1. Introduction
In 1972, Aoyagi proposed the principle of pulse spectrophotometry. In 1980, Minolta verified this principle and developed the OXIMET. In 1983, Nellcor launched the N-100, marking a new era in modern blood oxygen saturation development with the introduction of [1]. With the emergence and popularity of wearable devices, the application scope of pulse oximeters has expanded from clinical settings to fitness and daily activities. However, current blood oxygen meters still have shortcomings in accuracy and portability. Therefore, developing more powerful flexible sensors has become a new necessity.
In recent years, with the advancement of material science and manufacturing technology, such as the application of materials like graphene and the development of nanolithography techniques, flexible wearable devices have made significant progress. Flexible wearable sensors are made from flexible, stretchable, and transparent materials that can closely adhere to the human body surface, enabling efficient biological signal acquisition and monitoring. In comparison to traditional monitoring instruments, these devices provide advantages such as high comfort, robust real-time monitoring capabilities, excellent wearability, and high precision [2]. They offer more comprehensive and accurate monitoring data for the medical health field, are suitable for long-term wear, and hold significant value in disease prevention. This paper employs qualitative methods, focusing on the photoelectric properties and practical applications of organic semiconductor materials PEDOT, to provide material insights for improving the accuracy and sensitivity of blood oxygen analyzers.
2. The photoelectric characteristics of PEDOT
PEDOT, a distinguished organic conductive polymer, possesses distinctive and superior photoelectric properties. In terms of optical characteristics, it exhibits high transparency, a pronounced response to light, and the capability to effectively absorb photons across the visible spectrum, furthermore, it demonstrates photochromic behavior. Regarding electrical properties, its superior conductivity, good stability, and high carrier mobility make it highly promising for applications in optoelectronics, potentially leading to new breakthroughs in various optoelectronic devices. Currently, PEDOT is being used as a high-quality organic semiconductor material in numerous studies on flexible wearable electronic devices.
2.1. Optical characteristics
PEDOT, a prominent organic conductive polymer, exhibits exceptional optical properties, including high transparency, rapid light response, broad spectral absorption, and unique photochromic behavior. Its transparency in the oxidized state is attributed to a conjugated molecular structure that permits free electron movement, minimizing light scattering and absorption. PEDOT: PSS films maintain high transparency across UV, visible, and near-infrared regions, with slight absorption increases in the NIR spectrum.
PEDOT’s light sensitivity enables nanosecond responses to light signal changes, allowing precise detection and adjustment of optical properties, suitable for optical sensing and light regulation applications. Its absorption spectrum, primarily in the visible light region, facilitates efficient photon absorption and energy conversion, with adjustable absorption peaks through varying preparation methods and dopants, influencing the molecular structure and spectrum characteristics.
Additionally, PEDOT’s photochromic properties cause significant optical changes under light exposure, such as color and refractive index shifts, due to photon absorption and intramolecular electronic structure alterations triggering redox reactions. These reactions modify both electrical conductivity and optical properties, resulting in diverse optical characteristics under different lighting conditions, thereby affecting optical performance and practical applications.
In addition, DMSO and EG act as surfactants with PSS sulfonic groups, which reduces the attraction between PEDOT and PSS chains, precipitatePEDOTPolymer chain rearrangement reduces surface roughness [3]. PEDOT: The morphology and structural properties of PSS film have a significant impact on the efficiency of solar cells. Changes in surface roughness will affect the scattering and absorption of light, which will play an important role in the photoelectric conversion efficiency.
2.2. Electrical properties
PEDOT showcases superior electrical properties, including high conductivity, stability, and carrier mobility. Pure PEDOT reaches 600 S/cm conductivity, while PEDOT/PSS films average around 10 S/cm. These films offer low sheet resistance and optical transparency, with conductivity adjustable by doping, such as with LiCl, which also enhances energy level structure and hole injection efficiency [4], optimizing device performance. Temperature and surfactants like DMSO and EG further influence conductivity and the Seebeck coefficient. For instance, DMSO or EG-sensitized surfaces prior to PEDOT: PSS deposition increase conductivity and extend relaxation times: conductivity relaxation time increases tenfold, and photoconductive excitation relaxation time rises by 2 and 1.2 times for DMSO and EG, respectively, as measured by elliptically polarized spectroscopy and direct methods. These adjustments highlight the tunability of PEDOT’s electrical properties for various applications.
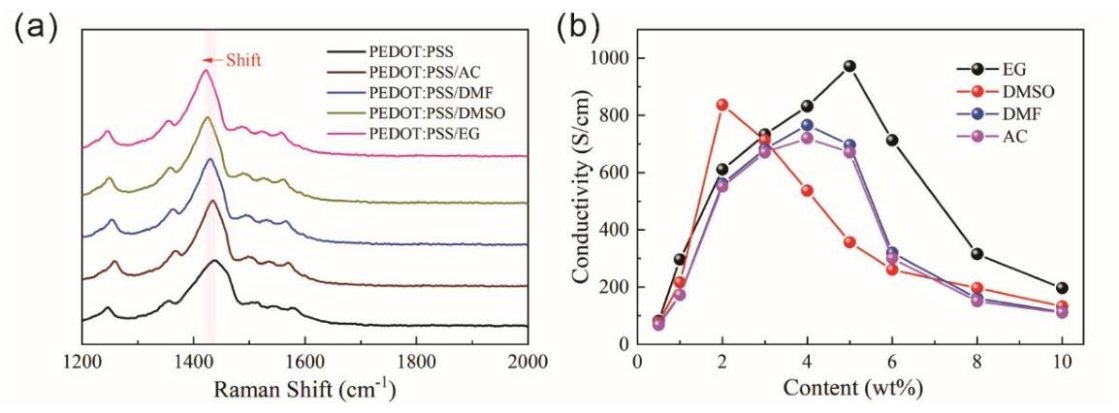
Figure 1: PEDOT: PSS after adding different solvents : (a) Raman spectrum (b) conductivity
Figure 1 demonstrates the Raman spectra and conductivity of PEDOT:PSS with various solvents, revealing EG as the most effective enhancer, particularly at 5 wt% doping, where conductivity peaks [5]. PEDOT’s stability is remarkable, retaining over 95% of its initial conductivity in air over years and resisting acid and alkali corrosion, ensuring reliable performance across diverse environments, from indoor electronics to outdoor chemical exposure.
PEDOT’s high carrier mobility facilitates rapid charge transport, crucial for photodetectors’ quick response to weak light signals and for solar cells’ reduced charge recombination losses, thereby enhancing photoelectric conversion efficiency. Lateral conduction in solar cells further boosts efficiency by increasing photogenerated carriers, underscoring PEDOT’s versatile applications in electronic devices.
This concise summary maintains the key points of the original text while reducing the word count to approximately 300 words, preserving the reference to Figure 1 and literature [6].
2.3. Photoelectric conversion process
The photoelectric conversion process of PEDOT is divided into three parts. When light is absorbed, the photon energy must be equal to or greater than its bandgap energy, which ranges from 1.5 to 2.5 eV, to absorb visible light in the 400-800 nm range and some near-infrared light, forming electron-hole pairs in the π electronic system of the thiophene ring. After photoexcitation generates electron-hole pairs, they enter the charge separation and transport process. The crystallinity and molecular order of PEDOT enable effective charge separation both within and between molecules. Within the molecule, charge is transferred through conjugated structures, while between molecules, it is facilitated by π-π stacking and hydrogen bonding. In organic solar cells and other devices, the synergistic effect of the photovoltaic active layer with other functional layers (such as the electron transport layer and hole transport layer) also aids in the effective separation and transport of charges [7]. In the process of electrode transport and collection, using a solar cell as a case study, the application of an electric field results in the injection of electrons into PEDOT, while holes concurrently migrate toward the anode. These charge carriers are then respectively collected by the anode and cathode, facilitating the efficient operation of the device. The hole transport layer (such as pedot: PSS) suppresses hole backflow and promotes transport. Interface engineering is crucial here; by optimizing the interface between electrodes and PEDOT, charge transport resistance can be effectively reduced, improving charge collection efficiency and thus enhancing the photovoltaic conversion efficiency of solar cells [8].
3. Application of PEDOT
PEDOT has a wide range of applications in healthcare-related fields, including medical imaging, health monitoring, and potential areas such as artificial retinas and drug delivery. Notably, it stands out in blood oxygen detection. Additionally, due to its excellent photoelectric properties, PEDOT is also widely used in various fields like photodetectors.
3.1. Application mechanism
The current application mechanisms of PEDOT are mainly divided into photoelectric conversion and chemical sensing. In terms of photoelectric conversion, PEDOT, as a conductive polymer, has conjugated double bonds in its molecular structure, which can absorb photons and generate electron-hole pairs. Under the influence of light, the energy of photons is excited to produce free electrons under the electric field, thus generating a photocurrent while leaving holes in the valence band. PEDOT can serve as a hole transport layer in the OPD structure AG (20nm)/PEDOT : PSS/C60(100nm)/BCP(20nm)/AL(100nm)centre, PEDOT: PSSAs a hole transport layer.In the process of converting optical signals into electrical signals, it provides a transmission path for holes and helps charge transfer, thus enhancing the photoelectric current signal and improving the sensitivity of OPD to optical signals. For instance, experimental comparisons of different PEDOT:PSS materials used as hole transport layers in OPDs reveal that PEDOT: PSS 8000 can achieve a low dark current, indicative of higher sensitivity and a larger dark-to-light current ratio. This underscores its significant role in hole transport. Moreover, PEDOT’s photoconductive properties enable it to modulate its conductivity in response to the intensity and wavelength of incident light. Illumination leads to an increased concentration of carriers, thereby enhancing the material’s conductivity. These characteristics render PEDOT highly promising for applications in photodetectors and solar cells.
In addition to photoelectric conversion, PEDOT is widely used as a chemical sensing material. The chemical structure of PEDOT allows it to interact with specific molecules, achieving molecular recognition through chemical bonding and electrostatic interactions. When in contact with target molecules, the electrical conductivity of PEDOT changes, which can be detected using electrical measurement methods, thus enabling the sensing and detection of target molecules. Moreover, PEDOT has excellent redox activity; during the redox process, its molecular structure and electrical properties undergo reversible changes. This characteristic makes PEDOT a sensitive material suitable for chemical sensors that detect redox active substances such as oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, as well as for constructing biosensors to detect biomolecules within living organisms.
3.2. Application status
PEDOT exhibits significant potential in the innovation of pulse oximeters. The novel PEDOT-based pulse oximeter can be integrated with LED technology for manufacturing. This device detects pulse wave signals across various light wavelengths and calculates blood oxygen saturation using the photoplethysmographic principle. PEDOT’s wide spectral response, spanning from the visible to the short-infrared region, fulfills the photodetection requirements of pulse oximeters. Compared to traditional inorganic, rigid blood oxygen meters, PEDOT-based oximeters offer advantages such as superior flexibility, enhanced wearability, and high biocompatibility.
3.2.1. Application in the field of medical and health care
PEDOT: PSS is used in the relevant sensors of pulse oximeters and is a key component. Reflective pulse oximeters, as an emerging technology in healthcare, have not yet been widely applied. In related research, Lee et al. designed an organic pulse blood oxygen monitoring patch with a reflective configuration, featuring a unique "V" shaped OPD ring surrounding red and green micro-OLEDs. In this patch, PEDOT: PSS is used as the anode material, working together with other components to form the sensor. The average power consumption of this sensor patch is extremely low, only 24μW, which allows for reduced energy consumption during long-term wear and use, enhancing the practicality and convenience of the device. After calibration, the patch is suitable for monitoring blood oxygen saturation at various body sites, showcasing its stability and accuracy in continuous blood oxygen monitoring. This capability enables round-the-clock health monitoring services for users. Khan et al. developed a flexible organic reflective pulse oximeter array, incorporating 4 red and 4 near-infrared OLEDs, and 8 OPDs within a 4.3cm×4.3cm area, where PEDOT: PSS served as the anode material. This material synergizes with the OLEDs and OPDs to facilitate blood oxygen saturation detection. The device can generate a 2D “SPO2 map,” enabling point-to-surface oxygen saturation detection, which is crucial for real-time monitoring of chronic diseases and the recovery of wounds, flaps, and transplanted organs, thereby offering more comprehensive medical diagnostic information. These design innovations contribute to a reduction in the device’s size and power consumption, enhancing its portability and practicality [9].
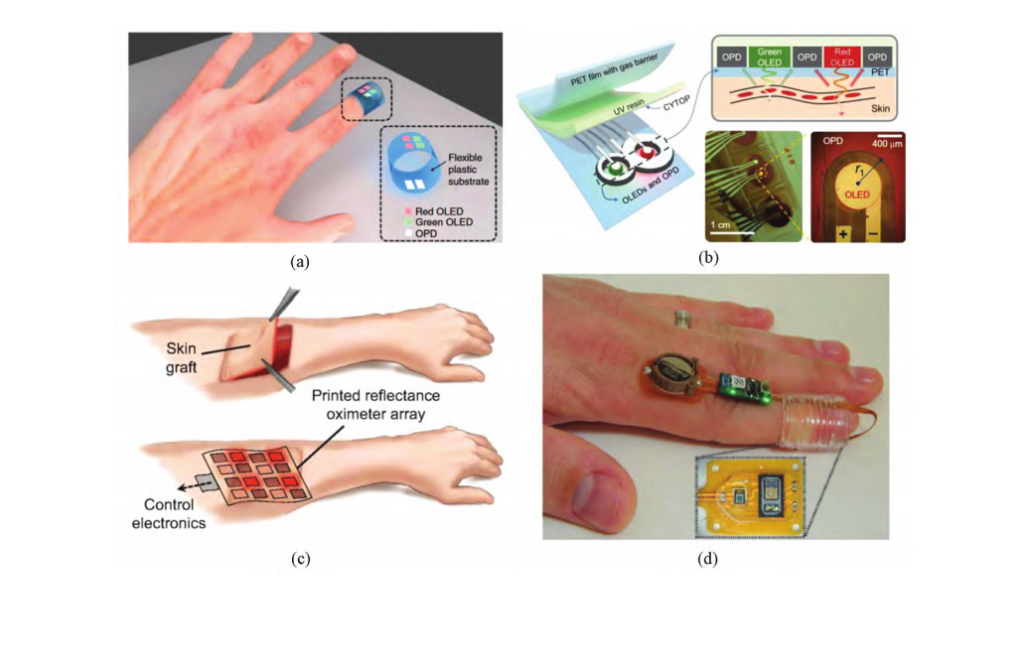
Figure 2: Applications of flexible wearable sensors in blood oxygen saturation monitoring. (a) A transmission-type pulse oximeter based on all-organic materials; (b) An organic pulse oximetry patch with a reflective configuration; (c) Schematic diagram of an organic reflective oximeter array; (d) Flexible blood oxygen finger sleeve monitoring.
As shown in Figure 2, OLEDs with PEDOT as anode material have great potential in current flexible wearable blood oxygen monitoring devices.
In summary, PEDOT primarily functions as an anode material in blood oxygen meters, significantly enhancing device performance, reducing costs, and minimizing size and power consumption. Its application provides robust support for the advancement of flexible, wearable blood oxygen monitoring technology.
3.2.2. Other areas
PEDOT also excels in domains beyond healthcare. Notably, PEDOT: PSS serves as an effective light detector.
Part of it can be improved by combining it with other materials, such as narrow band gap donor polymer materials.
PEDOT: PSS has excellent photoelectric properties, with high photoconductivity gain, enabling effective detection of optical signals. Additionally, it is suitable for solution processing and exhibits good flexibility, making it easy to fabricate into flexible devices that meet the demand for wearable devices in the medical health field [10]. Health monitoring based on PPG, when used with OPD, can precisely detect physiological parameters such as pulse waves and blood oxygen saturation. For example, by measuring changes in PPG signals, real-time monitoring of heart function and circulatory status can be achieved, providing crucial evidence for disease diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, PEDOT can use VPP grown in situ on carbon cloth as a supercapacitor material, supporting its growth and serving as an electronic transport channel. The carbon cloth acts as a flexible substrate and current collector. PEDOT nanotubes uniformly wrap around the carbon cloth, forming a three-dimensional conductive network structure as an electrode material, performing excellently in supercapacitors, such as high specific capacitance, good cycling stability, and flexibility. By optimizing gas-phase polymerization conditions, such as temperature and time, the growth and structure of PEDOT nanotubes can be controlled, enhancing the electrochemical performance of the electrode material. When the polymerization temperature is 130℃ and the polymerization time is 120min, the PEDOT/CC electrode material exhibits optimal electrochemical performance, with a specific capacitance of 6 at 1A/g63.34F/g. Asymmetric supercapacitors are assembled with NiCo-MOF as the positive electrode and PEDOT/CC as the negative electrode. The specific capacitance can reach 178.19F/g at 1 A/g, with an energy density of 53.84Wh/kg. After 10,000 cycle tests, the capacity retention rate remains at 90.4%, demonstrating excellent cycling stability [11]. This high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor provides an efficient energy storage solution for flexible electronic devices and is expected to be widely applied in wearable devices, smart sensors, and other fields.
4. Conclusion
PEDOT, a superior organic conductive polymer, offers exceptional optical and electrical properties, including high transparency, sensitive light response, broad spectral absorption, photochromic behavior, excellent conductivity, stability, and high carrier mobility. These attributes facilitate efficient photoelectric conversion, crucial for developing flexible wearable devices and other applications. In healthcare, PEDOT excels particularly in pulse oximeters, integrating with LEDs for wide-spectrum response. PEDOT: PSS, used as an anode material in sensors like reflective pulse oximetry patches, enhances device stability, accuracy, portability, and reduces power consumption and size, supporting flexible wearable pulse oximeter development. PEDOT also finds applications in light detectors, PPG-based health monitoring, and supercapacitors.
Future development of PEDOT aims to optimize material properties and expand applications. Enhancements in molecular design and synthesis could improve light absorption, carrier mobility, and photonic response sensitivity. Research into PEDOT's photoelectric conversion mechanism could advance its use in high-performance light detectors and solar cells. Minimizing chemical erosion and degradation will enhance its longevity and reliability in harsh environments, achievable through molecular structure modifications, protective groups, or composite materials.
PEDOT's potential in flexible electronics and medical health equipment is yet to be fully realized. Combining PEDOT with other materials could lead to multifunctional integrated sensors for comprehensive health monitoring, offering precise and timely information for disease diagnosis and treatment. As flexible electronics evolve, PEDOT is poised to play a pivotal role, leveraging its flexibility and stretchability in a broader range of devices.
References
[1]. Liao Guojie, Zhang Zhiqiang, Gao Bo, Mou Ling & Wei Wei (2009). Study on reflective blood oxygen saturation detection method. Journal of Light Scattering (03), 274-278. doi:10.13883/j.issn1004-5929.2009.03.011.
[2]. Chen, S. W., Qi, J. M., Fan, S. C., et al. (2021). Flexible wearable sensors for cardiovascular health monitoring. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 10(17), e2100116.
[3]. Girtan, M., Mallet, R., Socol, M., & Stanculescu, A.Girtan, M., Mallet, R., Socol, M., & Stanculescu, A. (2020). On the Physical Properties PEDOT:PSS Thin Films. Materials Today Communications, 23, 100735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100735
[4]. Wang Yanlin, Cao Song, Yu Chunyan, Zhou Litong, & Zhai Guangmei. (2024). Enhancement of Blue Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode Performance by LiCl-Doped PEDOT:PSS. Liquid Crystals and Displays (06), 771-780.
[5]. Li Junliang (2023). Preparation of ultra-sensitive flexible strain sensor based on PEDOT: PSS/WPU and blood pressure monitoring research (Masters thesis, Hefei University of Technology). Master https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27101/d.cnki.ghfgu.2023.002484doi:10.27101/d.cnki.ghfgu.2023.002484.
[6]. Zhao, Y., Wu, X., & Sun, Y. (2021). The relationship between crystallinity and charge transport in PEDOT - based materials. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 125(40), 22474 - 22482.
[7]. Liu, H., Zhang, Y., & Chen, X. (2023). Interface engineering for high - efficiency organic solar cells. Nano Energy, 107, 108177.
[8]. Zhang, L., Li, X., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Interface engineering strategies for enhancing charge collection efficiency in solar cells. Energy & Environmental Science, 16(3), 1235 - 1250.
[9]. Huang Qiufan, Ma Ye & Xu Zhiyun. (2024). Research progress on flexible wearable sensors for cardiovascular disease monitoring. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering (02), 214-226.
[10]. Cao Yunhao, Yang Xiyeh, Liu Chunchen & Huang Fei. (2022). Application of organic/polymer photodetectors in medical and health fields. Polymer Journal (04), 307-330.
[11]. Mao Xiling, Niu Tingting, Liu Hao & Liu Jia. (2024). Study on energy storage characteristics of supercapacitors based on PEDOT flexible nanotubes. Electronic Components and Materials (10), 1199-1206. doi:10.14106/j.cnki.1001-2028.2024.0365.
Cite this article
Wang,R. (2025). Optoelectronic Properties of PEDOT and Their Application in Flexible Wearable Blood Oxygen Monitors. Applied and Computational Engineering,147,49-55.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Smart Systems
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Liao Guojie, Zhang Zhiqiang, Gao Bo, Mou Ling & Wei Wei (2009). Study on reflective blood oxygen saturation detection method. Journal of Light Scattering (03), 274-278. doi:10.13883/j.issn1004-5929.2009.03.011.
[2]. Chen, S. W., Qi, J. M., Fan, S. C., et al. (2021). Flexible wearable sensors for cardiovascular health monitoring. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 10(17), e2100116.
[3]. Girtan, M., Mallet, R., Socol, M., & Stanculescu, A.Girtan, M., Mallet, R., Socol, M., & Stanculescu, A. (2020). On the Physical Properties PEDOT:PSS Thin Films. Materials Today Communications, 23, 100735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100735
[4]. Wang Yanlin, Cao Song, Yu Chunyan, Zhou Litong, & Zhai Guangmei. (2024). Enhancement of Blue Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode Performance by LiCl-Doped PEDOT:PSS. Liquid Crystals and Displays (06), 771-780.
[5]. Li Junliang (2023). Preparation of ultra-sensitive flexible strain sensor based on PEDOT: PSS/WPU and blood pressure monitoring research (Masters thesis, Hefei University of Technology). Master https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27101/d.cnki.ghfgu.2023.002484doi:10.27101/d.cnki.ghfgu.2023.002484.
[6]. Zhao, Y., Wu, X., & Sun, Y. (2021). The relationship between crystallinity and charge transport in PEDOT - based materials. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 125(40), 22474 - 22482.
[7]. Liu, H., Zhang, Y., & Chen, X. (2023). Interface engineering for high - efficiency organic solar cells. Nano Energy, 107, 108177.
[8]. Zhang, L., Li, X., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Interface engineering strategies for enhancing charge collection efficiency in solar cells. Energy & Environmental Science, 16(3), 1235 - 1250.
[9]. Huang Qiufan, Ma Ye & Xu Zhiyun. (2024). Research progress on flexible wearable sensors for cardiovascular disease monitoring. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering (02), 214-226.
[10]. Cao Yunhao, Yang Xiyeh, Liu Chunchen & Huang Fei. (2022). Application of organic/polymer photodetectors in medical and health fields. Polymer Journal (04), 307-330.
[11]. Mao Xiling, Niu Tingting, Liu Hao & Liu Jia. (2024). Study on energy storage characteristics of supercapacitors based on PEDOT flexible nanotubes. Electronic Components and Materials (10), 1199-1206. doi:10.14106/j.cnki.1001-2028.2024.0365.









