheap organ models for planning and surgical treatment analysis. High accuracy models can benefit treatments and medical education. The technology is also capable of printing non-bioactive implants; 3D printing is more customized than conventional technology, and can reach higher precision for implants that have complex structures with a short manufacturing period [5].
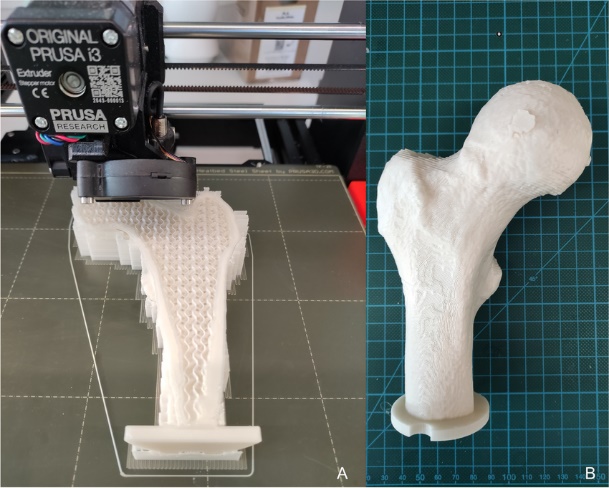
Figure 1. Printing Process and finally 3D printed bone example [6]
2.2.2. Construction industry. In the construction industry, 3D printing can be used to print construction components with all kinds of different structures in a shorter period of time compared to traditional manufacturing. Furthermore, the technology can also be used to print out facilities such as bridges; and because of its portability, it can be used to rebuild damaged facilities during or after disasters. Following up on the ability to print out facilities, the 3D printing technology can also be used to print out low buildings with less industrial waste compared to traditional construction. The technology does have the potential to print tall buildings; however, current technology is still not mature and saturated enough. The technology is also able to reuse materials again for printing, and it also requires less manufacturing labor, resulting in fewer labor injuries. These factors make 3D printing a sustainable, environmentally friendly, cost effective, efficient, and safe way of constructing [1-4].
2.2.3. Automobile industry. Recently, 3D printing technology in the automotive industry has been widely adopted. People can print out high quality prototypes of components or cars to carry out all kinds of automated testing. 3D-printed prototypes are extremely precise, and can increase design speed. At the same time, the technology can reuse the wasted materials, and convert them into other things or even new prototypes. This characteristic can reduce the average cost and speed up manufacturing times. 3D printing technology is also capable of producing materials that are lightweight but have a higher strength-to-weight ratio. As a result, automobiles with higher performance and durability can potentially be built [2,3].
2.3. Directions for future progression
For future progress, more research on the durability of the 3D-printed materials has to be done. More research on the different characteristics and performance of specific types of 3D-printed materials also has to be done. Furthermore, 3D printing is a relatively new technology, so printing on a large scale may result in an unstable yield rate. With that in mind, more improvements to the actual 3D printer also have to be made.
Speaking of the 3D printer, some technological difficulties will have to be faced. First of all, improvements must be made to the design of the print head; the print head has a direct impact on the efficiency of the 3D printer and also the quality of the final product. A good design is needed to let the material pass through the nozzle of the printer smoothly [4]. Second of all, because 3D printing technology is still in the development stage, there is a problem when it comes to printing constructions with height. Although it could potentially be used to print low buildings, it is now almost impossible to print high buildings at once [4]. Thus, research has to be done to overcome these technological challenges.
To make this 3D printing technology more efficient, it needs more cooperation and less interference between the software and hardware. This can make the modeling and designing process easier and quicker [4].
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing is an effective, efficient, and powerful technology that can be used in various industries. Its potential to suit large-scale construction is one of the key reasons this technology has been continuously developed. In addition, 3D-printed materials are geometrically unlimited, which means they could be geometrically complex; this ability also enables 3D-printed materials to consist of complex structures, which could be the key to their high performance and durability while still being cost-effective. It can be seen that there is a large potential in construction and materials with 3D printing technologies. However, there is still a lack of research, and further testing and popularization must be done to apply this technology on a large scale.
References
[1]. Xiao, J., Ji, G., Zhang, Y., Ma, G., Mechtcherine, V., Pan, J., ... & Du, S. (2021). Large-scale 3D printing concrete technology: Current status and future opportunities. Cement and Concrete Composites, 122, 104115.
[2]. Shahrubudin, N., Lee, T. C., & Ramlan, R. J. P. M. (2019). An overview on 3D printing technology: Technological, materials, and applications. Procedia Manufacturing, 35, 1286-1296.
[3]. Jandyal, A., Chaturvedi, I., Wazir, I., Raina, A., & Haq, M. I. U. (2022). 3D printing–A review of processes, materials and applications in industry 4.0. Sustainable Operations and Computers, 3, 33-42.
[4]. Lyu, F., Zhao, D., Hou, X., Sun, L., & Zhang, Q. (2021). Overview of the development of 3D-Printing concrete: A review. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 9822.
[5]. Yan, Q., Dong, H., Su, J., Han, J., Song, B., Wei, Q., & Shi, Y. (2018). A review of 3D printing technology for medical applications. Engineering, 4(5), 729-742.
[6]. Nägl, K., Reisinger, A., & Pahr, D. H. (2022). The biomechanical behavior of 3D printed human femoral bones based on generic and patient-specific geometries. 3D printing in medicine, 8(1), 35.
Cite this article
Tang,C. (2024). Research on the structure and materials of 3D printing technology. Applied and Computational Engineering,89,25-28.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Functional Materials and Civil Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Xiao, J., Ji, G., Zhang, Y., Ma, G., Mechtcherine, V., Pan, J., ... & Du, S. (2021). Large-scale 3D printing concrete technology: Current status and future opportunities. Cement and Concrete Composites, 122, 104115.
[2]. Shahrubudin, N., Lee, T. C., & Ramlan, R. J. P. M. (2019). An overview on 3D printing technology: Technological, materials, and applications. Procedia Manufacturing, 35, 1286-1296.
[3]. Jandyal, A., Chaturvedi, I., Wazir, I., Raina, A., & Haq, M. I. U. (2022). 3D printing–A review of processes, materials and applications in industry 4.0. Sustainable Operations and Computers, 3, 33-42.
[4]. Lyu, F., Zhao, D., Hou, X., Sun, L., & Zhang, Q. (2021). Overview of the development of 3D-Printing concrete: A review. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 9822.
[5]. Yan, Q., Dong, H., Su, J., Han, J., Song, B., Wei, Q., & Shi, Y. (2018). A review of 3D printing technology for medical applications. Engineering, 4(5), 729-742.
[6]. Nägl, K., Reisinger, A., & Pahr, D. H. (2022). The biomechanical behavior of 3D printed human femoral bones based on generic and patient-specific geometries. 3D printing in medicine, 8(1), 35.









