1. Introduction
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become essential for businesses seeking to optimize their operations, enhance productivity, and maintain a competitive edge. These systems integrate various functions and processes across an organization into a single, unified platform, enabling seamless data flow and improved decision-making. With the increasing complexity and diversity of business requirements, modular design in ERP systems has emerged as a popular approach. This design allows organizations to implement only the necessary modules, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, the modular approach also introduces challenges, particularly in terms of integration and maintaining system coherence. In response to the limitations of standard ERP solutions, custom development has gained traction as a means to tailor ERP systems to specific industry needs. Custom development methods range from utilizing vendor-provided tools for configuration to developing bespoke modules from scratch. These approaches enable businesses to address unique operational requirements and leverage industry-specific functionalities that off-the-shelf solutions may lack [1]. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of modular design and custom development in ERP systems, examining their advantages, challenges, and practical implementation strategies. Through detailed case studies from the manufacturing, healthcare, and retail industries, we explore the real-world applications and outcomes of modular ERP systems. By highlighting effective strategies for module integration and custom development, this study offers valuable insights for organizations seeking to optimize their ERP systems and achieve operational excellence.
2. Modular Design in ERP Systems
2.1. Advantages of Modular Design
Modular design in ERP systems offers several benefits that contribute to the overall efficiency and adaptability of the system. Firstly, it allows for a high degree of flexibility, as businesses can select and implement only the modules relevant to their operations. This reduces the complexity and cost associated with deploying a full-scale ERP system. Secondly, modular design facilitates incremental implementation, enabling organizations to gradually integrate new functionalities without disrupting existing processes. This phased approach minimizes risk and allows for better resource allocation. Thirdly, modular ERP systems can be easily scaled to accommodate business growth or changes in operational requirements [2]. As new modules can be added as needed, the system remains relevant and functional even as the organization evolves.
2.2. Disadvantages of Modular Design
Despite its advantages, modular design in ERP systems also presents several challenges. One significant drawback is the potential for integration issues between different modules. Each module may be developed by different vendors or teams, leading to compatibility problems and data inconsistencies. This can complicate the integration process and require additional time and resources to resolve. Additionally, the modular approach can result in a fragmented system architecture, where each module operates independently rather than as part of a cohesive whole [3]. This fragmentation can hinder seamless data flow and process automation across the organization. Furthermore, the reliance on multiple modules can increase the overall cost of system maintenance and upgrades, as each module may have its own set of requirements and dependencies.
2.3. Strategies for Efficient Module Integration
To address the challenges associated with modular design, several strategies can be employed to achieve efficient module integration. One effective approach is to adopt standardized integration protocols and frameworks that ensure compatibility between different modules. By using common data formats and communication protocols, organizations can facilitate seamless data exchange and process coordination. Another strategy is to implement a centralized data repository that serves as a single source of truth for all modules. This repository ensures data consistency and integrity, reducing the risk of discrepancies and errors. Additionally, organizations can leverage middleware solutions that act as intermediaries between modules, translating data and coordinating interactions. These solutions can simplify the integration process and enhance overall system interoperability. Table 1 shows the strategies for efficient module integration and their outcomes with a detailed comparison of the scores before and after implementation [4].
Table 1. Strategies For Efficient Module Integration Outcomes
Strategy | Outcome Measure | Before Implementation (Score out of 10) | After Implementation (Score out of 10) |
Standardized Integration Protocols | Data Exchange Efficiency | 4 | 8 |
Centralized Data Repository | Data Consistency | 5 | 9 |
Middleware Solutions | System Interoperability | 3 | 7 |
API Integration | Integration Flexibility | 6 | 8 |
Real-time Data Sync | Data Availability | 4 | 9 |
Custom Integration Scripts | Customizability | 5 | 8 |
Batch Data Processing | Processing Speed | 5 | 8 |
Use of Integration Platforms | Ease of Integration | 4 | 8 |
Data Cleansing Procedures | Data Quality | 6 | 9 |
Automated Data Validation | Error Reduction | 5 | 9 |
3. Custom Development in ERP Systems
3.1. Importance of Custom Development
Custom development is crucial for ERP systems to address the unique needs and requirements of different industries and enterprises. Standard ERP solutions may not fully cater to the specific processes and workflows of certain businesses, necessitating custom development to bridge the gaps. Custom development allows organizations to tailor the system to their exact specifications, ensuring that it aligns with their operational goals and enhances productivity. Furthermore, custom solutions can provide a competitive advantage by incorporating industry-specific features and functionalities that are not available in off-the-shelf products [5]. This level of customization enables businesses to optimize their operations and achieve better outcomes.
3.2. Custom Development Methods
There are several methods for custom development in ERP systems, each with its own advantages and considerations. One common approach is to use configuration and customization tools provided by the ERP vendor. These tools allow organizations to modify existing modules or create new ones without extensive coding, making the process more accessible and less time-consuming. Another method is to develop custom modules from scratch using programming languages and development frameworks. This approach offers greater flexibility and control over the final product, but it requires significant technical expertise and resources. Additionally, organizations can collaborate with third-party developers or consultants who specialize in ERP customizations [6]. These external partners can provide valuable insights and assistance, helping to ensure that the custom solution meets the desired objectives. Table 2 shows the outcomes of various custom development methods for ERP systems.
Table 2. Custom Development Methods Outcomes
Development Method | Outcome Measure | Before Implementation (Score out of 10) | After Implementation (Score out of 10) |
Vendor Configuration Tools | Development Time | 5 | 8 |
Custom Modules from Scratch | Development Time | 4 | 7 |
Collaboration with Third-Party Developers | Development Time | 6 | 9 |
Vendor Configuration Tools | Flexibility | 5 | 8 |
Custom Modules from Scratch | Flexibility | 5 | 8 |
Collaboration with Third-Party Developers | Flexibility | 4 | 8 |
Vendor Configuration Tools | Expertise Required | 7 | 9 |
Custom Modules from Scratch | Expertise Required | 4 | 7 |
Collaboration with Third-Party Developers | Expertise Required | 6 | 9 |
Vendor Configuration Tools | Cost Efficiency | 5 | 8 |
3.3. Challenges and Solutions in Custom Development
Custom development in ERP systems is not without its challenges. One major challenge is ensuring that custom modules integrate seamlessly with the existing system architecture. Incompatibilities can lead to functionality issues and data inconsistencies, undermining the effectiveness of the custom solution. To mitigate this risk, organizations should conduct thorough testing and validation of custom modules before deployment. Another challenge is managing the complexity of custom development projects, which can involve multiple stakeholders and intricate requirements. Effective project management practices, such as clear communication and comprehensive documentation, are essential to keep the development process on track and within budget [7].
4. Implementation and Case Studies of Modular ERP Systems
4.1. Implementation Strategies
The implementation of modular ERP systems requires a well-defined strategy to ensure a smooth transition and optimal utilization of the system. One effective strategy is to conduct a comprehensive needs assessment before the implementation process begins. This assessment should involve identifying the specific business processes and workflows that need to be integrated into the ERP system. By understanding these requirements in detail, organizations can select the appropriate modules and plan their implementation in a phased manner [8]. Another important strategy is to involve key stakeholders from various departments in the planning and implementation stages. Their input and feedback are crucial for tailoring the system to meet the practical needs of end-users. Additionally, it is essential to provide thorough training for all users to ensure they are comfortable and proficient with the new system. Training sessions should be hands-on and include real-world scenarios to help users understand how the ERP system can improve their daily tasks. Figure 1 compares the scores before and after the implementation of various modular ERP system strategies.
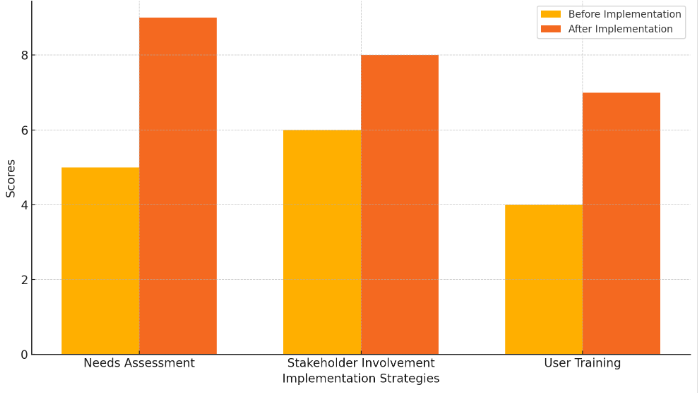
Figure 1. Scores Before and After Implementation of Modular ERP System Strategies
4.2. Case Study: Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing industry, ERP systems play a critical role in streamlining production processes, managing inventory, and ensuring quality control. A case study of a mid-sized manufacturing company implementing a modular ERP system illustrates the practical benefits and challenges of this approach. The company faced issues with inefficient inventory management and lack of coordination between production and sales departments [9]. By implementing a modular ERP system, they were able to integrate their inventory management, production planning, and sales order processing into a single, cohesive platform. This integration led to a significant reduction in inventory carrying costs and improved coordination between departments, resulting in faster order fulfillment and enhanced customer satisfaction. However, the company also encountered challenges related to data migration and user training, which were addressed through careful planning and ongoing support from the ERP vendor.
4.3. Case Study: Healthcare Sector
The healthcare sector presents unique challenges and requirements for ERP systems, particularly in managing patient records, billing, and regulatory compliance. A case study of a large hospital network implementing a modular ERP system highlights the transformative impact of this technology. The hospital network struggled with fragmented patient records and billing systems, leading to inefficiencies and errors. By adopting a modular ERP system, they were able to integrate electronic health records (EHR), patient billing, and compliance management into a unified platform. This integration improved the accuracy and accessibility of patient information, streamlined billing processes, and ensured compliance with healthcare regulations [10].
4.4. Case Study: Retail Industry
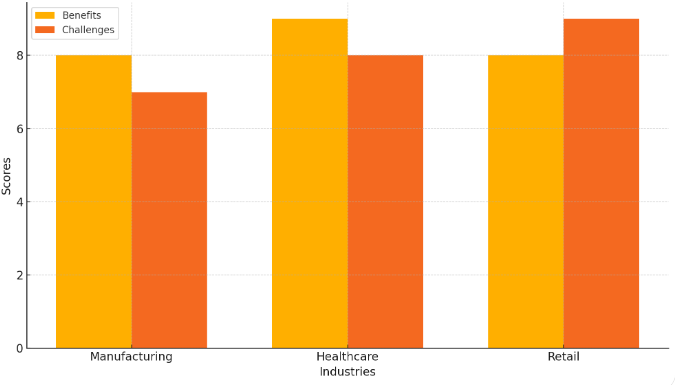
Figure 2. Impact of Modular ERP System in Different Industries
The retail industry requires ERP systems that can handle high transaction volumes, diverse product ranges, and complex supply chain logistics. A case study of a large retail chain implementing a modular ERP system demonstrates the benefits of this approach. The retail chain faced challenges in managing inventory across multiple locations and ensuring consistent pricing and promotions. By implementing a modular ERP system, they were able to centralize inventory management, standardize pricing strategies, and automate promotional campaigns. This centralization led to better inventory visibility, reduced stockouts, and increased sales through targeted promotions. The retail chain also integrated their ERP system with e-commerce platforms, enabling seamless online and offline shopping experiences for customers. However, the integration process required significant customization to accommodate the unique requirements of their diverse product categories, which was managed through close collaboration with the ERP vendor and internal IT teams.
Figure 2 shows the impact of modular ERP systems in different industries, highlighting both the benefits and challenges.
5. Conclusion
The adoption of modular design and custom development in ERP systems presents both opportunities and challenges for organizations. Modular design offers flexibility, scalability, and cost savings by allowing businesses to implement only the necessary modules. However, it also introduces potential integration issues and system fragmentation. Effective strategies, such as standardized integration protocols, centralized data repositories, and middleware solutions, are crucial for achieving seamless module integration and enhancing overall system interoperability. Custom development methods, including vendor configuration tools, bespoke module development, and third-party collaborations, enable organizations to tailor their ERP systems to specific industry needs. These methods provide the flexibility and functionality required to optimize operations and maintain a competitive edge. The case studies from the manufacturing, healthcare, and retail industries illustrate the practical benefits and challenges of implementing modular ERP systems, highlighting the importance of thorough planning, stakeholder involvement, and comprehensive training. In conclusion, the successful implementation of modular and custom ERP systems requires a strategic approach that addresses both technical and organizational challenges.
Contributions
Xu Li and Xiaoheng Ji: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation, Visualization, Investigation.
References
[1]. Amini, Mohammad, and Arnold Mashud Abukari. "ERP systems architecture for the modern age: A review of the state of the art technologies." Journal of Applied Intelligent Systems and Information Sciences 1.2 (2020): 70-90.
[2]. Kunduru, Arjun Reddy. "Blockchain Technology for ERP Systems: A Review." American Journal of Engineering, Mechanics and Architecture (2993-2637) 1.7 (2023): 56-63.
[3]. Chopra, R., et al. "Utilization of ERP systems in manufacturing industry for productivity improvement." Materials today: proceedings 62 (2022): 1238-1245.
[4]. Al-Okaily, Aws, Manaf Al-Okaily, and Ai Ping Teoh. "Evaluating ERP systems success: evidence from Jordanian firms in the age of the digital business." VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems 53.6 (2023): 1025-1040.
[5]. Naveen, Kenkera Rayappa, et al. "Modular design for constructing narrowband deep-blue multiresonant thermally activated delayed fluorescent emitters for efficient organic light emitting diodes." Chemical Engineering Journal 451 (2023): 138498.
[6]. Szmeja, Paweł, et al. "ASSIST-IoT: A modular implementation of a reference architecture for the next generation Internet of Things." Electronics 12.4 (2023): 854.
[7]. Krishnan, Nishta, et al. "A modular approach to enhancing cell membrane-coated nanoparticle functionality using genetic engineering." Nature Nanotechnology 19.3 (2024): 345-353.
[8]. Pfeiffer, Jonas, et al. "Modular deep learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11529 (2023).
[9]. Whitman, Julian, Matthew Travers, and Howie Choset. "Learning modular robot control policies." IEEE Transactions on Robotics (2023).
[10]. Akinradewo, Opeoluwa, et al. "Modular method of construction in developing countries: the underlying challenges." International Journal of Construction Management 23.8 (2023): 1344-1354.
Cite this article
Li,X.;Ji,X.;He,J. (2024). Modular design and custom development in ERP systems. Applied and Computational Engineering,93,155-160.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Amini, Mohammad, and Arnold Mashud Abukari. "ERP systems architecture for the modern age: A review of the state of the art technologies." Journal of Applied Intelligent Systems and Information Sciences 1.2 (2020): 70-90.
[2]. Kunduru, Arjun Reddy. "Blockchain Technology for ERP Systems: A Review." American Journal of Engineering, Mechanics and Architecture (2993-2637) 1.7 (2023): 56-63.
[3]. Chopra, R., et al. "Utilization of ERP systems in manufacturing industry for productivity improvement." Materials today: proceedings 62 (2022): 1238-1245.
[4]. Al-Okaily, Aws, Manaf Al-Okaily, and Ai Ping Teoh. "Evaluating ERP systems success: evidence from Jordanian firms in the age of the digital business." VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems 53.6 (2023): 1025-1040.
[5]. Naveen, Kenkera Rayappa, et al. "Modular design for constructing narrowband deep-blue multiresonant thermally activated delayed fluorescent emitters for efficient organic light emitting diodes." Chemical Engineering Journal 451 (2023): 138498.
[6]. Szmeja, Paweł, et al. "ASSIST-IoT: A modular implementation of a reference architecture for the next generation Internet of Things." Electronics 12.4 (2023): 854.
[7]. Krishnan, Nishta, et al. "A modular approach to enhancing cell membrane-coated nanoparticle functionality using genetic engineering." Nature Nanotechnology 19.3 (2024): 345-353.
[8]. Pfeiffer, Jonas, et al. "Modular deep learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11529 (2023).
[9]. Whitman, Julian, Matthew Travers, and Howie Choset. "Learning modular robot control policies." IEEE Transactions on Robotics (2023).
[10]. Akinradewo, Opeoluwa, et al. "Modular method of construction in developing countries: the underlying challenges." International Journal of Construction Management 23.8 (2023): 1344-1354.









