1. Introduction
Sludge is the solid component of sewage, that is, the sediment produced in the process of sewage treatment and the residual obtained after treatment of the floating foam from the sewage surface. With the development of global industrial production and the increase of urban population, the discharge of industrial wastewater and domestic sewage continues to rise, resulting in a rapid increase in the production of sludge. China's sludge production is also increasing year by year with the development of social economy, and it is expected that by 2025, the sludge production will exceed 90 million tons [1]. China's sludge treatment technology is diverse, covering sludge concentration, dehydration, stabilization, drying, incineration, et al. Part of the water in the sludge is removed by gravity or mechanical means to reduce the volume of the sludge. Anaerobic digestion, aerobic fermentation and other biological treatment technologies are used to stabilize the sludge. Fluidized bed drying, belt drying and other drying technologies were used to further reduce the moisture content of sludge. Sludge incineration technology can completely decompose sludge into gas, tar and ash residue at high temperature to achieve complete stabilization and reduction of sludge. It is the process of using the heat in the sludge and the additional auxiliary fuel to achieve the complete harmless disposal of the sludge through combustion in the high temperature range (500 to 1000°C). This treatment is mainly for cement cake with a higher moisture content, between 45% and 86%. After drying treatment, the moisture content of the sludge can be reduced to the range of 20% to 40%, and then the moisture content can be reduced to zero for incineration treatment, while the volume is greatly reduced, which is convenient for subsequent transportation and disposal. This paper describes the development and trend of sludge incineration technology, emphatically analyzes the problems and prospects of this technology, and provides reference for the selection of sludge incineration technology.
2. Process and technical characteristics of sludge incineration
2.1. Incineration process
Sludge incineration technology is an efficient method to treat sludge, the core step of which involves pre-dewatering the sludge and then feeding it into the incinerator. In the incineration process, through high temperature heating and drying, the original pathogens and other harmful substances in the sludge are completely inactivated or decomposed, at the same time, the water in the sludge is effectively removed, and the reduction and harmfulness of the sludge is achieved. Typical sludge incineration process can be seen in Figure 1. In addition, before using incineration technology to treat sludge, it is necessary to comprehensively investigate the situation of the incineration plant, thermal power plant and kiln of the cement plant at the project site, so as to reduce the investment of the sludge treatment and disposal project by collaborative incineration of sludge [2].
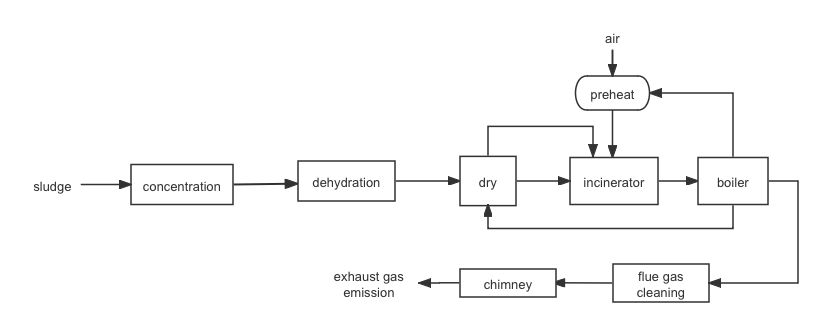
Figure 1: Sludge incineration process.
Sludge incineration can be divided into two types as separate incineration and collaborative incineration. In the former, sludge is the main heat source, and the mass ratio of sludge in feed is usually greater than 85%. In the latter, the sludge blending ratio is usually maintained at 5% ~ 15%, and the sludge calorific value has limited contribution to the total incineration. At present, the sludge in the Netherlands is treated by heat treatment, while 97% of the sludge in Switzerland, 89% of the sludge in Belgium and 70% of the sludge in Germany are treated by heat treatment [3]. The implementation of sludge incineration technology is relatively late in our country, but it has developed rapidly in recent years. According to the data of E20 environmental platform, among the new sludge disposal projects in China from 2019 to 2021, the proportion of sludge incineration process is as high as about 70% [4].
According to the different sludge pretreatment process, the separate incineration technology of sludge can be subdivided into three categories: direct incineration, semi-dry incineration and full dry incineration. Under normal circumstances, the water content of the sludge after conventional mechanical dehydration treatment is still maintained at a higher level of about 80%, and the calorific value of the sludge in this state is low, which is difficult to meet the energy efficiency requirements of direct incineration, so it is usually necessary to add additional auxiliary fuel in the direct incineration process to improve the combustion efficiency. Sludge semi-drying incineration process is a common treatment method, which uses external heat source to further dry the mechanically dehydrated sludge with a moisture content of about 80%. Through this process, the moisture content of the sludge can be significantly reduced to between 30% and 40% [4].
Subsequently, the semi-dried sludge is sent to the incinerator, and the whole process is shown in Figure 2. The sludge drying incineration process is further on this basis, and the drying process is more thorough, aiming to reduce the moisture content of the sludge to less than 10%, ensuring that the thermal efficiency and stability of the sludge in the incineration process reach a better level. This process is similar to semi-dry incineration, but the requirements are more stringent at the drying stage to achieve a more thorough treatment of the sludge.
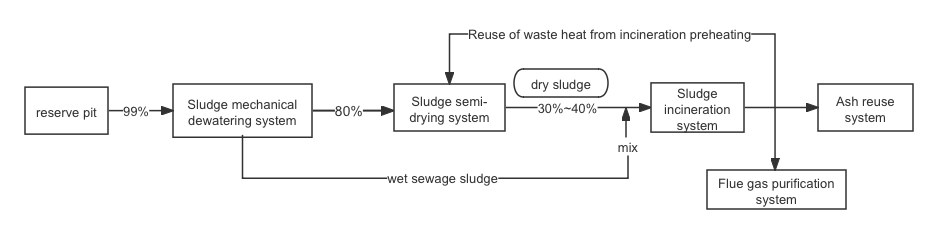
Figure 2: Sludge semi-drying incineration process.
Sludge collaborative incineration technology covers a variety of efficient utilization ways, including the cooperation with cement kilns, coal-fired thermal power plants and waste incineration power plants. Among them, the cement kiln collaborative incineration technology can not only directly integrate the ash after sludge incineration into the production of cement clinker, to achieve the maximum utilization of resources, but also the flue gas waste heat generated in the incineration process can also be cleverly used for sludge drying treatment, forming a closed-loop system of resource recycling and energy recovery. Sludge collaborative incineration of coal-fired thermal power plants means that dry sludge and coal are mixed and directly burned into the boiler, which can not only solve the problem of sludge disposal, but also save boiler fuel and reduce power generation costs for thermal power plants [5]. However, with the increase of the sludge blending ratio, the ash melting point of the mixed fuel gradually decreases, the compound is easy to sintering, and the wear degree of the heating surface and the flue gas flow rate are also restricted by the sludge blending ratio, which is generally controlled below 5% [4]. The co-incineration technology of waste incineration power plant is a sludge treatment method of co-incineration of sludge and waste. Because the combustion characteristics of sludge and waste are complementary to a certain extent, the direct impact of collaborative incineration on the boiler is relatively small, which helps to maintain the stable operation of the boiler. The process can make full use of the existing infrastructure and incineration equipment of the waste incineration power plant, avoiding additional equipment investment and construction costs. At the same time, because the addition of sludge improves the calorific value of the incineration raw materials to a certain extent, it helps to improve the incineration efficiency, thus further reducing the unit treatment cost.
2.2. Operation Parameters
2.2.1. Temperature
Increasing the incineration temperature does help to accelerate the pyrolysis and oxidation process of organic matter and improve the incineration efficiency. However, this process must be strictly controlled to avoid the problem of sludge crushing and fly ash increase caused by too fast a heating rate. In addition, too high incineration temperature will not only increase energy consumption, but also may trigger a series of adverse chemical reactions, such as the generation of nitrogen oxides and the volatilization of heavy metals, thereby causing secondary pollution to the environment.
Therefore, in the sludge incineration process, the incineration temperature is usually set in a suitable range, which is usually considered to be 850℃ to 1100 ℃ [6]. In the specific operation, the choice of incineration temperature also needs to be adjusted according to the actual nature of the sludge and the specific situation of the incinerator. For example, for sludge containing high volatile organic compounds or heavy metals, lower incineration temperatures or more stringent flue gas purification measures may be required to reduce pollutant emissions.In addition, in order to improve the stability and efficiency of the incineration process, some advanced control technologies can be used, such as automatic combustion control system, online monitoring system and so on, to monitor and adjust the temperature, oxygen content, flue gas composition and other parameters in the incineration process in real time to ensure that the incineration process is carried out in the best state.
2.2.2. Sludge moisture content
During incineration process, the moisture content of sludge is required to meet the requirement of the smoke temperature of the incineration furnace, so as to achieve self-sustained combustion [5]. The water in the sludge consumes energy significantly during the heating and evaporation process. The higher the initial water content of the sludge, the energy consumption required for evaporation will also increase, which may threaten the stable progress of incineration due to insufficient energy supply, and may even cause combustion interruption in extreme cases. The water in the sludge consumes energy significantly during the heating and evaporation process. The higher the initial water content of the sludge, the energy consumption required for evaporation will also increase, which may threaten the stable progress of incineration due to insufficient energy supply, and may even cause combustion interruption in extreme cases. Therefore, in order to ensure the continuous stability and high efficiency and energy saving of the incineration process, it is particularly important to accurately control the water content of the sludge.
Usually, the moisture content of sludge is still as high as 80% ~ 85% after concentration and direct mechanical dehydration [7]. In general, adjusting the moisture content of the sludge to a ratio of no more than 3.5 to its volatile content [8] is regarded as an optimized operating parameter. This ratio is set to balance the water evaporation energy consumption and the effective use of the combustible components of the sludge, not only to avoid unnecessary energy loss, but also to promote the full combustion of organic matter in the sludge, so as to achieve the saving of fuel resources and reduce the overall energy consumption. In addition, through scientific and reasonable sludge pretreatment technology, such as mechanical dehydration, thermal drying, to further reduce the moisture content of the sludge, not only can improve the incineration efficiency, but also reduce the amount of fly ash generated during the incineration process, reduce the load of the subsequent flue gas purification system, and promote the sustainable development of sludge incineration treatment technology and the improvement of environmental benefits from many aspects.
2.2.3. Air
In sludge incineration process, air plays as a combustion medium and its supply has a crucial impact on the efficiency and stability of the incineration process. Insufficient gas supply will lead to inadequate combustion, so that the organic matter in the sludge can not be completely oxidized and decomposed, thereby reducing the incineration efficiency and may produce harmful gases. On the contrary, if the gas supply is excessive, the excess air will consume a lot of heat during the heating process, resulting in a decrease in the furnace temperature, which will also inhibit the combustion reaction, resulting in inadequate combustion and energy waste.
Therefore, precise control of air supply is the key to achieve efficient and stable sludge incineration. In general, the air supply should be controlled between 50% and 100% of the theoretical air demand [8], which is based on the comprehensive consideration of the combustion characteristics of the sludge, the design parameters of the incinerator and the combustion efficiency. Through the adjustment in this range, it can ensure that the oxygen concentration in the combustion area is moderate, which not only meets the needs of the full combustion of the sludge, but also avoids the heat loss and the decrease of the furnace temperature caused by excessive air.
3. Bottlenecks
3.1. Energy cost
Incineration of sludge is an effective treatment method, but the incineration process also generates a lot of heat energy, which would be wasted if not recycled. One of the core goals of energy recovery is to convert the thermal energy generated by incineration into useful forms of energy, thereby improving the energy efficiency of the entire system. This is crucial in a world of limited resources. By converting thermal energy into electricity or other forms of energy, cities can be provided with more sustainable energy sources and reduce their dependence on traditional energy sources [9]. First of all, the heat generated by incineration sludge is used in urban heating systems, which is an efficient and environmentally friendly way to use energy. This method can not only effectively use the high temperature flue gas and hot water generated in the sludge incineration process, reduce the waste of these heat energy, but also transfer the heat energy to the heating network through the heat exchanger to meet the winter heating needs of residential, industrial and commercial buildings. This not only reduces the dependence on traditional energy sources, such as coal, oil and other fossil fuels, but also reduces the greenhouse gas emissions generated by burning these fossil fuels, which is of great significance for improving urban air quality and combating climate change.
Secondly, converting the heat generated by incineration into electricity and supplying it to the urban power network is another important way of energy utilization. Through technologies such as steam turbine power generation, heat energy can be converted into electricity and injected into the city grid to improve the stability of power supply. This approach not only helps to reduce the dependence on coal or nuclear power plants, reduce carbon emissions, but also promotes the access of renewable energy and the development of distributed energy, and promotes the optimization and upgrading of the energy structure.
3.2. Exhaust Gas
The main reason for the waste gas problem of sludge incineration is the complex composition of sludge itself and its chemical changes during incineration. The organic matter in the sludge is oxidized and decomposed at high temperature, while the inorganic matter and volatile matter in the sludge are also involved in the reaction, generating a variety of pollutants. During sludge incineration, waste gases containing complex components are produced, mainly including particulate matter, acidic gases (such as SO2、NOx、HCl, etc.), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and possibly harmful substances such as dioxins. These exhaust gases pose a potential threat to the environment and human health. Unlike coal combustion, about 80% of the carbon in sludge is completely burned in the form of volatile substances, so the gaseous incineration of volatile substances dominates sludge combustion. The O2 and CO2 concentration change curves of the incineration process are similar to those of propane-air mixture incineration, indicating that theoretically sludge incineration can be very thorough [10].
Optimization of incinerators, such as the fluidized bed incinerator used in Germany, due to its reasonable design, can effectively control NOx emissions in the sludge incineration process, so that it is maintained in the range of 150 ~ 200 mg/m3, which fully explains the importance of incinerator design for waste gas treatment. By optimizing furnace structure, improving combustion efficiency and increasing gas mixing uniformity, the generation of pollutants can be reduced.
4. Development trend
4.1. High Efficiency
As an efficient and environmentally friendly sludge treatment method, rotary kiln incineration technology has indeed shown its unique advantages and application value in many fields. This technology can not only effectively treat domestic sludge, industrial sludge and construction sludge and other wastes, reduce environmental pollution, but also achieve sludge reduction and harmless through high temperature incineration, and even recover some energy or resources.
Enterprises in the actual use of rotary kiln incinerator sludge treatment, can continue to innovate calcining system equipment, the use of domestic and foreign most advanced hydraulic wheel stop device and measurement accuracy of high metering piston pump, contact graphite block sealing device, high precision speed control valve and other advanced technology and optimization, to further improve the reliability and stability of equipment operation. Compared with other equipment, these measures can reduce heat consumption by about 15%, increase output by 5% to 10%, and increase operation rate by about 10% [11].
4.2. Low Emission
When burning temperature exceeds a certain limit, not only increase in fuel consumption, still can make the volatilization of the metal in the sludge quantity and the quantity increase of nitrogen oxide in flue gas, cause secondary pollution [12]. The moisture content of sludge has a significant impact on its incineration effect and waste gas generation. By strengthening the pretreatment and drying process and reducing the moisture content of sludge, the incineration efficiency can be improved and the waste gas generation can be reduced. At the same time, the exhaust gas generated during the drying process also needs to be effectively treated to avoid secondary pollution to the environment. For example, the flue gas purification system can be added in the future. In addition, flue gas purification systems can be added in the future, the 4 000 t/d sludge treatment project in Xiaoshan District of Hangzhou adopted the deep dewatering circulating fluidized bed incinerator incineration process, and its successful operation provides a new idea for sludge treatment in China, which is expected to be applied in more centralized sludge disposal projects in metropolitan areas [13]. This is mainly due to its perfect flue gas purification system, including desulfurization, denitrification and dust removal and other links by using efficient dry desulfurization and denitrification equipment electrostatic precipitator or bag dust collector, can greatly reduce the concentration of pollutants in the exhaust gas.
4.3. Energy
One of the core goals of energy recovery is to convert the thermal energy generated by incineration into useful forms of energy, thereby improving the energy efficiency of the entire system. This is crucial in a world of limited resources. By converting heat into electricity or other forms of energy, it can provide cities with more sustainable energy sources and reduce their dependence on traditional energy sources.
For example, the high-temperature and high-pressure steam produced by the incineration process can be used to drive a turbine generator, thereby generating electricity. The high temperature flue gas from the incineration sludge enters a heat exchanger and exchanges heat with water or another working medium. This allows the heat energy in the flue gas to be effectively transferred to the working medium, heating it into high temperature and high-pressure steam. A significant advantage of this method is its high efficiency, which can convert the heat generated by the incineration of the sludge almost entirely into electricity, and therefore has a high energy recovery rate [9].
5. Conclusion
Sludge incineration technology, as an efficient and thorough means of sludge treatment, plays an important role in the field of sludge treatment. In the process of research and application of sludge incineration treatment technology, the characteristics of sludge incineration technology, operating parameters and bottleneck problems should be comprehensively considered in order to achieve sustainable development of sludge incineration technology. Scientific and effective treatment and comprehensive utilization of sludge resources can not only reduce its impact on the environment and human health, but also promote the implementation of China's environmental protection, circular economy and green low-carbon development strategy. In the future, with the continuous innovation of technology and the guidance and support of policies, sludge incineration technology will be more widely used and promoted, providing strong support for the sustainable development of sludge treatment technology.
References
[1]. DAI X H. Status and development trend of sludge treatment and disposal in China [J]. Science, 2019, 72 (06): 5.
[2]. Zhang Qiquan. Development of sludge treatment and disposal technology in China [J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2024, 44 (06): 45-48 264.
[3]. Schnell M, Horst T., Ouicker P. Thermal treatment of sewage sludge in Germany :A review [J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2020 (263):110367.
[4]. Wang Cheng, Chen Baixiao, Xia Yukun, et al. Current situation and development trend of sludge incineration technology [J]. China Comprehensive Utilization of Resources, 2022, 40 (06): 121-124.
[5]. LI Qiaoyang. Status and development trend of municipal sludge disposal based on carbon emission reduction analysis in China [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020:17-18.
[6]. Zhao Famin. Feasibility study on cooperative incineration of sludge and general solid waste [J]. Green Mining and Metallurgy, 2023, 39 (05): 78-82.
[7]. Zhao Yingying, Zhao Qingling. The research progress of sludge recycle technology [J]. Journal of research and utilization of energy, 2023, (5): 40-44.
[8]. He Xiaoyu, Peng Xianhui, Li Qingquan, et al. Technology analysis of municipal sludge treatment and recycling [J]. Zhejiang Chemical Industry, 2024, 55 (06): 43-49.
[9]. Chen X H. Research on energy recovery and utilization technology of municipal sludge incineration collaborative treatment [J]. Modern agriculture research, 2023, 29 (12): 120-123.
[10]. Ogada T., Werther J. Combustion characteristics of wet sludge in a fluidized bed:Release and combustion of the volatiles[J].Fuel,1996(5):617-626.
[11]. Chen Y. Application and consideration of rotary kiln incineration technology in sludge drying incineration treatment [J]. Science and Technology of Leather Making and Environmental Protection, 2024, 5 (07): 115-117.
[12]. Wang Zhi-Guo, LAN Mei, Liu Xiao-Lin. Research on sludge incineration technology [J]. Municipal technology, 2016 (4): 148-149, 172.
[13]. Meng Xin, Chen Wei, Chen Baixiao.Practice of 4 000 t/d sludge centralized incineration treatment project in Xiaoshan [J]. China Water Supply and Drainage, 2022 (8): 127-132.
Cite this article
Ma,Z. (2025). Development and Trend of Sludge Incineration Technology. Applied and Computational Engineering,124,54-60.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. DAI X H. Status and development trend of sludge treatment and disposal in China [J]. Science, 2019, 72 (06): 5.
[2]. Zhang Qiquan. Development of sludge treatment and disposal technology in China [J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2024, 44 (06): 45-48 264.
[3]. Schnell M, Horst T., Ouicker P. Thermal treatment of sewage sludge in Germany :A review [J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2020 (263):110367.
[4]. Wang Cheng, Chen Baixiao, Xia Yukun, et al. Current situation and development trend of sludge incineration technology [J]. China Comprehensive Utilization of Resources, 2022, 40 (06): 121-124.
[5]. LI Qiaoyang. Status and development trend of municipal sludge disposal based on carbon emission reduction analysis in China [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020:17-18.
[6]. Zhao Famin. Feasibility study on cooperative incineration of sludge and general solid waste [J]. Green Mining and Metallurgy, 2023, 39 (05): 78-82.
[7]. Zhao Yingying, Zhao Qingling. The research progress of sludge recycle technology [J]. Journal of research and utilization of energy, 2023, (5): 40-44.
[8]. He Xiaoyu, Peng Xianhui, Li Qingquan, et al. Technology analysis of municipal sludge treatment and recycling [J]. Zhejiang Chemical Industry, 2024, 55 (06): 43-49.
[9]. Chen X H. Research on energy recovery and utilization technology of municipal sludge incineration collaborative treatment [J]. Modern agriculture research, 2023, 29 (12): 120-123.
[10]. Ogada T., Werther J. Combustion characteristics of wet sludge in a fluidized bed:Release and combustion of the volatiles[J].Fuel,1996(5):617-626.
[11]. Chen Y. Application and consideration of rotary kiln incineration technology in sludge drying incineration treatment [J]. Science and Technology of Leather Making and Environmental Protection, 2024, 5 (07): 115-117.
[12]. Wang Zhi-Guo, LAN Mei, Liu Xiao-Lin. Research on sludge incineration technology [J]. Municipal technology, 2016 (4): 148-149, 172.
[13]. Meng Xin, Chen Wei, Chen Baixiao.Practice of 4 000 t/d sludge centralized incineration treatment project in Xiaoshan [J]. China Water Supply and Drainage, 2022 (8): 127-132.









