1. Introduction
In recent years, AI has become a transformative force in the game development industry, profoundly altering the ways in which games are created, played, and experienced. AI's integration into game development has enabled new levels of innovation and engagement, with applications ranging from procedural content generation to advanced non-player character (NPC) behavior and automated game testing. These technologies not only streamline the development process but also enhance the overall player experience by providing dynamic, responsive, and personalized interactions [1].
The significance of AI in game development is underscored by its ability to push the boundaries of creativity and immersion. As players demand more complex and realistic gaming experiences, AI offers tools that can adapt to and anticipate these evolving expectations. For instance, procedural content generation, a technique where AI is used to create game environments, levels, and narratives on-the-fly, has been extensively explored to create more varied and engaging game worlds [2]. Additionally, AI-driven player modeling has been employed to tailor gaming experiences to individual players, optimizing entertainment and engagement [3, 4].
Despite these advancements, the integration of AI into game development also presents significant challenges. Ethical concerns, such as the potential for AI to introduce biases in gameplay or to erode the uniqueness of human creativity, have been increasingly discussed in the academic community [5]. Moreover, technical limitations, including the scalability and performance of AI systems, continue to pose hurdles for developers, particularly in complex and resource-intensive games [6]. Additionally, the economic implications for smaller studios and independent developers, who may struggle with the costs associated with adopting advanced AI technologies, cannot be overlooked [7].
Current research on AI in game development has provided valuable insights into specific applications, such as procedural content generation and NPC behavior. For example, Cook and Colton [8] discuss aesthetic considerations in automated platformer design, while Guzdial and Riedl [6] explore the use of gameplay videos to generate new game levels. However, there remains a gap in the literature regarding a comprehensive analysis that addresses the broader implications of AI across the entire gaming industry. This gap highlights the need for a more holistic understanding of AI's role in game development, considering not only its technical aspects but also its broader impact on creativity, economics, and player engagement.
Motivated by this research gap, this review article aims to provide a thorough examination of the applications and challenges of AI in game development. The article will explore the various ways AI is utilized in the industry, discuss the benefits and drawbacks of these applications. By doing so, it seeks to offer a comprehensive understanding of the current state of AI in game development and identify areas where further research and innovation are needed.
2. Applications of AI in game development
AI has significantly transformed game development by enabling more dynamic, interactive, and personalized gaming experiences. This section explores the key applications of AI in game development, comparing AI-based methods with traditional approaches, and delving into the specific algorithms used, along with their basic principles.
2.1. Procedural content generation (PCG)
PCG is one of the most prominent applications of AI in game development. PCG refers to the use of algorithms to automatically generate game content, such as levels, maps, and narratives, in a dynamic and often random manner. Traditional game development relies heavily on manually created content, which is time-consuming and lacks variability. In contrast, AI-driven PCG techniques enable developers to create vast, varied, and unpredictable game worlds that enhance replayability and user engagement. By leveraging different algorithms, PCG opens up a new dimension of possibilities for game design shown in table 1, each with unique advantages and challenges. Among these algorithms, Markov Chains, Genetic Algorithms (GAs), and Wave Function Collapse (WFC) are particularly noteworthy.
Table 1. Comparison of Traditional and AI-Driven Techniques for PCG in Game Development.
Technique | Algorithm | Traditional Approach | Comparison and Benefits |
Level Design | Markov Chains | Manually designed levels | Provides endless variations; reduces design workload; enhances replayability |
Dynamic Environments | Genetic Algorithms (GA) | Predefined static environments | Evolve content based on player behavior; enhances adaptability and personalization |
Coherent Worlds | Wave Function Collapse (WFC) | Handcrafted, rigid world creation | Ensures aesthetic and functional coherence; minimizes manual effort and maximizes diversity |
To begin with, Markov Chains are widely used in PCG for generating sequences where the next state depends only on the current state. This property is particularly valuable in generating game environments that need to be coherent yet varied. For example, in dungeon generation, Markov Chains can produce diverse layouts by defining state transitions for room types and connectivity. The ability of Markov Chains to efficiently generate a vast number of permutations allows developers to create unique player experiences without additional design time. This method, therefore, contrasts sharply with traditional manual design, which requires significant effort for each new layout. Markov Chains provide a foundation for content diversity, setting the stage for more sophisticated algorithms that can build upon this variability.
While Markov Chains are excellent for generating sequences and layouts, they are limited when it comes to optimization based on specific criteria, such as player engagement or difficulty levels. To address these more complex requirements, Genetic Algorithms (GAs) come into play. GAs simulate the process of natural evolution, making them particularly effective for generating content that needs to adapt or optimize over time. For example, the game Galactic Arms Race (figure 1) employed GAs to evolve weapons based on player behavior, creating a personalized experience that adapts to each player's style and preferences [9]. This adaptability provides a stark contrast to static, pre-designed content, which remains unchanged regardless of player interaction. By introducing evolution-based mechanics, GAs extend the capabilities of PCG beyond static randomness, paving the way for more personalized and dynamic experiences.
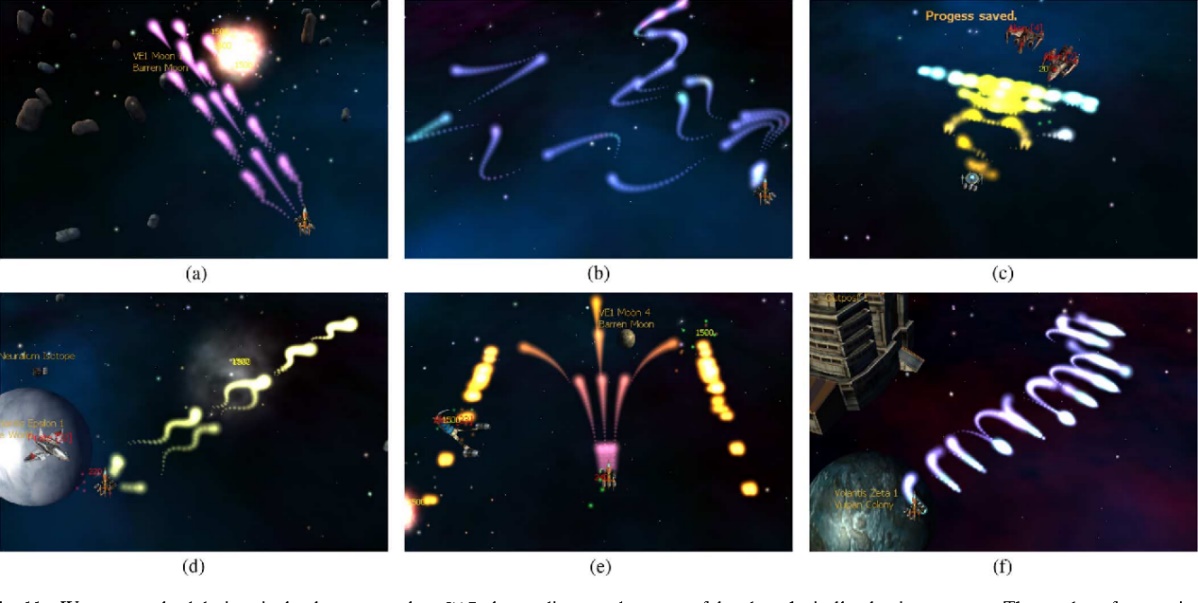

Figure 1. Automatic Content Generation in the Galactic Arms Race Video Game [9].
However, while GAs introduce the concept of optimization and evolution, there are scenarios where maintaining aesthetic coherence and functional diversity is crucial. In such cases, Wave Function Collapse (WFC) serves as a powerful tool. WFC is a constraint-based algorithm designed to generate content that respects a set of predefined rules, ensuring both coherence and variability. This algorithm has been effectively used in games like Noita (figure 2) for generating complex pixel-based environments that are both aesthetically pleasing and functionally diverse [10]. Unlike traditional methods, which often require extensive manual effort to achieve this level of complexity, WFC seamlessly combines structure with variation, making it highly suitable for creating procedurally generated worlds that feel handcrafted. As a result, WFC offers a balanced approach that marries the random generation of Markov Chains with the optimization focus of GAs.
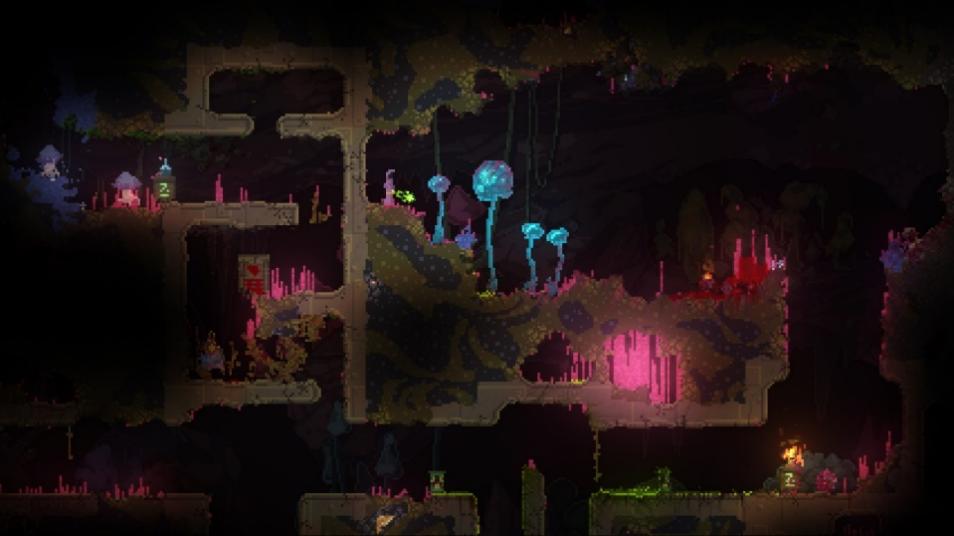

Figure 2. Noita - generating complex pixel-based environments [10].
Each of these algorithms, Markov Chains, Genetic Algorithms, and Wave Function Collapse, brings unique strengths to the realm of Procedural Content Generation.
2.2. Non-player character (NPC) behavior and control
AI has revolutionized the way Non-Player Characters (NPCs) behave and interact within games, making them more adaptive, intelligent, and lifelike. Traditionally, NPCs were designed to follow scripted behaviors or predefined patterns, which often resulted in predictable and repetitive gameplay. These scripted NPCs, while sufficient for simpler games, can diminish the immersive experience in more complex, modern games as players can easily anticipate and manipulate their actions. AI-driven NPCs, however, have brought a paradigm shift by allowing for behaviors that can dynamically adapt and respond to player actions, providing more engaging and challenging interactions.
At the core of early AI-driven NPCs are simpler models like Decision Trees and Finite State Machines (FSMs), which are still widely used for their simplicity, efficiency, and ease of implementation. These models are particularly effective in games where NPCs do not require a high degree of autonomy or intelligence. For instance, in many action or role-playing games, FSMs are employed to model basic enemy behaviors, such as patrolling, attacking, or retreating based on a set of defined conditions. While these traditional approaches are straightforward and computationally inexpensive, they are inherently limited in adaptability, making them less effective in complex, unpredictable environments.
To overcome the rigidity of FSMs and Decision Trees, modern game development has increasingly turned to more sophisticated AI techniques such as Reinforcement Learning (RL). RL enables NPCs to learn optimal actions by interacting with their environment and maximizing cumulative rewards over time. Unlike static decision-making models, RL allows NPCs to adapt their strategies dynamically, leading to more challenging and varied gameplay experiences. A notable example is the game F.E.A.R. (figure 3), where the enemies use RL-based models to adapt their tactics according to the player’s strategy, making encounters more unpredictable and engaging. This dynamic adaptability is a significant advancement over traditional methods, where NPCs would merely follow predetermined scripts or respond to a narrow set of inputs.

Figure 3. Game F.E.A.R -- Enemies use RL-based models to adapt tactics [11].
Building upon the foundations of RL, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of NPC behavior. DRL combines the power of deep neural networks with reinforcement learning, enabling NPCs to navigate highly complex environments and learn strategies that require an understanding of long-term consequences. In the realm of competitive games, Dota 2 (figure 4) serves as a groundbreaking example where OpenAI Five utilized DRL to train NPCs (or bots) to play at a professional level. These bots learned from millions of simulated games, demonstrating advanced strategies such as teamwork, coordination, and adaptability that traditional scripted approaches simply cannot replicate. The success of DRL in Dota 2 underscores its potential to handle the complexity and depth required in modern games, pushing the boundaries of what NPCs can achieve.
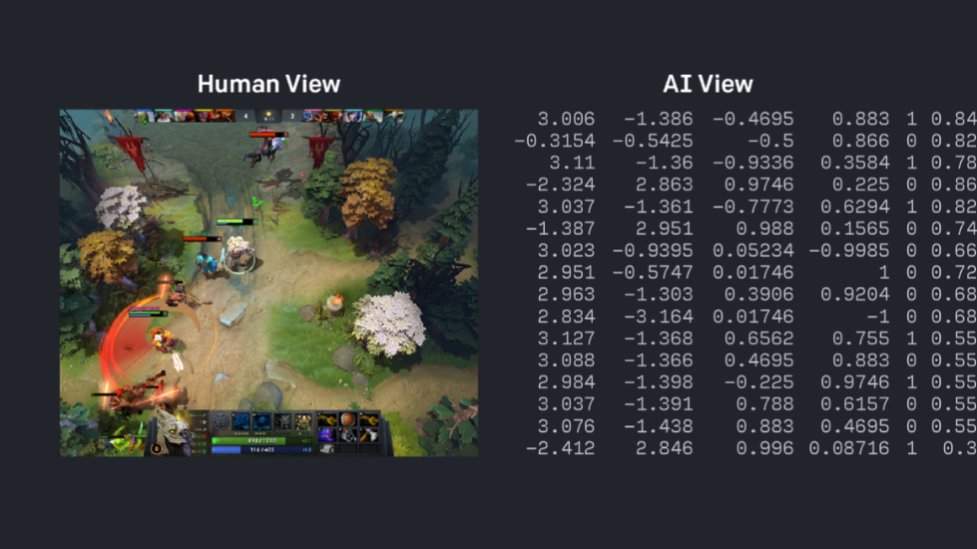
Figure 4. OpenAI Five defeats Dota 2 world champions [12].
While DRL excels in dynamic adaptation and complex problem-solving, it can be computationally expensive and requires substantial training data. To balance complexity and computational efficiency, Behavior Trees (BTs) have gained popularity in recent years for structuring NPC decision-making in a more hierarchical and modular manner. Unlike FSMs, which can become unwieldy as the number of states grows, BTs allow for more scalable and flexible AI design. This structure is particularly advantageous in open-world games, where NPCs must perform a wide range of actions based on diverse environmental contexts and player interactions. Games like The Last of Us have effectively utilized BTs to manage complex NPC behaviors, enabling them to switch seamlessly between different tasks such as searching, attacking, or evading, depending on the evolving situation. The modular nature of BTs also allows developers to fine-tune specific behaviors without disrupting the entire decision-making process, offering a balance between simplicity and sophistication.
The evolution of AI techniques for NPC behavior—ranging from traditional Decision Trees and FSMs to more advanced approaches like RL, DRL, and BTs—illustrates the industry's ongoing effort to create more engaging and lifelike game experiences.
2.3. Automated game testing and quality assurance
Automated game testing is another area where AI significantly outperforms traditional methods. Traditional testing relies heavily on human testers, which is time-consuming and costly. AI-driven automated testing utilizes machine learning algorithms to detect bugs, exploits, and performance issues more efficiently.
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) is widely used in automated playtesting to explore possible game states and find optimal paths or strategies. Compared to manual testing, which is limited by human cognition and time, MCTS allows for extensive and rapid testing across a wide range of scenarios. For example, the Angry Birds AI competition utilizes MCTS to develop bots that can solve levels more effectively than humans. In stress testing, Genetic Algorithms simulate various player behaviors to discover unexpected bugs or crashes. By evolving diverse strategies, GAs provide a more comprehensive coverage of possible game states than traditional methods. This approach was used in Ubisoft's AI-driven game testing tool to automate QA processes, significantly reducing the time and resources needed for testing.
3. Benefits of AI in game development
The integration of AI in game development has brought a range of significant benefits that enhance the creative process, improve player engagement, and increase the overall efficiency of game production. AI technologies have enabled game developers to push the boundaries of what is possible in gaming, providing tools and techniques that transform both the creation and experience of games.
3.1. Enhanced creativity
AI has opened up new avenues for creativity in game design by enabling the automatic generation of vast amounts of content that would be infeasible to create manually. PCG allows developers to create endless variations of game environments, levels, and narratives. This technique not only reduces the time and cost associated with manual content creation but also introduces a level of randomness and uniqueness that can make games more engaging. A notable example is the game No Man's Sky, which utilizes AI-driven PCG to generate a universe comprising 18 quintillion unique planets, each with its own ecosystems and terrains. This generation algorithm often relies on methods such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or rule-based systems to create diverse environments.
Furthermore, AI-driven narrative design tools are enabling more dynamic storytelling. For instance, games like Prom Week use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Graph Models to create branching storylines and character interactions that respond to player choices in real-time. These systems might employ Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) or Transformer architectures to generate coherent dialogues and narrative logic. This not only enriches the storytelling experience but also encourages multiple playthroughs as players explore different narrative paths, further increasing the depth and richness of the game's content.
3.2. Improved player engagement
AI has the potential to revolutionize player engagement by making game experiences more personalized and adaptive. Through techniques like Machine Learning (ML) and Reinforcement Learning (RL), AI can analyze player behavior and adjust gameplay elements in real-time to match the player’s skill level, preferences, and play style. This dynamic adjustment can result in a more engaging and satisfying gaming experience. For example, in Left 4 Dead, an AI “Director” employs Reinforcement Learning techniques such as Q-learning or Deep Q-Networks (DQN) to monitor player performance and adjust the pacing of the game by altering enemy placement, difficulty, and item distribution, ensuring a constantly challenging yet fair experience that keeps players engaged.
Player modeling is another area where AI significantly enhances engagement. By using data analytics to understand player behavior, preferences, and emotions, AI can create tailored experiences that resonate more deeply with players. For instance, the AI in The Sims franchise uses Clustering Algorithms like K-means or Support Vector Machines (SVM) to identify player types and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) to capture changes in player sentiment. Such adaptive systems lead to more immersive gameplay, where each player feels that their choices and actions have a meaningful impact on the game world.
3.3. Increased efficiency in the development process
AI technologies have also streamlined various aspects of the game development process, making it more efficient and cost-effective. Automated testing is one area where AI has made a significant impact. Traditionally, game testing is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, requiring large teams to manually test different scenarios and outcomes. AI-driven automated testing tools can simulate thousands of gameplay scenarios in a fraction of the time, quickly identifying bugs, balance issues, and potential exploits. This not only accelerates the development cycle but also reduces costs associated with human testers. For example, Ubisoft has implemented an AI-based tool named “Commit Assistant” that uses Static Analysis and Pattern Recognition to predict potential bugs and errors in code before they are committed, reducing the time spent on debugging and increasing overall productivity. These tools often utilize Symbolic Execution and Fuzz Testing techniques to discover defects in the codebase.
Additionally, AI can assist in optimizing game performance by automatically adjusting graphics settings, network usage, and other resource-intensive processes based on real-time analysis. This kind of AI-driven optimization helps ensure that games run smoothly across various hardware configurations, providing a consistent experience for players and reducing the need for extensive manual optimization by developers. Techniques such as Dynamic Resolution Scaling can detect performance bottlenecks and adjust rendering resolution accordingly to improve frame rates, thereby leveraging Deep Learning algorithms like CNNs for image processing and RNNs for time-series data handling. This optimization ensures smooth gameplay across a wide range of devices, enhancing the overall user experience.
4. Challenges and problems of AI in game development
While AI has brought numerous advantages to game development, it also comes with a set of challenges and limitations. These issues span ethical considerations, technical obstacles, creative constraints, and economic implications.
4.1. Ethical concerns
Issues surrounding AI decision-making, fairness, and potential biases form significant ethical considerations. The lack of transparency in AI decision-making processes, often referred to as the "black box" problem, can lead to situations where players do not understand the reasons behind certain in-game events. When AI systems make decisions without adequate explanation, players may become confused or dissatisfied, impacting their gaming experience. Moreover, if AI systems are not properly trained or designed, they can inadvertently introduce biases, such as treating certain types of players unfairly. This not only affects player experience but can also lead to social controversies and damage the reputation of game companies. Therefore, ensuring that AI systems operate fairly and without bias is essential.
4.2. Technical challenges
Integrating AI systems into games presents complexities, including performance and scalability issues. Although AI can enhance the gaming experience, doing so requires substantial computational resources. High-performance AI systems often necessitate robust hardware support, meaning that games may perform poorly on low-end devices, limiting the potential player base. For instance, complex deep learning models require GPUs for efficient training and inference, which not all players' devices can provide. The integration and maintenance of AI systems also involve significant engineering efforts. Game developers not only need to understand how to train AI models but also ensure that these models function reliably within the game environment. Real-time AI systems must respond swiftly to changes in game states; otherwise, they can affect the fluidity and player experience. Additionally, the deployment of AI systems in games raises concerns about data privacy and security. AI technologies typically rely on large datasets for model training, which may contain personal information or player behavioral patterns. If not managed properly, there is a risk of data breaches or misuse, potentially eroding player trust.
4.3. Creative limitations
Reliance on AI may stifle human creativity or lead to homogenized gaming experiences. While AI can generate vast amounts of content, it may lack the unique creativity and inspiration inherent in human creators. Current AI systems cannot fully grasp human emotions and cultural contexts, leading to generated content that lacks deeper meaning and resonance. For example, in narrative design, although AI can produce grammatically correct text, it may fail to capture the subtleties and depths of human storytelling. Over-reliance on AI-generated content can result in overly standardized game designs, reducing the space for innovation. AI systems typically learn from existing datasets, tending to reproduce known patterns rather than creating novel concepts. Excessive dependence on AI might lead to games that lack distinctiveness and struggle to stand out. It is crucial to strike a balance where AI complements rather than replaces human creativity, preserving the freshness and uniqueness of game content.
5. Conclusion
This paper has comprehensively examined the multifaceted applications of AI in game development, revealing how AI technologies have driven innovation and transformation within the gaming industry. Through PCG, AI has enabled the design of game worlds to be more diverse and unpredictable, thereby enhancing player experience and engagement. In the realm of NPC behavior and control, the application of AI has made characters more realistic and interactive, offering players a richer and more challenging gaming experience. Furthermore, the application of AI in automated game testing and quality assurance has significantly improved development efficiency and product quality.Despite the significant benefits that AI brings to game development, it also comes with a range of challenges, including ethical concerns, technical difficulties, creative constraints, and economic impacts. Issues such as the transparency of AI decision-making, potential biases, performance and scalability concerns, and the financial burden on small studios and independent developers, all require careful consideration and resolution. To ensure the responsible and effective application of AI technologies, close collaboration between game developers, researchers, and policymakers is necessary.
In summary, the application of AI in game development holds vast potential, but the realization of this potential necessitates a deep understanding of existing challenges and the development of innovative solutions. Through interdisciplinary efforts and cooperation, we can anticipate that AI will continue to bring revolutionary changes to the gaming industry while ensuring the quality of player experiences and the innovation of game content. Future research should continue to explore new applications of AI in game development while focusing on how to overcome existing challenges to achieve sustainable and responsible integration of AI technologies.
References
[1]. Yannakakis, G. N., & Togelius, J. (2018). Artificial intelligence and games. Springer.
[2]. Togelius, J., Kastbjerg, E., Schedl, D., & Yannakakis, G. N. (2011). What is procedural content generation? Mario on the borderline. Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Procedural Content Generation in Games, 3, 1-6.
[3]. Drachen, A., Canossa, A., & Yannakakis, G. N. (2009). Player modeling using self-organization in Tomb Raider: Underworld. 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Games, 1-8.
[4]. Yannakakis, G. N., & Hallam, J. (2007). Towards optimizing entertainment in computer games. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 21(10), 933-971.
[5]. McCoy, J., Treanor, M., Samuel, B., Mateas, M., & Wardrip-Fruin, N. (2011). Prom Week: Designing past the game/story dilemma. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Foundations of Digital Games, 235-237.
[6]. Guzdial, M., & Riedl, M. O. (2016). Game level generation from gameplay videos. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, 377-387.
[7]. El-Nasr, M. S., Drachen, A., & Canossa, A. (2013). Game analytics: Maximizing the value of player data. Springer.
[8]. Cook, M., & Colton, S. (2014). Aesthetic considerations for automated platformer design. Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment Conference, 123-129.
[9]. Jallov, D., Risi, S., & Togelius, J. (2016). EvoCommander: A novel game based on evolving and switching between artificial brains. IEEE Transactions on Computational Intelligence and AI in Games, 9(2), 181-191.
[10]. Nie, Y., Zheng, S., Zhuang, Z., & Togelius, J. (2024). Nested Wave Function Collapse Enables Large-Scale Content Generation. IEEE Transactions on Games.
[11]. John Papadopoulos (2020). 4.17GB AI-enhanced HD Texture Pack for the classic FEAR game available for download. https://www.dsogaming.com/news/4-17gb-ai-enhanced-hd-texture-pack-classic-fear-download/
[12]. OpenAI (2019). OpenAI Five defeats Dota 2 world champions. https://openai. com/index/openai-five-defeats-dota-2-world-champions/
Cite this article
Zhao,Z. (2024). Application and Problems of AI in Game Development. Applied and Computational Engineering,110,13-21.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA 2024 Workshop: Securing the Future: Empowering Cyber Defense with Machine Learning and Deep Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Yannakakis, G. N., & Togelius, J. (2018). Artificial intelligence and games. Springer.
[2]. Togelius, J., Kastbjerg, E., Schedl, D., & Yannakakis, G. N. (2011). What is procedural content generation? Mario on the borderline. Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Procedural Content Generation in Games, 3, 1-6.
[3]. Drachen, A., Canossa, A., & Yannakakis, G. N. (2009). Player modeling using self-organization in Tomb Raider: Underworld. 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Games, 1-8.
[4]. Yannakakis, G. N., & Hallam, J. (2007). Towards optimizing entertainment in computer games. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 21(10), 933-971.
[5]. McCoy, J., Treanor, M., Samuel, B., Mateas, M., & Wardrip-Fruin, N. (2011). Prom Week: Designing past the game/story dilemma. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Foundations of Digital Games, 235-237.
[6]. Guzdial, M., & Riedl, M. O. (2016). Game level generation from gameplay videos. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, 377-387.
[7]. El-Nasr, M. S., Drachen, A., & Canossa, A. (2013). Game analytics: Maximizing the value of player data. Springer.
[8]. Cook, M., & Colton, S. (2014). Aesthetic considerations for automated platformer design. Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment Conference, 123-129.
[9]. Jallov, D., Risi, S., & Togelius, J. (2016). EvoCommander: A novel game based on evolving and switching between artificial brains. IEEE Transactions on Computational Intelligence and AI in Games, 9(2), 181-191.
[10]. Nie, Y., Zheng, S., Zhuang, Z., & Togelius, J. (2024). Nested Wave Function Collapse Enables Large-Scale Content Generation. IEEE Transactions on Games.
[11]. John Papadopoulos (2020). 4.17GB AI-enhanced HD Texture Pack for the classic FEAR game available for download. https://www.dsogaming.com/news/4-17gb-ai-enhanced-hd-texture-pack-classic-fear-download/
[12]. OpenAI (2019). OpenAI Five defeats Dota 2 world champions. https://openai. com/index/openai-five-defeats-dota-2-world-champions/









