1. Introduction
There are still many problems in the traditional database, especially in the supervision and accountability of the supply chain. For example, the data is not transparent, and the steps for consumers to query product information are cumbersome. The personnel who manage the database are only individual and the data can be tampered and stolen easily. Each piece of data in the supply chain is stored in a different database, which make it not easy to trace when the interests of consumers are violated, However, the advancement and application of blockchain technology provide a solution to these problems. This paper aims to design a more reasonable food supply chain traceability system based on blockchain technology. This paper mainly uses the blockchain smart contract, the hyperledger fabric blockchain framework, Go and Java languages to design and design a supply chain traceability system that can better protect consumers' rights. In a previous research, Alam Shadab pointed out that the isolation of electronic health records characterizes the contemporary health sector. As a result, it is difficult for clinicians to obtain patients' medical histories because the patient's information is dispersed over different systems. Blockchain is a decentralized and secure technology that may be used to retain and exchange medical records and control the pharmaceutical supply chain, which will benefit the healthcare industry [1]. Saha Adit points out that Supply chains are becoming even more complicated because many businesses are outsourcing portions of their supply chain operations to other companies and placing their manufacturing and distribution hubs in low-cost regions. Global warming results from rising pollution levels from more intricate supply chains. According to the World Resources Institute, global greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural production comprise 11% of the total and have grown 14% since 2000. The production and supply chain processes can reduce CO2 emissions because of blockchain technology's application [2].
2. Research background
2.1. Blockchain technology
The Blockchain has the advantages of decentralization, non-tampering, transparency, and openness [3]. Blockchains are distributed digital ledgers impenetrable and immune to tampering, implemented without a central repository and typically without a centralized authority [3, 4]. The blockchain system allows a user community to record transactions in a shared ledger so that no transaction can be modified after it has been recorded [5]. Decentralization means the data on the Blockchain has a back-up on each peer in the cluster, and the blockchain system ensures that the data is exact and correct on each node through consensus mechanisms such as Raft and BFT [6]. The non-tamperable modification of the Blockchain is reflected in its asymmetric cryptography, hash function, and P2P network. The data can only be uploaded to the chain when sufficient digital signatures are obtained. The working principle of digital signature technology is firstly to generate a digest of the information sent through the hash function operation, then encrypt the digest with its private key to develop its digital signature. Therefore, digital signatures are difficult to forge and guarantee Data reliability. A group of legitimate transactions is collected in a block. These transactions are hashed, and the parameters that link these blocks together—including the present-block hash and the previous-block hash—are used to create the block hash [7]. The fundamental building block for connecting the entire Blockchain is this linkage of the current block and previous blocks. Even the slight modification affects every block of data on the Blockchain. This characteristic gives Blockchain technology the element of trust and data integrity. Each block on the Blockchain includes blocks and hash [8]. Each block includes an index, Timestamp, hash, pre-hash (previous block's hash), Data, and nonce. Data stored in Data. For example, the transaction records of the digital currency bitcoin are stored in Data, and the hash value is calculated by hashing all the block information. Each record on the Blockchain is connected in series through two adjacent blocks to be traced back to any transaction. The P2P network means that the data on the Blockchain is not only stored on one computer or server, but all nodes. All nodes will have a complete backup. Even if criminals change the data on one or two computers, it will be impossible to synchronize all the data in the cluster, so the Food supply chain system based on blockchain technology can effectively solve the problems as mentioned in this paper.
2.2. Smart contract and hyperledger fabric
The smart contract is one of the core technologies of the blockchain. Compared with traditional digital contracts, smart contracts are deployed on the blockchain. Because of the decentralized infrastructure, smart contracts have higher security and reliability [9]. A smart contract is the critical use case for Blockchain technology that is still developing. Since the pre-smart-contract incorporates some agreement conditions, such as payments, it will automatically carry out the condition. The pre-agreement that all parties make in advance will be transparently carried out via the smart contract [10]. Smart contracts use the P2P decentralized network to execute the contract terms, reducing the intermediary to extract benefits, which is fairer and more efficient.
The food traceability system in this paper is based on the hyperledger fabric (HLF) platform. Hyperledger Fabric is an open-source licensed blockchain framework launched by The Linux Foundation in 2015 [11]. Currently, HLF has been used by major companies in the world for transactions, asset transfers, insurance, and other industries. The HLF is composed of a block ledger and a state database. The block ledger records the transaction information generated during the transaction and cannot be modified. This feature ensures the traceability of the blockchain, while the state database stores data in the form of key-value, which significantly facilitates data processing [11,12]. Fabric runs based on a docker container. When using fabric, users join different channels according to their needs. Each channel contains one or more organizations (org). Each organization consists of one or more nodes (peer). When the client requests data, when going to the chain, the orderer service sorts the information received by the nodes and distributes it to each node through the consensus algorithm. The alliance information is stored in the orderer admin, ensuring the cluster's data consistency and security.
2.3. Food supply chain with blockchain
The "food supply chain"(FSC) refers to the network chain structure in which various actors collaborate to produce, process, transport, and sell food to achieve the circulation of food from producers to consumers [13]. The food supply chain includes processing raw food into edible food for consumers, including raw material picking, storage, transportation, food processing, processed product transportation, storage, and sales [14].
There are many problems in the current food supply chain system as follows: (1) The reliability of the data is low. Most of the current food supply chain traceability systems are dominated by local governments or core enterprises in the supply chain. Central enterprises or other single institutions record the information. Consumers can only get the information queried by the traceability system, which leads to the low reliability of the traceability system. (2) The security of data is low. The data is easy to be modified. Traditional databases such as MySQL and Oracle are relational databases. Criminals will modify the data recorded in the database for some purpose so that the data queried by users is false [15]. For example, some fruits are rotten because of bad weather during transportation. At this time, the administrator modifies the delivery date of the food. Consumers' legal rights will be harmed [16]. After using blockchain technology, the traceability system can be improved. The reasons are as follow:(1) The blockchain is a distributed system. All nodes in the cluster record the blockchain's data. Compared with a single institutional record, the blockchain has more information sources, and the data's credibility is higher. The traceability system applying blockchain technology has higher credibility and practicability [17]. (2) The blockchain adopts an Irreversible hash algorithm. The information of each block is highly correlated with the previous block's information. If the data is modified, the data of all data centers (nodes) must be modified simultaneously. Only when the number of nodes willing to modify exceeds a certain percentage can modify the data discarded. To complete the modification of the data, at least 51% of the computing power on the blockchain needs to be mastered, which is almost impossible to achieve. Any attempt to intrude and tamper with the data information in the blockchain can be easily traced, thus limiting the illegal activities as mentioned.
3. System design
3.1. Demand analysis
The food supply chain traceability system mainly focuses on solving the shortcomings of the traditional traceability system, such as insecurity and lack of data concentration. The traceability system includes login interface, data upload interface, data traceability query interface, and complaint reporting interface. After logging in, consumers can query the data on the supply chain and report when their rights are violated. Supply chain members can add data and other operations after logging in. The system mainly uses the hyperledger fabric framework, go language’s smart contracts. The system mainly uses the java language and java-fabric-sdk.
3.2. Interface design
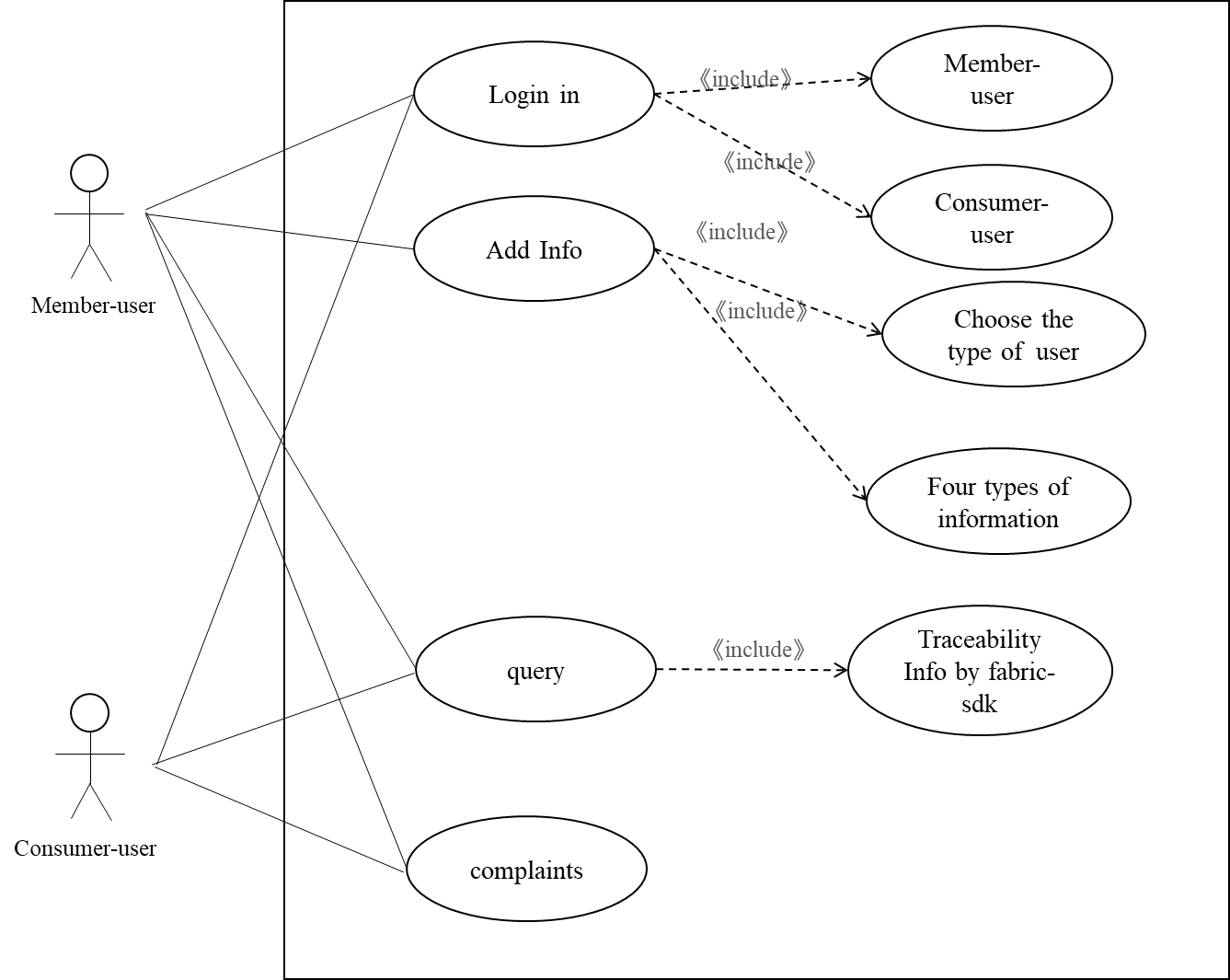
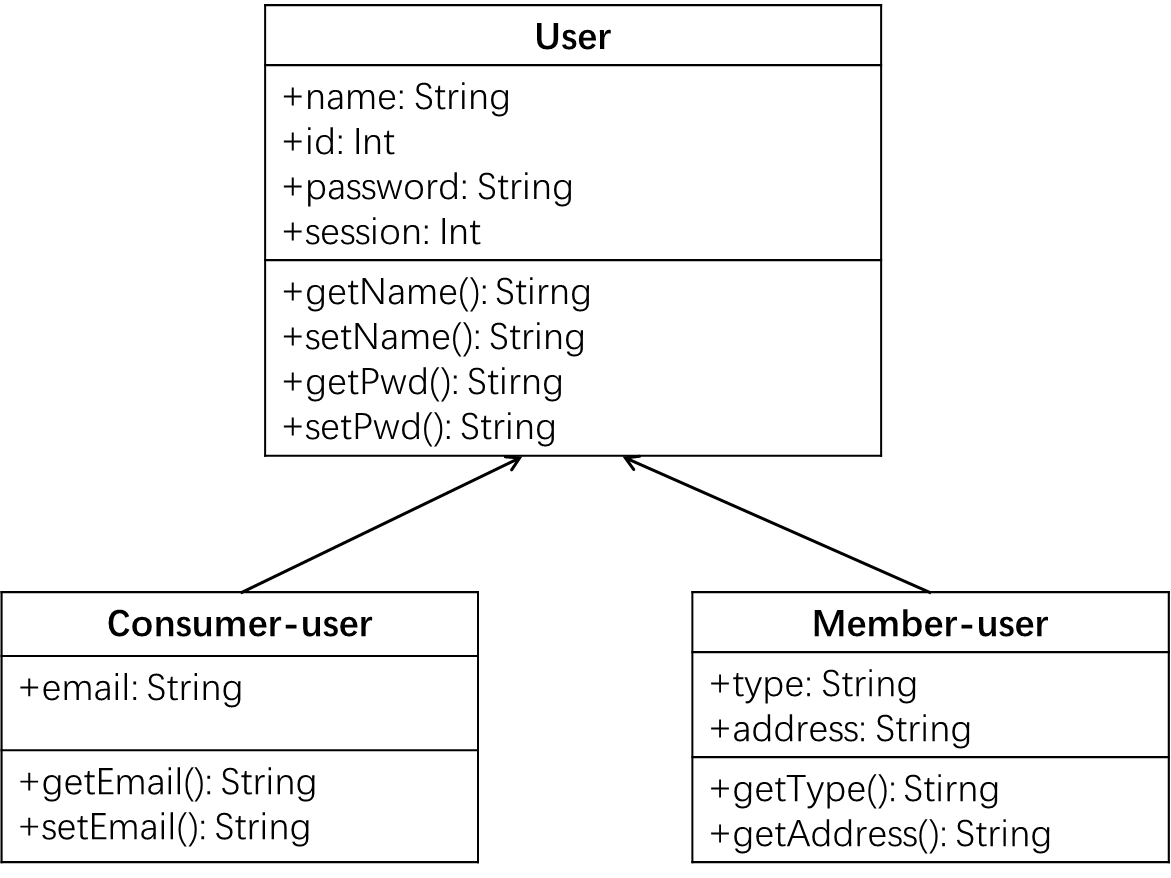
The development of the system is divided into two parts. In Figure 1 Interface design, one part is the development of the system interface and java-fabric-sdk, and the other is the smart contract. The system interface is divided into a user login interface, data an adding interface, a data traceability interface, and reporting interface.
|
Figure 1. Interface design. |
3.3. Login interface
There are two types of users in the food supply chain traceability system. Figure 2 shows the Login design, consumer, and blockchain member users. Consumer users have the authority to query and report. To ensure the security and authenticity of the data, consumer users do not have the session to upload data. Only blockchain member users can upload data. Blockchain member users are divided into four types of users: raw material origin, logistics, processing plants, and sales points. These users' accounts come from blockchain members and are authorized by relevant regulatory authorities.
|
Figure 2. Login design. |
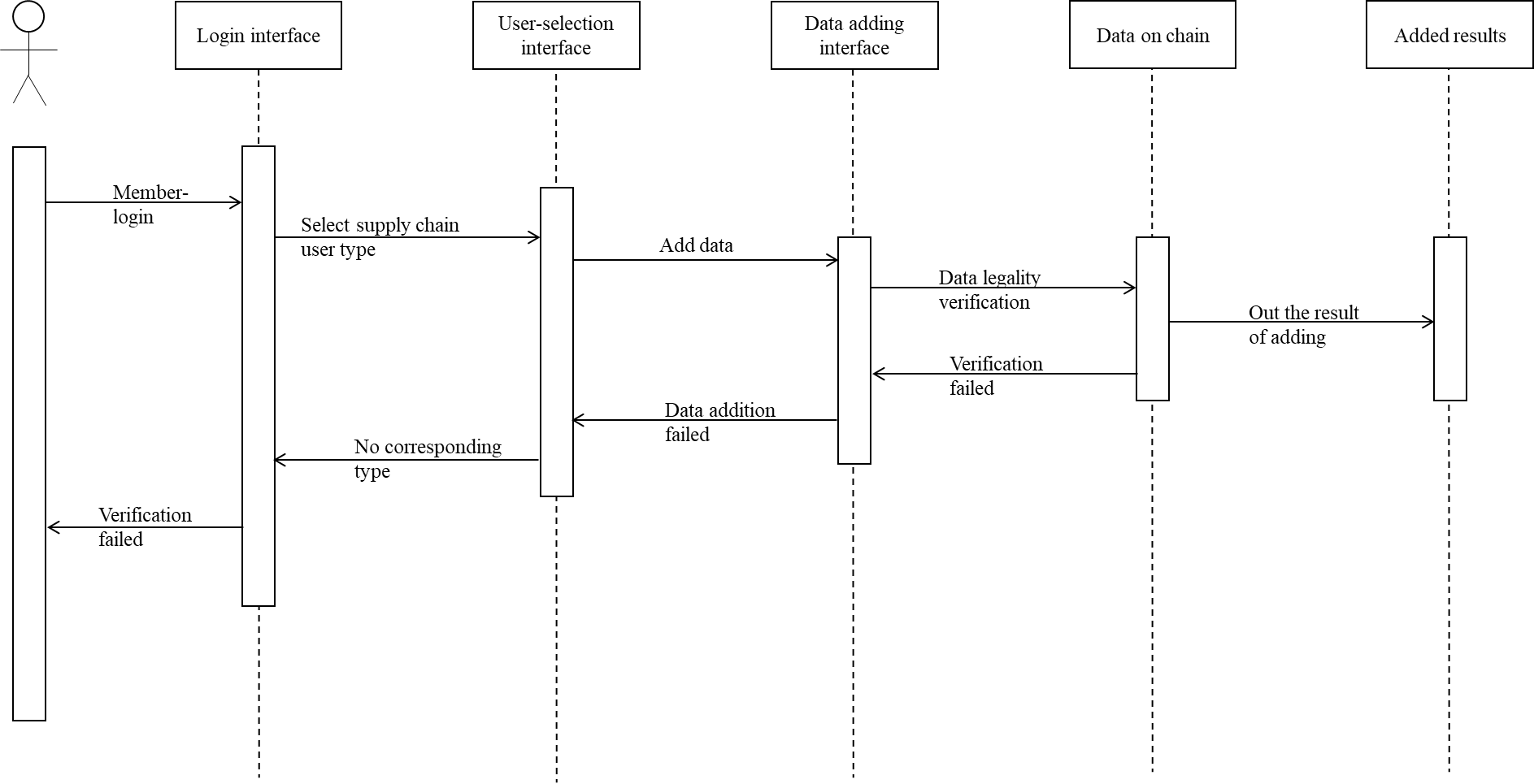
3.4. Data adding
Before entering the data addition interface, the user is authenticated first. After the blockchain user is approved by most of the members, the supervisory department will issue it. After obtaining the identification code and the blockchain member user, the data can be recorded on the chain. Only the blockchain member user can use permission to enter the interface. The user's data addition is divided into four categories according to the blockchain members.
3.5. Four types of members
The supplier needs to fill in the name of the supplied raw material, the name of the unit/farmer who provided the raw material, the supervisor, and the address after sending out the raw material. At the same time, if there are other circumstances, the supervisor can also make notes, such as the quality of the raw material, the quality of the raw material, planting, and the storage environment.
The logistics system focuses on recording the names of items in the delivery supply chain, logistics merchants, logistics routes, etc. The remarks can be used to fill in logistics orders. Well, you can connect to the database of the logistics system itself to query the transportation information of the goods on the road.
The processing plant is the center of the food processing product supply chain. Because there may be several types of raw materials and distribution points, the processing plant should issue the product's identification code. Different processing plants of the same brand should use different processing plants to prevent. For the problem of messy traceability information of corporate branches, and it is essential to fill in the company name and address at this stage. While performing supervisory duties, the processing plant supervisor must also be supervised by corporate employees and relevant government departments. When filling in the data, focus on filling in the Company address and person in charge.
Processed food products' distribution points are generally large and widely distributed. Therefore, it is important to record the geographical location and person in charge of the distribution point when recording data. Consumers can check the address to ensure the correctness of the traceability information.
3.6. Query interface
In Figure 3, the query interface. After logging in, the users can query the traceability information after entering the traceability code of processed food products in the query interface. The operation steps of this part are as follows: the user first logs in to his account, enters the traceability code of the food to be queried, and the system receives the traceability code. After the code is verified, the user’s identity is first verified. If the identity is verified, the traceability code is passed to the client part of the blockchain. After receiving the traceability code, the client sends the information in the traceability code to the query method part of the smart contract and then verifies the access. The certificate file of the node, the output result after the identity verification is correct, that is, the complete supply chain information of the food.
|
Figure 3. Query interface. |
4. Discussion
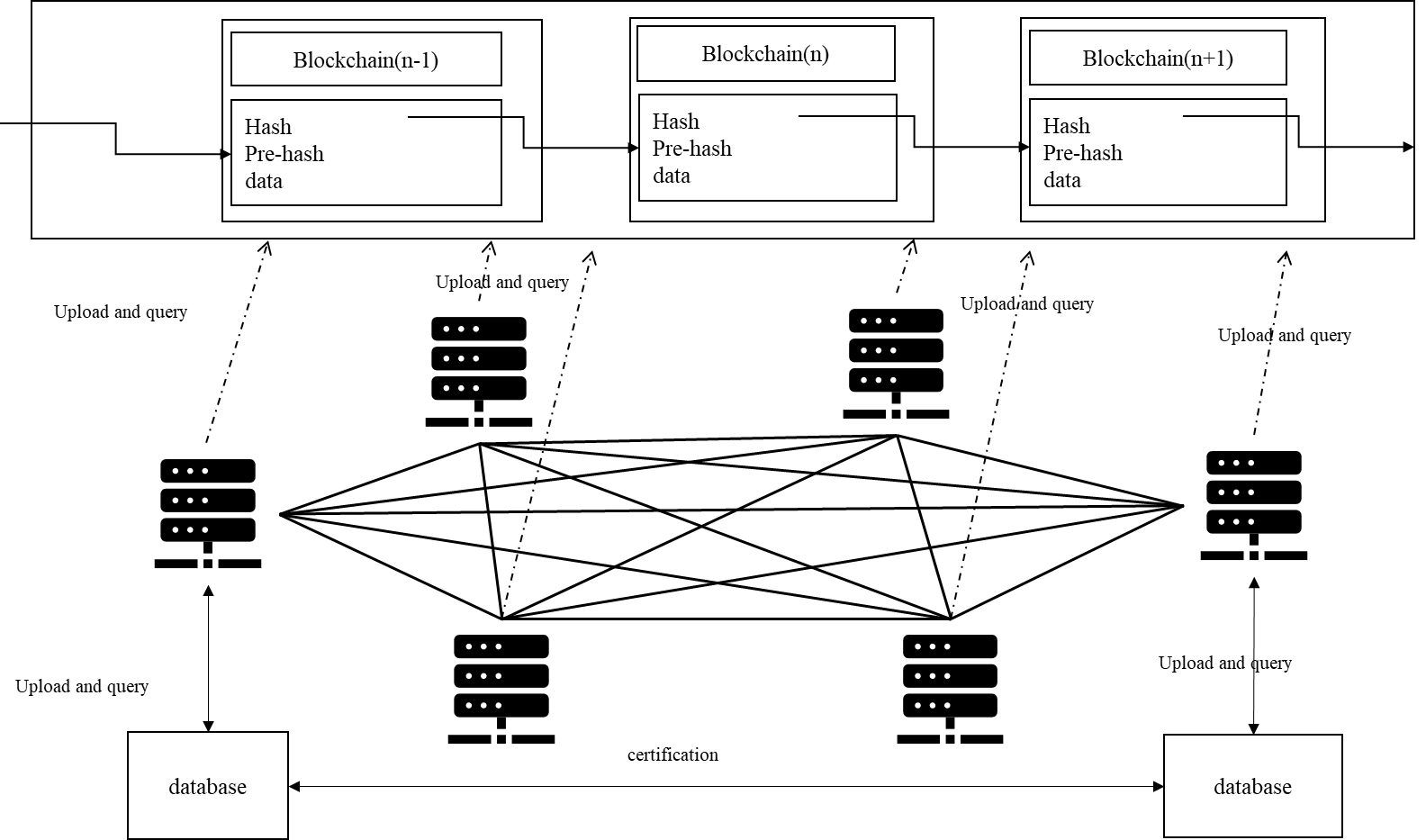
There are many types of food, and the length of the food supply chain is also very long. The data size is difficult to estimate. The old data of the blockchain guarantees the authenticity of the new data, so the blockchain cannot quickly delete the previous data. There will be more and more data on the chain. The food supply chain traceability system based on blockchain technology will face tremendous difficulties when it is promoted. To solve such problems, this paper provides the following solutions:
|
Figure 4. Improvement plan. |
As shown in Figure 4, The combination with traditional databases and blockchain technology can be used to reduce the space occupied by data. On the one hand, the data of the conventional database is stored in the central database, which occupies less space and is easy to update. On the other hand, the data on the blockchain is more credible, highly secure, and not easily tampered with. There is a lot of repetitive information in the food supply chain. The duplicate data can take up a lot of space. In a traditional relational database, the user can store this large space, high storage requirements, and highly repetitive information as a mapping table. For example, a food processing factory has a large scale. The company name and address of the company are always the same. Therefore, the factory information can be stored in the traditional database, and this data can be given a corresponding index (the index occupies much less storage space than the original data), assign the name and address of the factory an index, and then upload the index to the chain. When users query the index in the traceability data, users can use the index in which the corresponding data is queried in the traditional database. Distributed storage methods can also be used for the security of traditional databases. For example, there are N nodes in the traceability system, and traditional databases with duplicate information and indexes can be randomly assigned to N/3 nodes on the nodes. During the traceability process, the index of i is queried on the blockchain, and the query operation can be performed in all databases simultaneously. The result will be returned to the user if the obtained data is the same. This can also reduce the storage space occupied by the data on the chain. As mentioned in the System test part, in the last part of the demonstration, the data is encoded with uft-8, so the total space occupied by the original data d1 = 360Byte. In the java, The int type is \( 32bit=4B \) , and the space occupied after compression is \( d2= 121*4 (text data)+8*4 (index data) = 153 Byte \) . After compression, the space occupied by the data on the chain is reduced by 57.5%.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, the food supply chain traceability system based on blockchain technology is realized by using the hyperledger fabric framework, Java language and Go. To improve the problems encountered in the promotion of the blockchain, such as taking up too much storage space. This paper also proposes a method of combining traditional relational databases and blockchain technology to store data together. The results show that the data storage occupation has been significantly reduced. The test link of the food supply chain traceability system shows that the application of blockchain technology in the traditional food supply chain has great potential. The decentralized distributed blockchain technology can store the data of the food supply chain more securely. The immutability and traceability of the chain guarantee the security of the food supply chain traceability system and the traceability of data. With the unique advantages of blockchain technology, blockchain can also be widely used in the pharmaceutical supply chain, supply chain finance, and other aspects. With the deepening of future research, the current problems of the blockchain will be better solved, and future blockchain technology can be applied and promoted in more fields, creating more wealth for society.
References
[1]. Alam Shadab et al. Blockchain-based Initiatives: Current state and challenges[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 198(prepublish): 108395-.
[2]. Saha Aditi S. et al. Blockchain Changing the Outlook of the Sustainable Food Supply Chain to Achieve Net Zero? [J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(24): 16916-16916.
[3]. Yuan Yong, Wang Feiyue. Current status and prospect of blockchain technology development [J].
[4]. AlShamsi Mohammed and AlEmran Mostafa and Shaalan Khaled. A Systematic Review on Blockchain Adoption[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(9): 4245-4245.
[5]. Li Xiteng, Wang Lin, Qin Hongnan, Wang Baoqing, Li Xin. Construction of emergency material dispatching model based on blockchain Fabric [J]. China Safety Science
[6]. Nijsse Jeff and Litchfield Alan. A Taxonomy of Blockchain Consensus Methods[J].
[7]. Wadhwa Shivani et al. Energy Efficient Consensus Approach of Blockchain for IoT Networks with Edge Computing[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(10): 3733-3733.Cryptography, 2020, 4(4): 32-32.
[8]. Fiorentino Stefania and Bartolucci Silvia. Blockchain-based smart contracts as new governance tools for the sharing economy[J]. Cities, 2021, 117
[9]. John William A D, Rajendran S, Pranam P, et al. Blockchain Technologies: Smart Contracts for Consumer Electronics Data Sharing and Secure Payment[J]. Electronics, 2022, 12(1): 208.
[10]. He Haiwu, Yan'an, Chen Zehua. A review of blockchain-based smart contract technology and applications [J]. Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(11): 2452-2466.
[11]. Guggenberger Tobias et al. An in-depth investigation of the performance characteristics of Hyperledger Fabric[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 173
[12]. Meng Wutong, Zhang Dawei. Optimizing Scheme of Hyperledger Fabric Consensus Mechanism [J].
[13]. Wang Ermei, Su Jing. Food supply chain traceability platform based on blockchain [J]. Food Industry, 2022,43(11):227-230.
[14]. Liu Fangfang, Li Yibin, Jia Juan. Research on food quality and safety assurance system in food supply chain [J]. Chinese Seasoning, 2022,47(12):186-189.
[15]. Fan Hongping, Feng Zhongze, Yang Ling, Ren Aisheng. Application and Discussion of Traceability System in Food Supply Chain [J]. Ecological Economy, 2007, No.181(04):63-65.
[16]. Arpášová Michaela and Rajčániová Miroslava. Legal Regulation of Unfair Trade Practices in Food Supply Chain[J]. EU agrarian Law, 2022, 11(1): 1-8.
[17]. Lin Ling, Zhou Deyi, Huang Qiju. Design of food quality and safety traceability system based on Internet [J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2005(05):546-549.
Cite this article
Tang,J. (2023). Food Supply Chain Traceability System Based on Blockchain Technology. Applied and Computational Engineering,8,311-317.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Alam Shadab et al. Blockchain-based Initiatives: Current state and challenges[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 198(prepublish): 108395-.
[2]. Saha Aditi S. et al. Blockchain Changing the Outlook of the Sustainable Food Supply Chain to Achieve Net Zero? [J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(24): 16916-16916.
[3]. Yuan Yong, Wang Feiyue. Current status and prospect of blockchain technology development [J].
[4]. AlShamsi Mohammed and AlEmran Mostafa and Shaalan Khaled. A Systematic Review on Blockchain Adoption[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(9): 4245-4245.
[5]. Li Xiteng, Wang Lin, Qin Hongnan, Wang Baoqing, Li Xin. Construction of emergency material dispatching model based on blockchain Fabric [J]. China Safety Science
[6]. Nijsse Jeff and Litchfield Alan. A Taxonomy of Blockchain Consensus Methods[J].
[7]. Wadhwa Shivani et al. Energy Efficient Consensus Approach of Blockchain for IoT Networks with Edge Computing[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(10): 3733-3733.Cryptography, 2020, 4(4): 32-32.
[8]. Fiorentino Stefania and Bartolucci Silvia. Blockchain-based smart contracts as new governance tools for the sharing economy[J]. Cities, 2021, 117
[9]. John William A D, Rajendran S, Pranam P, et al. Blockchain Technologies: Smart Contracts for Consumer Electronics Data Sharing and Secure Payment[J]. Electronics, 2022, 12(1): 208.
[10]. He Haiwu, Yan'an, Chen Zehua. A review of blockchain-based smart contract technology and applications [J]. Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(11): 2452-2466.
[11]. Guggenberger Tobias et al. An in-depth investigation of the performance characteristics of Hyperledger Fabric[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 173
[12]. Meng Wutong, Zhang Dawei. Optimizing Scheme of Hyperledger Fabric Consensus Mechanism [J].
[13]. Wang Ermei, Su Jing. Food supply chain traceability platform based on blockchain [J]. Food Industry, 2022,43(11):227-230.
[14]. Liu Fangfang, Li Yibin, Jia Juan. Research on food quality and safety assurance system in food supply chain [J]. Chinese Seasoning, 2022,47(12):186-189.
[15]. Fan Hongping, Feng Zhongze, Yang Ling, Ren Aisheng. Application and Discussion of Traceability System in Food Supply Chain [J]. Ecological Economy, 2007, No.181(04):63-65.
[16]. Arpášová Michaela and Rajčániová Miroslava. Legal Regulation of Unfair Trade Practices in Food Supply Chain[J]. EU agrarian Law, 2022, 11(1): 1-8.
[17]. Lin Ling, Zhou Deyi, Huang Qiju. Design of food quality and safety traceability system based on Internet [J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2005(05):546-549.